Spring事务总结
一、声明式事务 @Transactional
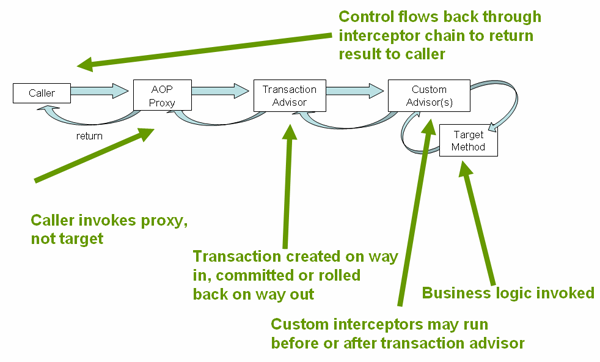
在事务代理上调用方法的执行路径示意图:
@Transactional注解配置
默认配置:
1、传播行为 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
2、隔离级别 ISOLATION_DEFAULT
3、事务是读写的 read-write
4、事务超时默认为基础事务系统的默认超时,如果不支持超时,则默认为无。
5、任何 RuntimeException 异常触发回滚,但是任何已检查异常不会
@Transactional注解属性介绍
1、propagation Spring事务传播机制:
| PROPAGATION_REQUIRED | Spring的默认传播级别,如果上下文中存在事务则加入当前事务,如果不存在事务则新建事务执行。 |
| PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS | 如果上下文中存在事务则加入当前事务,如果没有事务则以非事务方式执行。 |
| PROPAGATION_MANDATORY | 该传播级别要求上下文中必须存在事务,否则抛出异常。 |
| PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW | 该传播级别每次执行都会创建新事务,并同时将上下文中的事务挂起,执行完当前线程后再恢复上下文中事务。(子事务的执行结果不影响父事务的执行和回滚) |
| PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED | 当上下文中有事务则挂起当前事务,执行完当前逻辑后再恢复上下文事务。(降低事务大小,将非核心的执行逻辑包裹执行。) |
| PROPAGATION_NEVER | 该传播级别要求上下文中不能存在事务,否则抛出异常。 |
| PROPAGATION_NESTED | 嵌套事务,如果上下文中存在事务则嵌套执行,如果不存在则新建事务。(save point概念) |
常用传播机制:
1、PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
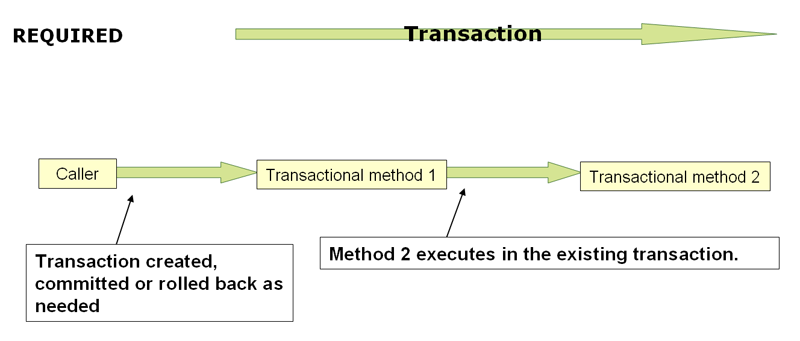
Spring的默认传播级别,如果上下文中存在事务则加入当前事务,如果不存在事务则新建事务执行。
2、PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW
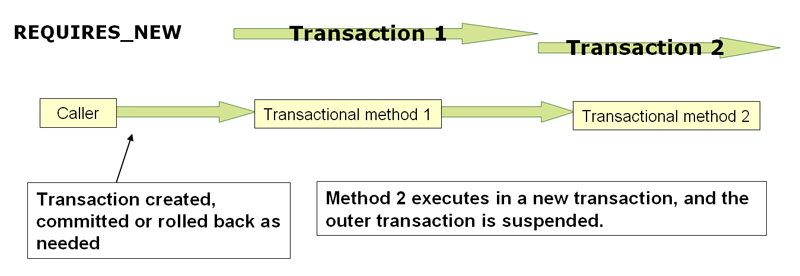
该传播级别每次执行都会创建新事务,并同时将上下文中的事务挂起,执行完当前线程后再恢复上下文中事务。(子事务的执行结果不影响父事务的执行和回滚)
3、PROPAGATION_NESTED
嵌套事务,如果上下文中存在事务则嵌套执行,如果不存在则新建事务。
PROPAGATION_NESTED 使用具有多个可还原到的保存点的单个物理事务。这种部分回滚使内部事务范围触发其范围的回滚,尽管某些操作已回滚,但外部事务仍能够继续物理事务。此设置通常映射到JDBC保存点,因此它仅适用于JDBC资源事务
2、isolation 隔离级别
| DEFAULT | 使用底层数据库默认的隔离级别 |
| READ_UNCOMMITTED | 读未提交 |
| READ_COMMITTED | 读已提交 |
| REPEATABLE_READ | 可重复度 |
| SERIALIZABLE | 串行化 |
3、timeout 事务超时时间
默认值为-1。如果超过该时间限制但事务还没有完成,则自动回滚事务
4、readOnly 事务是否为只读事务
默认值为 false;为了忽略那些不需要事务的方法,比如读取数据,可以设置 read-only 为 true。
5、rollbackFor
指定能够触发事务回滚的异常类型,可以指定多个异常类型。
6、noRollbackFor
抛出指定的异常类型,不回滚事务,也可以指定多个异常类型
总结:
注意:spring声明式事务是基于aop实现的。(只有来自外部方法的调用才会被aop代理捕获,类的内部方法调用不会被aop代理,即使此方法上面加了@Transactional注解)
Spring默认回滚 RuntimeException和error 异常
Spring声明式事务失效的几种情况:
1、事务方法不是public修饰的
Spring官方文档说明:When using proxies, you should apply the @Transactional annotation only to methods with public visibility. If you do annotate protected, private or package-visible methods with the @Transactional annotation, no error is raised, but the annotated method does not exhibit the configured transactional settings. Consider the use of AspectJ (see below) if you need to annotate non-public methods.
即:@Transactional 只能用于 public 的方法上,否则事务不会失效,如果要用在非 public 方法上,可以开启 AspectJ 代理模式。
2、方法用final修饰,或者static修饰的静态方法
Spring事务底层使用了aop,也就是通过jdk动态代理或者cglib,帮我们生成了代理类,在代理类中实现的事务功能
如果某个方法用final修饰或者static修饰,那么在它的代理类中,就无法重写该方法,而添加事务功能
3、自身调用问题
①:REQUIRED 传播机制下,没有@Transactional 标识的非事务方法内部调用 @Transactional标识的事务方法,事务失效
②:@Transactional标识的方法内部调用了 @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW) 标识的新开启一个事务的方法,这个新开的事务 不会生效。 不过,如果发生了异常,是可以回滚的。
因为发生自身调用的时候,就调用该类自己的方法,而没有经过Spring的代理类,默认只有在外部调用事务才会生效。
4、异常被方法内部捕获,没有向上抛出
如果必须要捕获异常,请在finally代码块中手动回滚:TransactionAspectSupport.currentTransactionStatus().setRollbackOnly();
5、异常类型不符
Spring事务默认回滚的是 RuntimeException(Exception的子类) ,如果你想触发其他异常的回滚,如不是RuntimeException子类的自定义异常,需要在@Transaction注解上配置回滚的异常类型:
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
6、数据源没有配置事务管理器被Spring管理,需配置如下:
@Bean public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() { return new DataSourceTransactionManager(myDataSource()); } }
7、@Transaction注解,指定的传播机制不支持事务,如 :@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED)
8、未开启事务、数据库存储引擎不支持事务
声明式事务配置
一、Spring 单数据源xml事务配置
1、定义数据源
2、用DataSourceTransactionManager事务管理器管理数据源
3、注册需要事务拦截的service <bean/>
4、要应用事务的方法规则 <tx:advice/>
5、aop切点配置,指定增强器,确保定义的事务通知在程序中的适当位置执行 <aop:config/>
<!-- from the file 'context.xml' --> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- this is the service object that we want to make transactional --> <bean id="fooService" class="x.y.service.DefaultFooService"/> <!-- the transactional advice (what 'happens'; see the <aop:advisor/> bean below) --> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager"> <!-- the transactional semantics... --> <tx:attributes> <!-- all methods starting with 'get' are read-only --> <tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/> //rollback-for="Throwable" no-rollback-for="InstrumentNotFoundException" <!-- other methods use the default transaction settings (see below) --> <tx:method name="*"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- ensure that the above transactional advice runs for any execution of an operation defined by the FooService interface --> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="fooServiceOperation" expression="execution(* x.y.service.FooService.*(..))"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="fooServiceOperation"/> </aop:config> <!-- don't forget the DataSource --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close"> <property name="driverClassName" value="oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@rj-t42:1521:elvis"/> <property name="username" value="scott"/> <property name="password" value="tiger"/> </bean> <!-- similarly, don't forget the PlatformTransactionManager --> <bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- other <bean/> definitions here --> </beans>
二、Spring 单数据源声明式事务配置
1、将@Transactional 注解声明在方法或类上;声明在类上,则声明类及其子类的所有方法都执行事务通知。注意:只作用于public修饰的方法。
2、若使用JavaConfig配置,则要在其中一个有@Configuration注解的配置类上@EnableTransactionManagement
3、在xml中使用<tx:annotation-driven/>
<!-- from the file 'context.xml' --> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- this is the service object that we want to make transactional --> <bean id="fooService" class="x.y.service.DefaultFooService"/> <!-- enable the configuration of transactional behavior based on annotations --> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/><!-- a PlatformTransactionManager is still required --> <bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <!-- (this dependency is defined somewhere else) --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- other <bean/> definitions here --> </beans>
注意:
@EnableTransactionManagement and <tx:annotation-driven/> looks for @Transactional only on beans in the same application context in which they are defined.
This means that, if you put annotation-driven configuration in a WebApplicationContext for a DispatcherServlet, it checks for @Transactional beans only in
your controllers and not your services. See MVC for more information.
@EnableTransactionManagement 注解和<tx:annotation-driven/>仅在定义和他们的相同应用程序上下文中的bean上去查找@Transactional注解。也就是说,如果将<tx:annotation-driven/>注解驱动的配置放在DispatcherServlet的WebApplicationContext中,它将仅在控制器controller中而不是service中检查@Transactional bean。
三、Spring多数据源声明式事务配置
四、Spring动态数据源AbstractRoutingDataSource声明式事务配置
手动回滚事务
有些情况下需要在事务目标方法内捕获异常,那么就需要手动回滚事务,在catch块中
// 手动回滚 TransactionAspectSupport.currentTransactionStatus().setRollbackOnly();
或者可以在上游捕获异常,异常回滚之后,仍会向上游抛出异常,就不用手动回滚。
二、编程式事务
声明式事务的问题:
1、数据库连接占用的时间过长
事务开始则创建连接,一直到事务结束再释放连接。如果中间有其他非数据库操作,也会占用数据库连接。高并发情况下,会造成数据库连接资源浪费
如果一个方法中的存在较多耗时操作,就容易引发长事务问题,而长事务会带来锁的竞争影响性能,同时也会导致数据库连接池被耗尽,影响程序的正常执行
2、使用不当会导致事务失效
如果方法存在嵌套调用,而被嵌套调用的方法也声明了@Transaction事物,就会出现事物的嵌套调用行为,容易引起事物的混乱造成程序运行结果出现异常
3、粒度粗,最小粒度是方法,不能是代码块
@Transaction声明式事务是将事物控制逻辑放在注解中,如果项目的复杂度增加,事务的控制可能会变得更加复杂,导致代码可读性和维护性下降
Spring事务管理:
Spring中对事务抽象出三个核心接口:TransactionDefinition、PlatformTransactionManager和TransactionStatus
1、TransactionDefinition:
存放事务的配置信息,如事务隔离级别、事务传播特性、超时、只读事务等等
2、PlatformTransactionManager
事务管理器,提供了与事务相关的三个操作:事务创建、事务提交、事务回滚
3、TransactionStatus
代表具体某一个事务的运行状态,通过它可以判断对一个事务是执行提交或者回滚操作
简单梳理下它们三者关系:平台事务管理器真正管理事务对象,其会根据事务定义信息TransactionDefinition进行事务管理,在管理事务中产生一些状态信息会记录到TransactionStatus中
编程式事务实践
1、创建事务管理器
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
return dataSourceTransactionManager;
}2、事务操作
@Resource
private DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager;
@Test
public void testTransaction() {
DefaultTransactionDefinition def = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
//1.开启一个事务
TransactionStatus transactionStatus = transactionManager.getTransaction(def);
try {
// 执行sql1
// 执行sql2
//4.正常时进行事务提交
transactionManager.commit(transactionStatus);
} catch (Exception e) {
//5.出现异常后进行事务回滚
transactionManager.rollback(transactionStatus);
}
}
Spring编程式事务实践
Spring提供了一个专门处理事务工具类:TransactionTemplate
1、创建TransactionTemplate实例
@Bean
public TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate(PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) {
return new TransactionTemplate(transactionManager);
}2、事务操作
@Resource
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
@Test
public void testTransactionTemplate() {
transactionTemplate.executeWithoutResult(transactionStatus -> {
try {
//执行sql1
//执行sql2
} catch (Exception e) {
//5.出现异常后进行事务回滚,注意,如果这里不进行回滚依然提交,sql1会被提交,sql2由于异常导致没有执行到
transactionStatus.setRollbackOnly();
}
});
}transactionTemplate通过接口回调方式,在方法中可以获取到事务运行状态信息TransactionStatus,然后通过它即可实现提交or回滚。如果需要回滚事务,只需要执行status.setRollbackOnly()即可,否则就会进行事务提交
execute、executeWithoutResult
①、execute 带返回值
/*
* 执行带有返回值<Object>的事务管理
*/
transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallback<Object>() {
@Override
public Object doInTransaction(TransactionStatus transactionStatus) {
try {
...
//....... 业务代码
return new Object();
} catch (Exception e) {
//回滚
transactionStatus.setRollbackOnly();
return null;
}
}
});②、executeWithoutResult无返回值
和execute的区别的地方就在于:看返回值是否有对应的结果。如果有返回值,那么就直接使用execute方法;如果没有返回值,就直接使用executeWithoutResult方法即可
/*
* 执行无返回值的事务管理
*/
transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() {
@Override
protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus transactionStatus) {
try {
// .... 业务代码
} catch (Exception e) {
//回滚
transactionStatus.setRollbackOnly();
}
}
});
编程式事务管理
MyBatis 的 SqlSession 提供几个方法来在代码中处理事务。但是当使用 MyBatis-Spring 时,你的 bean 将会注入由 Spring 管理的 SqlSession 或Mapper(映射器)。也就是说,Spring 总是为你处理了事务
不能在 Spring 管理的 SqlSession 上调用 SqlSession.commit(),SqlSession.rollback() 或 SqlSession.close() 方法。如果这样做了,就会抛出 UnsupportedOperationException 异常。在使用注入的Mapper(映射器)时,这些方法也不会暴露出来。
无论 JDBC 连接是否设置为自动提交,调用 SqlSession 数据方法或在 Spring 事务之外调用任何在Mapper(映射器)中方法,事务都将会自动被提交
如果你想编程式地控制事务,请参考 the Spring reference document(Data Access -Programmatic transaction management-)
下面的代码展示了如何使用 PlatformTransactionManager 手工管理事务:
public class TestService { private final PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager; public TestService(PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) { this.transactionManager = transactionManager; } @Autowired private TestMapper testMapper; public void createUser() { TransactionStatus txStatus = transactionManager.getTransaction(new DefaultTransactionDefinition()); try { testMapper.insertUser(user); } catch (Exception e) { transactionManager.rollback(txStatus); throw e; } transactionManager.commit(txStatus); } }
在使用 TransactionTemplate 的时候,可以省略对 commit 和 rollback 方法的调用
public class UserService { private final PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager; public UserService(PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) { this.transactionManager = transactionManager; } public void createUser() { TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate = new TransactionTemplate(transactionManager); transactionTemplate.execute(txStatus -> { userMapper.insertUser(user); return null; }); } }
注意:虽然这段代码使用的是一个Mapper映射器,但换成 SqlSession 也是可以工作的。
问题
for循环中的一个循环如何回滚?
场景:for循环中的一个循环出现异常的话,会将所有执行过的循环全部回滚,如果只想回滚出现异常的那条循环,该怎么办?
方案:
情况1:for循环所在的方法有事务,在for循环之外有修改操作,for循环之外的异常也需要回滚
①:将for循环内的逻辑封装成一个方法,并放在一个单独的bean中
②:在新的bean上的此方法上加上注解:@Transactional(transactionManager = "dataSourceTransactionManager", propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW, rollbackFor = Exception.class)
使用 PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 传播机制
ServiceA: @Autowired private ServiceB serviceB; @Transactional(transactionManager = "dataSourceTransactionManager", rollbackFor = Exception.class) @Override public void handle() { LOGGER.info("转码任务开始"); // 转码模块CODE为 TRANS_CODE,查询转码模块的id AuditModule auditModule = auditModuleDao.queryByCode(CommonConstants.TRANS_CODE); if (auditModule == null) { return; } // 插入或者修改操作 auditModuleDao.update(xxx); // 查询拿到令牌的待转码的子流程 Integer moduleId = auditModule.getId(); List<AuditSubFlow> auditSubFlows = auditSubFlowDao.queryToAudit(moduleId); for (AuditSubFlow auditSubFlow : auditSubFlows) { serviceB.execute(moduleId, auditSubFlow); } LOGGER.info("转码任务结束"); }
ServiceB: @Transactional(transactionManager = "dataSourceTransactionManager", propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW, rollbackFor = Exception.class) public void execute(Integer moduleId, AuditSubFlow auditSubFlow) { ... }
情况2:for循环之外之外没有修改操作,不需要回滚,只需对for循环内进行回滚
①:将for循环内的逻辑封装成一个方法,并放在一个单独的bean中
②:在新的bean上的此方法上加上注解:@Transactional(transactionManager = "dataSourceTransactionManager", rollbackFor = Exception.class) 即可
END.





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(六):基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
2019-04-02 JDK 1.8 JVM的变化
2019-04-02 JDK1.8 hashMap源码分析