02-Spring-IOC
文章目录
1. IOC容器
-
什么是IOC
对象的创建和对象的调用交由spring去管理,目的是为了降低耦合性
-
IOC底层实现
-
xml解析、工厂模式、反射

-
-
IOC 接口
IOC思想基于IOC容器完成,IOC容器底层就是对象工厂
Spring提供IOC容器实现两种方式:(两个接口)
-
BeanFactory: Spring内部使用的接口,不提供开发人员进行使用
*加载配置文件时不会创建对象,在使用对象时才创建对象
-
ApplicationContext: BeanFactory接口的子接口,提供强大的功能,供开发人人员使用
*加载配置文件时就会创建对象
-
ApplicationContext的实现类
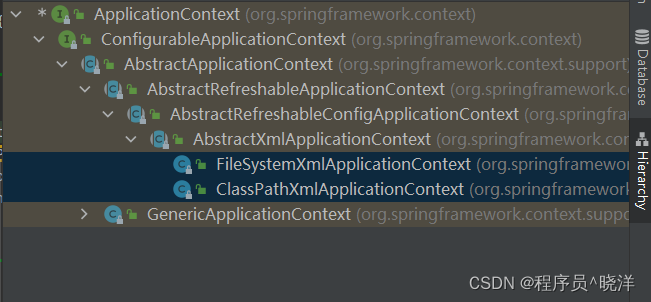
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 指定全路径加载bean.xml配置文件
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 指定类路径加载bean.xml配置文件
-
如何通过对象工厂获取bean
@Test public void testAdd() { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:bean1.xml"); User user = context.getBean("user", User.class); System.out.println(user.add(8, 9)); } @Test public void testAdd2() { BeanFactory factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:bean1.xml"); User user = factory.getBean("user", User.class); System.out.println(user.add(1, 2)); }
-
2. IOC操作bean管理
1. 什么bean管理
- 创建对象
- 注入属性
2. bean管理的实现方式
1. 注解方式
-
需要引入 spring-aop 依赖
-
开启组件扫描的位置
<!-- 1.通过context命名空间 开启组件扫描 如果扫描多个包,用”,“隔开。 如果多个包的上层目录一样,直接扫描上层目录 --> <context:component-scan base-package=" com.potato2"/> <!-- 指定扫描包内的那些内容--> <!-- use-default-filters 默认值为true 扫描包内所有内容 include-filter 指定扫描的内容 exclude-filter 指定不扫描的内容 <context:component-scan base-package="com.potato2" use-default-filters="false"> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/> </context:component-scan> 此处是指: 只扫描com.potato2 包下 用了 @Controller注解的bean -->
1. 对象创建
- @Component
- @Controller
- @Service
- @Repository
上面注解功能一模一样
使用在类上,目的是把bean交由spring来管理
每个注解都有value属性 作用是设置当前bean的名称 默认值为当前类名 首字母小写
//等价于 <bean id="userService" class="com.potato2.service.UserService">
@Component(value = "userService")
public class UserService {
}
2. 属性注入
@Autowired 根据属性类型进行注入
@Qualifier 根据属性名称进行注入
@Resource 可以根据属性类型或者名称进行注入 ,默认根据类型注入,通过name属性 进行名称注入
@Value 注入普通数据类型
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
public void add(int a,int b) {
userDao.add(a, b);
}
}
3. 完全注解开发
-
创建配置类
@Configuration //表示当前类是配置类 @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.potato2") //指定扫描的组件位置 public class SpringConfig { } -
加载配置类
通过 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 对象可以加载配置类
@Test public void test02() { ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); }
2 .xml实现
1.无参构造、有参构造、基本属性注入、特殊符号注入、NULL值注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
<!-- 创建对象 id:对当前bean进行取名 然后通过getBean("idValue",Object.class) 获取-->
<!-- 需要注入值的属性 需要有set方法 -->
<!-- 1.无参构造-->
<bean id="user1" class="com.potato.testDemo.User">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="用户01"/>
<property name="hobby">
<list>
<value>打球</value>
<value>跑步</value>
<value>游泳</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!--2.有参构造-->
<bean id="user2" class="com.potato.testDemo.User">
<constructor-arg name="id" value="2"/>
<constructor-arg name="name" value="<![CDATA[<<用户02>>]]>"/>/>
<constructor-arg name="hobby">
<null></null>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 3. p名称空间注入 配置文件需要引入p名称空间 在set注入上进行的简化-->
<bean id="user3" class="com.potato.testDemo.User"
p:id="3" p:name="用户03" p:hobby-ref="hobbyList">
</bean>
<!-- 特殊符号 可以使用转义字符 < 或者CDATA -->
<!-- <<用户02>> <![CDATA[<<用户02>>]]> -->
2.外部bean、内部bean、级联bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 1.外部bean ref属性 -->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.potato.dao.UserDao"/>
<bean id="userService" class="com.potato.service.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>
<!-- 2.内部bean 内部使用bean标签 -->
<bean name="emp" class="com.potato.pojo.Emp">
<property name="gender" value="1"/>
<property name="ename" value="用户1"/>
<property name="dept">
<bean class="com.potato.pojo.Dept">
<property name="dname" value="研发部"/>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 3.级联bean -->
<bean name="emp2" class="com.potato.pojo.Emp">
<property name="gender" value="2"/>
<property name="ename" value="用户2"/>
<property name="dept" ref="dept"></property>
<!-- 级联赋值-->
<property name="dept.dname" value="研发部"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="dept" class="com.potato.pojo.Dept"></bean>
</beans>
3. 集合属性注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="clazz" class="com.potato.pojo.Clazz">
<!-- 1.注入数组-->
<property name="courses">
<array>
<value>语文</value>
<value>数学</value>
<value>英语</value>
</array>
</property>
<!-- 2.注入List -->
<property name="student">
<list>
<bean class="com.potato.pojo.User">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="用户1"/>
</bean>
<ref bean="user2"/>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 3.注入Set-->
<property name="set">
<list>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
<value>3</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 4.注入Map-->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="key01" value="1"/>
<entry key="key02" value="2"/>
<entry key="key03" value="3"/>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
通过util 命名空间 注入集合
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
<bean id="clazz" class="com.potato.pojo.Clazz">
<property name="student" ref="student"/>
<property name="courses" ref="courses"/>
<property name="set" ref="set"/>
<property name="map" ref="map"/>
</bean>
<!-- list\array -->
<util:list id="courses">
<value>语文</value>
<value>数学</value>
<value>英语</value>
</util:list>
<!-- set -->
<util:set id="set">
<value>易筋经</value>
<value>九阴真经</value>
<value>九阳神功</value>
</util:set>
<!-- map -->
<util:map id="map">
<entry key="key01" value="1"/>
<entry key="key02" value="2"/>
<entry key="key03" value="3"/>
</util:map>
<!-- list bean -->
<util:list id="student">
<ref bean="user1"/>
<ref bean="user2"/>
</util:list>
<bean id="user1" class="com.potato.pojo.User">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="用户1"/>
</bean>
<bean id="user2" class="com.potato.pojo.User">
<property name="id" value="2"/>
<property name="name" value="用户2"/>
</bean>
</beans>
3. Spring中的两种Bean 普通bean 和 工厂bean(FactoryBean)
-
普通bean:在配置文件中定义的类型 就是返回的类型
-
工厂bean:在配置文件中定义的类型 和返回的类型不一样
1.创建类 实现接口FactoryBean 作为工厂Bean
2.实现接口里的方法,在方法中返回具体的bean
bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="myBean" class="com.potato.factoryBean.MyBean"> </bean> </beans>MyBean.java
public class MyBean implements FactoryBean<User> { @Override public User getObject() throws Exception { // 此方法返回具体的bean 可以根据泛型、反射 返回不同的bean return new User(1, "用户1", null); } @Override public Class<?> getObjectType() { return null; } @Override public boolean isSingleton() { return FactoryBean.super.isSingleton(); } }测试 Test.java
// FactoryBean @Test public void test9() { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:beanIOC-FactoryBean.xml"); User user = context.getBean("myBean", User.class); System.out.println(user) } // myBean 的class 为 MyBean.class 但是我们返回的是User.class
4. bean的作用域
Spring里默认的bean是单实例
如何设置多实例
<!-- scope 常用值: singleton:单实例(默认值) / prototype:多实例-->
<!--
scope 值为 singleton 时,加载配置文件时就完成实例对象的创建
scope 值为 prototype 时,对象在调用getBean时才创建,每次调用都会产生新的实例对象
request
session
-->
<bean id="user1" class="com.potato.pojo.User" scope="singleton">
<!-- set 方法注入-->
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="用户01"/>
<property name="hobby">
<list>
<value>打球</value>
<value>跑步</value>
<value>游泳</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
5. bean的生命周期
第一步 执行无参构造创建bean实例
第二步 调用set方法设置属性值
第三步 执行初始化方法 (需要配置 init-method)
第四步 获取创建bean实例对象
第五步 执行销毁方法 (需要配置 destroy-method)
<bean id="userService" class="com.potato.service.UserServiceImpl"
init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>
销毁发生在 ApplicationContext关闭的时候
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)context).close();
6. 自动装配
通过value/ref 进行值的配置都属于手动装配
-
什么是自动装配
根据指定装配规则(属性名称、属性类型),spring自动将匹配的属性值进行注入
-
如何进行自动装配 配置
<!-- 实现自动装配 bean 标签设置autowire autowire 常用值 1.byName 根据属性名称注入,注入值的ID 和 属性名称一样 2.byType 根据属性类型注入,注入值的class 和属性值的class一样。 前提条件:注入值的class 只配置了一个bean --> <bean id="emp" class="com.potato.autowire.Emp" autowire="byType"> <!--<property name="dept" ref="dept"/>--> </bean> <bean id="dept" class="com.potato.autowire.Dept" />
7. 外部属性文件
druid.properties
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/spring5
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--
通过 context名称空间 引入外部文件
通过 ${} 调用
-->
<context:property-placeholder location="druid.properties"/>
<bean class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
</beans>```



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现