Spring有哪些配置方式
1、XML 配置文件。
Bean 所需的依赖项和服务在 XML 格式的配置文件中指定。这些配置文件通常包含许多 bean 定义和特定于应用程序的配置选项。它们通常以 bean 标签开头。例如:
<bean id="studentBean" class="org.edureka.firstSpring.StudentBean">
<property name="name" value="Edureka"></property>
</bean>
2、注解配置。
您可以通过在相关的类,方法或字段声明上使用注解,将 Bean 配置为组件类本身,而不是使用 XML 来描述 Bean 装配。默认情况下,Spring 容器中未打开注解装配。因此,您需要在使用它之前在 Spring 配置文件中启用它。例如:
<beans> <context:annotation-config/> <!-- bean definitions go here --> </beans>
@Service @Component @Repository @Controlle
3、Java Config 配置。
Spring 的 Java 配置是通过使用 @Bean 和 @Configuration 来实现。
@Bean注解扮演与<bean />元素相同的角色。用到方法上,表示当前方法的返回值是一个bean@Configuration类允许通过简单地调用同一个类中的其他@Bean方法来定义 Bean 间依赖关系。相当于spring的配置文件XML
例如:
@Configuration
public class StudentConfig {
@Bean
public StudentBean myStudent() {
return new StudentBean();
}
}
这几种方式没有什么所谓的优劣之分,主要看使用情况,一般来说是这样:
涉及到全局配置的,例如数据库相关配置、MVC相关配置等,就用Java Config 配置的方式
涉及到业务配置的,就使用注解方式
*****************************************************************************
*****************************************************************************
Java Config 配置 解释:https://blog.csdn.net/peng86788/article/details/81188049
定义 JavaConfig 类 对于一个 POJO 类,在类上使用@Configuration 注解,将会使当前类作为一个 Spring 的容器来使用,用于完成 Bean 的创建。在该 JavaConfig 的方法上使用@Bean,将会使一个普通方法所返回的结果变为指定名称的 Bean 实例。
package com.lzl.spring.entity;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowire;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
//该注解表示这个类为javaConfig类
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
//该注解表示:向容器中注册一个叫做myCar的对象
@Bean("myCar")
public Car getCar() {
return new Car("保时捷","911",300);
}
//该注解表示:向容器中注册一个叫做person的对象
//并且通过byType的方式注入car
@Bean(name="person",autowire=Autowire.BY_TYPE)
public Person getPerson() {
return new Person(1001,"望穿秋水见伊人");
}
}
xml文件只需要添加自动扫描包配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.lzl.spring" />
</beans>
测试类
package com.lzl.spring.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.lzl.spring.entity.Car;
import com.lzl.spring.entity.Person;
public class SpringTest {
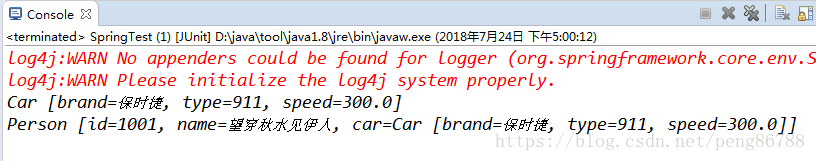
@Test
public void test1() {
//读取配置文件
ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
Car car = ctx.getBean("myCar", Car.class);
System.out.println(car);
Person person = ctx.getBean("person", Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
}
控制台输出