Kibana使用
一、什么是Kibana
Kibana 是一个开源的分析和可视化平台,Kibana 提供搜索、查看和与存储在 Elasticsearch 索引中的数据进行交互的功能。开发者或运维人员可以轻松地执行高级数据分析,并在各种图表、表格和地图中可视化数据
二、安装使用
①:下载Kibana https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/kibana
②:配置Kibana
Open config/kibana.yml in an editor.
Set elasticsearch.hosts to point at your Elasticsearch instance.
默认情况下,Kibana 会连接运行在 localhost 上的 Elasticsearch 实例。如果需要连接不同的 Elasticsearch实例,可以修改 kibana.yml 配置文件中的 Elasticsearch URL 配置项并重启 Kibana
如:elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"]
③:运行
Run bin/kibana (or bin\kibana.bat on Windows)
④:访问
Point your browser at http://localhost:5601

Kibana使用:
①:导入数据文件
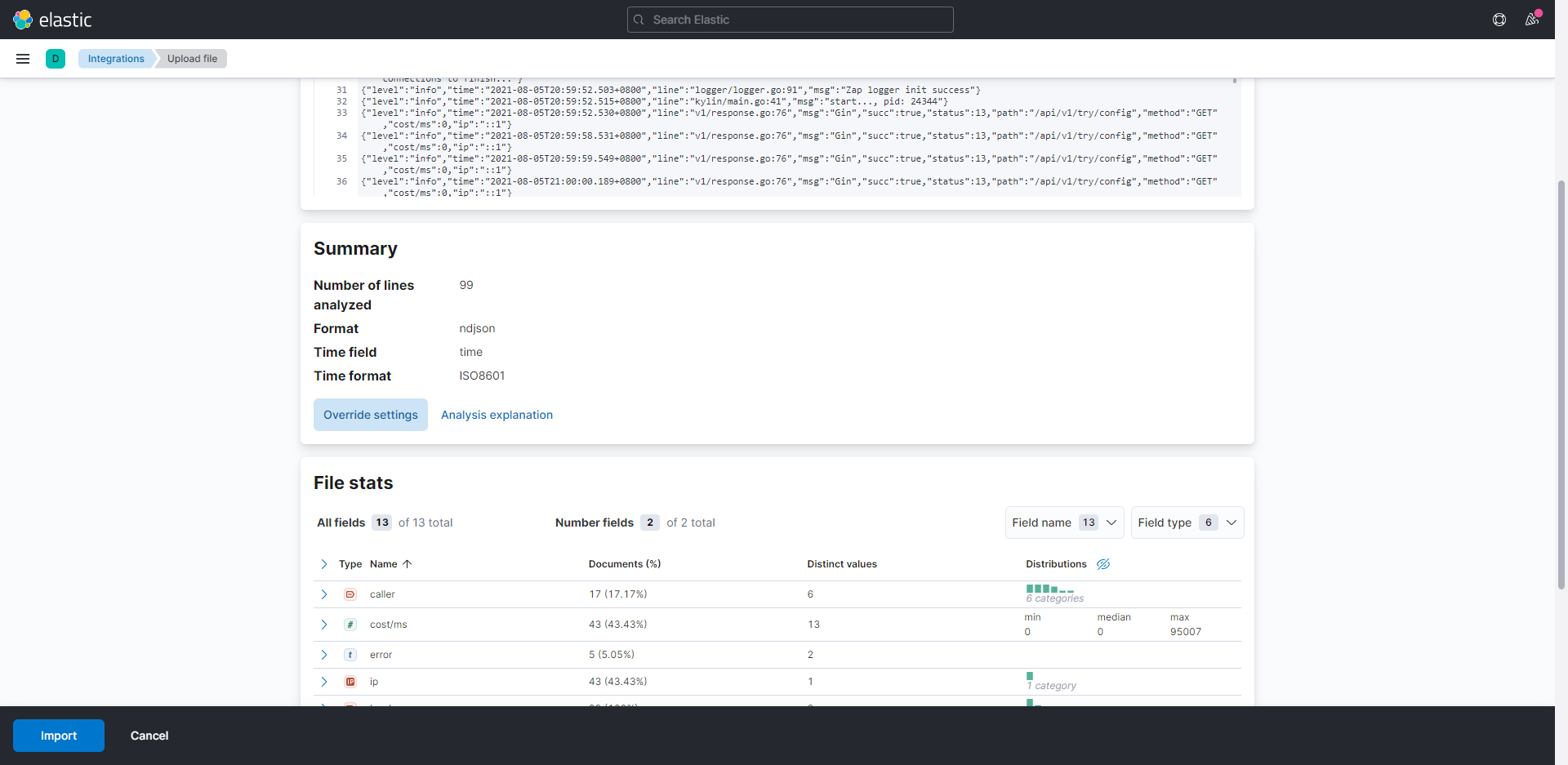
②:预览并确认导入
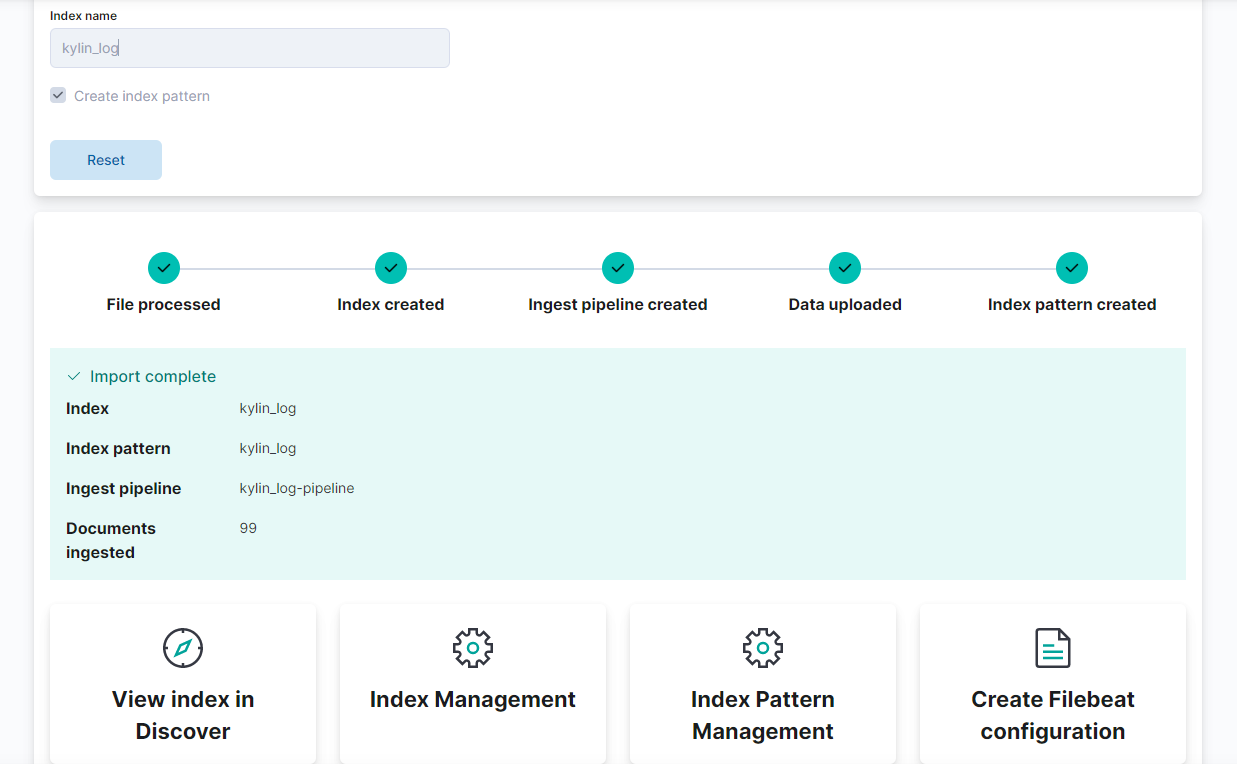
③:创建索引模式
④:在Discover中查看数据

Kibana左侧的Toolbar主要分为一下几块功能:
Discovery 发现:用于查看和搜索原始数据
Visualize 可视化:用来创建图表、表格和地图等
Dashboard:多个图表和合并为一个 Dashboard 仪表盘
Timelion 时间线:用于分析时序数据,以二维图形的方式展示
Dev Tools 开发工具:用于进行DSL查询、Query性能分析等
Management 管理:主要用于创建 Index Patterns,ES中的索引在创建 Index Patterns 之后,才能在 Discover 中被搜索,在 Visualize 和 Dashboard 中制图。
三、检索
1、选择日期
2、左侧栏目展示可用的字段列表:
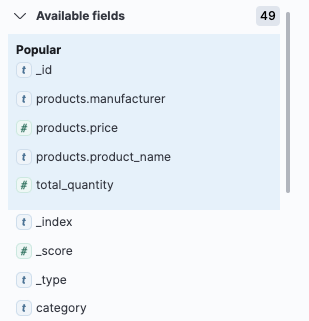
如果只想展示某个字段的内容,则在字段栏目上将鼠标悬停在类别字段上,然后单击 +
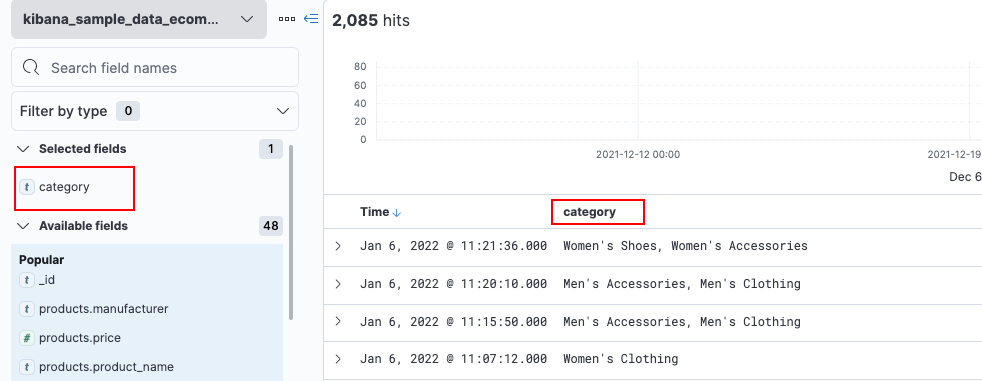
KQL(Kibana Query Language):
KQL是一种使用自由文本搜索或基于字段的搜索过滤 Elasticsearch 数据的简单语法。KQL 仅用于过滤数据,并没有对数据进行排序或聚合的作用
1、Terms Query
空格分隔每个搜索词,并且只需要一个词来匹配文档。使用引号表示短语匹配(phrase match)
①:要使用精确搜索词进行查询,请输入字段名称,后跟 :,然后输入以空格分隔的值:
如message中包含deduct的文档:
message: deduct②:匹配多个字符串,每个字段都会单独匹配。如:force and clean
只要匹配到其中的任何一个force、and、clean,那么搜索的结果都会显示出来
③:匹配单个确切的字符串或者匹配字符串短语(phrase),用双引号括起来。如"force and clean"
2、Boolean queries
KQL 支持 or、and 和 not。默认情况下,and 的优先级高于 or。要覆盖默认优先级,请在括号中将运算符分组。这些运算符可以是大写或小写
①:or,要匹配response为200、或者geo.dest 为 CN. 或两者都满足的文档:
response: 200 or geo.dest: "CN"②:or,匹配 response 为 200 或 404 的文档:
response:(200 or 404)③:and,匹配 response 为 200 且 geo.dest 为 CN 的文档
response: 200 and geo.dest: "CN"匹配包含术语列表的多值字段:
tags:(success and info and security)④:and or结合使用,要匹配 response 为 200 且 extension 为 php 或 css 的文档:
response:200 and (extension:php or extension:css)⑤:要匹配 response 为 200 且 extension 为 php 或 extension 为 css 且 response 为任何内容的文档(and 的优先级比 or 要高)
response:200 and extension:php or extension:css
等同于:
(response:200 and extension:php) or extension:css⑥:not,匹配 response 不是 200 的文档:
not response:200⑦:匹配 response 为 200 但 extension 不是 php 或 css 的文档:
response:200 and not (extension:php or extension:css)3、Range queries
KQL 支持数字和日期类型的 >、>=、< 和 <=,如:
bytes > 1000 and (hour_of_day>10 and hour_of_day <14 )日期范围过滤:
@timestamp < "2024-01-01"
4、Exits queries
①:Exist 查询匹配包含任何字段值的文档:
response:*②:如查询message中包含某个子串的 message : *n0317gfq8j20231221155303574*
5、Wildcard queries
通配符查询可用于按术语前缀搜索或搜索多个字段。Kibana 的默认设置出于性能原因禁止使用前导通配符,但可以通过高级设置允许
要匹配 machine.os 以 win 开头的文档,例如 “windows 7” 和 “windows 10”:
machine.os:win*参考:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/x2NZMKAgRuxpzY7FOTwCYg
补充:通过filter:

选择过滤的字段,和值的包含关系:
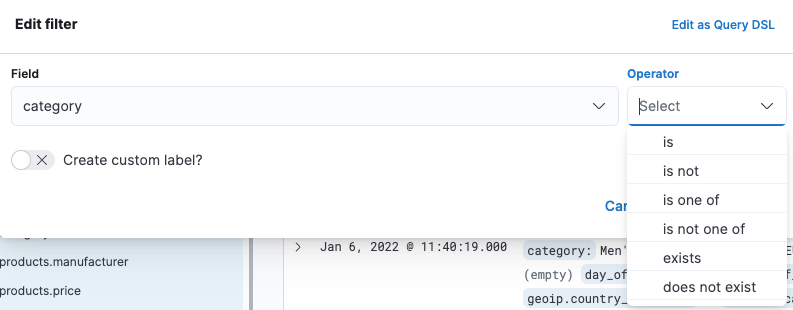
填入值,保存即可检索:

Lucene:
1、根据字段查询
限定字段全文搜索:field:value
精确搜索:关键字加上双引号 filed:"value"
2、通配符
? 匹配单个字符
* 匹配0到多个字符
3、模糊搜索
~:在一个单词后面加上~启用模糊搜索,可以搜到一些拼写错误的单词
4、近似搜索
在短语后面加上~,可以搜到被隔开或顺序不同的单词
"where select"~5 表示 select 和 where 中间可以隔着5个单词,可以搜到 select password from users where id=1
5、范围搜索
mod_date:[20020101 TO 20030101]:查找 mod_date 字段的值介于 20020101 和 20030101 之间的文档
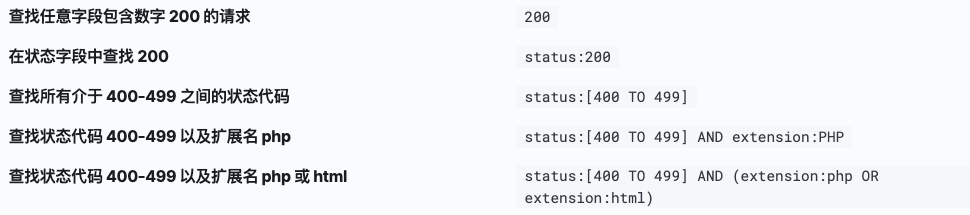
Dev Tools:
Kinaba > Management > Dev Tools
PUT(修改),POST(添加),DELETE(删除),GET(查询)
1、GET / 等价于 http://localhost:9200/,对应的curl为:curl -XGET "http://localhost:9200/"
2、创建一个索引及文档
PUT index_name/_doc(type_name)/document_id
{文档内容} 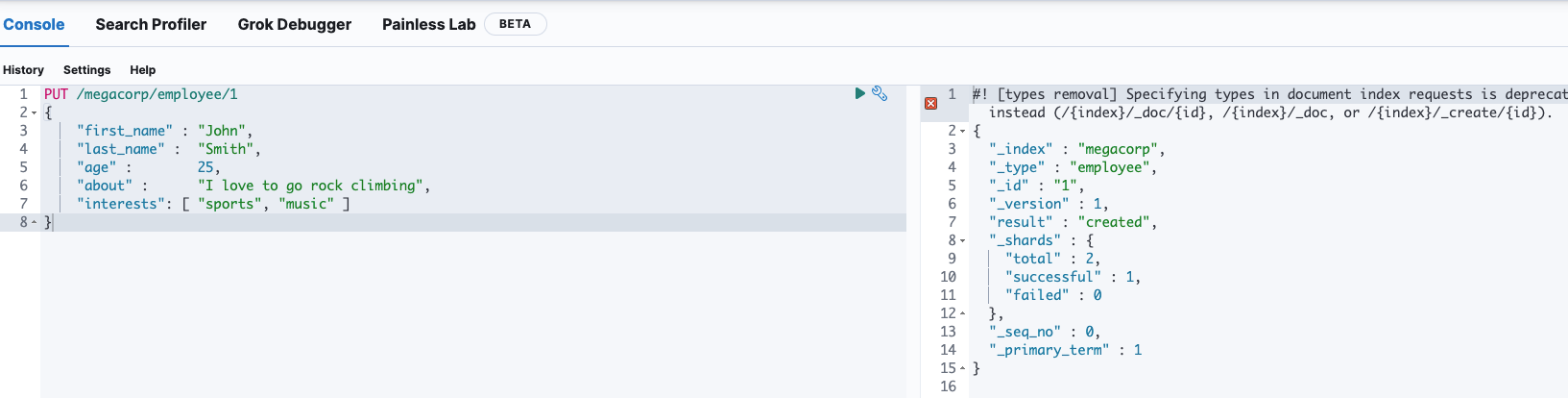
3、简单检索文档
①:GET /index_name/type_name/document_id
对应的curl:curl -X GET "localhost:9200/megacorp/employee/1?pretty"
如 GET /megacorp/employee/1 的返回,_source属性里的是原始JSON文档
{ "_index" : "megacorp", "_type" : "employee", "_id" : "1", "_version" : 1, "_seq_no" : 0, "_primary_term" : 1, "found" : true, "_source" : { "first_name" : "John", "last_name" : "Smith", "age" : 25, "about" : "I love to go rock climbing", "interests" : [ "sports", "music" ] } }
②:搜索索引下的全部文档:
GET /megacorp/employee/_search
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/megacorp/employee/_search?pretty"
搜索结果放在了hit数组中,一个搜索默认返回10条结果

#! [types removal] Specifying types in search requests is deprecated. { "took" : 12, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 3, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 1.0, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "megacorp", "_type" : "employee", "_id" : "1", "_score" : 1.0, "_source" : { "first_name" : "John", "last_name" : "Smith", "age" : 25, "about" : "I love to go rock climbing", "interests" : [ "sports", "music" ] } }, { "_index" : "megacorp", "_type" : "employee", "_id" : "2", "_score" : 1.0, "_source" : { "first_name" : "Jane", "last_name" : "Smith", "age" : 32, "about" : "I like to collect rock albums", "interests" : [ "music" ] } }, { "_index" : "megacorp", "_type" : "employee", "_id" : "3", "_score" : 1.0, "_source" : { "first_name" : "Douglas", "last_name" : "Fir", "age" : 35, "about" : "I like to build cabinets", "interests" : [ "forestry" ] } } ] } }
③:根据文档中的属性值搜索
搜索lastname属性值为Smith的文档,使用q参数:
GET /megacorp/employee/_search?q=last_name:Smith
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/megacorp/employee/_search?q=last_name:Smith&pretty"
4、查询表达式搜索
查询表达式支持构建更加复杂和健壮的查询
①:使用 match 查询属性last_name值为Smith的文档
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query" : { "match" : { "last_name" : "Smith" } } }
对应curl为:
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/megacorp/employee/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' { "query" : { "match" : { "last_name" : "Smith" } } } '
②:使用过滤器filter,搜索last_name属性值为Smith、age属性值大于30的文档
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query" : { "bool": { "must": { "match" : { "last_name" : "smith" } }, "filter": { "range" : { "age" : { "gt" : 30 } } } } } }
5、全文搜索
Elasticsearch会在全文属性上搜索并返回相关性最强的结果,区别于传统关系数据库的一条记录要么匹配要么不匹配
如在`about` 属性上搜索 “rock climbing”
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query" : { "match" : { "about" : "rock climbing" } } }
返回结果:
{ "took" : 67, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 2, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 1.4167401, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "megacorp", "_type" : "employee", "_id" : "1", "_score" : 1.4167401, # 相关性得分 "_source" : { "first_name" : "John", "last_name" : "Smith", "age" : 25, "about" : "I love to go rock climbing", "interests" : [ "sports", "music" ] } }, { "_index" : "megacorp", "_type" : "employee", "_id" : "2", "_score" : 0.4589591, # 相关性得分 "_source" : { "first_name" : "Jane", "last_name" : "Smith", "age" : 32, "about" : "I like to collect rock albums", "interests" : [ "music" ] } } ] } }
Elasticsearch 默认按照相关性得分排序,即每个文档跟查询的匹配程度。第一个最高得分的结果很明显:John Smith 的 about 属性清楚地写着 “rock climbing”
但为什么 Jane Smith 也作为结果返回了呢?原因是她的 about 属性里提到了 “rock” 。因为只有 “rock” 而没有 “climbing” ,所以她的相关性得分低于 John 的
6、短语搜索
找出一个属性中的独立单词是没有问题的,但有时候想要精确匹配一系列单词或者_短语_ 。 比如, 我们想执行这样一个查询,仅匹配同时包含 “rock” 和 “climbing” ,并且 二者以短语 “rock climbing” 的形式紧挨着文档
为此对 match 查询稍作调整,使用一个叫做 match_phrase 的查询:
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query" : { "match_phrase" : { "about" : "rock climbing" } } }
7、高亮搜索
在搜索结果中高亮显示部分文本片段,以便让用户知道为何该文档符合查询条件
使用highlight参数即可:
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query" : { "match_phrase" : { "about" : "rock climbing" } }, "highlight": { "fields" : { "about" : {} } } }
8、聚合搜索
Elasticsearch 有一个功能叫聚合(aggregations),允许我们基于数据生成一些精细的分析结果。聚合与 SQL 中的 GROUP BY 类似但更强大。
聚合使用aggs,如聚合搜索文档中所有age的值:
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "aggs": { "all_ages": { "terms": { "field": "age" } } } }
结果:
{ ... "aggregations" : { "all_ages" : { "doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0, "sum_other_doc_count" : 0, "buckets" : [ # age 所有出现的值,及出现改之文档的个数 { "key" : 25, "doc_count" : 1 }, { "key" : 32, "doc_count" : 1 }, { "key" : 35, "doc_count" : 1 } ] } } }
Elasticsearch搜索语法中文文档:https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/2.x/_retrieving_a_document.html
9、清空索引数据
POST index_name/_delete_by_query
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}10、根据id删除一条数据
DELETE index_name/_doc/${_id}
更多API:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/rest-apis.html
END.






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(六):基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类