kernel——中断
1. 理论
早期的51单片机只有4个中断,中断可以直接发给cpu

ARM SoC有GIC,中断发给GIC,GIC发给cpu。
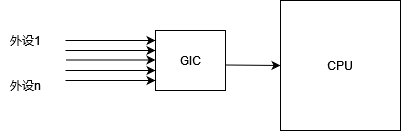
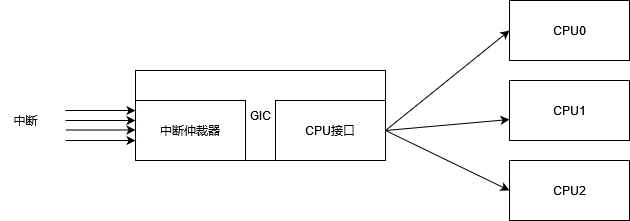
GIC有两个重要部分,
中断仲裁器,根据中断优先级,屏蔽,决定发送哪个中断,
cpu接口,由于现在都是多核cpu,所以需要决定发送给哪个cpu
中断分类
SGI:16 software generated interrupts
id0-id15,用于多核之间通信
PPI: 16 external private peripheral interrupts
每个core私有的中断,如本地时钟,id16-id31
SPI: shared peripheral interrupt
所有core共享的中断,可以在多个core上运行
支持范围可配置,从id32开始
中断触发类型
边缘触发,水平触发
中断号
HW interrupt ID , 硬件中断号
IRQ number, Linux软件实现的中断号
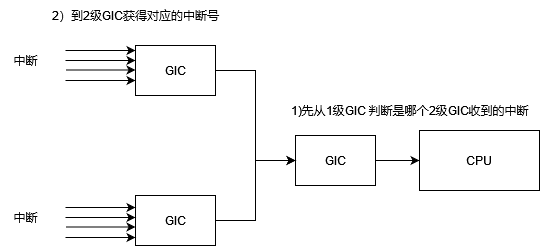
IRQ domain
现在硬件中断太多了(外设太多了),所以出现了多级GIC,当cpu收到中断后,应该先判断是哪个2级GIC发的,再到对应GIC获得中断号。
2、 Linux下中断的使用
/**
* request_irq - Add a handler for an interrupt line
* @irq: The interrupt line to allocate
* @handler: Function to be called when the IRQ occurs.
* Primary handler for threaded interrupts
* If NULL, the default primary handler is installed
* @flags: Handling flags
* @name: Name of the device generating this interrupt
* @dev: A cookie passed to the handler function
*
* This call allocates an interrupt and establishes a handler; see
* the documentation for request_threaded_irq() for details.
*/
static inline int __must_check
request_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler, unsigned long flags,
const char *name, void *dev);
extern const void *free_irq(unsigned int, void *);
以 vexpress板子为例
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/rtc.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
typedef volatile struct {
unsigned long RTCDR; // 0x00 data register
unsigned long RTCMR; // 0x04 match register
unsigned long RTCLR; // 0x08 load register
unsigned long RTCCR; // 0x0c Control register
unsigned long RTCIMSC; // 0x10 interrupt mask set and clear register
unsigned long RTCRIS; // 0x14 raw interrupt register
unsigned long RTCMIS; // 0x18 Masked interrupt status register
unsigned long RTCICR; // 0x1c interrupt clear register
} rtc_reg_t;
#define RTC_BASE 0x10017000
volatile rtc_reg_t *regs = NULL;
int counter = 0;
void set_rtc_alarm(rtc_reg_t *regs)
{
unsigned long tmp = 0;
tmp = regs->RTCCR; // write enable
tmp &= 0xFFFFFFFE;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
tmp = regs->RTCDR; // get current time
regs->RTCMR = tmp + 1; // set alarm time
regs->RTCICR = 1; // clear RTCINTR interrupt
regs->RTCIMSC = 1; // set the mask
tmp = regs->RTCCR; // write disable
tmp = tmp | 0x01;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
}
static irqreturn_t rtc_alarm_handler(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
printk("counter : %d, irqnum : %d\n", counter++, irq);
// 下一秒继续发送中断
set_rtc_alarm(regs);
return IRQ_HANDLED; // 表示中断已经处理完成
}
static int __init rtc_init(void)
{
irqreturn_t ret = 0;
// 通过数据手册直到 RTC 寄存器的物理地址,
// 但Linux运行在保护模式,所以需要得到能映射到 RTC_BASE(物理地址) 的虚拟地址。
regs = (rtc_reg_t *)ioremap(RTC_BASE, sizeof(rtc_reg_t));
printk("rtc_init\n");
// 设置RTC下一秒发送一个中断
set_rtc_alarm(regs);
// 绑定中断服务程序, 这里的39是软中断号
ret = request_irq(39, rtc_alarm_handler, 0, "rtc0-test", NULL);
if (ret == -1) {
printk("request_irq failed\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
static void __exit rtc_exit(void)
{
// 注意回收资源
free_irq(39, NULL);
printk("Goodbye rtc module\n");
}
module_init(rtc_init);
module_exit(rtc_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
2.1 Linux中断分析
异常向量表
内核定义了异常向量表,当异常发生,可以跳到 L__vectors_start + 偏移地址
>>.L__vectors_start:
>> W(b) vector_rst
>> W(b) vector_und
>> W(ldr) pc, .L__vectors_start + 0x1000
>> W(b) vector_pabt
>> W(b) vector_dabt
>> W(b) vector_addrexcptn
>> W(b) vector_irq
W(b) vector_fiq
将异常向量表重定位到 新的虚拟地址 vectors
void __init early_trap_init(void *vectors_base)
{
...
memcpy((void *)vectors, __vectors_start, __vectors_end - __vectors_start);
memcpy((void *)vectors + 0x1000, __stubs_start, __stubs_end - __stubs_start);
...
}
异常向量表中 vector_xxx 都是使用宏实现,如 vector_irq
vector_stub irq, IRQ_MODE, 4
vector_stub是宏
.macro vector_stub, name, mode, correction=0
.align 5
vector_\name:
.if \correction
sub lr, lr, #\correction
.endif
@
@ Save r0, lr_<exception> (parent PC) and spsr_<exception>
@ (parent CPSR)
@
stmia sp, {r0, lr} @ save r0, lr
mrs lr, spsr
str lr, [sp, #8] @ save spsr
@
@ Prepare for SVC32 mode. IRQs remain disabled.
@
mrs r0, cpsr
eor r0, r0, #(\mode ^ SVC_MODE | PSR_ISETSTATE)
msr spsr_cxsf, r0
@
@ the branch table must immediately follow this code
@
and lr, lr, #0x0f
THUMB( adr r0, 1f )
THUMB( ldr lr, [r0, lr, lsl #2] )
mov r0, sp
ARM( ldr lr, [pc, lr, lsl #2] )
movs pc, lr @ branch to handler in SVC mode 修改pc,进行跳转
ENDPROC(vector_\name)
跳转表,跳转到 __irq_usr
>> .long __irq_usr @ 0 (USR_26 / USR_32)
>> .long __irq_invalid @ 1 (FIQ_26 / FIQ_32)
>> .long __irq_invalid @ 2 (IRQ_26 / IRQ_32)
>> .long __irq_svc @ 3 (SVC_26 / SVC_32)
>> .long __irq_invalid @ 4
>> .long __irq_invalid @ 5
>> .long __irq_invalid @ 6
所以跳转到 generic_handle_arch_irq
.macro irq_handler
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_MULTI_HANDLER
mov r0, sp
bl generic_handle_arch_irq
#else
arch_irq_handler_default
#endif
.endm
__irq_usr:
>> usr_entry @ 保存现场
>> kuser_cmpxchg_check
>> irq_handler @ 处理中断
>> get_thread_info tsk
>> mov why, #0
>> b ret_to_user_from_irq @ 恢复
>> UNWIND(.fnend )
>>ENDPROC(__irq_usr)
进入c实现部分
asmlinkage void noinstr generic_handle_arch_irq(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
struct pt_regs *old_regs;
irq_enter();
old_regs = set_irq_regs(regs);
handle_arch_irq(regs);
set_irq_regs(old_regs);
irq_exit();
}
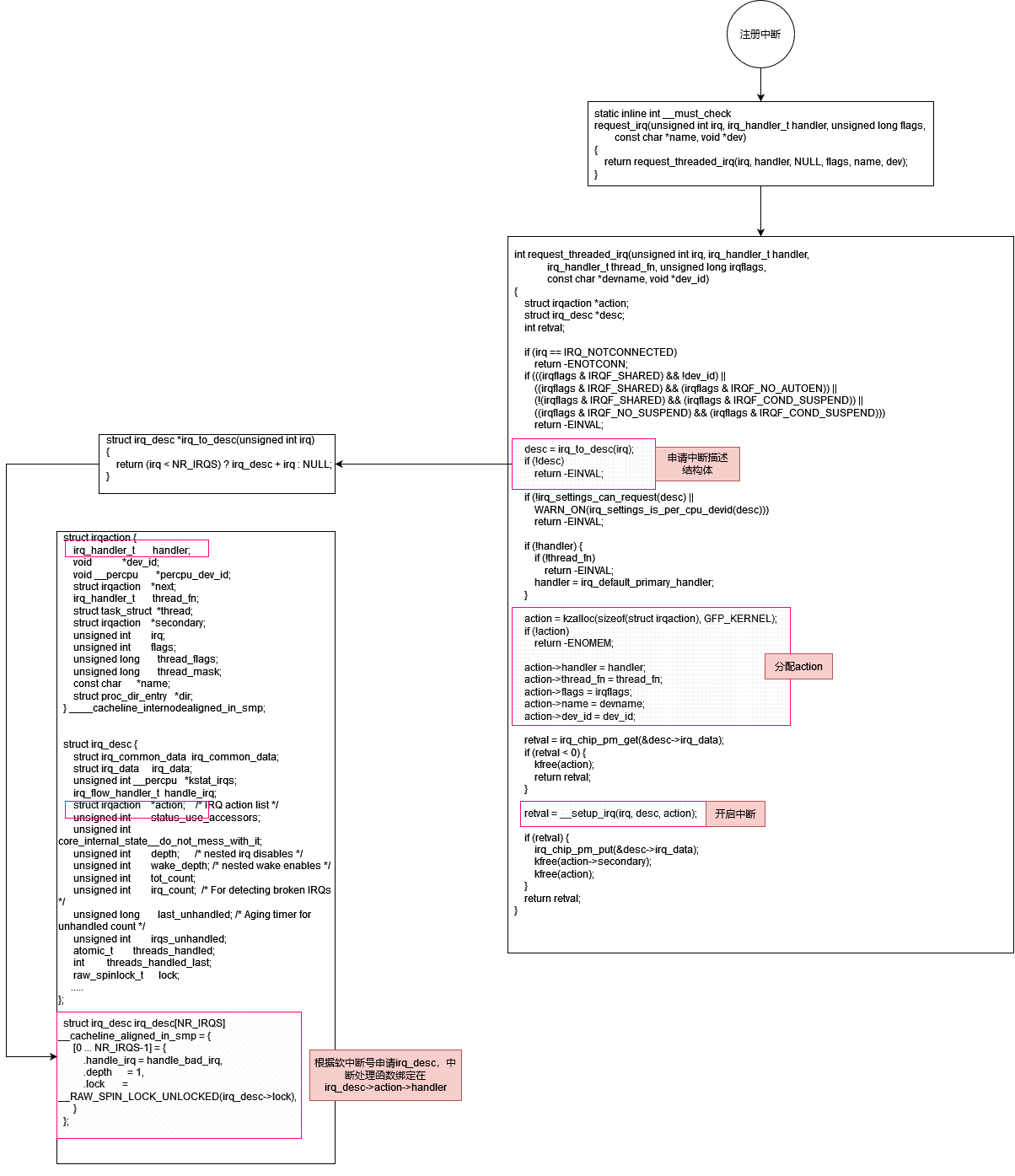
中断注册
根据中断号找到 struct irq_desc,desc->action是个链表,分配一个action,action->handler绑定为中断的回调函数
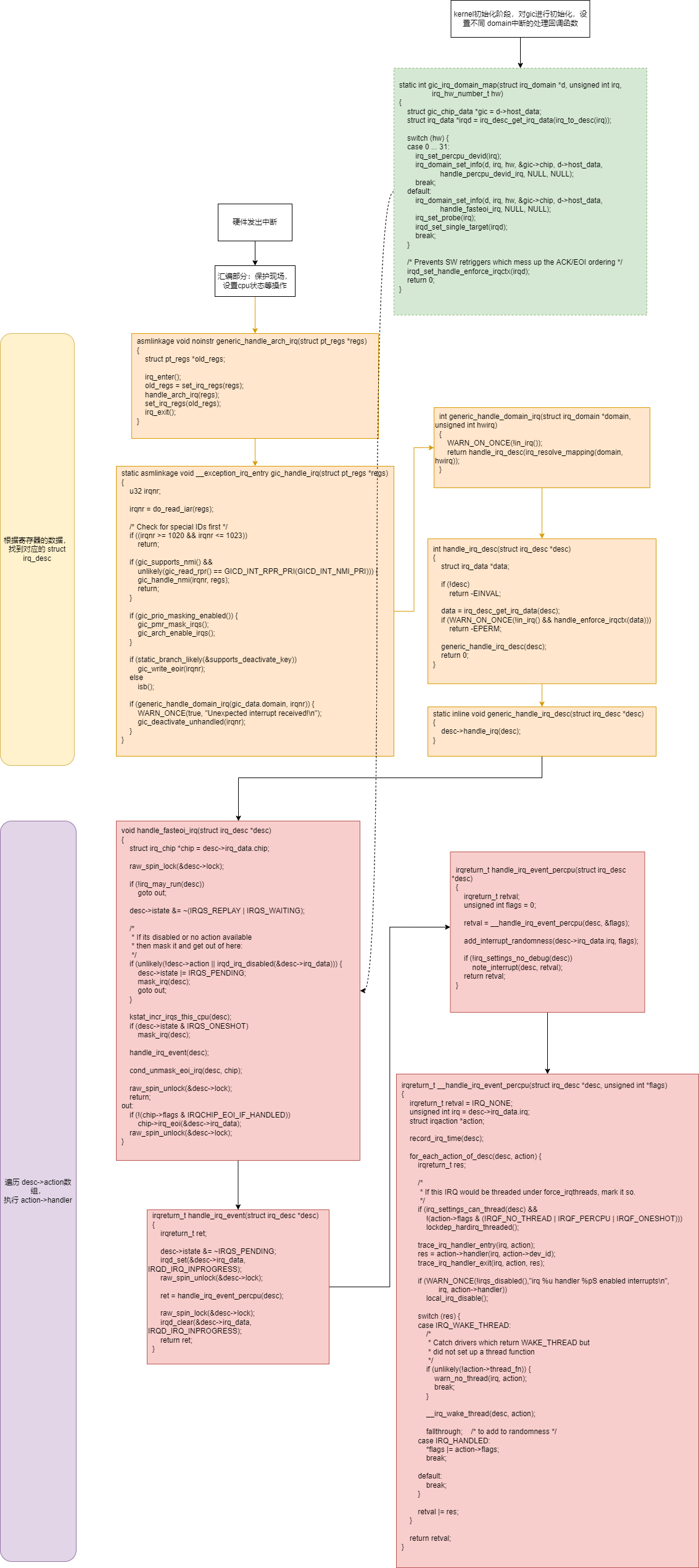
中断触发
根据中断号找到 struct irq_desc,遍历desc->action链表,执行action->handler
2.2 中断上半部和下半部
处理中断时,会禁止中断,严重影响实时性,所以将中断工作分为上下半部
上半部:响应中断,硬件配置,发送EOI给GIC
下半部:完成真正工作,如,数据复制,数据包封装转发,硬编码
依赖机制
软中断
tasklet
工作队列
中断线程化
2.2.1 软中断
软中断的使用
enum
{
HI_SOFTIRQ=0,
TIMER_SOFTIRQ,
NET_TX_SOFTIRQ,
NET_RX_SOFTIRQ,
BLOCK_SOFTIRQ,
IRQ_POLL_SOFTIRQ,
TASKLET_SOFTIRQ,
SCHED_SOFTIRQ,
HRTIMER_SOFTIRQ,
RCU_SOFTIRQ, /* Preferable RCU should always be the last softirq */
NR_SOFTIRQS
};
void open_softirq(int nr, void (*action)(struct softirq_action *));
void raise_softirq(unsigned int nr);
inline void raise_softirq_irqoff(unsigned int nr);
内核开发者没有导出软中断的接口,如果要用软中断,应该使用 tasklet。
为了实验,自己导出 open_softirq , raise_softirq ,并修改 rtc.c。
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/rtc.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
extern void open_softirq(int nr, void (*action)(struct softirq_action *));
extern void raise_softirq(unsigned int nr);
typedef volatile struct {
unsigned long RTCDR; // 0x00 data register
unsigned long RTCMR; // 0x04 match register
unsigned long RTCLR; // 0x08 load register
unsigned long RTCCR; // 0x0c Control register
unsigned long RTCIMSC; // 0x10 interrupt mask set and clear register
unsigned long RTCRIS; // 0x14 raw interrupt register
unsigned long RTCMIS; // 0x18 Masked interrupt status register
unsigned long RTCICR; // 0x1c interrupt clear register
} rtc_reg_t;
#define RTC_BASE 0x10017000
volatile rtc_reg_t *regs = NULL;
int counter = 0;
void set_rtc_alarm(rtc_reg_t *regs)
{
unsigned long tmp = 0;
tmp = regs->RTCCR; // write enable
tmp &= 0xFFFFFFFE;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
tmp = regs->RTCDR; // get current time
regs->RTCMR = tmp + 1; // set alarm time
regs->RTCICR = 1; // clear RTCINTR interrupt
regs->RTCIMSC = 1; // set the mask
tmp = regs->RTCCR; // write disable
tmp = tmp | 0x01;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
}
// 如果执行软中断时发送硬件中断,则先处理硬件中断,所以能增加系统实时性
static void rtc_softirq_handler(struct softirq_action *act)
{
unsigned int i, j;
// 做一些耗时的工作
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 100; j++)
;
printk("counter : %d\n", counter++);
}
static irqreturn_t rtc_alarm_handler(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
// 中断上半部工作
// 下一秒继续发送中断
set_rtc_alarm(regs);
// 发送软中断
raise_softirq(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
static int __init rtc_init(void)
{
irqreturn_t ret = 0;
// 通过数据手册直到 RTC 寄存器的物理地址,
// 但Linux运行在保护模式,所以需要得到能映射到 RTC_BASE(物理地址) 的虚拟地址。
regs = (rtc_reg_t *)ioremap(RTC_BASE, sizeof(rtc_reg_t));
printk("rtc_init\n");
// 设置RTC下一秒发送一个中断
set_rtc_alarm(regs);
// 绑定中断服务程序, 这里的39是软中断号
ret = request_irq(39, rtc_alarm_handler, 0, "rtc0-test", NULL);
if (ret == -1) {
printk("request_irq failed\n");
return -1;
}
// 开启软中断,绑定处理中断下半部工作
// 由于耗时的工作不占用中断处理,所以能增加系统实时性
open_softirq(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ, rtc_softirq_handler);
return 0;
}
static void __exit rtc_exit(void)
{
// 注意回收资源
free_irq(39, NULL);
printk("Goodbye rtc module\n");
}
module_init(rtc_init);
module_exit(rtc_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
软中断分析
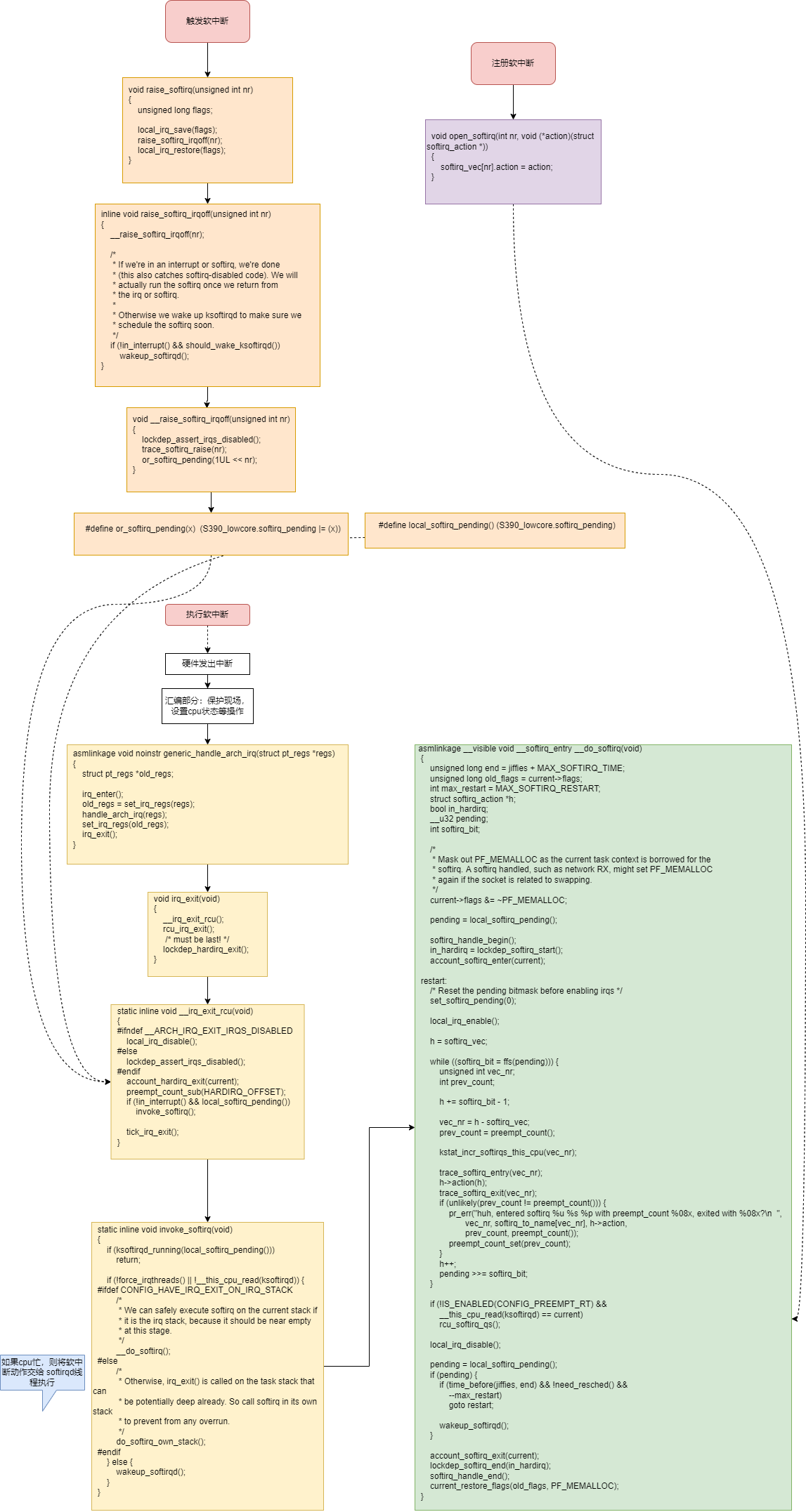
软中断的执行时机
普通进程1正在运行,一个IRQ中断产生
CPU自动执行部分:关闭IRQ中断,寄存器备份
跳转到中断向量表执行流程:vector_irq
irq_handler
asm_do_IRQ->handle_IRQ->__handle_domain_irq
irq_enter
generic_handle_irq: 具体的外设IRQ中断处理
irq_exit
检查是否有pending的软中断,有则执行
软中断是否频繁执行,有则放到softirqd执行
退出中断,检查是否有更高优先级的进程,调度当前最高优先级进程执行
软中断之所以能解决中断的副作用(中断处理时,cpu不能处理其他中断,导致实时性差),是因为 irq_exit时,cpu已经复位,即处理软中断时,cpu可以立即处理其他中断。
软中断之所以要避免频繁执行,是为了避免实时性高的进程等待太久。softirqd是内核线程,优先级较低,将过多的软中断交给softirqd以延后执行。
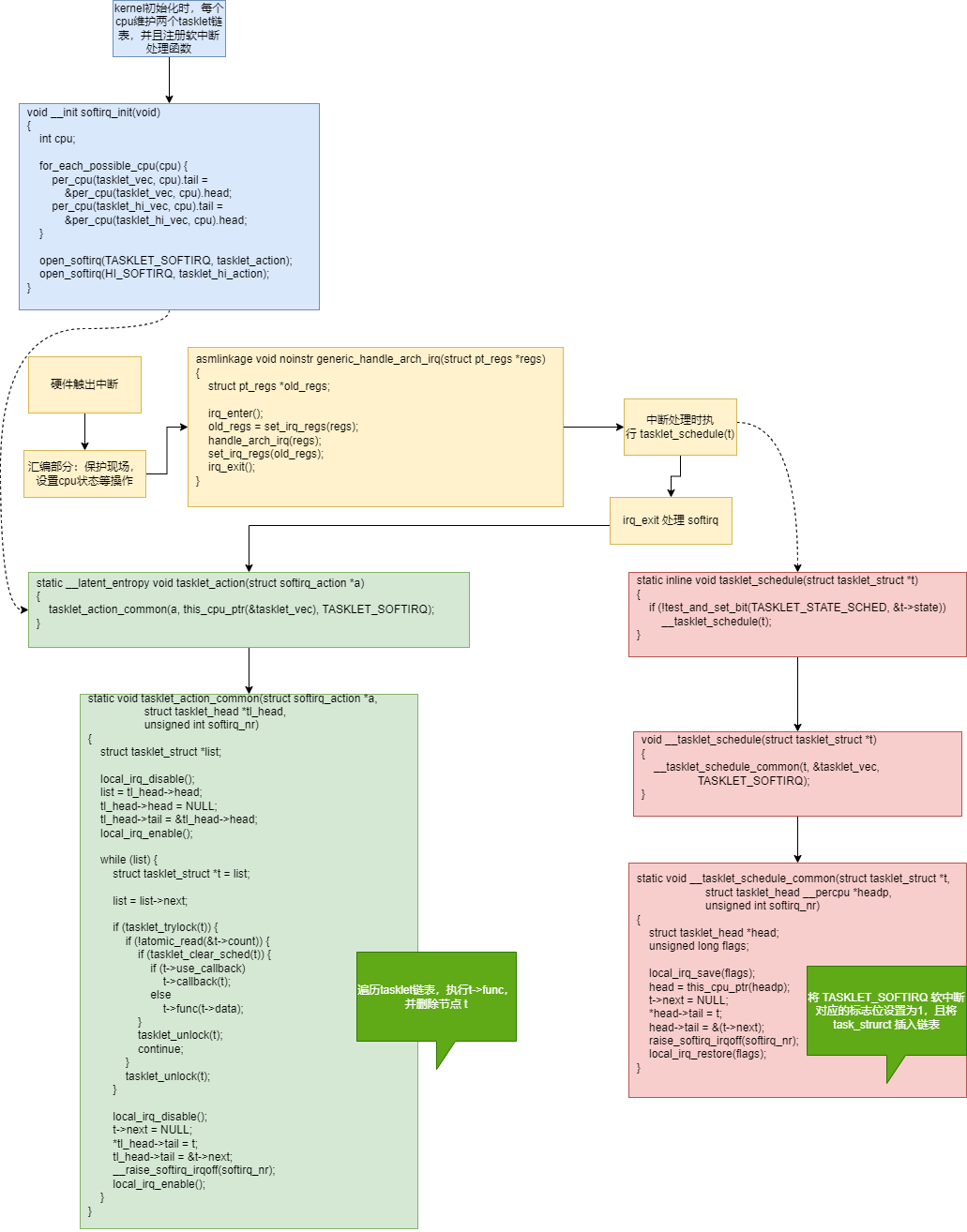
2.2.2 tasklet
softirq资源有限,
tasklet是对softirq的封装,能动态增删中断下半部
tasklet就是 TASKLET_SOFTIRQ 优先级的软中断,每个cpu都有两个软中断链表,一个是TASKLET_SOFTIRQ 优先级的,一个是HI_SOFTIRQ优先级的。
struct tasklet_struct
{
struct tasklet_struct *next;
unsigned long state;
atomic_t count;
bool use_callback;
union {
void (*func)(unsigned long data);
void (*callback)(struct tasklet_struct *t);
};
unsigned long data;
};
void tasklet_init(struct tasklet_struct *t,
void (*func)(unsigned long), unsigned long data)
static inline void tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
static inline void tasklet_hi_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
void tasklet_kill(struct tasklet_struct *t)
示例
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/rtc.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
struct tasklet_struct tasklet_rtc;
typedef volatile struct {
unsigned long RTCDR; // 0x00 data register
unsigned long RTCMR; // 0x04 match register
unsigned long RTCLR; // 0x08 load register
unsigned long RTCCR; // 0x0c Control register
unsigned long RTCIMSC; // 0x10 interrupt mask set and clear register
unsigned long RTCRIS; // 0x14 raw interrupt register
unsigned long RTCMIS; // 0x18 Masked interrupt status register
unsigned long RTCICR; // 0x1c interrupt clear register
} rtc_reg_t;
#define RTC_BASE 0x10017000
volatile rtc_reg_t *regs = NULL;
int counter = 0;
void set_rtc_alarm(rtc_reg_t *regs)
{
unsigned long tmp = 0;
tmp = regs->RTCCR; // write enable
tmp &= 0xFFFFFFFE;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
tmp = regs->RTCDR; // get current time
regs->RTCMR = tmp + 1; // set alarm time
regs->RTCICR = 1; // clear RTCINTR interrupt
regs->RTCIMSC = 1; // set the mask
tmp = regs->RTCCR; // write disable
tmp = tmp | 0x01;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
}
static irqreturn_t rtc_alarm_handler(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
tasklet_rtc.data = irq;
tasklet_schedule(&tasklet_rtc);
set_rtc_alarm(regs);
return IRQ_HANDLED; // 表示中断已经处理完成
}
static void tasklet_alarm_handler(unsigned long data)
{
printk("counter : %d, irqnum : %ld\n", counter++, data);
}
static int __init rtc_init(void)
{
if (request_irq(39, rtc_alarm_handler, 0, "rtc-test", NULL) < 0) {
printk("failed to request_irq\n");
return -1;
}
tasklet_init(&tasklet_rtc, tasklet_alarm_handler, 10);
regs = (rtc_reg_t *)ioremap(RTC_BASE, sizeof(rtc_reg_t));
set_rtc_alarm(regs);
return 0;
}
static void __exit rtc_exit(void)
{
printk("Goodbye rtc module\n");
tasklet_kill(&tasklet_rtc);
free_irq(39, NULL);
}
module_init(rtc_init);
module_exit(rtc_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
tasklet代码分析
workqueue
tasklet是工作在中断上下文,且tasklet是线性执行,所以一旦某个 t->func 阻塞,会导致整个链表阻塞,且由于在中断上下文,无法挂起,导致整个系统性能下降。
workqueue将中断下半部放到进程上下文,所以可以挂起,调度。
接口
typedef void (*work_func_t)(struct work_struct *work);
struct work_struct {
atomic_long_t data;
struct list_head entry;
work_func_t func;
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
struct lockdep_map lockdep_map;
#endif
};
#define DECLARE_WORK(n, f) \
struct work_struct n = __WORK_INITIALIZER(n, f)
#define INIT_WORK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_WORK((_work), (_func), 0)
/**
* schedule_work - put work task in global workqueue
* @work: job to be done
*
* Returns %false if @work was already on the kernel-global workqueue and
* %true otherwise.
*
* This puts a job in the kernel-global workqueue if it was not already
* queued and leaves it in the same position on the kernel-global
* workqueue otherwise.
*
* Shares the same memory-ordering properties of queue_work(), cf. the
* DocBook header of queue_work().
*/
static inline bool schedule_work(struct work_struct *work)
{
return queue_work(system_wq, work);
}
extern bool cancel_work_sync(struct work_struct *work);
示例
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/rtc.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
struct work_struct rtc_work;
typedef volatile struct {
unsigned long RTCDR; // 0x00 data register
unsigned long RTCMR; // 0x04 match register
unsigned long RTCLR; // 0x08 load register
unsigned long RTCCR; // 0x0c Control register
unsigned long RTCIMSC; // 0x10 interrupt mask set and clear register
unsigned long RTCRIS; // 0x14 raw interrupt register
unsigned long RTCMIS; // 0x18 Masked interrupt status register
unsigned long RTCICR; // 0x1c interrupt clear register
} rtc_reg_t;
#define RTC_BASE 0x10017000
volatile rtc_reg_t *regs = NULL;
int counter = 0;
void set_rtc_alarm(rtc_reg_t *regs)
{
unsigned long tmp = 0;
tmp = regs->RTCCR; // write enable
tmp &= 0xFFFFFFFE;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
tmp = regs->RTCDR; // get current time
regs->RTCMR = tmp + 1; // set alarm time
regs->RTCICR = 1; // clear RTCINTR interrupt
regs->RTCIMSC = 1; // set the mask
tmp = regs->RTCCR; // write disable
tmp = tmp | 0x01;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
}
static irqreturn_t rtc_alarm_handler(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
set_rtc_alarm(regs);
schedule_work(&rtc_work);
return IRQ_HANDLED; // 表示中断已经处理完成
}
static void rtc_work_handler(struct work_struct *work)
{
printk("counter : %d\n", counter++);
}
static int __init rtc_init(void)
{
if (request_irq(39, rtc_alarm_handler, 0, "rtc-test", NULL) < 0) {
printk("failed to request_irq\n");
return -1;
}
INIT_WORK(&rtc_work, rtc_work_handler);
regs = (rtc_reg_t *)ioremap(RTC_BASE, sizeof(rtc_reg_t));
set_rtc_alarm(regs);
return 0;
}
static void __exit rtc_exit(void)
{
printk("Goodbye rtc module\n");
cancel_work_sync(&rtc_work);
free_irq(39, NULL);
}
module_init(rtc_init);
module_exit(rtc_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
delayed_work
使用 schedule_work 后,只要cpu不是太忙,则内核很快会分配内核线程执行中断下半部,
有时我们希望内核延迟一段时间再执行中断下半部,如解决按键抖动。则可以使用延迟工作队列
接口
typedef void (*work_func_t)(struct work_struct *work);
struct delayed_work {
struct work_struct work;
struct timer_list timer;
/* target workqueue and CPU ->timer uses to queue ->work */
struct workqueue_struct *wq;
int cpu;
};
#define INIT_DELAYED_WORK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_DELAYED_WORK(_work, _func, 0)
/**
* schedule_delayed_work - put work task in global workqueue after delay
* @dwork: job to be done
* @delay: number of jiffies to wait or 0 for immediate execution
*
* After waiting for a given time this puts a job in the kernel-global
* workqueue.
*/
static inline bool schedule_delayed_work(struct delayed_work *dwork,
unsigned long delay)
{
return queue_delayed_work(system_wq, dwork, delay);
}
#
extern bool flush_delayed_work(struct delayed_work *dwork);
extern bool cancel_delayed_work_sync(struct delayed_work *dwork);
示例
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/rtc.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
struct delayed_work work;
typedef volatile struct {
unsigned long RTCDR; // 0x00 data register
unsigned long RTCMR; // 0x04 match register
unsigned long RTCLR; // 0x08 load register
unsigned long RTCCR; // 0x0c Control register
unsigned long RTCIMSC; // 0x10 interrupt mask set and clear register
unsigned long RTCRIS; // 0x14 raw interrupt register
unsigned long RTCMIS; // 0x18 Masked interrupt status register
unsigned long RTCICR; // 0x1c interrupt clear register
} rtc_reg_t;
#define RTC_BASE 0x10017000
volatile rtc_reg_t *regs = NULL;
int counter = 0;
void set_rtc_alarm(rtc_reg_t *regs)
{
unsigned long tmp = 0;
tmp = regs->RTCCR; // write enable
tmp &= 0xFFFFFFFE;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
tmp = regs->RTCDR; // get current time
regs->RTCMR = tmp + 1; // set alarm time
regs->RTCICR = 1; // clear RTCINTR interrupt
regs->RTCIMSC = 1; // set the mask
tmp = regs->RTCCR; // write disable
tmp = tmp | 0x01;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
}
static irqreturn_t rtc_alarm_handler(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
set_rtc_alarm(regs);
schedule_delayed_work(&work, 2*HZ);
return IRQ_HANDLED; // 表示中断已经处理完成
}
static void rtc_work_handler(struct work_struct *work)
{
printk("counter : %d\n", counter++);
}
static int __init rtc_init(void)
{
if (request_irq(39, rtc_alarm_handler, 0, "rtc-test", NULL) < 0) {
printk("failed to request_irq\n");
return -1;
}
INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&work, rtc_work_handler);
regs = (rtc_reg_t *)ioremap(RTC_BASE, sizeof(rtc_reg_t));
set_rtc_alarm(regs);
return 0;
}
static void __exit rtc_exit(void)
{
printk("Goodbye rtc module\n");
cancel_delayed_work_sync(&work);
flush_scheduled_work();
free_irq(39, NULL);
}
module_init(rtc_init);
module_exit(rtc_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
工作队列的运行
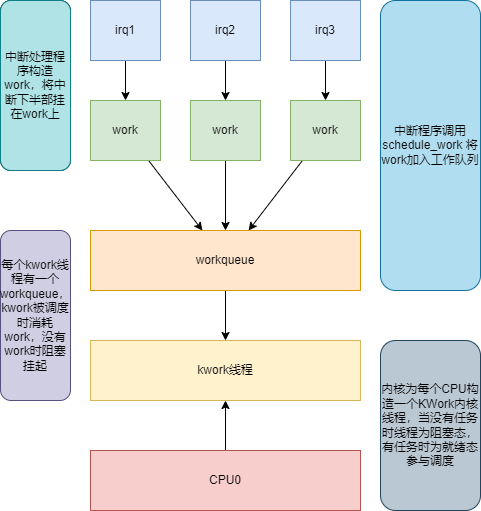
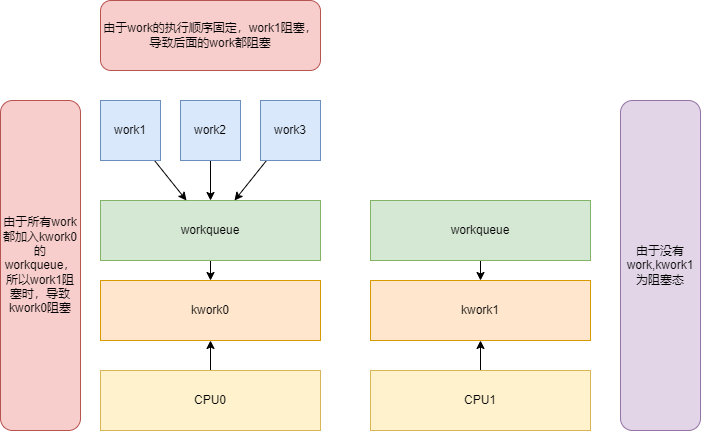
由于 kwork 和 CPU绑定,workqueue也和 kwork 绑定,所以会出现一个work阻塞,导致其他work阻塞的问题,如下
CMWQ 并发管理工作队列
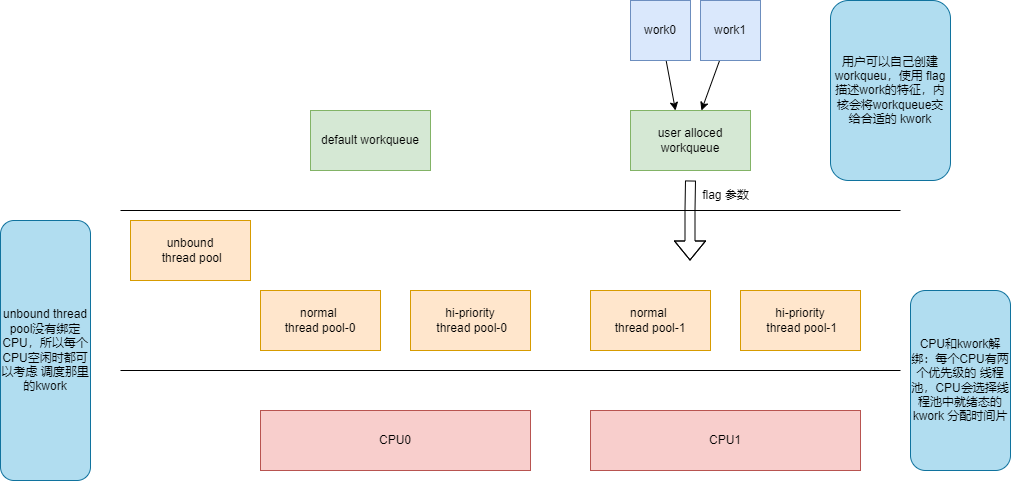
work可以添加到默认workqueue,或自己创建的workqueue
线程池有 unbound 和 bound
workqueue 根据flag添加到指定类型的线程池
max_active : 工作队列在每个CPU上并发处理的work个数
接口
struct workqueue_struct {
....
};
static inline bool queue_work(struct workqueue_struct *wq,
struct work_struct *work)
struct workqueue_struct *alloc_workqueue(const char *fmt,
unsigned int flags,
int max_active, ...)
void flush_workqueue(struct workqueue_struct *wq)
/*
* Workqueue flags and constants. For details, please refer to
* Documentation/core-api/workqueue.rst.
*/
enum {
WQ_UNBOUND = 1 << 1, /* not bound to any cpu */
WQ_FREEZABLE = 1 << 2, /* freeze during suspend */
WQ_MEM_RECLAIM = 1 << 3, /* may be used for memory reclaim */
WQ_HIGHPRI = 1 << 4, /* high priority */
WQ_CPU_INTENSIVE = 1 << 5, /* cpu intensive workqueue */
WQ_SYSFS = 1 << 6, /* visible in sysfs, see workqueue_sysfs_register() */
/*
* Per-cpu workqueues are generally preferred because they tend to
* show better performance thanks to cache locality. Per-cpu
* workqueues exclude the scheduler from choosing the CPU to
* execute the worker threads, which has an unfortunate side effect
* of increasing power consumption.
*
* The scheduler considers a CPU idle if it doesn't have any task
* to execute and tries to keep idle cores idle to conserve power;
* however, for example, a per-cpu work item scheduled from an
* interrupt handler on an idle CPU will force the scheduler to
* execute the work item on that CPU breaking the idleness, which in
* turn may lead to more scheduling choices which are sub-optimal
* in terms of power consumption.
*
* Workqueues marked with WQ_POWER_EFFICIENT are per-cpu by default
* but become unbound if workqueue.power_efficient kernel param is
* specified. Per-cpu workqueues which are identified to
* contribute significantly to power-consumption are identified and
* marked with this flag and enabling the power_efficient mode
* leads to noticeable power saving at the cost of small
* performance disadvantage.
*
* http://thread.gmane.org/gmane.linux.kernel/1480396
*/
WQ_POWER_EFFICIENT = 1 << 7,
__WQ_DRAINING = 1 << 16, /* internal: workqueue is draining */
__WQ_ORDERED = 1 << 17, /* internal: workqueue is ordered */
__WQ_LEGACY = 1 << 18, /* internal: create*_workqueue() */
__WQ_ORDERED_EXPLICIT = 1 << 19, /* internal: alloc_ordered_workqueue() */
WQ_MAX_ACTIVE = 512, /* I like 512, better ideas? */
WQ_MAX_UNBOUND_PER_CPU = 4, /* 4 * #cpus for unbound wq */
WQ_DFL_ACTIVE = WQ_MAX_ACTIVE / 2,
};
示例
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/rtc.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
struct workqueue_struct *cmwq_queue;
struct work_struct work;
typedef volatile struct {
unsigned long RTCDR; // 0x00 data register
unsigned long RTCMR; // 0x04 match register
unsigned long RTCLR; // 0x08 load register
unsigned long RTCCR; // 0x0c Control register
unsigned long RTCIMSC; // 0x10 interrupt mask set and clear register
unsigned long RTCRIS; // 0x14 raw interrupt register
unsigned long RTCMIS; // 0x18 Masked interrupt status register
unsigned long RTCICR; // 0x1c interrupt clear register
} rtc_reg_t;
#define RTC_BASE 0x10017000
volatile rtc_reg_t *regs = NULL;
int counter = 0;
void set_rtc_alarm(rtc_reg_t *regs)
{
unsigned long tmp = 0;
tmp = regs->RTCCR; // write enable
tmp &= 0xFFFFFFFE;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
tmp = regs->RTCDR; // get current time
regs->RTCMR = tmp + 1; // set alarm time
regs->RTCICR = 1; // clear RTCINTR interrupt
regs->RTCIMSC = 1; // set the mask
tmp = regs->RTCCR; // write disable
tmp = tmp | 0x01;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
}
static irqreturn_t rtc_alarm_handler(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
set_rtc_alarm(regs);
queue_work(cmwq_queue, &work);
return IRQ_HANDLED; // 表示中断已经处理完成
}
static void rtc_work_handler(struct work_struct *work)
{
printk("counter : %d\n", counter++);
}
static int __init rtc_init(void)
{
if (request_irq(39, rtc_alarm_handler, 0, "rtc-test", NULL) < 0) {
printk("failed to request_irq\n");
return -1;
}
if ((cmwq_queue = alloc_workqueue("rtc-test", WQ_MEM_RECLAIM , 2)) == NULL) {
printk("failed to alloc_workqueue\n");
return -1;
}
INIT_WORK(&work, rtc_work_handler);
regs = (rtc_reg_t *)ioremap(RTC_BASE, sizeof(rtc_reg_t));
set_rtc_alarm(regs);
return 0;
}
static void __exit rtc_exit(void)
{
flush_workqueue(cmwq_queue);
cancel_work_sync(&work);
free_irq(39, NULL);
printk("Goodbye rtc module\n");
}
module_init(rtc_init);
module_exit(rtc_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
中断线程化
CMWQ让CPU和workqueue解绑,增大了cpu的利用率,但是同一个workqueue中work的执行顺序固定,无法满足高优先级work的实时性。
中断线程化,为每个中断下半部分配一个线程,保证实时性。
接口
int request_threaded_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler,
irq_handler_t thread_fn, unsigned long irqflags,
const char *devname, void *dev_id)
示例
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/rtc.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
typedef volatile struct {
unsigned long RTCDR; // 0x00 data register
unsigned long RTCMR; // 0x04 match register
unsigned long RTCLR; // 0x08 load register
unsigned long RTCCR; // 0x0c Control register
unsigned long RTCIMSC; // 0x10 interrupt mask set and clear register
unsigned long RTCRIS; // 0x14 raw interrupt register
unsigned long RTCMIS; // 0x18 Masked interrupt status register
unsigned long RTCICR; // 0x1c interrupt clear register
} rtc_reg_t;
#define RTC_BASE 0x10017000
volatile rtc_reg_t *regs = NULL;
int counter = 0;
void set_rtc_alarm(rtc_reg_t *regs)
{
unsigned long tmp = 0;
tmp = regs->RTCCR; // write enable
tmp &= 0xFFFFFFFE;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
tmp = regs->RTCDR; // get current time
regs->RTCMR = tmp + 1; // set alarm time
regs->RTCICR = 1; // clear RTCINTR interrupt
regs->RTCIMSC = 1; // set the mask
tmp = regs->RTCCR; // write disable
tmp = tmp | 0x01;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
}
static irqreturn_t rtc_alarm_handler(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
set_rtc_alarm(regs);
return IRQ_WAKE_THREAD; // 让中断下半部的线程为就绪态
}
static irqreturn_t rtc_thread_fn(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
printk("counter : %d\n", counter++);
return IRQ_HANDLED; // 表示中断处理完成
}
static int __init rtc_init(void)
{
if (request_threaded_irq(39, rtc_alarm_handler, rtc_thread_fn, 0, NULL, NULL) < 0) {
printk("failed to request_threaded_irq\n");
return -1;
}
regs = (rtc_reg_t *)ioremap(RTC_BASE, sizeof(rtc_reg_t));
set_rtc_alarm(regs);
return 0;
}
static void __exit rtc_exit(void)
{
free_irq(39, NULL);
printk("Goodbye rtc module\n");
}
module_init(rtc_init);
module_exit(rtc_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· Vue3状态管理终极指南:Pinia保姆级教程