netty之 -- 手写rpc框架
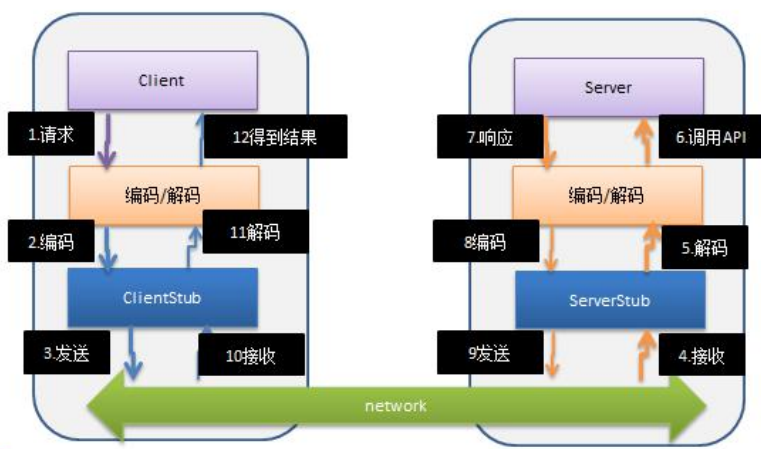
接下来手写一个简陋的rpc框架,首先分析一下调用流程
话不多说,直接上代码:
一个公共接口,相当于protobuf协议中的proto文件
package com.yang.java.main.netty.rpc.publicInterface; /** * Description: * * @author mark * Date 2020/9/16 */ public interface PublicInterface { String hello(String msg); }
服务端实现:
实现声明的接口
package com.yang.java.main.netty.rpc.provider; import com.yang.java.main.netty.rpc.publicInterface.PublicInterface; /** * Description: * * @author mark * Date 2020/9/16 */ public class PublicInterfaceImpl implements PublicInterface { @Override public String hello(String msg) { System.out.println("receive from customer: " + msg); return "provider receive the message: " + msg; } }
netty的服务端
package com.yang.java.main.netty.rpc.netty; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder; /** * Description: * * @author mark * Date 2020/9/16 */ public class NettyServer { // 学习一下netty的命名方法 public static void startServer(String host, int port){ startServer0(host, port); } private static void startServer0(String host, int port){ EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder()); pipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder()); pipeline.addLast(new NettyServerHandler()); //业务处理器 } } ); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(host, port).sync(); System.out.println("provider is start ~~"); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
package com.yang.java.main.netty.rpc.netty; import com.yang.java.main.netty.rpc.provider.PublicInterfaceImpl; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter; /** * Description: * * @author mark * Date 2020/9/16 */ public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { //获取客户端发送的消息,并调用服务 System.out.println("msg: " + msg); String result = new PublicInterfaceImpl().hello(msg.toString()); ctx.writeAndFlush(result); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { ctx.close(); } }
package com.yang.java.main.netty.rpc.provider; import com.yang.java.main.netty.rpc.netty.NettyServer; /** * Description: * * @author mark * Date 2020/9/16 */ public class ProviderBootstrap { public static void main(String[] args) { NettyServer.startServer("127.0.0.1", 7000); } }
netty的客户端
package com.yang.java.main.netty.rpc.netty; import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; /** * Description: * * @author mark * Date 2020/9/16 */ public class NettyClient { //创建线程池 private static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()); private static NettyClientHandler client; private int count = 0; public Object getBean(final Class<?> providerClass) { return Proxy.newProxyInstance(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{providerClass}, (proxy, method, args) -> { System.out.println("(proxy, method, args) come " + (++count) + "time"); if (client == null) { initClient(); } client.setParas((String) args[0]); return executor.submit(client).get(); // 这个其实就是调用call方法 }); } // 初始化客户端 private static void initClient() { client = new NettyClientHandler(); //创建EventLoopGroup NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); bootstrap.group(group) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) .handler( new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder()); pipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder()); pipeline.addLast(client); } } ); try { bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 7000).sync(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
package com.yang.java.main.netty.rpc.netty; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; /** * Description: * 需要继承CallAble * * @author mark * Date 2020/9/16 */ public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter implements Callable { //上下文,因此需要正在call方法中使用,因此缓存起来 private ChannelHandlerContext context; //返回的结果 private String result; //客户端调用方法时,传入的参数 private String paras; // 必须加同步锁,通过wait等到channelRead @Override public synchronized Object call() throws Exception { System.out.println("call before wait"); context.writeAndFlush(paras); wait(); System.out.println("call after wait"); return result; } @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("channelActive"); context = ctx; } // 必须加同步锁,完成之后通过notify告知call已收到消息 @Override public synchronized void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { System.out.println("channelRead"); result = msg.toString(); notify(); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { ctx.close(); } public void setParas(String paras) { System.out.println("set paras"); this.paras = paras; } }
package com.yang.java.main.netty.rpc.consumer; import com.yang.java.main.netty.rpc.netty.NettyClient; import com.yang.java.main.netty.rpc.publicInterface.PublicInterface; /** * Description: * * @author mark * Date 2020/9/16 */ public class ClientBootstrap { public static void main(String[] args){ //创建一个消费者 NettyClient customer = new NettyClient(); //创建代理对象 PublicInterface provider = (PublicInterface) customer.getBean(PublicInterface.class); for (;; ) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } //通过代理对象调用服务提供者的方法(服务) String res = provider.hello("hello rpc~"); System.out.println("result: " + res); } } }
结果分析,符合预期
proxy, method, args) come 1time set paras channelActive call before wait channelRead call after wait result: provider receive the message: hello rpc~ (proxy, method, args) come 2time set paras call before wait channelRead call after wait result: provider receive the message: hello rpc~
简要步骤如下:
- 服务消费方(customer)以本地调用方式调用服务
- customer stub(grpc一般这样简写) 接收到调用后负责将方法、参数等封装成能够进行网络传输的消息体
- customer stub 将消息进行编码并发送到服务端
- provider stub 收到消息后进行解码
- provider stub 根据解码结果调用本地的服务
- 本地服务执行并将结果返回给 provider stub
- provider stub 将返回导入结果进行编码并发送至消费方
- client stub 接收到消息并进行解码
- 服务消费方(customer)得到结果



