寒假学习进度5:tensorflow2.0常用函数
常用函数:
1.

import tensorflow as tf x1 = tf.constant([1,2,3],dtype=tf.int8) print(x1) x2 = tf.cast(x1,dtype=tf.float16) x3 = tf.reduce_min(x1) x4 = tf.reduce_max(x2) print(x1,x2,x3,x4) tf.Tensor([1 2 3], shape=(3,), dtype=int8) tf.Tensor([1 2 3], shape=(3,), dtype=int8) tf.Tensor([1. 2. 3.], shape=(3,), dtype=float16) tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int8) tf.Tensor(3.0, shape=(),dtype=float16)
2.求平均,求和
① 轴向:axis:
axis=0:代表按列计算
axis=1:代表按行计算
不指定时,计算所有元素
② 平均值:
tf.reduce_mean(张量名,axis=操作轴)
③ 求和:
tf.reduce_sum(张量名,axis=操作轴)
t=tf.constant([[1,2,3],[5,6,7]]) print(t) m=tf.reduce_mean(t,axis=0)#按列计算平均值 print(m) s=tf.reduce_sum(t,axis=1)#按行计算和 print(s) >>tf.Tensor([[1 2 3] [5 6 7]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=int32) tf.Tensor([3 4 5], shape=(3,), dtype=int32) tf.Tensor([ 6 18], shape=(2,), dtype=int32)
3.标记可训练量
tf.variable(初始值):将变量标记为“可训练”,被标记的变量会在反向传播中记录梯度信息。可用于神经网络训练中标记带训练参数。
tf.Variable(tf.constant([[1,2,3],[5,6,7]])) >><tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(2, 3) dtype=int32, numpy=array([[1, 2, 3], [5, 6, 7]])>
4.运算
四则运算:只有张量维度相同才可计算
对应元素相加:tf.add(张量1,张量2)
对应元素相减:tf.subtract(张量1,张量2)
对应元素相乘:tf.multiply(张量1,张量2)
对应元素相除:tf.divide(张量1,张量2)
平方:tf.square(张量名)
次方:tf.pow(张量名,n次方数)
开方:tf.sqrt(张量名)
矩阵乘:tf.matmul(张量1,张量2)
t1=tf.fill([2,2],1.0) t2=tf.fill([2,2],3.0) print("t1:",t1) print("t2:",t2) print("t1+t2:",tf.add(t1,t2)) print("t1-t2:",tf.subtract(t1,t2)) print("t1*t2:",tf.multiply(t1,t2)) print("t1/t2:",tf.divide(t1,t2)) print("t1的平方:",tf.square(t1)) print("t1的三次方:",tf.pow(t1,3)) print("t1的开方:",tf.sqrt(t1)) >>t1: tf.Tensor([[1. 1.] [1. 1.]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32) t2: tf.Tensor([[3. 3.] [3. 3.]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32) t1+t2: tf.Tensor([[4. 4.] [4. 4.]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32) t1-t2: tf.Tensor([[-2. -2.] [-2. -2.]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32) t1*t2: tf.Tensor([[3. 3.] [3. 3.]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32) t1/t2: tf.Tensor([[0.33333334 0.33333334] [0.33333334 0.33333334]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32) t1的平方: tf.Tensor([[1. 1.] [1. 1.]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32) t1的三次方: tf.Tensor([[1. 1.] [1. 1.]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32) t1的开方: tf.Tensor([[1. 1.] [1. 1.]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32)
5.切分传入张量的第一维度,生成特征/标签对,构建数据集。
data=tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((输入特征,标签))
import tensorflow as tf features = tf.constant([12,23,10,17]) label = tf.constant([0,1,1,0]) dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((features,label)) print(dataset) for x in dataset: print(x) <TensorSliceDataset shapes: ((), ()), types: (tf.int32, tf.int32)> (<tf.Tensor: id=9, shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=12>, <tf.Tensor: id=10, shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=0>) (<tf.Tensor: id=11, shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=23>, <tf.Tensor: id=12, shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=1>) (<tf.Tensor: id=13, shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=10>, <tf.Tensor: id=14, shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=1>) (<tf.Tensor: id=15, shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=17>, <tf.Tensor: id=16, shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=0>)
6.计算张量梯度(tf.GradientTape)
with结构记录计算过程,gradient求出张量梯度
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
若干计算步骤
grad=tape.gradient(函数,对谁求导)
import tensorflow as tf with tf.GradientTape() as tape: w = tf.Variable(tf.constant(3.0)) loss = tf.pow(w,2) grap = tape.gradient(loss,w) print(grap) tf.Tensor(6.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
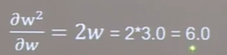
7.enumerate(列表名)遍历列表,并以(索引,元素)形式输出
m=['a','b','c'] for i,element in enumerate(m): print(i,element) >>0 a 1 b 2 c
8.独热编码:在分类问题中常用独热码做标签,标记类别,1表示是,0表示非。
将待转换数据转换为one_hot形式的数据输出:tf.one_hot(待转换数据,depth=几分类)
l=tf.constant([1,2,0]) print("l为:",l) oh=tf.one_hot(l,depth=3) print("独热编码为:",oh) >>l为: tf.Tensor([1 2 0], shape=(3,), dtype=int32) 独热编码为: tf.Tensor([[0. 1. 0.] [0. 0. 1.] [1. 0. 0.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
9、激活函数softmax(y) tf.nn.softmax
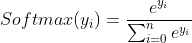
y=tf.constant([1.5,2.9,-0.8]) y_pro=tf.nn.softmax(y) print("概率分布为:",y_pro) >>概率分布为: tf.Tensor([0.19396915 0.7865837 0.01944712], shape=(3,), dtype=float32)
10、自更新函数
w.assign_sub(w要自减的内容)注意这里是自减
在神经网络中需要不断更新迭代超参数,该函数可用于更新超参数.在调用自更新之前需要先将变量定义为可训练
#自更新 w=tf.Variable(2.0)#先设置W为可训练,初值为2 w.assign_sub(0.1)#自减0.1 print(w) >><tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=() dtype=float32, numpy=1.9>
11、tf.argmax(张量名,axis=操作轴) 注:索引是从0开始的
t=tf.constant([[1,4,3],[4,3,6]]) print(t) print(tf.argmax(t,axis=0))#按列输出最大值的索引 >>tf.Tensor([[1 4 3] [4 3 6]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=int32) tf.Tensor([1 0 1], shape=(3,), dtype=int64)



