Java 比较两个字符串的相似度算法(Levenshtein Distance)
转载自: https://blog.csdn.net/JavaReact/article/details/82144732
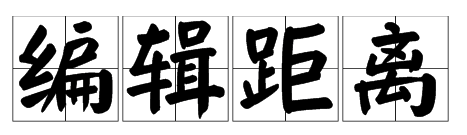
算法简介:
Levenshtein Distance,又称编辑距离,指的是两个字符串之间,由一个转换成另一个所需的最少编辑操作次数。
许可的编辑操作包括将一个字符替换成另一个字符,插入一个字符,删除一个字符。
编辑距离的算法是首先由俄国科学家Levenshtein提出的,故又叫Levenshtein Distance。
-
/**
-
* 比较两个字符串的相识度
-
* 核心算法:用一个二维数组记录每个字符串是否相同,如果相同记为0,不相同记为1,每行每列相同个数累加
-
* 则数组最后一个数为不相同的总数,从而判断这两个字符的相识度
-
*
-
* @param str
-
* @param target
-
* @return
-
*/
-
private static int compare(String str, String target) {
-
int d[][]; // 矩阵
-
int n = str.length();
-
int m = target.length();
-
int i; // 遍历str的
-
int j; // 遍历target的
-
char ch1; // str的
-
char ch2; // target的
-
int temp; // 记录相同字符,在某个矩阵位置值的增量,不是0就是1
-
if (n == 0) {
-
return m;
-
}
-
if (m == 0) {
-
return n;
-
}
-
d = new int[n + 1][m + 1];
-
// 初始化第一列
-
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
-
d[i][0] = i;
-
}
-
// 初始化第一行
-
for (j = 0; j <= m; j++) {
-
d[0][j] = j;
-
}
-
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
-
// 遍历str
-
ch1 = str.charAt(i - 1);
-
// 去匹配target
-
for (j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
-
ch2 = target.charAt(j - 1);
-
if (ch1 == ch2 || ch1 == ch2 + 32 || ch1 + 32 == ch2) {
-
temp = 0;
-
} else {
-
temp = 1;
-
}
-
// 左边+1,上边+1, 左上角+temp取最小
-
d[i][j] = min(d[i - 1][j] + 1, d[i][j - 1] + 1, d[i - 1][j - 1] + temp);
-
}
-
}
-
return d[n][m];
-
}
-
-
-
/**
-
* 获取最小的值
-
*/
-
private static int min(int one, int two, int three) {
-
return (one = one < two ? one : two) < three ? one : three;
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 获取两字符串的相似度
-
*/
-
public static float getSimilarityRatio(String str, String target) {
-
int max = Math.max(str.length(), target.length());
-
return 1 - (float) compare(str, target) / max;
-
}
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
String a= "Steel";
-
String b = "Steel Pipe";
-
System.out.println("相似度:"+getSimilarityRatio(a,b));
-
}
算法原理:
该算法的解决是基于动态规划的思想,具体如下:
设 s 的长度为 n,t 的长度为 m。如果 n = 0,则返回 m 并退出;如果 m=0,则返回 n 并退出。否则构建一个数组 d[0..m, 0..n]。
将第0行初始化为 0..n,第0列初始化为0..m。
依次检查 s 的每个字母(i=1..n)。
依次检查 t 的每个字母(j=1..m)。
如果 s[i]=t[j],则 cost=0;如果 s[i]!=t[j],则 cost=1。将 d[i,j] 设置为以下三个值中的最小值:
紧邻当前格上方的格的值加一,即 d[i-1,j]+1
紧邻当前格左方的格的值加一,即 d[i,j-1]+1
当前格左上方的格的值加cost,即 d[i-1,j-1]+cost
重复3-6步直到循环结束。d[n,m]即为莱茵斯坦距离。
参考链接:
http://wdhdmx.iteye.com/blog/1343856
https://www.cnblogs.com/ymind/archive/2012/03/27/fast-memory-efficient-Levenshtein-algorithm.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号