使用chrome tracing 可视化benchmark结果
打开chrome内核的浏览器,输入:chrome://tracing
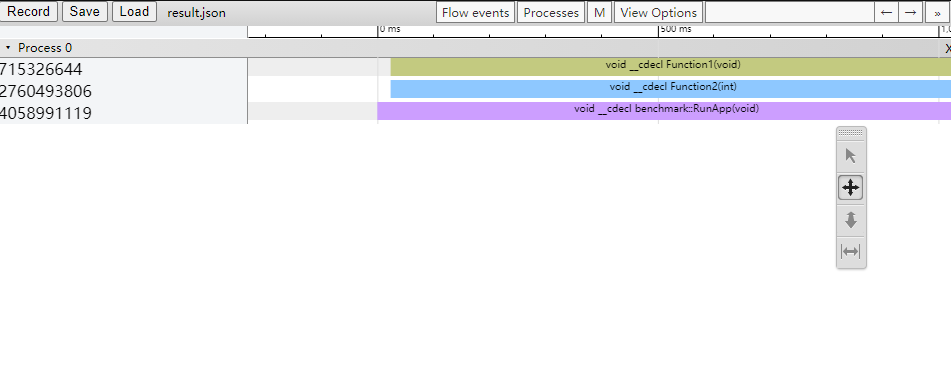
将我们benchmark结果的json文件直接拖动到浏览器中就可以看到benchmark的结果。效果图如下:
C++实现
实现计时器类,并输出调用函数相关的调用信息到文件中,具体实现如下:
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <chrono>
#include <algorithm>
#include <thread>
#define PROFILING 1
#if PROFILING
#define PROFILE_SCOPE(name) InstrumentationTimer timer##__LINE__(name)
#define PROFILE_FUNCTION() PROFILE_SCOPE(__FUNCSIG__)
#else
#define PROFILE_SCORE(name)
#endif
//当前监测的会话
struct InstrumentationSession
{
std::string name;
};
//检测结果数据
struct ProfileResult
{
std::string name; //调用栈函数名称
long long start, stop; //起止时间
uint32_t threadID; //线程ID
};
class Instrumentor
{
private:
InstrumentationSession* m_CurrentSession;
std::ofstream m_OutputStream;
int m_ProfileCount;
public:
Instrumentor() : m_CurrentSession(nullptr), m_ProfileCount(0)
{
}
void BeginSession(const std::string& name, const std::string& filepath = "result.json")
{
m_OutputStream.open(filepath);
WriteHeader();
m_CurrentSession = new InstrumentationSession{ name };
}
void EndSession()
{
WriteFooter();
m_OutputStream.close();
delete m_CurrentSession;
m_CurrentSession = nullptr;
m_ProfileCount = 0;
}
void WriteProfile(const ProfileResult& result)
{
if (m_ProfileCount++ > 0)
{
m_OutputStream << ",";
}
std::string name = result.name;
std::replace(name.begin(), name.end(), '"', '\'');
m_OutputStream << "{";
m_OutputStream << "\"cat\":\"function\",";
m_OutputStream << "\"dur\":" << (result.stop - result.start) << ",";
m_OutputStream << "\"name\":\"" << name << "\",";
m_OutputStream << "\"ph\":\"X\",";
m_OutputStream << "\"pid\": 0,";
m_OutputStream << "\"tid\": \"" << result.threadID << "\",";
m_OutputStream << "\"ts\": " << result.start;
m_OutputStream << "}";
m_OutputStream.flush();
}
void WriteHeader()
{
m_OutputStream << "{\"otherData\": {}, \"traceEvents\": [";
m_OutputStream.flush();
}
void WriteFooter()
{
m_OutputStream << "]}";
m_OutputStream.flush();
}
static Instrumentor& Get()
{
static Instrumentor* instance = new Instrumentor();
return *instance;
}
};
//计时器
class InstrumentationTimer
{
private:
std::string title;
std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::time_point m_start;
bool m_stoped;
public:
InstrumentationTimer(const std::string& title) : title(title), m_stoped(false)
{
m_start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
}
~InstrumentationTimer()
{
if (!m_stoped)
{
stop();
}
}
void stop()
{
auto m_stop = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
long long start = std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(m_start).time_since_epoch().count();
long long stop = std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(m_stop).time_since_epoch().count();
uint32_t threadID = std::hash<std::thread::id>{}(std::this_thread::get_id());
Instrumentor::Get().WriteProfile({ title, start, stop, threadID});
m_stoped = true;
}
};
测试调用:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "Timer.h"
#include <cmath>
void Function1()
{
PROFILE_FUNCTION();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
std::cout << pow(i, sqrt(sqrt(i))) << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void Function2(int v)
{
PROFILE_FUNCTION();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
std::cout << abs(i * v) << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
namespace benchmark {
void RunApp()
{
PROFILE_FUNCTION();
std::thread a([]() {Function1(); });
std::thread b([]() {Function2(10); });
a.join();
b.join();
}
}
int main()
{
Instrumentor::Get().BeginSession("profile");
benchmark::RunApp();
Instrumentor::Get().EndSession();
}
将执行结果的result.json文件拖到浏览器内:

参考:
https://www.chromium.org/developers/how-tos/trace-event-profiling-tool



