pandas——pandas的数据结构与创建数据对象
1.pandas的数据结构
Series
- series是一维数据
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5])
print(s.index) #获取series的索引
print(s.values)#获取series的值
DataFrame
- DataFrame为二维数据
df.values #获取数据的值
df.index #获取行索引
df.columns #获取列索引
axis = 1/axis = columns #沿着列索引的方向进行运算
axis = 0/axis = index #沿着行索引的方向进行运算
2.创建数据对象
Series
- 创建series一般有以下6种方法
- 通过list创建
- 通过字典创建
- 通过ndrray创建
- 通过标量创建
- 创建空的Series
- 通过读取数据文件创建
通过list创建
import pandas as pd
#直接通过列表进行创建
s = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5])
#指定索引
s = pd.Series([1,2,3],index = ["a","b","c"])#values与index的个数必须相同,否则会报错
#指定表明
s = pd.Series([1,2,3],index = ["a","b","c"],name="hello")
通过字典创建
- 此时字典的keys便是Series的index
import pandas as pd
d1 = {"a":1,"b":2,"c":3}
s = pd.Series(d1)
print(s)
通过numpy的ndrray创建
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
np.random.seed(0)
s = pd.Series(np.random.randint(5,size=3))
print(s)
#此处还不太懂哎,等学到numpy时再回过头来看看吧
通过标量创建
- 标量:具体的单个数据
- 通过设置索引的长度控制行数
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series(1,index = ["a","b","c"])
print(s)
'''
输出结果
a 1
b 1
c 1
'''
创建空的Series
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series()
print(s)
DataFrame
-
与Series类似DataFrame同样有6种创建数据的方法
-
通过list创建
-
通过字典创建
-
通过ndrray创建
-
通过标量创建
-
创建空的DataFrame
-
通过读取数据文件创建
-
创建空的DataFrame
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame()
print(df)
通过list创建
import pandas as pd
#一维列表
lst = [1,2,3,4]
df = pd.DataFrame(lst)
print(df)
#二维列表,二维列表有很多累
#**************list of list***************
lst = [["lemo","长沙",80,90],
["jack","上海",90,75],
["peter","深圳",60,80],]
df = pd.DataFrame(data=lst,columns=["name","city","math","chem"])
print(df)
'''
输出结果
name city math chem
0 lemo 长沙 80 90
1 jack 上海 90 75
2 peter 深圳 60 80
'''
# **************************************list of dict*****************************************
lst = [ {"name":"lemo","city":"长沙","math":80,"chem":90},
{"name":"jack","city":"上海","math":90,"chem":75},
{"name":"peter","city":"深圳","math":60,"chem":80}]
df = pd.DataFrame(data=lst,columns=["name","city","math","chem"])
print(df)
'''
输出结果
name city math chem
0 lemo 长沙 80 90
1 jack 上海 90 75
2 peter 深圳 60 80
'''
#最后的字典少了一个元素,最后生成的结果为NaN
lst = [ {"name":"lemo","city":"长沙","math":80,"chem":90},
{"name":"jack","city":"上海","math":90,"chem":75},
{"name":"peter","city":"深圳","math":60}]
df = pd.DataFrame(data=lst,columns=["name","city","math","chem"])
print(df)
"""
输出结果
name city math chem
0 lemo 长沙 80 90.0
1 jack 上海 90 75.0
2 peter 深圳 60 NaN
"""
#创建数据框时,只选取特定的列,生成时只生成指定的列
lst = [ {"name":"lemo","city":"长沙","math":80,"chem":90},
{"name":"jack","city":"上海","math":90,"chem":75},
{"name":"peter","city":"深圳","math":60}]
df = pd.DataFrame(data=lst,columns=["name","city","math"])
print(df)
"""
输出结果
name city math
0 lemo 长沙 80
1 jack 上海 90
2 peter 深圳 60
"""
#设置列索引时,与字典的key值不匹配,创建的数据框会有nan值
lst = [ {"name":"lemo","city":"长沙","math":80,"chem":90},
{"name":"jack","city":"上海","math":90,"chem":75},
{"name":"peter","city":"深圳","math":60}]
df = pd.DataFrame(data=lst,columns=["name","city","math","化学"])
print(df)
"""
输出结果
name city math 化学
0 lemo 长沙 80 NaN
1 jack 上海 90 NaN
2 peter 深圳 60 NaN
"""
# **************************************list of tuple*****************************************
#此时是和list of list是非常相似的
lst = [ ("lemo","长沙",80,90),
("jack","上海",90,75),
("peter","深圳",60,85)]
df = pd.DataFrame(data=lst,columns=["name","city","math","化学"])
print(df)
"""
输出结果
name city math 化学
0 lemo 长沙 80 90
1 jack 上海 90 75
2 peter 深圳 60 85
"""
#通过zip方式将列表整合成元组后再生成数据
list1 = ["lemo","jack","peter","yang"]
list2 = ["长沙","上海","深圳","宁波"]
list3 = [80,90,60,20]
list4 = [90,75,80,10]
lis = zip(list1,list2,list3,list4)#zip把其压缩成一个元组包含在列表中
df = pd.DataFrame(data=lis,columns=("name","city","chem","mach"))
print(df)
'''
输出结果
name city chem mach
0 lemo 长沙 80 90
1 jack 上海 90 75
2 peter 深圳 60 80
3 yang 宁波 20 10
'''
通过字典创建数据框
#普通模式
d = {"name":["lemo","jack","peter","yang"],"city":["长沙","上海","深圳","宁波"],
"chem":[80,90,60,20],"mach":[90,75,80,10]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=d)
#或者df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(data=d)
print(df)
"""
输出结果
name city chem mach
0 lemo 长沙 80 90
1 jack 上海 90 75
2 peter 深圳 60 80
3 yang 宁波 20 10
"""
#通过嵌套型的字典,此时可指定index的次序
d = {"name":{1:"lemo",2:"jack",3:"peter",4:"yang"},"city":{0:"长沙",1:"上海",2:"深圳",3:"宁波"},
"chem":{0:80,1:90,2:60,3:20},"mach":{0:90,1:75,2:80,3:10}}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=d)
print(df)
"""
输出结果
name city chem mach
1 lemo 上海 90.0 75.0
2 jack 深圳 60.0 80.0
3 peter 宁波 20.0 10.0
4 yang NaN NaN NaN
0 NaN 长沙 80.0 90.0
"""
通过标量创建数据框
df = pd.DataFrame(1,index=[1,2,3],columns=list("abcde"))
print(df)
'''
输出结果
a b c d e
1 1 1 1 1 1
2 1 1 1 1 1
3 1 1 1 1 1
'''
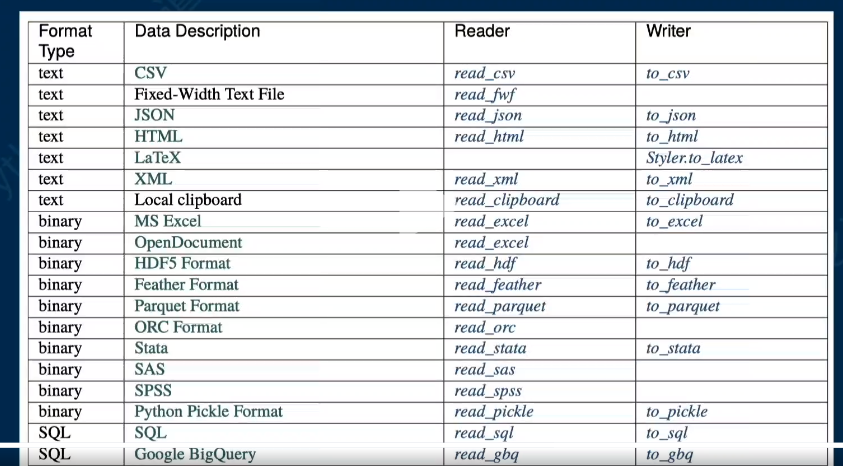
通过读取数据文件创建
记录学习的点点滴滴


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号