Java重试
ChatGPT:
在Java中,有一些重试框架可以帮助处理在执行某些操作时可能发生的错误,并尝试重新执行这些操作。以下是一些常用的Java重试框架:
-
Spring Retry:
- 特点: Spring Retry是Spring框架的一部分,提供了在方法执行失败时进行重试的机制。它通过注解或者编程方式来配置重试策略。
-
Guava Retryer:
- 特点: Google的Guava库提供了一个Retryer类,允许你指定重试的条件和策略。它具有灵活的配置选项。
-
Resilience4j:
- 特点: Resilience4j是一个轻量级且模块化的容错库,提供了重试、断路器、限流等功能。它与函数式编程兼容。
-
Failsafe:
- 特点: Failsafe是一个功能强大的库,支持失败重试、断路器、超时等。它具有简单的API和丰富的配置选项。
Guava-Retry
和 Spring Retry 相比,Guava Retry 具有更强的灵活性,并且能够根据 返回值 来判断是否需要重试,比如返回false我们就重试
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.github.rholder/guava-retrying -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.rholder</groupId>
<artifactId>guava-retrying</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>demo:
// RetryerBuilder 构建重试实例 retryer,可以设置重试源且可以支持多个重试源,可以配置重试次数或重试超时时间,以及可以配置等待时间间隔
Retryer<Boolean> retryer = RetryerBuilder.<Boolean> newBuilder()
.retryIfExceptionOfType(RemoteAccessException.class)//设置异常重试源
.retryIfResult(res-> res==false) //设置根据结果重试
.withWaitStrategy(WaitStrategies.fixedWait(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) //设置等待间隔时间
.withStopStrategy(StopStrategies.stopAfterAttempt(3)) //设置最大重试次数
.build();
try {
retryer.call(() -> RetryDemoTask.retryTask("abc"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}Retryer 是线程安全的:
Guava Retryer 是线程安全的,可以在多线程环境中使用。
Retryer 实例是不可变的(immutable),这意味着一旦创建,它的配置就不能被修改。因此,你可以在多个线程中共享相同的 Retryer 实例,而不必担心线程安全问题。
如果你需要在多个线程中同时使用 Retryer,建议创建一个全局共享的 Retryer 实例,而不是每个线程都创建一个新的实例。这有助于提高性能,因为不必反复创建对象,而且由于 Retryer 是不可变的,多个线程之间共享它是安全的。
以下是一个简单的示例,演示如何创建一个全局共享的 Retryer 实例:
import com.github.rholder.retry.Retryer;
import com.github.rholder.retry.RetryerBuilder;
public class GlobalRetryer {
private static final Retryer<Object> globalRetryer = RetryerBuilder.newBuilder()
// 配置重试策略
.retryIfException()
.retryIfRuntimeException()
.withMaxAttempts(3)
.build();
public static Retryer<Object> getGlobalRetryer() {
return globalRetryer;
}
}在多个线程中,你可以共享 GlobalRetryer.getGlobalRetryer() 实例来执行需要重试的操作
方式1、sisyphus
github:https://github.com/houbb/sisyphus
一、工具类方式使用
1、POM
<!-- retry -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.houbb</groupId>
<artifactId>sisyphus-core</artifactId>
<version>0.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.houbb</groupId>
<artifactId>sisyphus-annotation</artifactId>
<version>0.1.0</version>
</dependency>
2、SisyphusUtil:
package com.xxx.mitv.common.util; import com.github.houbb.sisyphus.core.core.RetryWaiter; import com.github.houbb.sisyphus.core.core.Retryer; import com.github.houbb.sisyphus.core.support.condition.RetryConditions; import com.github.houbb.sisyphus.core.support.listen.RetryListens; import com.github.houbb.sisyphus.core.support.recover.Recovers; import com.github.houbb.sisyphus.core.support.wait.ExponentialRetryWait; import com.github.houbb.sisyphus.core.support.wait.NoRetryWait; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; /** * 重试工具类
*/ public class SisyphusUtil { /** * 默认配置 * * @param callable 待重试执行方法 */ public static void defaultAttempt(final Callable<String> callable) { Retryer.<String>newInstance() //重试触发的条件,可以指定多个条件,默认为抛出异常。 .condition(RetryConditions.hasExceptionCause()) //重试等待的策略,可以指定多个,默认为不做任何等待。 .retryWaitContext(RetryWaiter.<String>retryWait(NoRetryWait.class).context()) //指定最大重试次数,包括第一次执行,默认3次 .maxAttempt(3) //指定重试的监听实现,默认为不做监听。 .listen(RetryListens.noListen()) //当重试完成之后,依然满足重试条件,则可以指定恢复的策略。默认不做恢复。 .recover(Recovers.noRecover()) //待重试执行的方法。 .callable(callable) //触发重试执行。 .retryCall(); } /** * 根据返回值等于期望值定制重试规则 * * @param condition 触发条件 * @param maxAttempt 最大重试次数 * @param initValue 第一次重试时间间隔 单位:毫秒。初始建议设置60000 * @param factor 递增因子 小于1越来越快,大于1越来越慢,等于1保持不变。 大部分场景设置2.0可满足需求 * @param callable 待重试执行方法 */ public static void attemptForEqualsResult(final String condition, final int maxAttempt, final int initValue, final double factor, final Callable<String> callable) { Retryer.<String>newInstance() .condition(RetryConditions.isEqualsResult(condition)) //递增策略 .retryWaitContext(RetryWaiter.<String>retryWait(ExponentialRetryWait.class).value(initValue).factor(factor).context()) .maxAttempt(maxAttempt) .listen(RetryListens.noListen()) .recover(Recovers.noRecover()) .callable(callable) .retryCall(); } /** * 根据返回值不等于期望值定制重试规则 * * @param condition 触发条件 * @param maxAttempt 最大重试次数 * @param initValue 第一次重试时间间隔 单位:毫秒。初始建议设置60000 * @param factor 递增因子 小于1越来越快,大于1越来越慢,等于1保持不变。 大部分场景设置2.0可满足需求 * @param callable 待重试执行方法 */ public static void attemptForNotEqualsResult(final String condition, final int maxAttempt, final int initValue, final double factor, final Callable<String> callable) { Retryer.<String>newInstance() .condition(RetryConditions.isNotEqualsResult(condition)) //递增策略 .retryWaitContext(RetryWaiter.<String>retryWait(ExponentialRetryWait.class).value(initValue).factor(factor).context()) .maxAttempt(maxAttempt) .listen(RetryListens.noListen()) .recover(Recovers.noRecover()) .callable(callable) .retryCall(); } /** * 根据是否存在异常定制重试规则 * * @param maxAttempt 最大重试次数 * @param initValue 第一次重试时间间隔 单位:毫秒。初始建议设置60000 * @param factor 递增因子 小于1越来越快,大于1越来越慢,等于1保持不变。 大部分场景设置2.0可满足需求 * @param callable 待重试执行方法 */ public static void attemptForException(final int maxAttempt, final int initValue, final double factor, final Callable<String> callable) { Retryer.<String>newInstance() .condition(RetryConditions.hasExceptionCause()) .retryWaitContext(RetryWaiter.<String>retryWait(ExponentialRetryWait.class).value(initValue).factor(factor).context()) .maxAttempt(maxAttempt) .listen(RetryListens.noListen()) .recover(Recovers.noRecover()) .callable(callable) .retryCall(); } }
3、应用
工具类方式:
//重试3次 SisyphusUtil.attemptForNotEqualsResult( "true", 3, 60000, 2.0, new Callable<String>() { @Override public String call() throws Exception { return autoRenewService.wechatAdvanceNotify(info) == true ? "true" : "false"; } });
注解方式:与Spring整合
@Retry :
/** * 重试注解 * 1. 实际需要,只允许放在方法上。 * 2. 如果放在接口上,是否所有的子类都生效?为了简单明确,不提供这种实现。 * 3. 保持注解和接口的一致性。{@link com.github.houbb.sisyphus.api.core.Retry} 接口 * @since 0.0.3 */ @Documented @Inherited @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @RetryAble(DefaultRetryAbleHandler.class) public @interface Retry { /** * 重试类实现 * @return 重试 * @since 0.0.5 */ Class<? extends com.github.houbb.sisyphus.api.core.Retry> retry() default DefaultRetry.class; /** * 最大尝试次数 * 1. 包含方法第一次正常执行的次数 * @return 次数 */ int maxAttempt() default 3; /** * 重试触发的场景 * @return 重试触发的场景 */ Class<? extends RetryCondition> condition() default ExceptionCauseRetryCondition.class; /** * 监听器 * 1. 默认不进行监听 * @return 监听器 */ Class<? extends RetryListen> listen() default NoRetryListen.class; /** * 恢复操作 * 1. 默认不进行任何恢复操作 * @return 恢复操作对应的类 */ Class<? extends Recover> recover() default NoRecover.class; /** * 等待策略 * 1. 支持指定多个,如果不指定,则不进行任何等待, * @return 等待策略 */ RetryWait[] waits() default {}; }
二、与Spring整合:
1、POM
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.houbb</groupId>
<artifactId>sisyphus-spring</artifactId>
<version>0.1.0</version>
</dependency>会默认引入 spring 以及 AOP 相关 jar
2、开启重试
@EnableRetry
/** * 启用重试注解 * @since 0.0.4 */ @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Import(RetryAopConfig.class) @EnableAspectJAutoProxy public @interface EnableRetry { }
3、使用 @Retry 标识方法需要进行重试。
如:
@Retry @Override public void test() { LOGGER.info("test"); int i=1/0; }
方式2、spring retry
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-retry#javaConfigForRetryProxies
翻译的中文文档:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000019932970
总结好文:https://albenw.github.io/posts/69a9647f/
spring retry是通过 AOP 实现的
1、依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.retry</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-retry</artifactId>
<version>1.2.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
如果使用 @Retryable 注解还需额外添加 aop和aspectj的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、在启动类或配置类加上 @EnableRetry 注解,表示启用重试机制
3、举例:
@Configuration @EnableRetry public class Application { @Bean public Service service() { return new Service(); } } @Service class Service { @Retryable(RemoteAccessException.class) public void service() { // ... do something } @Recover public void recover(RemoteAccessException e) { // ... panic } }
在此例中,当调用service()方法出现 RemoteAccessException 异常时,默认重试 3次(包含第一次的失败),如果仍失败,则会调用 recover 方法。
@Retryable 注解属性中有各种选项,用于包含和排除异常类型、限制重试次数和回退策略。
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface Retryable { /** * 为重试方法应用重试拦截器的bean名称。与其他属性互斥 */ String interceptor() default ""; /** * 可以重试的异常类型。与includes属性同义。默认值为空(并且如果exclude也是空的话,所有的异常都会重试) */ Class<? extends Throwable>[] value() default {}; Class<? extends Throwable>[] include() default {}; /** * 不重试的异常类型,默认为空(并且如果exclude也是空的话,所有的异常都会重试) */ Class<? extends Throwable>[] exclude() default {}; /** * A unique label for statistics reporting. If not provided the caller may choose to * ignore it, or provide a default. * * @return the label for the statistics */ String label() default ""; /** * 标识重试是有状态的。如果异常在重试的时候重新抛出, * Flag to say that the retry is stateful: i.e. exceptions are re-thrown, but the * retry policy is applied with the same policy to subsequent invocations with the * same arguments. If false then retryable exceptions are not re-thrown. * @return true if retry is stateful, default false */ boolean stateful() default false; /** * 尝试的最大次数(包含第一次失败),默认为3 */ int maxAttempts() default 3; /** * 返回一个求尝试最大次数值的表达式(包含第一次失败),默认为3 * 重写 {@link #maxAttempts()}。 */ String maxAttemptsExpression() default ""; /** * 退避策略,指怎么去做下一次的重试,在这里其实就是两次重试之间的间隔 */ Backoff backoff() default @Backoff(); /** * 在SimpleRetryPolicy.canRetry()返回true之后执行一个计算表达式,可用来有条件的取消重试 * 只在抛出异常后调用,求值的root对象为上一次的异常,可以引用上下文中的其他beans */ String exceptionExpression() default ""; }
@Backoff
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Import(RetryConfiguration.class) @Documented public @interface Backoff { /** * 与 delay() 属性同义 * 返回延迟多少毫秒后重试(默认为1000毫秒) */ long value() default 1000; /** * 一个标准的再重试周期,默认1000毫秒 * @return the initial or canonical backoff period in milliseconds (default 1000) */ long delay() default 0; /** * 重试之间最大等待(毫秒)时间。如果小于 {@link #delay()} 则忽略。 * @return the maximum delay between retries (default 0 = ignored) */ long maxDelay() default 0; /** * 如果是正数,则用于生成下次再重试等待时间的乘数 * 返回一个乘数用于计算下次再重试延迟(默认为0忽略) */ double multiplier() default 0; /** * 标准再重试周期求值表达式。在指数情况下用作初始值,始终如一的情况下用作最小值。 * Overrides {@link #delay()}. * @return the initial or canonical backoff period in milliseconds. * @since 1.2 */ String delayExpression() default ""; /** * 在重试之间最大等待(毫秒)数的求值表达式。 * * 如果小于 {@link #delay()} 则忽略。 * Overrides {@link #maxDelay()} * @return the maximum delay between retries (default 0 = ignored) * @since 1.2 */ String maxDelayExpression() default ""; /** * 表达式求值作为生成下次再重试延迟的乘数 * Overrides {@link #multiplier()}. * @since 1.2 */ String multiplierExpression() default ""; /** * 在指数情况下 ({@link #multiplier()} > 0) 设置该值为true将使再重试延迟随机化, * 使最大延迟为先前延迟的乘数倍数,并使这两个延迟值之间分布均匀。 * 默认为false */ boolean random() default false; }
实例:
/** * 第一次延迟1000ms,第二次延迟2*1000ms,第三次延迟2*2*1000ms,之后都是延迟5000ms */ @Retryable(maxAttempts = 6, backoff = @Backoff(delay = 1000, maxDelay = 5000, multiplier = 2)) @Override public void test() { LOGGER.error("spring retry:{}", DateUtil.formatDate(new Date())); throw new RuntimeException("my test"); }
输出:
2020-09-28 14:12:24.536|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|RetryTemplate#doExecute:282|Retry: count=0 2020-09-28 14:12:24.539|http-nio-8080-exec-1|ERROR|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|TaskServiceImpl#test:198|spring retry:Mon, 28 Sep 2020 06:12:24 GMT 2020-09-28 14:12:24.539|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|ExponentialBackOffPolicy#backOff:179|Sleeping for 1000 2020-09-28 14:12:25.541|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|RetryTemplate#doExecute:321|Checking for rethrow: count=1
2020-09-28 14:12:25.541|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|RetryTemplate#doExecute:282|Retry: count=1 2020-09-28 14:12:25.541|http-nio-8080-exec-1|ERROR|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|TaskServiceImpl#test:198|spring retry:Mon, 28 Sep 2020 06:12:25 GMT 2020-09-28 14:12:25.541|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|ExponentialBackOffPolicy#backOff:179|Sleeping for 2000 2020-09-28 14:12:27.542|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|RetryTemplate#doExecute:321|Checking for rethrow: count=2
2020-09-28 14:12:27.542|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|RetryTemplate#doExecute:282|Retry: count=2 2020-09-28 14:12:27.542|http-nio-8080-exec-1|ERROR|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|TaskServiceImpl#test:198|spring retry:Mon, 28 Sep 2020 06:12:27 GMT 2020-09-28 14:12:27.542|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|ExponentialBackOffPolicy#backOff:179|Sleeping for 40002020-09-28 14:12:31.542|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|RetryTemplate#doExecute:321|Checking for rethrow: count=3
2020-09-28 14:12:31.542|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|RetryTemplate#doExecute:282|Retry: count=3 2020-09-28 14:12:31.542|http-nio-8080-exec-1|ERROR|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|TaskServiceImpl#test:198|spring retry:Mon, 28 Sep 2020 06:12:31 GMT 2020-09-28 14:12:31.542|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|ExponentialBackOffPolicy#backOff:179|Sleeping for 50002020-09-28 14:12:36.543|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|RetryTemplate#doExecute:321|Checking for rethrow: count=4
2020-09-28 14:12:36.543|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|RetryTemplate#doExecute:282|Retry: count=4 2020-09-28 14:12:36.543|http-nio-8080-exec-1|ERROR|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|TaskServiceImpl#test:198|spring retry:Mon, 28 Sep 2020 06:12:36 GMT 2020-09-28 14:12:36.543|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|ExponentialBackOffPolicy#backOff:179|Sleeping for 50002020-09-28 14:12:41.544|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|RetryTemplate#doExecute:321|Checking for rethrow: count=5
2020-09-28 14:12:41.544|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|RetryTemplate#doExecute:282|Retry: count=5 2020-09-28 14:12:41.544|http-nio-8080-exec-1|ERROR|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|TaskServiceImpl#test:198|spring retry:Mon, 28 Sep 2020 06:12:41 GMT 2020-09-28 14:12:41.544|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|RetryTemplate#doExecute:321|Checking for rethrow: count=6 2020-09-28 14:12:41.544|http-nio-8080-exec-1|DEBUG|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|RetryTemplate#doExecute:346|Retry failed last attempt: count=6 2020-09-28 14:12:41.546|http-nio-8080-exec-1|ERROR|80e4d19848464ae1ac00ee957ca88a39|LogAspect#around:59|test方法执行异常:my test java.lang.RuntimeException: my test
Spring Retry缺点
1、其回退策略,默认使用的是Thread.sleep方法,会导致当前的线程被阻塞,因此使用的时候要注意。
2、只能在异常后重试,重试条件单一
方式3:ScheduledExecutorService
ScheduledExecutorService源码:
public interface ScheduledExecutorService extends ExecutorService { /** * 创建并执行一个一次性操作,该操作在给定的延迟后调用*/ public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit); /** * 创建和执行一个ScheduleFuture,该future在给定的延迟之后调用*/ public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit); /** * 每次执行时间为上一次任务开始起向后推一个时间间隔*/ public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit); /** * 每次执行时间为上一次任务结束后向后推一个时间间隔*/ public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit); }
Dubbo 2.6.x 及以下版本对ScheduleExecutorService的使用:
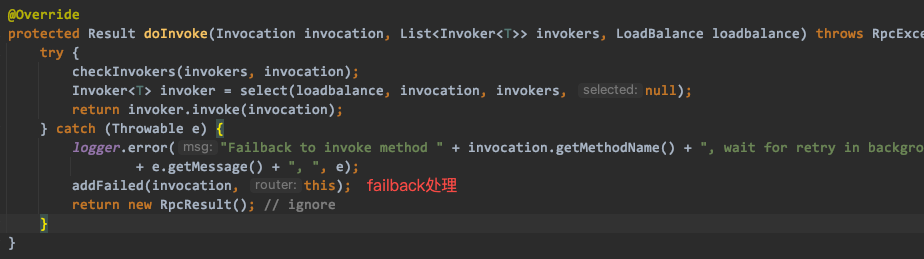
addFailed:
/** * 当失败时,记录失败请求,并计划在一个常规的间隔重试。特别适用于通知服务 */ public class FailbackClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FailbackClusterInvoker.class); private static final long RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD = 5 * 1000; // 重试时间间隔 /** * ScheduledExecutorService线程池 */ private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2, new NamedInternalThreadFactory("failback-cluster-timer", true)); // 缓存失败的调用,如果失败太多,有内存溢出风险 private final ConcurrentMap<Invocation, AbstractClusterInvoker<?>> failed = new ConcurrentHashMap<Invocation, AbstractClusterInvoker<?>>(); private volatile ScheduledFuture<?> retryFuture; public FailbackClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) { super(directory); } private void addFailed(Invocation invocation, AbstractClusterInvoker<?> router) { if (retryFuture == null) { synchronized (this) { if (retryFuture == null) { retryFuture = scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { // collect retry statistics try { retryFailed(); // 遍历failed map,对失败的调用发起重试 } catch (Throwable t) { // Defensive fault tolerance logger.error("Unexpected error occur at collect statistic", t); } } }, RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD, RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } } } // 如果retryFuture不为null,则将失败的调用添加在map缓存中 failed.put(invocation, router); } void retryFailed() { if (failed.size() == 0) { return; } for (Map.Entry<Invocation, AbstractClusterInvoker<?>> entry : new HashMap<Invocation, AbstractClusterInvoker<?>>( failed).entrySet()) { Invocation invocation = entry.getKey(); Invoker<?> invoker = entry.getValue(); try { invoker.invoke(invocation); failed.remove(invocation); // 成功之后将调用从缓存中移除 } catch (Throwable e) { logger.error("Failed retry to invoke method " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", waiting again.", e); } } } @Override protected Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException { try { checkInvokers(invokers, invocation); Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null); return invoker.invoke(invocation); } catch (Throwable e) { logger.error("Failback to invoke method " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", wait for retry in background. Ignored exception: " + e.getMessage() + ", ", e); addFailed(invocation, this); return new RpcResult(); // ignore } } }
但是这种方式,有个风险,就是如果失败的调用太多,缓存失败调用的ConcurrentHashMap存在内存溢出风险。
总结:
①:失败之后,将失败的调用添加到ConcurrentMap中缓存
②:scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay遍历需要重试的调用Map,依次发起重试,成功后从Map中移除
END.





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(六):基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
2019-09-17 HTTP协议