C++--day07
目录:
1. C的提高 1-131P 时间七天
2. C++的基础 132-286P 时间八天
3. C++的提高 287-378P 时间五天
4. C/C++的数据结构 379-482P 时间五天
5. C/C++的设计模式基础 483-540P 时间三天
视频资料:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av27904891?from=search&seid=10891514449061956870
P200 const修饰的谁
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Test { public: Test(int a, int b) //---> Test(Test *this, int a, int b) { this->a = a;//this就是t1取地址,谁调用它它就是谁 this->b = b; } void printT() { cout<<"a: " <<a <<endl; cout<< "b: " << this->b <<endl; } //1. const写在什么位置 没有关系 //2. const修饰的是谁 // 1. const修饰的是形参a 不是 // 2. const修饰的是属性this->a this->b // 3. const修饰的是this指针所指向的内存空间,指针所指向的内存空间不能被修改 void OpVar(int a,int b) const // void OpVar(const Test *const this, int a, int b) { a=100; //this->a=100; this->b=100; cout<< "b: " << this->b <<endl; } protected: private: int a; int b; }; void main() { Test t1(1, 2); t1.printT();// ===> printT(&t1) cout<<"hello..."<<endl; system("pause"); return ; }
P202 全局函数PK成员函数
1、把全局函数转化成成员函数,通过this指针隐藏左操作数
Test add(Test &t1, Test &t2)===》Test add( Test &t2)
2、把成员函数转换成全局函数,多了一个参数
void printAB()===》void printAB(Test *pthis)
3、函数返回元素和返回引用
Test& add(Test &t2) //*this //函数返回引用 { this->a = this->a + t2.getA(); this->b = this->b + t2.getB(); return *this; //*操作让this指针回到元素状态 } Test add2(Test &t2) //*this //函数返回元素 { //t3是局部变量 Test t3(this->a+t2.getA(), this->b + t2.getB()) ; return t3; } void add3(Test &t2) //*this //函数返回元素 { //t3是局部变量 Test t3(this->a+t2.getA(), this->b + t2.getB()) ; //return t3; }
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class Test { public: int a; int b; public: ~Test() { cout<<"a:"<<a<<"b:"<<b; cout<<"析构函数自动调用"<<endl; } public: Test(int a=0,int b=0) { this->a=a; this->b=b; } public: //t3=t1.TestAdd(t2); Test TestAdd(Test &t2) { Test tmp(this->a+t2.a,this->b+t2.b); return tmp; } //t1.TestAdd2(t2); //返回一个引用,相当于返回一个变量自身 //返回t1这个元素 this就是t1的地址 Test& TestAdd2(Test &t2) { this->a=this->a+t2.a; this->b=this->b+t2.b; return *this;//把(&t1)又回到了t1元素 } public: void printT() { cout<<"a:"<<a<<"b:"<<b<<endl; } protected: private: }; //全局函数的方法 //全局函数 转成 成员函数 少了一个参数 Test TestAdd(Test &t1,Test &t2) { Test tmp; return tmp; } //把成员函数转成全局函数 多了一个参数 void printT(Test *pT) { cout<<"a:"<<pT->a<<"b:"<<pT->b<<endl; } void main() { Test t1(1,2); Test t2(3,4); //t1=t1+t2 t1.TestAdd2(t2); t1.printT(); system("pause"); } void main181() { Test t1(1,2); Test t2(3,4); Test t3; //全局函数方法 //t1+t2 t3=TestAdd(t1,t2); t3.printT(); //成员函数方法 { //先把测试案例写出来 Test t4=t1.TestAdd(t2);//匿名对象直接转化成t4 t4.printT(); Test t5; t5=t1.TestAdd(t2);//匿名对象复制给t5 t5.printT(); } t3=t1.TestAdd(t2); system("pause"); }
P203 强化训练数组类--类的设计和测试程序
P204 类的实现和测试
MyArray.h
#pragma once //保证头文件只被编译一次
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Array
{
public:
Array(int length);
Array(const Array& obj);
~Array();
public:
void setData(int index,int value);
int getData(int index);
int length();
private:
int m_length;
int *m_space;
};
MyArray.cpp
#include "MyArray.h"
//Array a1(10);
Array::Array(int length)
{
if (length<0)
{
length=0;
}
else
{
m_length=length;
m_space=new int[m_length];
}
}
//Array a2=a1;
Array::Array(const Array& obj)
{
this->m_length=obj.m_length;
//深拷贝 分配内存空间
this->m_space=new int[this->m_length];
for(int i=0;i<obj.m_length;i++)//数组元素赋值
{
this->m_space[i]=obj.m_space[i];
}
}
Array::~Array()
{
if (m_space!=NULL)
{
delete[] m_space;
m_length=0;
}
}
//a1.setData(i,i);
void Array::setData(int index,int value)
{
m_space[index]=value;
}
int Array::getData(int index)
{
return m_space[index];
}
int Array::length()
{
return m_length;
}
TestArray.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include "MyArray.h"
using namespace std;
//类的框架设计完毕
//类的测试案例
void main()
{
Array a1(10);
//赋值
for(int i=0;i<a1.length();i++)
{
a1.setData(i,i);
}
//获取
cout<<"打印a1"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<a1.length();i++)
{
cout<<a1.getData(i) <<endl;
}
Array a2=a1;
cout<<"输入a2"<<endl;
//获取
cout<<"打印a2"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<a2.length();i++)
{
cout<<a2.getData(i)<<endl;
}
system("pause");
}
P205 友元函数

友元函数是类的好朋友,在友元函数里可以修改这个类的私有属性,言外之意友元函数破坏了类的封装性
在这个类里声明了友元函数,这个友元函数是个全局函数,要想在友元函数去修改某一个变量的某个对象的私有属性,一般友元函数至少包含原类的参数,一个赋的值
说明语句的位置与访问描述无关

#include<iostream> using namespace std; class A { public: //声明的位置和public private没有关系 friend void modify(A *pA,int _a); //函数 modify是类A的好朋友 A(int a=0,int b=0) { this->a=a; this->b=b; } int getA() { return this->a; } private: int a; int b; }; void modify(A *pA,int _a) { //pA->a=100; pA->a=_a; } void main() { A a1(1, 2); cout<<a1.getA()<<endl; modify(&a1,300); cout<<a1.getA()<<endl; system("pause"); }
this是指A类 this->指类中的属性
类 *变量名 代表类的指针名为变量名,这个变量名就是这个类的指针
输出结果: 1 300
P206 友元类
- 若B类是A类的友员类,则B类的所有成员函数都是A类的友员函数
- 友员类通常设计为一种对数据操作或类之间传递消息的辅助类

#include<iostream> using namespace std; class A { public: friend class B;//声明B类是A的好朋友,在B中可以访问A的私有成员 私有函数 //声明的位置和public private没有关系 friend void modify(A *pA,int _a); //函数 modify是类A的好朋友 A(int a=0,int b=0) { this->a=a; this->b=b; } int getA() { return this->a; } private: int a; int b; }; void modify(A *pA,int _a) { //pA->a=100; pA->a=_a; } //为什么设计友元类函数 // 1.java--->1.class(字节码) ==》反射机制分析1.class 找到类对象。直接修改类的私有属性 // 反射机制 成为一种标准。。。。jdk ...sun 做成标准 。。。jdk 的 api函数中有体现 //AOP //2 1.cpp===>汇编 // 预编译 编译 连接 生成 。。gcc -E //gcc -s - // gcc -o 1.exe 1.c // 汇编往回找。。。。很难。。。。 //3 开了一个后门 。。。friend /* gcc -E hello.c -o hello.i(预处理) gcc -S hello.i -o hello.s(编译) gcc -c hello.s -o hello.o(汇编) gcc hello.o -o hello(链接) 以上四个步骤,可合成一个步骤 gcc hello.c -o hello(直接编译链接成可执行目标文件) gcc -c hello.c或gcc -c hello.c -o hello.o(编译生成可重定位目标文件) */ class B { public: void Set(int a) { Aobj.a=a; } void PirntB() { cout<<Aobj.a<<endl; } protected: private: A Aobj; }; void main() { B b1; b1.Set(400); b1.PirntB(); system("pause"); }
P207 运算符重载入门基础推演
运算符重载
1. 运算符重载入门技术推演
2. 运算符重载的两种方法,全局函数和成员函数
运算符重载基础
一元运算符重载(全局函数 类的成员函数)
二元运算符重载
+ -
前置++ 前置-- 后置++ 后置--
3. 统一正规写法
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class Complex { public: int a; int b; public: Complex(int a,int b) { this->a=a; this->b=b; } void printComp() { cout<<a<<"+"<<b<<"i"<<endl; } private: }; //1 定义了全局函数 Complex myAdd(Complex &c1,Complex &c2) { Complex tmp(c1.a+c2.a,c1.b+c2.b); return tmp; } //2 函数名升级 Complex operator+(Complex &c1,Complex &c2) { Complex tmp(c1.a+c2.a,c1.b+c2.b); return tmp; } void main() { int a=0; int b=0; int c; c=a+b;//1. 基础数据类型 编译器已经知道如何进行运算 //a+bi 复数运算规则 Complex c1(1,2),c2(3,4); //Complex c3;//2. 类也是一种数据类型 用户自定义数据类型 C++编译器是不知道如何进行运算 //c3=c1+c2; //3. c++编译器应该给程序员提供一种机制 //让自定义数据类型有机会进行运算符操作===>运算符重载机制 //4. 运算符重载机制 //步骤1 //Complex c4=myAdd(c1,c2); //c4.printComp(); //步骤2 Complex c4=c1+c2 //Complex c4=operator+(c1,c2); //c4.printComp(); //步骤3 Complex c4=c1+c2; c4.printComp(); //总结:运算符重载的本质 是 函数调用 // 定义 operator+ 表示重载了加法运算符 C++编译器会根据类型去找这个类型相加的函数 system("pause"); }
P208 运算符重载语法理论知识介绍


运算符重载编程基础

例如:
//全局函数 完成 +操作符 重载 Complex operator+(Complex &c1, Complex &c2) //类成员函数 完成 -操作符 重载 Complex operator-(Complex &c2)
运算符重载的两种方法


P210 成员函数和友元函数完成二元运算符重载
P211 成员函数和友元函数完成一元运算符重载(前置)

P212 成员函数和友元函数完成一元运算符重载(后置)

定义运算符重载函数名的步骤
全局函数、类成员函数方法实现运算符重载步骤
1)要承认操作符重载是一个函数,写出函数名称operator+ ()
2)根据操作数,写出函数参数
3)根据业务,完善函数返回值(看函数是返回引用 还是指针 元素),及实现函数业务
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Complex { private: int a; int b; //1. 全局函数 重载+运算符 friend Complex operator+(Complex &c1, Complex &c2); //重载 前置++ friend Complex& operator++(Complex &c1); friend Complex operator++(Complex &c1, int); public: Complex(int a=0, int b=0) { this->a = a; this->b = b; } void printCom() { cout<<a<<" + " << b << "i" <<endl; } public: //2. 成员函数法 实现 -运算符重载 Complex operator-(Complex &c2) { Complex tmp(this->a - c2.a, this->b - c2.b); return tmp; } //前置-- Complex& operator--() { this->a --; this->b --; return *this; } //后置-- Complex operator--(int) { Complex tmp = *this; this->a--; this->b--; return tmp; } }; //1. 全局函数法 实现 + 运算符重载 Complex operator+(Complex &c1, Complex &c2) { Complex tmp(c1.a + c2.a, c1.b + c2.b); return tmp; } //前置++ Complex& operator++(Complex &c1) { c1.a++; c1.b++; return c1; } //后置++ Complex operator++(Complex &c1, int) { //先使用 再让c1加加 Complex tmp = c1; //return c1; c1.a ++; c1.b ++; return tmp; } /* 全局函数、类成员函数方法实现运算符重载步骤 1)要承认操作符重载是一个函数,写出函数名称 2)根据操作数,写出函数参数 3)根据业务,完善函数返回值(看函数是返回引用 还是指针 元素),及实现函数业务 */ void main1901() { Complex c1(1, 2), c2(3, 4); //1.全局函数法 实现 + 运算符重载 // Complex operator+(Complex &c1, Complex &c2); Complex c3 = c1 + c2; c3.printCom(); //2.成员函数 法 实现 -运算符重载 // c1.operator-(c2); // Complex operator-(Complex &c2) Complex c4 = c1 - c2; c4.printCom(); //3. 前置++操作符 用全局函数实现 ++c1; c1.printCom(); //4. 前置--操作符 成员函数方法 --c1; c1.printCom(); //Complex& operator++(Complex &c1) //c1.operator--(); //5. 后置++操作符 用全局函数实现 c1++; c1.printCom(); //6. 后置--操作符 用成员函数实现 c1--; c1.printCom(); //c1.operator--() cout<<"hello..."<<endl; system("pause"); return ; }
P213 友元函数实现左移右移操作符重载(函数返回值当左值需返回引用)
友元函数实现操作符重载的应用场景
1)友元函数和成员函数选择方法
- 当无法修改左操作数的类时,使用全局函数进行重载
- =, [], ()和->操作符只能通过成员函数进行重载
2)用友元函数 重载 << >>操作符
- istream 和 ostream 是 C++ 的预定义流类
- cin 是 istream 的对象,cout 是 ostream 的对象
- 运算符 << 由ostream 重载为插入操作,用于输出基本类型数据
- 运算符 >> 由 istream 重载为提取操作,用于输入基本类型数据
- 用友员函数重载 << 和 >> ,输出和输入用户自定义的数据类型
3) 友元函数重载操作符使用注意点
a) 友员函数重载运算符常用于运算符的左右操作数类型不同的情况

b)其他
- 在第一个参数需要隐式转换的情形下,使用友员函数重载运算符是正确的选择
- 友员函数没有 this 指针,所需操作数都必须在参数表显式声明,很容易实现类型的隐式转换
- C++中不能用友员函数重载的运算符有
= () [] ->
using namespace std; /* class ostream { }; */ class Complex { private: int a; int b; //friend void operator<<(ostream &out, Complex &c1); friend ostream& operator<<(ostream &out, Complex &c1); public: Complex(int a=0, int b=0) { this->a = a; this->b = b; } void printCom() { cout<<a<<" + " << b << "i" <<endl; } public: //实现 + 运算符重载 Complex operator+(Complex &c2) { Complex tmp(a + c2.a, b + c2.b); return tmp; } //前置++ Complex& operator++() { a++; b++; return *this; } //后置++ Complex operator++(int) { //先使用 在让c1加加 Complex tmp = *this; //return c1; this->a ++; this->b ++; return tmp; } //成员函数法 实现 -运算符重载 Complex operator-(Complex &c2) { Complex tmp(this->a - c2.a, this->b - c2.b); return tmp; } //前置-- Complex& operator--() { this->a --; this->b --; return *this; } //后置-- Complex operator--(int) { Complex tmp = *this; this->a--; this->b--; return tmp; } }; /* void operator<<(ostream &out, Complex &c1) { out<<"12345 生活真是苦"<<endl; out<<c1.a << " + " << c1.b << "i" << endl; } */ ostream& operator<<(ostream &out, Complex &c1) { out<<"12345 生活真是苦"<<endl; out<<c1.a << " + " << c1.b << "i" << endl; return out; } void main() { int a = 10; Complex c1(1, 2), c2(3, 4); cout<<a<<endl; //a是基础数据类型,按照数据类型判断 //1. 用全局函数实现左移操作符重载 cout << c1 ;//Complex是自定义数据类型,C++编译器不知道如何进行输出,需要重载左移操作符 //2. 在ostream 类中 添加 成员函数 .operator<< //ostream //cout.operator<<(c1); //2. 函数返回值当左值 需要返回一个引用 cout << c1 << "aaddddd"; // //cout.operator<<(c1) .operator<<("aaddddd"); //void.operator<<("aaddddd"); system("pause"); }
P215 重载等号操作符
重载赋值运算符=
- 赋值运算符重载用于对象数据的复制
- operator= 必须重载为成员函数
- 重载函数原型为:
类型 & 类名 :: operator= ( const 类名 & ) ;

结论:
1. 先释放旧的内存
2. 返回一个引用
3. =操作符 从右向左
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Name { public: Name(const char *myp) { m_len = strlen(myp); m_p =(char *) malloc(m_len + 1); // strcpy(m_p, myp); } //Name obj2 = obj1; //解决方案: 手工的编写拷贝构造函数 使用深copy Name(const Name& obj1) { m_len = obj1.m_len; m_p = (char *)malloc(m_len + 1); strcpy(m_p, obj1.m_p); } //obj3 = obj1; //obj3.operator=(obj1) Name& operator=(Name &obj1) { //1. 先释放旧的内存 if (this->m_p != NULL) { delete[] m_p; m_len = 0; } //2. 根据obj1分配内存大小 this->m_len = obj1.m_len; this->m_p = new char [m_len+1]; //3. 把obj1赋值 strcpy(m_p, obj1.m_p); return *this; } ~Name() { if (m_p != NULL) { free(m_p); m_p = NULL; m_len = 0; } } protected: private: char *m_p ; int m_len; }; //对象析构的时候 出现coredump void objplaymain() { Name obj1("abcdefg"); Name obj2 = obj1; //C++编译器提供的 默认的copy构造函数 浅拷贝 Name obj3("obj3"); obj3 = obj1; // C++编译器提供的 等号操作 也属 浅拷贝 //obj3.operator=(obj1) //operato=(Name &obj1) obj1 = obj2 = obj3; //obj2.operator=(obj3); //obj1 = void; } void main() { objplaymain(); cout<<"hello..."<<endl; system("pause"); return ; }
P216 数组类小案例-操作符重载需求
P217 数组类小案例-重载[]
P218 数组类小案例-重载等号
P219 数组类小案例-重载==和!=
myarray.h
#pragma once #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Array { public: Array(int length); Array(const Array& obj); ~Array(); public: void setData(int index, int valude); int getData(int index); int length(); private: int m_length; int *m_space; public: //函数返回值当左值,需要返回一个引用 //应该返回一个引用(元素本身) 而不是一个值 int& operator[](int i); //重载= Array& operator=(Array &a1); //重载 == bool operator==(Array &a1); //重载 != bool operator!=(Array &a1); }; //要求重载以下操作符 // [] == !=
myarray.cpp
#include "myarray.h" Array::Array(int length) { if (length < 0) { length = 0; // } m_length = length; m_space = new int[m_length]; } //Array a2 = a1; Array::Array(const Array& obj) { this->m_length = obj.m_length; this->m_space = new int[this->m_length]; //分配内存空间 for (int i=0; i<m_length; i++) //数组元素复制 { this->m_space[i] = obj.m_space[i]; } } Array::~Array() { if (m_space != NULL) { delete[] m_space; m_space = NULL; m_length = -1; } } //a1.setData(i, i); void Array::setData(int index, int valude) { m_space[index] = valude; } int Array::getData(int index) { return m_space[index]; } int Array::length() { return m_length; } // int& Array::operator[](int i) { return m_space[i]; } //a3 = a1; Array& Array::operator=(Array &a1) { //1. 释放原来的内存空间 if (this->m_space != NULL) { delete [] m_space; m_length = 0; } //2. 根据a1大小 分配内存 m_length = a1.m_length; m_space = new int[m_length]; //3. copy数据 for (int i=0; i<m_length; i++) { //m_space[i] = a1.m_space[i]; m_space[i] = a1[i]; } return *this; } //if (a3 == a1) bool Array::operator==(Array &a1) { if (this->m_length != a1.m_length) { return false; } for (int i=0; i<m_length; i++) { if (this->m_space[i] != a1[i]) { return false; } } return true; } bool Array::operator!=(Array &a1) { /* if (*this == a1) { return true; } else { return false; } */ return !(*this == a1); }
myarray_test.cpp
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include "myarray.h" //类的框架设计完毕 //类的测试案例 //重载[] //void operator[](int i) //int operator[](int i); //int& operator[](int i); void main() { Array a1(10); for (int i=0; i<a1.length(); i++) { a1.setData(i, i); //2 a1[i] = i; // //函数返回值当左值,需要返回一个引用 //a1.operator [i] } cout<<"\n打印数组a1: "; for (int i=0; i<a1.length(); i++) { //cout<<a1.getData(i)<<" "; //1 cout<<a1[i]<<endl; } cout<<endl; Array a2 = a1; cout<<"\n打印数组a2: "; for (int i=0; i<a2.length(); i++) { cout<<a2.getData(i)<<" "; } cout<<endl; //3 Array a3(5); { a3 = a1; a3 = a2 = a1; cout<<"\n打印数组a3: "; for (int i=0; i<a3.length(); i++) { cout<<a3[i]<<" "; } //a3.operator=(a1) //Array& operator=(Array &a1) } //功能4 if (a3 == a1) { printf("相等\n"); } else { printf("不相等\n"); } //a3.operator==(a1); //bool operator==(Array &a1); if (a3 != a1) { printf("不相等\n"); } else { printf("相等\n"); } // //a3.operator!=(a1) // bool operator!=(Array &a1); cout<<"hello..."<<endl; system("pause"); return ; }
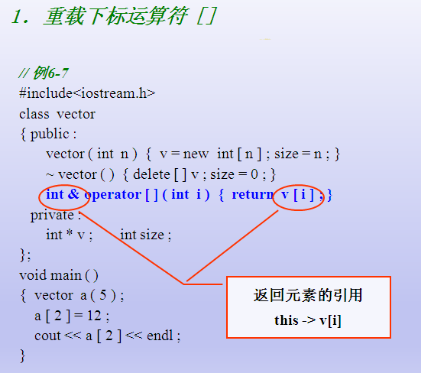
重载数组下表运算符[]
重载[]和()运算符
- 运算符 [] 和 () 是二元运算符
- [] 和 () 只能用成员函数重载,不能用友元函数重载
重载下标运算符 []
[] 运算符用于访问数据对象的元素
重载格式 类型 类 :: operator[] ( 类型 ) ;
设 x 是类 X 的一个对象,则表达式
x [ y ]
可被解释为
x . operator [ ] ( y )



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号