Mysql之查询数据
1. 基本查询语句
语法: select {*| <字段列表> } FROM <表1>,<表2>... where <表达式> [GROUP BY] [HAVING] [ORDER BY] [LIMIT]
2. 单表查询
1. 查询所有字段
select * from 表名;
2. 查询指定字段
1. 查询单个字段
select 字段名 from 表名;
2. 查询多个字段
select 字段名1,字段名2 from 表名;
3. 查询指定记录
select 字段名1,字段名2 from 表名 where 查询条件;
4. 带IN关键字的查询
select name from students where id in (1,2); 查询id等于1,id等于2的用户名称
select name from students where id not in (1,2); 查询id不等于1,也不等于2的用户名称
5. 带between and的范围查询
select name from students where id between 1 and 2; 查看id在1和2之间的用户名称,包含1和2
select name from students where id not between 1 and 2; 查询id不在1和2之间的用户名称
6. 带LIKE的字符匹配查询
select * from students where name like 'ya%';
select * from students where name like '%a%';
select * from students where name like '%g';
select * from students where name like '_g';
7. 查询空值
IS NULL
select * from students where classID is null;
IS NOT NULL
select * from students where classID is not null;
8. 带AND的多条件查询
select * from students where id=2 and classID=2;
9. 带OR的多条件查询
select * from students where id=2 or classID=2;
10. 查询结果不重复
select distinct 字段名 from 表名;
11. 对查询结果排序
1. 单列排序
select * from students order by name ; 默认是升序
2. 多列排序
select * from students order by classID,name desc;
在对多列进行排序的时候,首先第一列必须有相同的列值,才会对第二列进行排序呢。如果第一列都是唯一的值,将不会对第二列进行排序。
3. 指定排列顺序
DESC 降序
ASC 升序
12. 分组查询
1. 语法
group by 字段 having 条件表达式
group by常与MAX(),MIN(),COUNT(),SUM()结合使用
2. 创建分组
select classID,count(*) from students group by classID; 统计每个班级的人数
select classID,group_concat(name) from students group by classID; 统计每个班级的人姓名
3. 使用HAVING过滤分组
select classID,group_concat(name) from students group by classID having count(name)>1; 统计班级人数大于1的班级
4. GROUP BY子句中使用WITH ROLLUP
使用WITH ROLLUP之后,在所有查询出的分组记录之后增加一条记录,该记录计算查询出的所有记录的总和。
mysql> select classID,count(name) from students group by classID with rollup;
+---------+-------------+
| classID | count(name) |
+---------+-------------+
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 |
| NULL | 6 |
+---------+-------------+
5. 多字段分组
select * from students group by classID,name; 先按第一个字段分组,然后在第一个字段值相同的记录中,再根据第2个字段的值进行分组
13. 使用LIMIT限制查询结果的数量
语法: LIMIT [位置偏移量,] 行数 第一个位置偏移量参数指示从哪一行开始显示,如果不指定,将会从表中的第一条记录开始;第二个参数行数指示返回的记录条数。
select * from students limit 4; 返回前4行记录
select * from students limit 4,3; 从第5行开始,往后数3行
3. 使用聚合函数查询
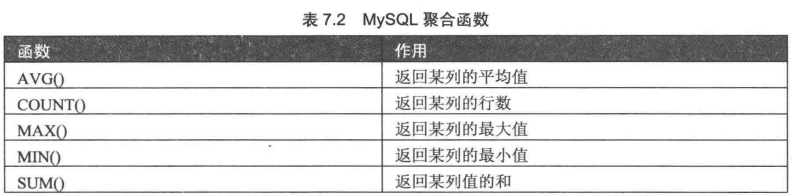
1. COUNT()
COUNT(*) 计算表中总的行数,不管某列有数值或者为空值
COUNT(字段名) 计算指定列下总的行数,计算式忽略空值的行
select count(*) from students; 返回10条记录
select count(classID) from students; 返回9条记录,其中一条为null
select classID,count(*) from students group by classID;
2. SUM()函数
select sum(classID) from students;
select classID,sum(classID) from students group by classID;
3. AVG()函数
select avg(classID) from students ;
select classID,avg(classID) from students group by classID;
4. MAX()函数
select max(classID) from students;
select max(classID) from students group by classID;
5. MIN()函数
select min(classID) from students group by classID;
4. 连接查询
1. 内连接查询
select * from students inner join class on students.classID=class.id;
+----+--------------+---------+----+--------+----------+
| id | name | classID | id | name | position |
+----+--------------+---------+----+--------+----------+
| 1 | yangjianbo | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
| 2 | yichangkun | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
| 3 | luoying | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
| 4 | zhangyan | 2 | 2 | dev | Beijing |
| 5 | wujie | 3 | 3 | test | Beijing |
| 7 | houzhen | 2 | 2 | dev | Beijing |
| 8 | wangzhiyong | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
| 9 | wangshiqiang | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
+----+--------------+---------+----+--------+----------+
select * from class inner join students on class.id=students.classID and students.name='yangjianbo';
+----+--------+----------+----+------------+---------+
| id | name | position | id | name | classID |
+----+--------+----------+----+------------+---------+
| 1 | yunwei | Beijing | 1 | yangjianbo | 1 |
+----+--------+----------+----+------------+---------+
2. 外连接查询
1. LEFT JOIN 返回包括左表中的所有记录和右表中连接字段相等的记录
select * from students left join class on students.classID=class.id;
+----+---------------+---------+------+--------+----------+
| id | name | classID | id | name | position |
+----+---------------+---------+------+--------+----------+
| 1 | yangjianbo | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
| 2 | yichangkun | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
| 3 | luoying | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
| 4 | zhangyan | 2 | 2 | dev | Beijing |
| 5 | wujie | 3 | 3 | test | Beijing |
| 6 | lexiang | 4 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| 7 | houzhen | 2 | 2 | dev | Beijing |
| 8 | wangzhiyong | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
| 9 | wangshiqiang | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
| 10 | maojiangzhong | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
+----+---------------+---------+------+--------+----------+
2. RIGHT JOIN 返回包括右表中的所有记录和右表中连接字段相等的记录
select * from students right join class on students.classID=class.id;
+------+--------------+---------+-----+--------+----------+
| id | name | classID | id | name | position |
+------+--------------+---------+-----+--------+----------+
| 1 | yangjianbo | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
| 2 | yichangkun | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
| 3 | luoying | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
| 4 | zhangyan | 2 | 2 | dev | Beijing |
| 5 | wujie | 3 | 3 | test | Beijing |
| 7 | houzhen | 2 | 2 | dev | Beijing |
| 8 | wangzhiyong | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
| 9 | wangshiqiang | 1 | 1 | yunwei | Beijing |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 100 | test | ShangHai |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 125 | test | ShangHai |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 127 | test | ShangHai |
+------+--------------+---------+-----+--------+----------+
5. 子查询
1. 带any和some子查询
只要条件满足任何一个,就返回值。
select num1 from tb1 where num1 > any(select num2 from tb2); 只要num1大于tb2的num2,任何一个值就列出
select num1 from tb1 where num1 > some(select num2 from tb2);
2. 带ALL的子查询
select num1 from tb1 where num1 > all(select num2 from tb2); num1必须大于tb2的所有num2
3. 带EXISTS的子查询
系统对子查询进行运算以判断它是否返回行,如果至少返回一行,那么EXISTS的结果为true,此时外层查询语句将进行查询;否则返回false,外层语句不进行查询。
mysql> select num1 from tb1 where exists (select * from tb2 where num2=3); num2=3有这个值,所以外层语句可以查询
+------+
| num1 |
+------+
| 1 |
| 11 |
| 18 |
| 27 |
+------+
mysql> select num1 from tb1 where exists (select * from tb2 where num2=1); num2=1没有这个值,所以外层语句不进行查询
Empty set (0.00 sec)
NOT EXISTS与EXISTS刚好相反
4. 带IN的子查询
select id,name from students where id in (select id from class where name="yunwei");
select id,name from students where id not in (select id from class where name="yunwei");
6. 合并查询
语法: select column,... from table1 UNION [ALL] select column,... from table2
UNION 使用关键字ALL不删除重复行也不对结果进行自动排序
不使用关键字,删除重复的记录,所有返回行都是唯一的。
要求两个表的列数和数据类型必须相同
7. 为表和字段取别名
1. 为表取别名
select * from students as a where a.name='yangjianbo';
2. 为字段取别名
select name as username from students as a where a.name='lexiang';
3. 表字段别名只在执行查询的时候使用,并不在返回结果中显示,而列别名定义之后,将返回给客户端显示,显示的结果字段为字段列的别名。
8. 使用正则表达式查询
1. 使用REGEXP关键字指定正则表达式的字符匹配模式
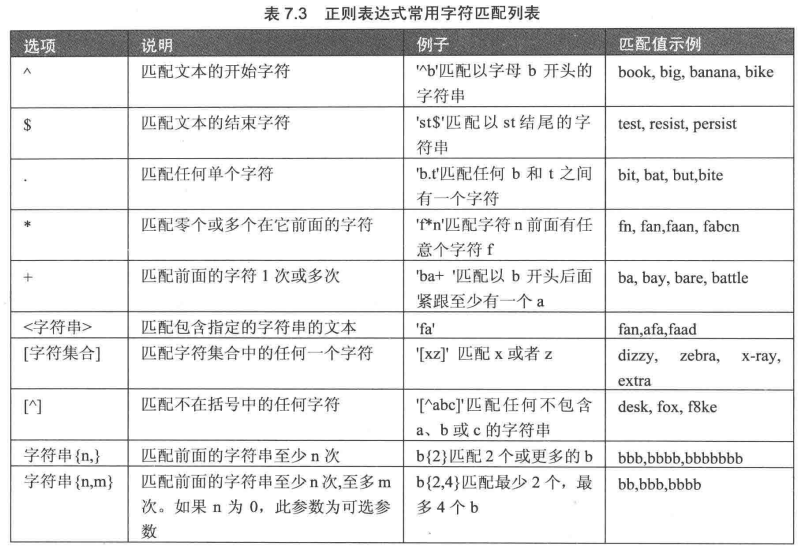
2. 查询以特定字符开头的记录
select * from students where name regexp '^y';
3. 查询以特定字符结尾的记录
select * from students where name regexp 'o$';
4. 用符号'.'来替代字符串中的任意一个字符
select * from students where name regexp 'y.c';
5. 使用"*"和"+"来匹配多个字符
*表示匹配前面的字符多次,包括0次
+表示匹配前面的字符至少一次
mysql> select * from students where name regexp 'wa*';
+----+--------------+---------+
| id | name | classID |
+----+--------------+---------+
| 5 | wujie | 3 |
| 8 | wangzhiyong | 1 |
| 9 | wangshiqiang | 1 |
+----+--------------+---------+
mysql> select * from students where name regexp 'wa+';
+----+--------------+---------+
| id | name | classID |
+----+--------------+---------+
| 8 | wangzhiyong | 1 |
| 9 | wangshiqiang | 1 |
+----+--------------+---------+
6. 匹配指定字符串
select * from students where name regexp 'yi';
select * from students where name regexp 'yi|wa';
7. 匹配指定字符中的任意一个
使用方括号[]指定一个字符集合,只匹配其中任何一个字符 [a-z] [0-9]
select * from students where name regexp '[oc]'; 匹配o或者c
8. 匹配指定字符以外的字符
select * from students where name regexp '[^a-w]';
8. 使用{n,}或者{n,m}来指定字符串连续出现的次数
字符串{n,}至少匹配n次前面的字符
字符串{n,m}匹配前面的字符,不少于n次,不多于m次
select * from students where name regexp 'y{1,3}';



