kernel——kobj
设备模型的意义
为了避免驱动开发中对相同功能的重复实现,内核按照面向对象的思想,实现了一套驱动开发通用的函数和对象,称为设备模型。
如下,根据开发驱动的不同,继承不同父类,简化开发。

kobject
kobj使用示例
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/kobject.h>
#include <linux/sysfs.h>
char hello_buf[100];
unsigned long hello_value;
static ssize_t value_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_attribute *attr,
char *buf)
{
return sprintf(buf, "hello_value = %lu\n", hello_value);
}
static ssize_t value_store(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count)
{
char tmp_buf[10] = {0};
strncpy(tmp_buf, buf, count);
hello_value = simple_strtoul(tmp_buf, NULL, 0);
return count;
}
static struct kobj_attribute value_attribute = {
.attr = {
.name = "value",
.mode = 0664,
},
.show = value_show,
.store = value_store,
};
static ssize_t hello_buf_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_attribute *attr,
char *buf)
{
strncpy(buf, hello_buf, strlen(hello_buf));
return strlen(hello_buf);
}
static ssize_t hello_buf_store(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count)
{
strncpy(hello_buf, buf, count);
return count;
}
static struct kobj_attribute foo_attribute =
__ATTR(buf, 0664, hello_buf_show, hello_buf_store);
static struct attribute *hello_attrs[] = {
&value_attribute.attr,
&foo_attribute.attr,
NULL,
};
#if 1
static struct attribute_group hello_group = {
.attrs = hello_attrs,
};
#else
ATTRIBUTE_GROUPS(hello);
#endif
static struct kobject *kobj_hello;
static int kobject_hello_init(void)
{
int retval;
// 创建目录 /sys/hello
kobj_hello = kobject_create_and_add("hello", NULL);
if (!kobj_hello)
return -ENOMEM;
// 在 /sys/hello 下创建一堆文件(属性)
retval = sysfs_create_group(kobj_hello, &hello_group);
if (retval) {
printk(KERN_ALERT "%s: create sysfs file group failed\n", __func__);
kobject_put(kobj_hello);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
void kobject_hello_exit(void){
// 将kobj_hello引用计数减一,若引用计数为0,则释放kobj和相关attr
kobject_put(kobj_hello);
}
module_init(kobject_hello_init);
module_exit(kobject_hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("wit@zhaixue.cc");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("how to create a file in sysfs");
sysfs
注册和挂载
注册

挂载

当 sysfs 完成挂载:
1)创建 sysfs的 superblock
2)创建 根节点,根目录项
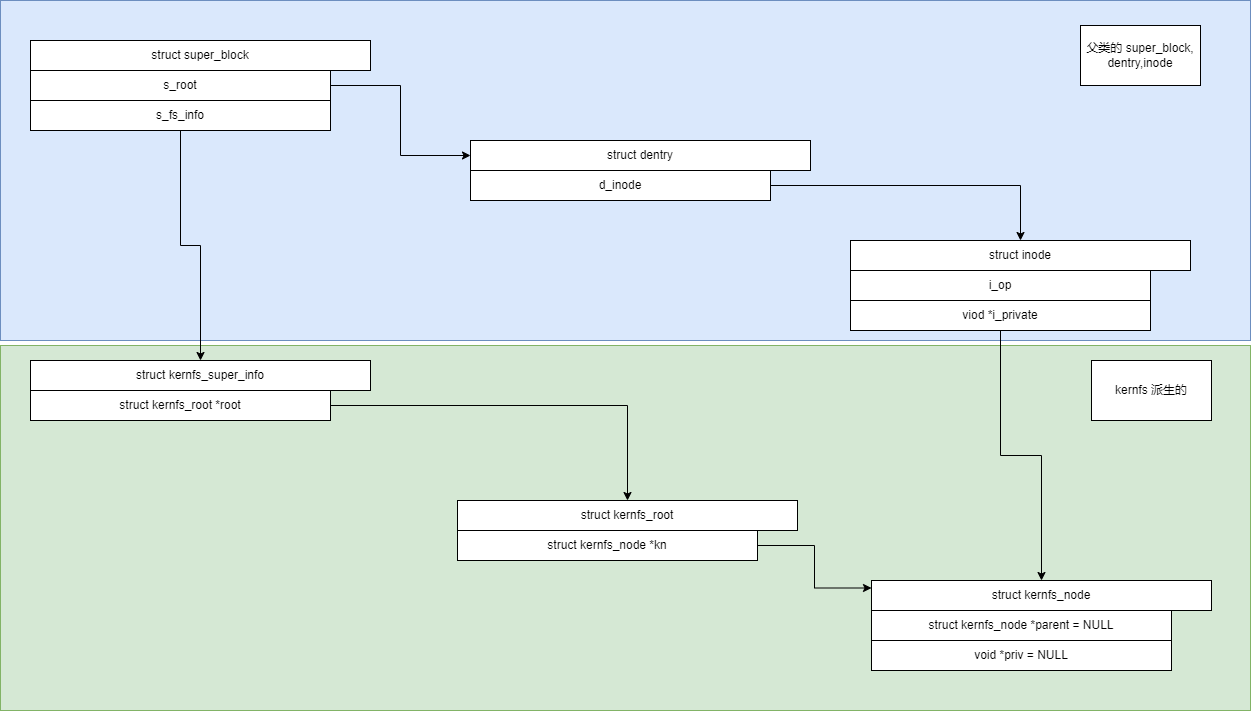
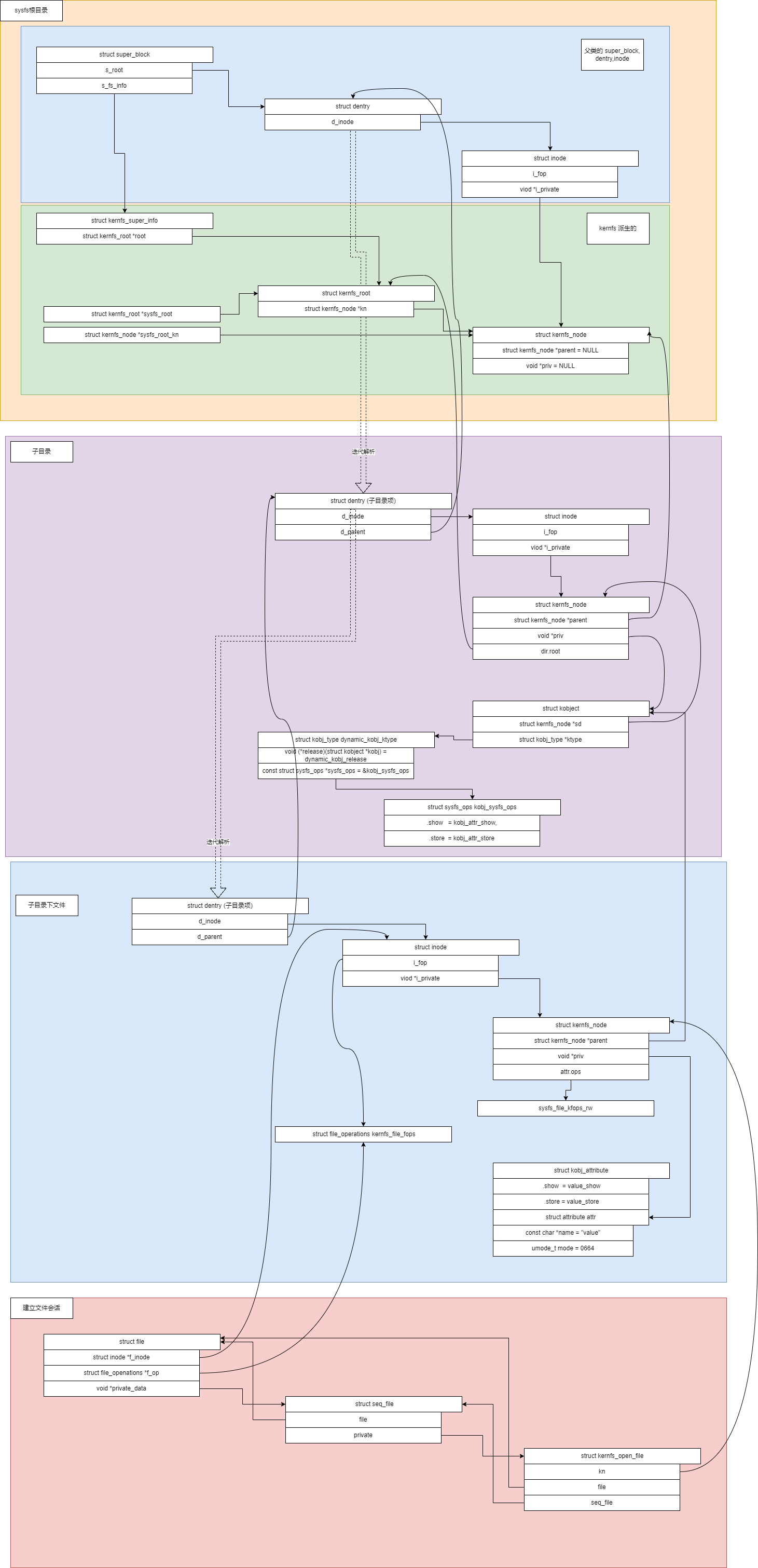
sysfs创建目录分析
代码分析

对象关系
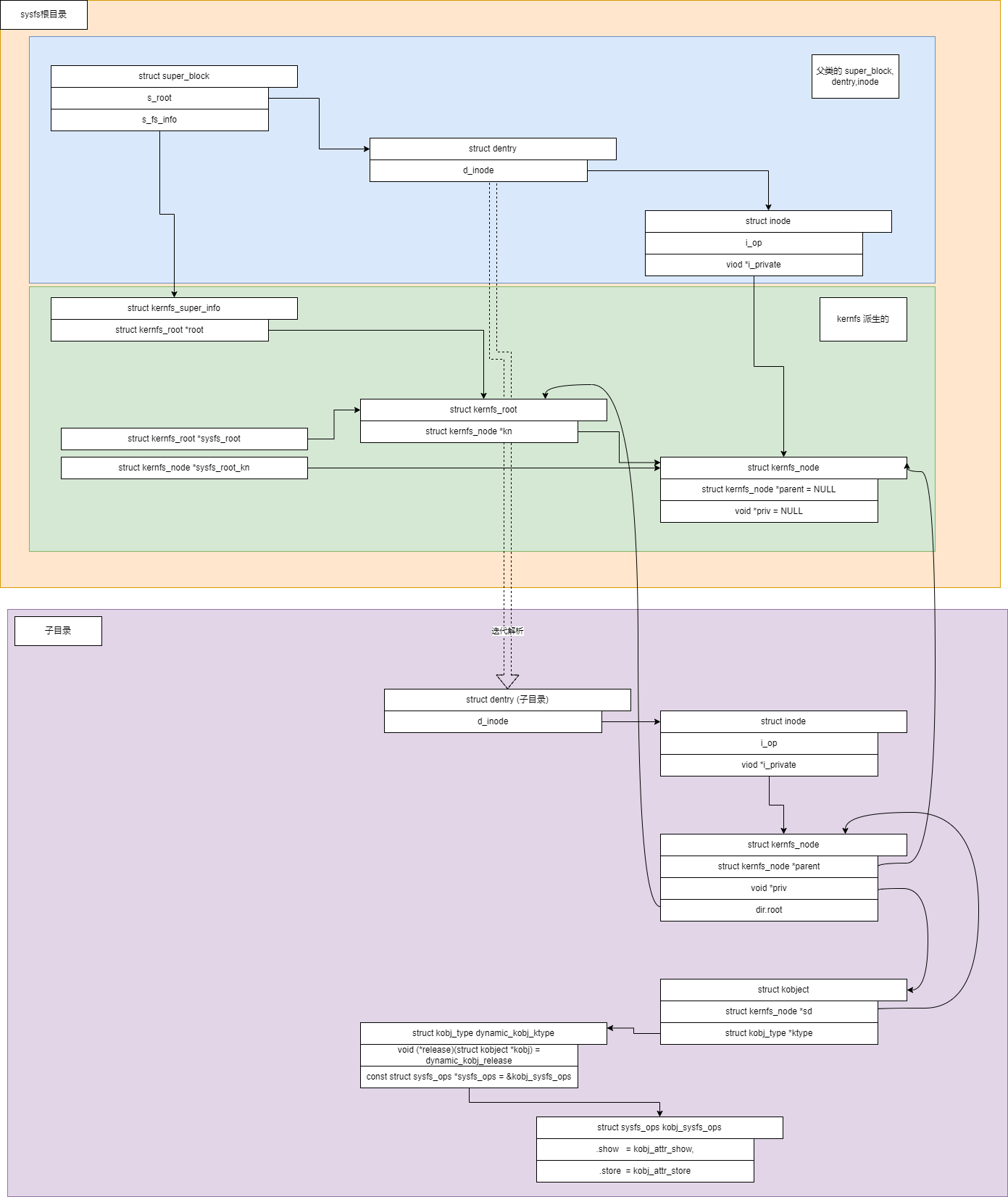
总结
sysfs创建目录:创建 VFS层节点和目录项,创建 kernfs节点,将inode和kernfs_node和 kobject 关联
sysfs创建文件
代码分析

对象关系

总结
sysfs创建文件不会关联kobj,只创建inode和kernfs_node,并指向父目录的kernfs_node
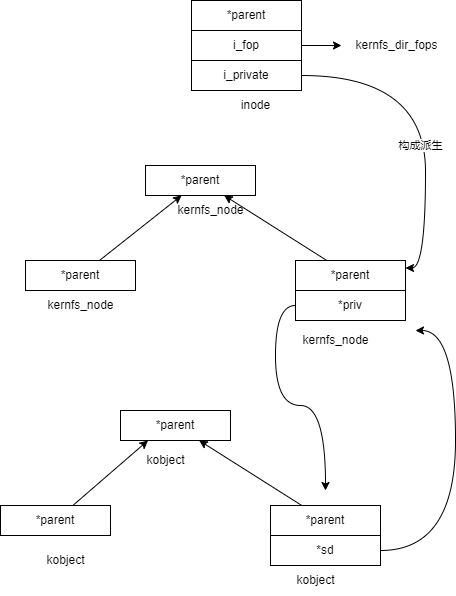
内核如何创建 VFS 节点
上面分析的代码中,直接构建的是 kernfs 的节点,VFS节点创建是通过 LSM的hook技术。
相关代码
static struct kernfs_node *__kernfs_new_node(struct kernfs_root *root,
struct kernfs_node *parent,
const char *name, umode_t mode,
kuid_t uid, kgid_t gid,
unsigned flags)
{
if (parent) {
ret = security_kernfs_init_security(parent, kn);
if (ret)
goto err_out3;
}
}
int security_kernfs_init_security(struct kernfs_node *kn_dir,
struct kernfs_node *kn)
{
return call_int_hook(kernfs_init_security, 0, kn_dir, kn);
}
当注册后,在打开 /sys/hello 节点和 /sys/hello/buf 节点时,会调用 i_op->lookup 以构造VFS 层的 dentry, inode
yangxr@vexpress:/root # echo "aa" > /sys/hello/buf
CPU: 0 PID: 61 Comm: sh Tainted: G O 5.16.2 #19
Hardware name: ARM-Versatile Express
[<8010f318>] (unwind_backtrace) from [<8010b204>] (show_stack+0x10/0x14)
[<8010b204>] (show_stack) from [<8083e450>] (dump_stack_lvl+0x40/0x4c)
[<8083e450>] (dump_stack_lvl) from [<8030a68c>] (kernfs_get_inode+0x24/0x154)
[<8030a68c>] (kernfs_get_inode) from [<8030b86c>] (kernfs_iop_lookup+0x58/0xac)
[<8030b86c>] (kernfs_iop_lookup) from [<8028c5dc>] (__lookup_slow+0x88/0x14c)
[<8028c5dc>] (__lookup_slow) from [<8028dd6c>] (walk_component+0x12c/0x19c)
[<8028dd6c>] (walk_component) from [<8028dfa8>] (link_path_walk+0x1cc/0x36c)
[<8028dfa8>] (link_path_walk) from [<8028e57c>] (path_openat+0x80/0xc8c)
[<8028e57c>] (path_openat) from [<8028fc80>] (do_filp_open+0x7c/0xe8)
[<8028fc80>] (do_filp_open) from [<8027b890>] (do_sys_openat2+0x28c/0x3d4)
[<8027b890>] (do_sys_openat2) from [<8027cd1c>] (do_sys_open+0x90/0xac)
[<8027cd1c>] (do_sys_open) from [<80100060>] (ret_fast_syscall+0x0/0x54)
Exception stack(0x81a59fa8 to 0x81a59ff0)
9fa0: 00000241 00000008 00217d64 00020241 000001b6 00000000
9fc0: 00000241 00000008 00217cec 00000005 0021b6a0 00214b48 ffffffff 00217ab8
9fe0: 7efdc560 7efdc398 0006ccf8 00143d4c
CPU: 0 PID: 61 Comm: sh Tainted: G O 5.16.2 #19
Hardware name: ARM-Versatile Express
[<8010f318>] (unwind_backtrace) from [<8010b204>] (show_stack+0x10/0x14)
[<8010b204>] (show_stack) from [<8083e450>] (dump_stack_lvl+0x40/0x4c)
[<8083e450>] (dump_stack_lvl) from [<8030a68c>] (kernfs_get_inode+0x24/0x154)
[<8030a68c>] (kernfs_get_inode) from [<8030b86c>] (kernfs_iop_lookup+0x58/0xac)
[<8030b86c>] (kernfs_iop_lookup) from [<8028efb0>] (path_openat+0xab4/0xc8c)
[<8028efb0>] (path_openat) from [<8028fc80>] (do_filp_open+0x7c/0xe8)
[<8028fc80>] (do_filp_open) from [<8027b890>] (do_sys_openat2+0x28c/0x3d4)
[<8027b890>] (do_sys_openat2) from [<8027cd1c>] (do_sys_open+0x90/0xac)
[<8027cd1c>] (do_sys_open) from [<80100060>] (ret_fast_syscall+0x0/0x54)
Exception stack(0x81a59fa8 to 0x81a59ff0)
9fa0: 00000241 00000008 00217d64 00020241 000001b6 00000000
9fc0: 00000241 00000008 00217cec 00000005 0021b6a0 00214b48 ffffffff 00217ab8
9fe0: 7efdc560 7efdc398 0006ccf8 00143d4c
代码分析如下

总结
kernfs通过 hook 完成了:
1)构建inode节点,并建立 inode 和 kernfs 节点间的关联
2)建立dentry和 inode间的关联
打开过程
代码分析
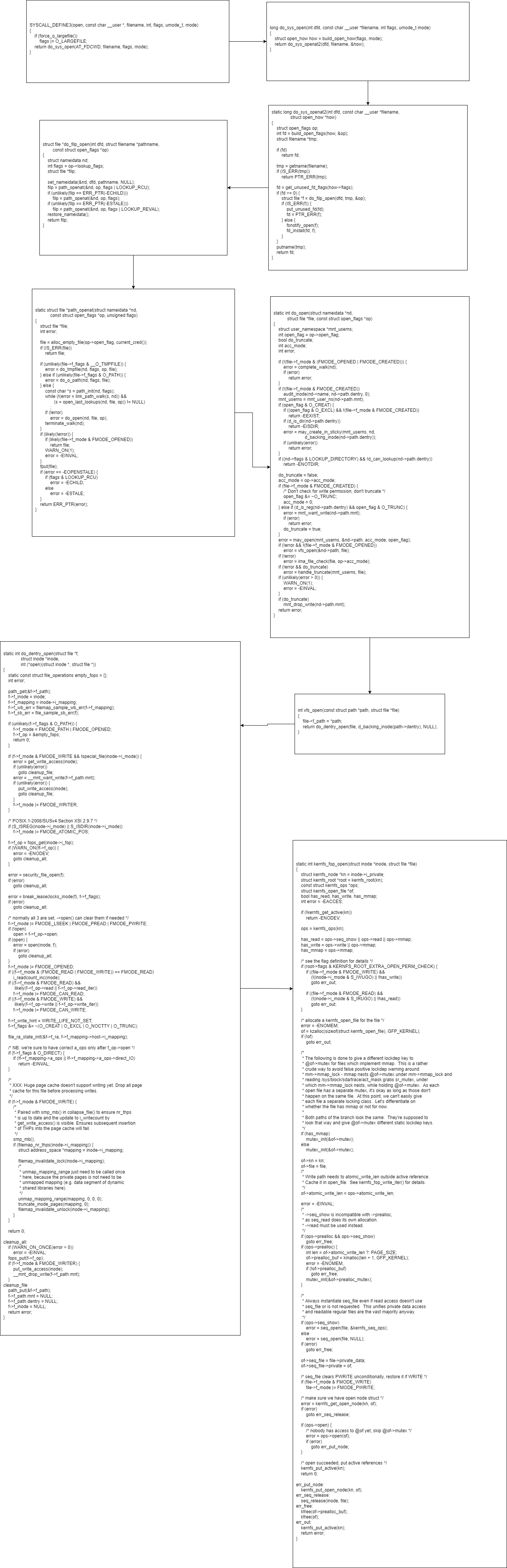
对象关系
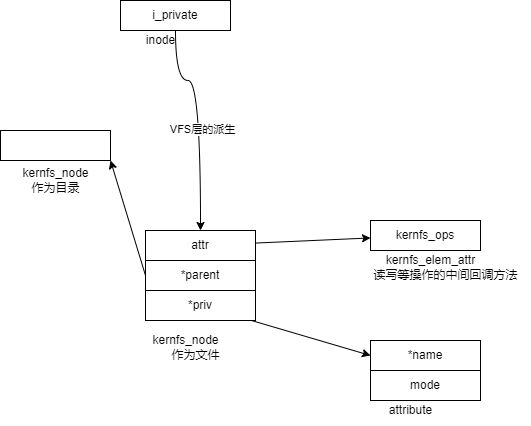
读过程
代码分析
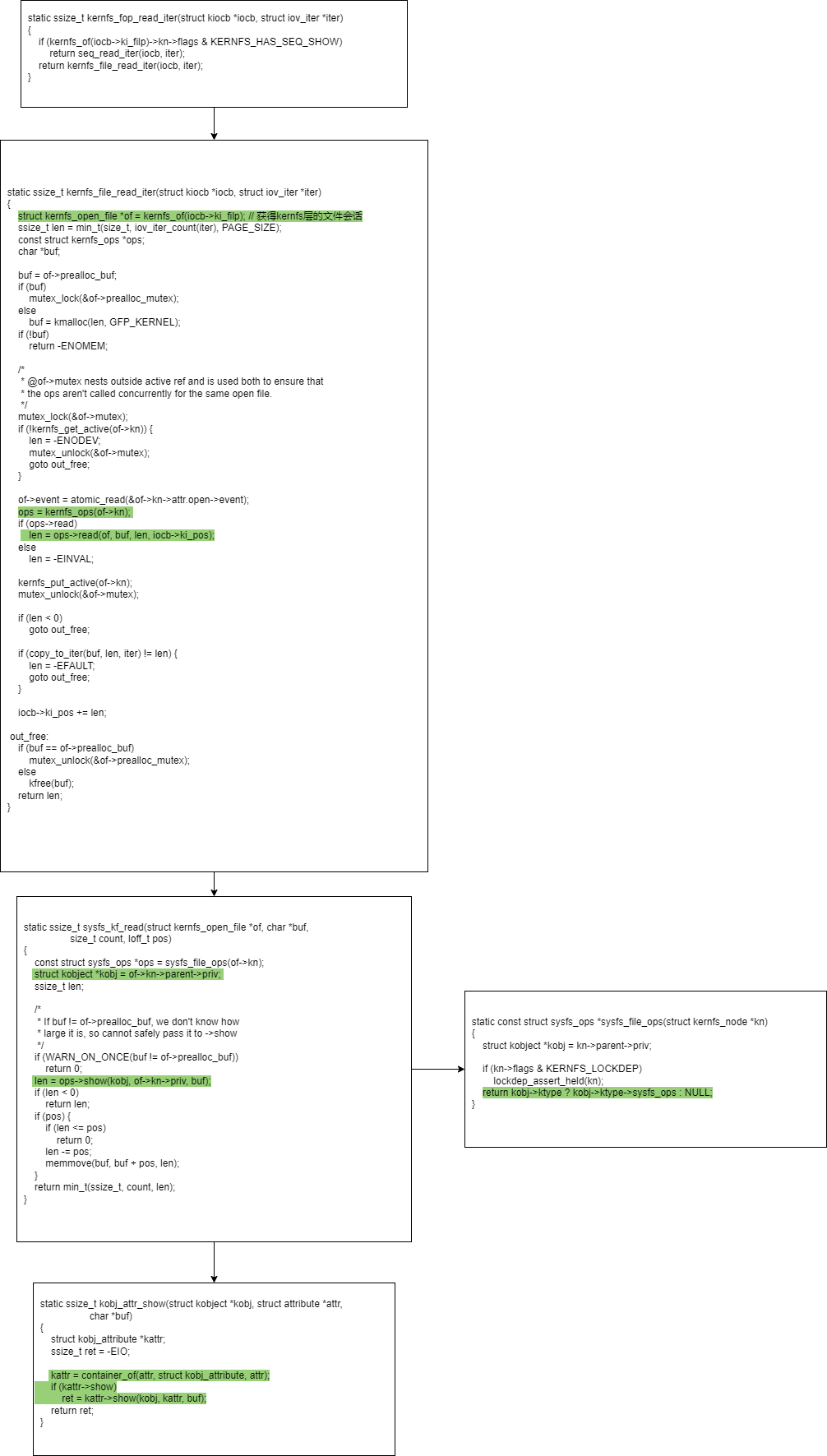
kobj 生命周期
kobj生命周期使用 kobject->kref管理
struct kobject {
const char *name;
struct list_head entry;
struct kobject *parent;
struct kset *kset;
struct kobj_type *ktype;
struct kernfs_node *sd; /* sysfs directory entry */
struct kref kref;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_KOBJECT_RELEASE
struct delayed_work release;
#endif
unsigned int state_initialized:1;
unsigned int state_in_sysfs:1;
unsigned int state_add_uevent_sent:1;
unsigned int state_remove_uevent_sent:1;
unsigned int uevent_suppress:1;
};
struct kref {
refcount_t refcount;
};
typedef struct refcount_struct {
atomic_t refs;
} refcount_t;
使用kobject_get,kobject_put 以加减引用计数,当引用计数为0,kobject_put会调用kobject_del释放空间
struct kobject *kobject_get(struct kobject *kobj)
{
if (kobj) {
if (!kobj->state_initialized)
WARN(1, KERN_WARNING
"kobject: '%s' (%p): is not initialized, yet kobject_get() is being called.\n",
kobject_name(kobj), kobj);
kref_get(&kobj->kref);
}
return kobj;
}
void kobject_put(struct kobject *kobj)
{
if (kobj) {
if (!kobj->state_initialized)
WARN(1, KERN_WARNING
"kobject: '%s' (%p): is not initialized, yet kobject_put() is being called.\n",
kobject_name(kobj), kobj);
kref_put(&kobj->kref, kobject_release);
}
}
static inline int kref_put(struct kref *kref, void (*release)(struct kref *kref))
{
if (refcount_dec_and_test(&kref->refcount)) {
release(kref);
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
当kobj被创建时,kobj会指向它的parent,parent 的 kref 会加一,同样kobj释放时,parent的kref会减一
所以模块退出函数中应该调用 kobject_put 将引用计数减少,以回收资源
kset
/**
* struct kset - a set of kobjects of a specific type, belonging to a specific subsystem.
*
* A kset defines a group of kobjects. They can be individually
* different "types" but overall these kobjects all want to be grouped
* together and operated on in the same manner. ksets are used to
* define the attribute callbacks and other common events that happen to
* a kobject.
*
* @list: the list of all kobjects for this kset
* @list_lock: a lock for iterating over the kobjects
* @kobj: the embedded kobject for this kset (recursion, isn't it fun...)
* @uevent_ops: the set of uevent operations for this kset. These are
* called whenever a kobject has something happen to it so that the kset
* can add new environment variables, or filter out the uevents if so
* desired.
*/
struct kset {
struct list_head list;
spinlock_t list_lock;
struct kobject kobj;
const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops;
} __randomize_layout;
kset是嵌套kobj,kset提供uevent给加入自己的kobj
示例代码
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/kobject.h>
#include <linux/sysfs.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
unsigned long hello_value;
static ssize_t value_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,
char *buf)
{
return sprintf(buf, "hello_value = %lu\n", hello_value);
}
static ssize_t value_store(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count)
{
char tmp_buf[10] = {0};
strncpy(tmp_buf, buf, count);
hello_value = simple_strtoul(tmp_buf, NULL, 0);
return count;
}
struct attribute value_attr = {
.name = "value",
.mode = 0644,
};
struct sysfs_ops value_sysfs_ops = {
.show = value_show,
.store = value_store,
};
static struct attribute *value_attr_array[] = {
&value_attr,
NULL,
};
/******************************************************************/
char hello_buf[100];
static ssize_t buf_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,
char *buf)
{
strncpy(buf, hello_buf, strlen(hello_buf));
return strlen(hello_buf);
}
static ssize_t buf_store(struct kobject *kobj, struct attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t count)
{
strncpy(hello_buf, buf, count);
return count;
}
static struct attribute buf_attr = {
.name = "buf",
.mode = 0644,
};
struct sysfs_ops buf_sysfs_ops = {
.show = buf_show,
.store = buf_store,
};
static struct attribute *buf_attr_array[] = {
&buf_attr,
NULL,
};
/*------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void my_obj_release(struct kobject *kobj)
{
printk("%s: kfree %s\n", __func__, kobj->name);
kfree(kobj);
}
static struct kobject *kobj_hello;
static struct kset *kset_hello;
static struct kobject *kobj_value, *kobj_buf;
static struct kobj_type value_type, buf_type;
static int kobject_hello_init(void)
{
int retval;
// struct kobject *kobject_create_and_add(const char *name, struct kobject *parent)
kobj_hello = kobject_create_and_add("hello", NULL);
if (!kobj_hello) {
return -ENOMEM;
}
/*
struct kset *kset_create_and_add(const char *name,
const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops,
struct kobject *parent_kobj)
*/
//kset_hello = kset_create_and_add("kset_hello", NULL, kobj_hello);
// 创建 /sys/kset_hello
kset_hello = kset_create_and_add("kset_hello", NULL, NULL);
if (!kset_hello) {
kobject_put(kobj_hello);
return -ENOMEM;
}
kobj_value = kzalloc(sizeof(struct kobject), GFP_KERNEL);
kobj_value->kset = kset_hello;
value_type.release = my_obj_release;
value_type.default_attrs = value_attr_array;
value_type.sysfs_ops = &value_sysfs_ops;
kobj_buf = kzalloc(sizeof(struct kobject), GFP_KERNEL);
kobj_buf->kset = kset_hello;
buf_type.release = my_obj_release;
buf_type.default_attrs = buf_attr_array;
buf_type.sysfs_ops = &buf_sysfs_ops;
/*
int kobject_init_and_add(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_type *ktype,
struct kobject *parent, const char *fmt, ...)
*/
// 创建 /sys/hello/value/value
retval = kobject_init_and_add(kobj_value, &value_type, kobj_hello, "value");
//retval = kobject_init_and_add(kobj_value, &value_type, NULL, "value");
// 创建 /sys/kset_hello/buf/buf
retval = kobject_init_and_add(kobj_buf, &buf_type, NULL, "buf");
return 0;
}
void kobject_hello_exit(void)
{
kobject_put(kobj_value);
kobject_put(kobj_buf);
kobject_put(kobj_hello);
kset_unregister(kset_hello);
}
module_init(kobject_hello_init);
module_exit(kobject_hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("wit@zhaixue.cc");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("create a kset object in sysfs");
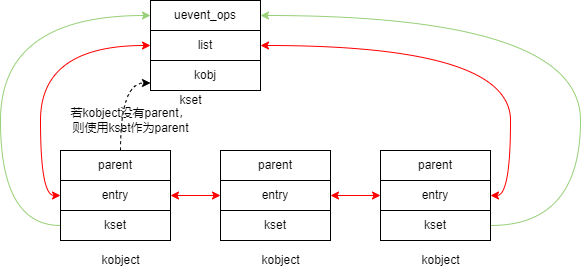
创建kobj时,如果kobj没有设置parent,但是设置了 kset,则使用 kset->kobj作为 父目录
/* add the kobject to its kset's list */
static void kobj_kset_join(struct kobject *kobj)
{
if (!kobj->kset)
return;
kset_get(kobj->kset);
spin_lock(&kobj->kset->list_lock);
list_add_tail(&kobj->entry, &kobj->kset->list);
spin_unlock(&kobj->kset->list_lock);
}
static int kobject_add_internal(struct kobject *kobj)
{
int error = 0;
struct kobject *parent;
if (!kobj)
return -ENOENT;
if (!kobj->name || !kobj->name[0]) {
WARN(1,
"kobject: (%p): attempted to be registered with empty name!\n",
kobj);
return -EINVAL;
}
parent = kobject_get(kobj->parent);
/* join kset if set, use it as parent if we do not already have one */
if (kobj->kset) {
if (!parent)
parent = kobject_get(&kobj->kset->kobj);
kobj_kset_join(kobj)
kobj->parent = parent;
}
...
}
uevent
uevent的使用
uevent是 内核向 用户空间发生事件,比如模块的安装和卸载会发送事件,运行 udevadm 可以接受事件
root@ubuntu:~/wlt# udevadm monitor
monitor will print the received events for:
UDEV - the event which udev sends out after rule processing
KERNEL - the kernel uevent
UDEV [517.342704] add /kernel/slab/:A-0000040/cgroup/eventpoll_pwq(459:session-2.scope) (cgroup)
KERNEL[525.395356] add /module/hello_uevent (module)
UDEV [525.396096] add /module/hello_uevent (module)
KERNEL[538.738109] remove /module/hello_uevent (module)
UDEV [538.738641] remove /module/hello_uevent (module)
内核层可以使用 kobject_uevent 发送事件,但是相关 kobj 或者其parent必须加入 kset
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/kobject.h>
#include <linux/sysfs.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
void value_obj_release(struct kobject *kobj)
{
printk("%s: %s released\n", __func__, kobj->name);
kfree(kobj);
}
static struct kobject *kobj_hello;
static struct kset *kset_hello;
static struct kobject *kobj_value;
static struct kobj_type value_type;
static int kobject_hello_init(void)
{
int retval;
#if 0
kobj_hello = kobject_create_and_add("hello", NULL);
if (!kobj_hello)
return -ENOMEM;
kobject_uevent(kobj_hello, KOBJ_CHANGE);
#endif
#if 1
kset_hello = kset_create_and_add("kset_hello", NULL, NULL);
if (!kset_hello)
return -ENOMEM;
kobj_value = kzalloc(sizeof(struct kobject), GFP_KERNEL);
kobj_value->kset = kset_hello;
value_type.release = value_obj_release;
retval = kobject_init_and_add(kobj_value, &value_type, NULL, "value");
kobject_uevent(kobj_value, KOBJ_CHANGE);
#endif
return 0;
}
void kobject_hello_exit(void)
{
#if 1
kobject_put(kobj_hello);
#endif
#if 1
kobject_put(kobj_value);
kset_unregister(kset_hello);
#endif
}
module_init(kobject_hello_init);
module_exit(kobject_hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("wit@zhaixue.cc");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("uevent demo");
用户层接受事件
KERNEL[979.155904] add /module/hello_uevent (module)
UDEV [979.156469] change /kset_hello/value (kset_hello)
UDEV [979.156611] add /module/hello_uevent (module)
除了使用 udevadm 做守护进程监控,还可以让 内核发送事件后,自动调用运行指定程序
要使用此功能需要配置内核,开启 uevent helper
│ │ [*] Support for uevent helper │ │
│ │ (/root/uevent_helper.sh) path to uevent helper │ │
kobject_uevent分析
int kobject_uevent(struct kobject *kobj, enum kobject_action action)
{
return kobject_uevent_env(kobj, action, NULL);
}
int kobject_uevent_env(struct kobject *kobj, enum kobject_action action,
char *envp_ext[])
{
struct kobj_uevent_env *env;
const char *action_string = kobject_actions[action];
const char *devpath = NULL;
const char *subsystem;
struct kobject *top_kobj;
struct kset *kset;
const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops;
int i = 0;
int retval = 0;
/*
* Mark "remove" event done regardless of result, for some subsystems
* do not want to re-trigger "remove" event via automatic cleanup.
*/
if (action == KOBJ_REMOVE)
kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent = 1;
pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s\n",
kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__);
// 找到支持 kset 的 kobj
/* search the kset we belong to */
top_kobj = kobj;
while (!top_kobj->kset && top_kobj->parent)
top_kobj = top_kobj->parent;
if (!top_kobj->kset) {
pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: attempted to send uevent "
"without kset!\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj,
__func__);
return -EINVAL;
}
kset = top_kobj->kset;
uevent_ops = kset->uevent_ops;
/* skip the event, if uevent_suppress is set*/
if (kobj->uevent_suppress) {
pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: uevent_suppress "
"caused the event to drop!\n",
kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__);
return 0;
}
// 如果 kset 使用了 filter,进行过滤
/* skip the event, if the filter returns zero. */
if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->filter)
if (!uevent_ops->filter(kset, kobj)) {
pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: filter function "
"caused the event to drop!\n",
kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__);
return 0;
}
/* originating subsystem */
if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->name)
subsystem = uevent_ops->name(kset, kobj);
else
subsystem = kobject_name(&kset->kobj);
if (!subsystem) {
pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: unset subsystem caused the "
"event to drop!\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj,
__func__);
return 0;
}
// 将发送的数据序列化到 env
/* environment buffer */
env = kzalloc(sizeof(struct kobj_uevent_env), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!env)
return -ENOMEM;
/* complete object path */
devpath = kobject_get_path(kobj, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!devpath) {
retval = -ENOENT;
goto exit;
}
/* default keys */
retval = add_uevent_var(env, "ACTION=%s", action_string);
if (retval)
goto exit;
retval = add_uevent_var(env, "DEVPATH=%s", devpath);
if (retval)
goto exit;
retval = add_uevent_var(env, "SUBSYSTEM=%s", subsystem);
if (retval)
goto exit;
/* keys passed in from the caller */
if (envp_ext) {
for (i = 0; envp_ext[i]; i++) {
retval = add_uevent_var(env, "%s", envp_ext[i]);
if (retval)
goto exit;
}
}
// 如果 kset 定义了 uevent,调用uevent
/* let the kset specific function add its stuff */
if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->uevent) {
retval = uevent_ops->uevent(kset, kobj, env);
if (retval) {
pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: uevent() returned "
"%d\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj,
__func__, retval);
goto exit;
}
}
switch (action) {
case KOBJ_ADD:
/*
* Mark "add" event so we can make sure we deliver "remove"
* event to userspace during automatic cleanup. If
* the object did send an "add" event, "remove" will
* automatically generated by the core, if not already done
* by the caller.
*/
kobj->state_add_uevent_sent = 1;
break;
case KOBJ_UNBIND:
zap_modalias_env(env);
break;
default:
break;
}
mutex_lock(&uevent_sock_mutex);
/* we will send an event, so request a new sequence number */
retval = add_uevent_var(env, "SEQNUM=%llu", ++uevent_seqnum);
if (retval) {
mutex_unlock(&uevent_sock_mutex);
goto exit;
}
// 使用 netlink 向用户层广播
retval = kobject_uevent_net_broadcast(kobj, env, action_string,
devpath);
mutex_unlock(&uevent_sock_mutex);
#ifdef CONFIG_UEVENT_HELPER
// 如果使用了 uevent_helper ,则运行
/* call uevent_helper, usually only enabled during early boot */
if (uevent_helper[0] && !kobj_usermode_filter(kobj)) {
struct subprocess_info *info;
retval = add_uevent_var(env, "HOME=/");
if (retval)
goto exit;
retval = add_uevent_var(env,
"PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin");
if (retval)
goto exit;
retval = init_uevent_argv(env, subsystem);
if (retval)
goto exit;
retval = -ENOMEM;
info = call_usermodehelper_setup(env->argv[0], env->argv,
env->envp, GFP_KERNEL,
NULL, cleanup_uevent_env, env);
if (info) {
retval = call_usermodehelper_exec(info, UMH_NO_WAIT);
env = NULL; /* freed by cleanup_uevent_env */
}
}
#endif
exit:
kfree(devpath);
kfree(env);
return retval;
}
uevent 的使用 和 应用层的接受
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/kobject.h>
#include <linux/sysfs.h>
struct kobject *kobj_hello;
struct kset *kset_hello;
static int hello_uevent(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj,
struct kobj_uevent_env *env)
{
add_uevent_var(env, "ADDR=%s", "China");
add_uevent_var(env, "NAME=%s", "yangxr");
add_uevent_var(env, "DEVNAME=%s", "hello");
add_uevent_var(env, "MAJOR=%d", 201);
add_uevent_var(env, "MINOR=%d", 0);
return 0;
}
static struct kset_uevent_ops hello_uevent_ops = {
.uevent = hello_uevent,
.filter = NULL,
.name = NULL,
};
static void dynamic_kobj_release(struct kobject *kobj)
{
kfree(kobj);
}
static struct kobj_type dynamic_kobj_ktype = {
.release = dynamic_kobj_release,
};
static int __init kobject_hello_init(void)
{
int ret;
// create /sys/kset_hello
kset_hello = kset_create_and_add("kset_hello", &hello_uevent_ops, NULL);
// create /sys/kset_hello/hello
kobj_hello = kzalloc(sizeof(*kobj_hello), GFP_KERNEL);
kobj_hello->kset = kset_hello;
ret = kobject_init_and_add(kobj_hello, &dynamic_kobj_ktype, NULL, "hello");
kobject_uevent(kobj_hello, KOBJ_ADD);
return 0;
}
static void __exit kobject_hello_exit(void)
{
kobject_put(kobj_hello);
kset_unregister(kset_hello);
}
module_init(kobject_hello_init);
module_exit(kobject_hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
应用层
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <linux/netlink.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
char *devpath, *subsystem, *addr, *name;
char *devname;
char *action;
int major;
int minor;
int open_socket()
{
int fd;
struct sockaddr_nl addr = {
.nl_family = AF_NETLINK,
.nl_pad = 1,
.nl_pid = getpid(),
.nl_groups = 0xFFFFFFFF,
};
fd = socket(PF_NETLINK, SOCK_DGRAM, NETLINK_KOBJECT_UEVENT);
if (fd < 0)
return -1;
if (bind(fd, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr)) < 0) {
close(fd);
return -1;
}
return fd;
}
int parse_event(char *msg)
{
while (*msg) {
printf("%s\n", msg);
if (!strncmp(msg, "ACTION=", 7)) {
msg += 7;
action = msg;
}
else if (!strncmp(msg, "DEVPATH=", 8)) {
msg += 8;
devpath = msg;
}
else if (!strncmp(msg, "SUBSYSTEM=", 10)) {
msg += 10;
subsystem = msg;
}
else if (!strncmp(msg, "MAJOR=", 6)) {
msg += 6;
major = atoi(msg);
}
else if (!strncmp(msg, "MINOR=", 6)) {
msg += 6;
minor = atoi(msg);
}
else if (!strncmp(msg, "ADDR=", 5)) {
msg += 5;
addr = msg;
}
else if (!strncmp(msg, "NAME=", 5)) {
msg += 5;
name = msg;
}
else if (!strncmp(msg, "DEVNAME=" ,8)) {
msg += 8;
devname = msg;
}
while (*msg++);
}
return 0;
}
int make_hello_node(const char *devname, int mode, int major, int minor)
{
char pathname[32] = "/dev/";
strncat(pathname, devname, sizeof(pathname));
if (strcmp(action, "add") == 0) {
printf("major : %d, minor : %d\n", major, minor);
mknod(pathname, mode, (major << 20) | minor);
}
if (strcmp(action, "remove") == 0)
remove(pathname);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int fd, len;
char recv_msg[4096];
fd = open_socket();
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open_socket : ");
return -1;
}
while (1) {
while ((len = recv(fd, recv_msg, sizeof(recv_msg), 0)) > 0) {
if (len == sizeof(recv_msg))
continue;
recv_msg[len] = '\0';
parse_event(recv_msg);
make_hello_node(devname, 0666, major, minor);
}
}
return 0;
}
bus
bus的定义
struct bus_type {
const char *name;
const char *dev_name;
struct device *dev_root;
const struct attribute_group **bus_groups;
const struct attribute_group **dev_groups;
const struct attribute_group **drv_groups;
int (*match)(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv);
int (*uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);
int (*probe)(struct device *dev);
void (*sync_state)(struct device *dev);
void (*remove)(struct device *dev);
void (*shutdown)(struct device *dev);
int (*online)(struct device *dev);
int (*offline)(struct device *dev);
int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct device *dev);
int (*num_vf)(struct device *dev);
int (*dma_configure)(struct device *dev);
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
const struct iommu_ops *iommu_ops;
struct subsys_private *p;
};
struct subsys_private {
struct kset subsys;
struct kset *devices_kset;
struct list_head interfaces;
struct mutex mutex;
struct kset *drivers_kset;
struct klist klist_devices;
struct klist klist_drivers;
struct blocking_notifier_head bus_notifier;
unsigned int drivers_autoprobe:1;
struct bus_type *bus;
struct kset glue_dirs;
struct class *class;
};
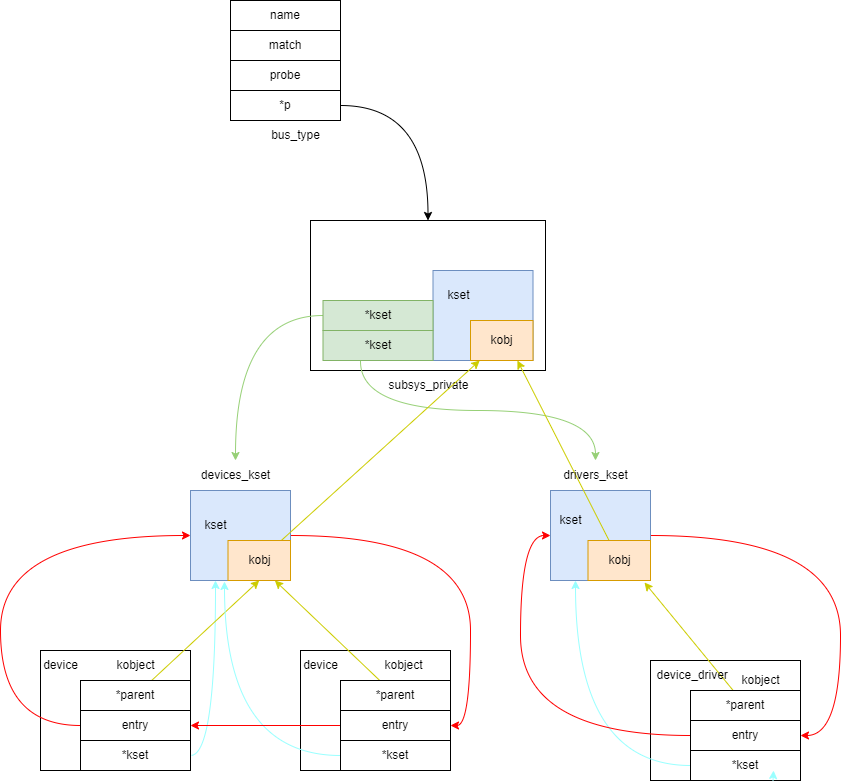
/sys/bus下是各种具体的总线
root@ubuntu:~# ls /sys/bus/
ac97 cpu gpio mdio_bus nvmem platform serial virtio
acpi edac hid memory parport pnp serio vme
clockevents eisa i2c mipi-dsi pci rapidio snd_seq workqueue
clocksource event_source isa mmc pci-epf scsi spi xen
container gameport machinecheck nd pci_express sdio usb xen-backend
每个中线下有 devices目录,为挂在本总线上的设备,drivers 目录,为挂在本总线上的驱动
root@ubuntu:~# tree /sys/bus/platform/ -L 2
/sys/bus/platform/
├── devices
│ ├── ACPI0003:00 -> ../../../devices/platform/ACPI0003:00
│ ├── alarmtimer -> ../../../devices/platform/alarmtimer
│ ├── eisa.0 -> ../../../devices/platform/eisa.0
│ ├── Fixed MDIO bus.0 -> ../../../devices/platform/Fixed MDIO bus.0
│ ├── i8042 -> ../../../devices/platform/i8042
│ ├── pcspkr -> ../../../devices/platform/pcspkr
│ ├── platform-framebuffer.0 -> ../../../devices/platform/platform-framebuffer.0
│ ├── PNP0001:00 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.0/PNP0001:00
│ ├── PNP0800:00 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.0/PNP0800:00
│ ├── reg-dummy -> ../../../devices/platform/reg-dummy
│ └── serial8250 -> ../../../devices/platform/serial8250
├── drivers
│ ├── acpi-fan
│ ├── alarmtimer
│ ├── amd_gpio
│ ├── byt_gpio
│ ├── cannonlake-pinctrl
│ ├── charger-manager
│ ├── clk-lpt
│ ├── clk-pmc-atom
│ ├── crystal_cove_pwm
│ ├── dwc2
│ ├── dw-pcie
│ ├── e820_pmem
│ ├── efi-framebuffer
│ ├── ehci-platform
│ ├── gpio-clk
│ ├── i2c_designware
│ ├── i8042
│ ├── intel_msic
│ ├── lp_gpio
│ ├── msic_gpio
│ ├── ohci-platform
│ ├── palmas-gpio
│ ├── parport_pc
│ ├── poweroff-restart
│ ├── rc5t583-gpio
│ ├── reg-dummy
│ ├── serial8250
│ ├── simple-framebuffer
│ ├── sram
│ ├── syscon
│ ├── timb-gpio
│ ├── tpm_tis
│ ├── tps6586x-gpio
│ ├── tps65910-gpio
│ ├── tps68470-gpio
│ ├── tps68470_pmic_opregion
│ ├── twl4030-audio
│ ├── uart-sccnxp
│ ├── vesa-framebuffer
│ └── virtio-mmio
├── drivers_autoprobe
├── drivers_probe
└── uevent
注册自定义总线
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
static int hello_bus_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *driver)
{
int match;
match = !strncmp(dev_name(dev), driver->name, strlen(driver->name));
return match;
}
static int hello_bus_probe(struct device *dev)
{
struct device_driver *drv = dev->driver;
if (drv->probe)
drv->probe(dev);
return 0;
}
struct bus_type hello_bus_type = {
.name = "hello_bus",
.match = hello_bus_match,
.probe = hello_bus_probe,
};
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(hello_bus_type);
static ssize_t hello_bus_show(struct bus_type *bus, char *buf)
{
return sprintf(buf, "bus name : %s\n", hello_bus_type.name);
}
static struct bus_attribute hello_bus_attr = {
.attr = {
.name = "hello_bus_attr",
.mode = 0644,
},
.show = hello_bus_show,
};
static int __init hello_bus_init(void)
{
int ret;
ret = bus_register(&hello_bus_type);
ret = bus_create_file(&hello_bus_type, &hello_bus_attr);
return 0;
}
static void __exit hello_bus_exit(void)
{
bus_remove_file(&hello_bus_type, &hello_bus_attr);
bus_unregister(&hello_bus_type);
}
module_init(hello_bus_init);
module_exit(hello_bus_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
yangxr@vexpress:/root # ls /sys/bus/hello_bus/
devices drivers_autoprobe hello_bus_attr
drivers drivers_probe uevent
bus注册代码分析
bus是对 kset的封装

bus注册对象分析
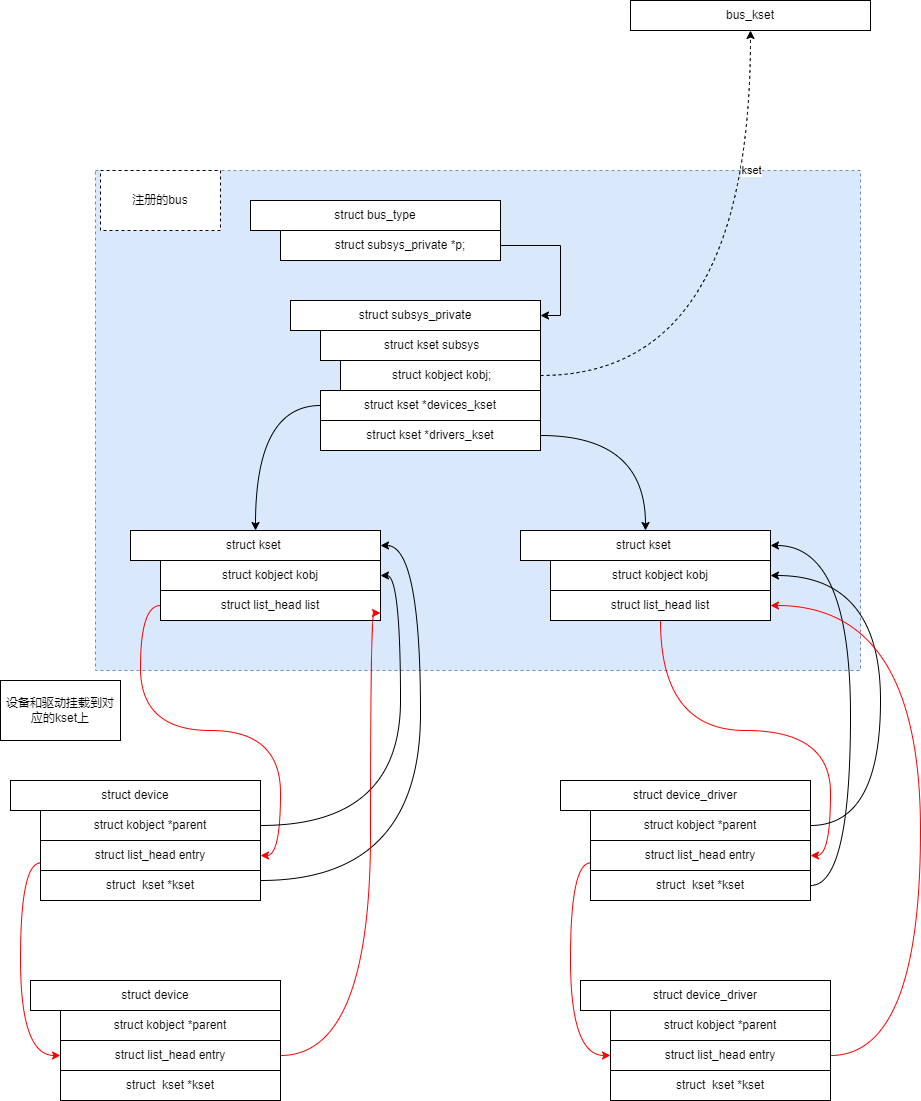
bus的结构分为两层:
- kobj层,kset是对kobj的封装,对象通过kob根据父子关系形成树形结构
- kset层,挂载的设备或驱动加入对应 kset的链表
device
device 是对 kobj的封装
struct device {
struct kobject kobj;
struct device *parent;
struct device_private *p;
struct bus_type *bus; /* type of bus device is on */
struct device_driver *driver; /* which driver has allocated this
device */
...
};
struct device_private {
struct klist klist_children;
struct klist_node knode_parent;
struct klist_node knode_driver;
struct klist_node knode_bus;
struct klist_node knode_class;
struct list_head deferred_probe;
struct device_driver *async_driver;
char *deferred_probe_reason;
struct device *device;
u8 dead:1;
};
在bus上添加device
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
extern struct bus_type hello_bus_type;
void hello_device_release(struct device *dev)
{
printk("%s\n", __func__);
}
static struct device hello_device = {
.init_name = "hello",
.bus = &hello_bus_type,
.release = hello_device_release,
.devt = ((251 << 20) | 0),
};
static ssize_t hello_device_show(struct device *dev,
struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf)
{
return sprintf(buf, "hello_device name : hello\n");
}
static struct device_attribute hello_device_attr = {
.attr = {
.name = "hello_device_attr",
.mode = 0444,
},
.show = hello_device_show,
};
static int __init hello_device_init(void)
{
int ret;
ret = device_register(&hello_device);
ret = device_create_file(&hello_device, &hello_device_attr);
return 0;
}
static void __exit hello_device_exit(void)
{
device_remove_file(&hello_device, &hello_device_attr);
device_unregister(&hello_device);
}
module_init(hello_device_init);
module_exit(hello_device_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
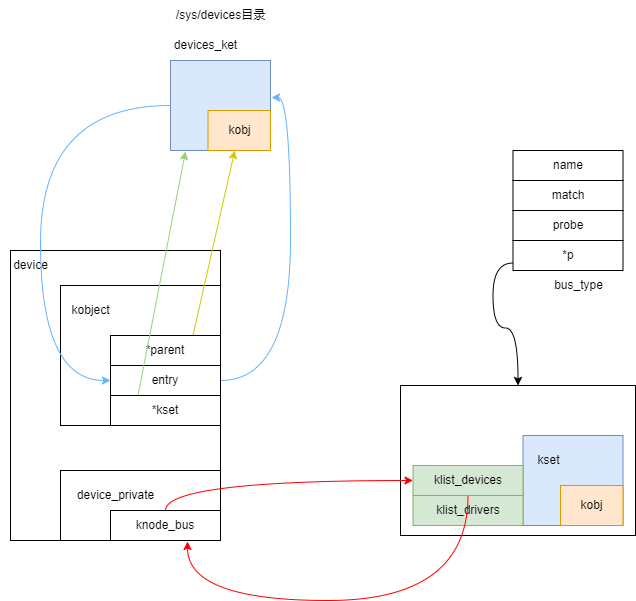
分析 device_register

1)device的kobj的parent为NULL,kset为 /sys/device,所以创建文件节点和knode时以 kset /sys/device 为父节点
2)加入bus,会创建几个链接文件
3)加入bus,dev会加入bus的链表 klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_bus, &bus->p->klist_devices)
总结
如下,通过将 device的kobj加入 /sys/devices kset中,让device和 sysfs 关联,
将 device->p->knode_bus 加入 bus->p->klist_devices 链表,让 device 和 bus 关联
在 bus->p->devices_kset 下添加kobj,并在该kobj下创建软连接文件,链接到 device,图中没有画出
device_driver
struct device_driver {
const char *name;
struct bus_type *bus;
struct module *owner;
const char *mod_name; /* used for built-in modules */
bool suppress_bind_attrs; /* disables bind/unbind via sysfs */
enum probe_type probe_type;
const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;
const struct acpi_device_id *acpi_match_table;
int (*probe) (struct device *dev);
void (*sync_state)(struct device *dev);
int (*remove) (struct device *dev);
void (*shutdown) (struct device *dev);
int (*suspend) (struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume) (struct device *dev);
const struct attribute_group **groups;
const struct attribute_group **dev_groups;
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
void (*coredump) (struct device *dev);
struct driver_private *p;
};
struct driver_private {
struct kobject kobj;
struct klist klist_devices;
struct klist_node knode_bus;
struct module_kobject *mkobj;
struct device_driver *driver;
};
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
extern struct bus_type hello_bus_type;
static int hello_driver_remove(struct device *dev)
{
printk("%s : driver remove\n", __func__);
return 0;
}
static int hello_driver_probe(struct device *dev)
{
printk("%s : probe and init hello_device\n", __func__);
return 0;
}
struct device_driver hello_driver = {
.name = "hello",
.bus = &hello_bus_type,
.probe = hello_driver_probe,
.remove = hello_driver_remove,
};
static int __init hello_driver_init(void)
{
int ret;
ret = driver_register(&hello_driver);
if (ret)
return ret;
printk("register hello_driver success\n");
return 0;
}
static void __exit hello_driver_exit(void)
{
driver_unregister(&hello_driver);
}
module_init(hello_driver_init);
module_exit(hello_driver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
安装device_drvier

1)driver加入 bus的 klist_driver链表,实现bus和driver的关联
2)driver->kobj 加入 bus/drivers 目录,实现driver和 sysfs的关联
分析 device 和 driver 的 match 和 probe
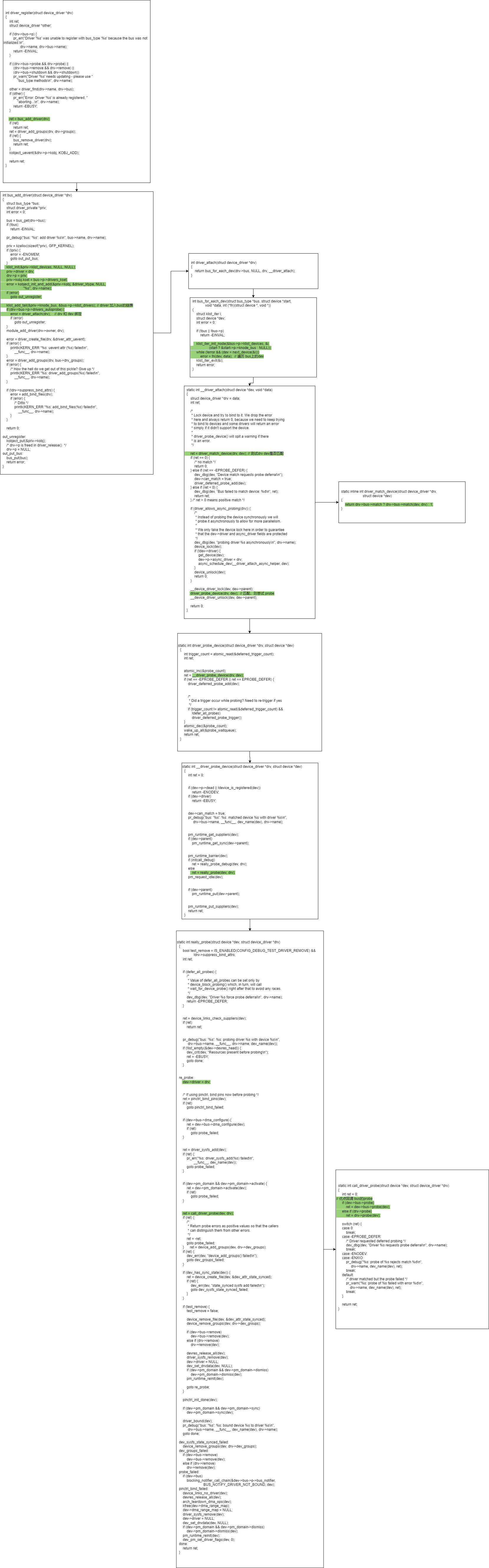
1)drv 加入 bus 的 klist_drivers 链表,dev 加入bus 的klist_devices 链表
2)回调bus的match返回 >0 为匹配,0为不匹配,<0 为错误
3)优先调用 bus->probe,没有则调用 drv->probe,也没有就默认成功,完成 probe后, dev->driver = drv,dev绑定drv
class
class 的作用
对某类设备的抽象,封装出一些标准的接口
示例1
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
struct class *hello_class;
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(hello_class);
static int __init hello_class_init(void)
{
int ret;
hello_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello_class");
ret = PTR_ERR(hello_class);
if (IS_ERR(hello_class))
return ret;
return 0;
}
static void __exit hello_class_exit(void)
{
class_destroy(hello_class);
}
module_init(hello_class_init);
module_exit(hello_class_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
extern struct class *hello_class;
static struct device *hello_device;
static int __init hello_device_init(void)
{
int ret;
hello_device = device_create(hello_class, NULL, (251 << 20 | 1), NULL, "hello_dev");
ret = PTR_ERR(hello_device);
if (IS_ERR(hello_device))
return ret;
return 0;
}
static void __exit hello_device_exit(void)
{
device_destroy(hello_class, 0);
}
module_init(hello_device_init);
module_exit(hello_device_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
class 工作原理
以rtc为例,看 ioctl set_time 时,调用流程

可知,当使用 class 时,系统调用最终回调 device 的 ops,
而这个 ops 时在设备绑定驱动时设置的。
static int pl031_probe(struct amba_device *adev, const struct amba_id *id)
{
int ret;
struct pl031_local *ldata;
struct pl031_vendor_data *vendor = id->data;
struct rtc_class_ops *ops;
unsigned long time, data;
ret = amba_request_regions(adev, NULL);
if (ret)
goto err_req;
ldata = devm_kzalloc(&adev->dev, sizeof(struct pl031_local),
GFP_KERNEL);
ops = devm_kmemdup(&adev->dev, &vendor->ops, sizeof(vendor->ops),
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!ldata || !ops) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto out;
}
ldata->vendor = vendor;
ldata->base = devm_ioremap(&adev->dev, adev->res.start,
resource_size(&adev->res));
if (!ldata->base) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto out;
}
ldata->rtc->ops = ops; // 完成迟绑定
ldata->rtc->range_min = vendor->range_min;
ldata->rtc->range_max = vendor->range_max;
使用 class 的好处
如果没有device class driver ,则 同一类设备的驱动,每个驱动都要一个cdev,因为cdev和 ops 在编码时绑定,当使用设备模型,则cdev和ops在probe时绑定,则只需要一个cdev
驱动复用
同类型设备使用相同驱动,关键在 match 时使用 id_table
static int hello_bus_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *driver)
{
int match;
struct device_id *id;
struct hello_driver *drv;
match = !strncmp(dev_name(dev), driver->name, strlen(driver->name));
if (match)
return match;
drv = container_of(driver, struct hello_driver, driver);
id = drv->id_table;
while (id->name[0]) {
if (strcmp(id->name, dev->init_name) == 0) {
return 1;
}
id++;
}
return 0;
}
struct bus_type hello_bus_type = {
.name = "hello_bus",
.match = hello_bus_match,
};
struct device_id compat_table[] = {
{ .name = "wit1", .dev_id = 1, },
{ .name = "wit2", .dev_id = 2, },
{ .name = "wit3", .dev_id = 3, },
{ },
};
static struct hello_driver hello_drv = {
.name = "wit",
.probe = hello_driver_probe,
.remove = hello_driver_remove,
.id_table = compat_table,
};
设备的热插拔
我们知道 通过 kset 提供的 uevent 机制可以自己实现热插拔,但有了 device ,就不需要自己实现,因为 device_add 时会发送ADD事件
int device_add(struct device *dev)
{
struct device *parent;
struct kobject *kobj;
struct class_interface *class_intf;
int error = -EINVAL;
struct kobject *glue_dir = NULL;
...
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
...



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?