C++ 实现B+树
在之前了解并复习了下B+树之后还是需要实战一下
之前的B+树文章https://www.cnblogs.com/yangj-Blog/p/12944301.html
演示如下
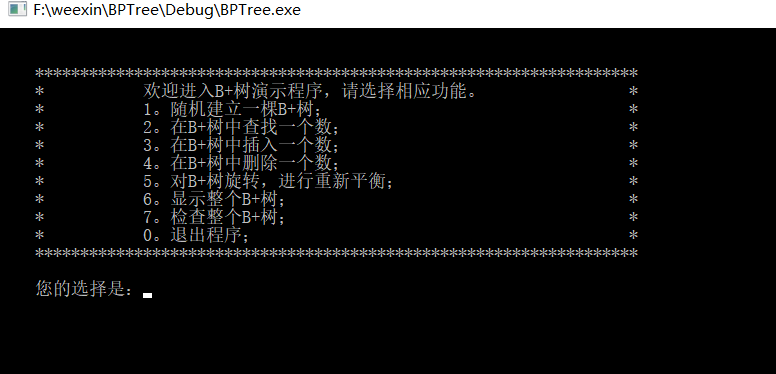
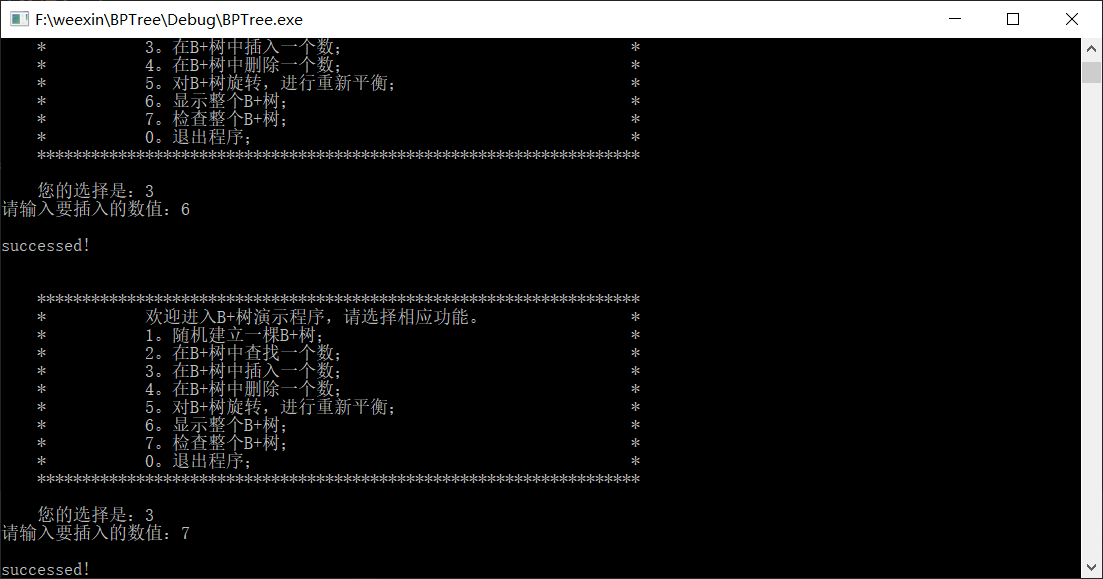
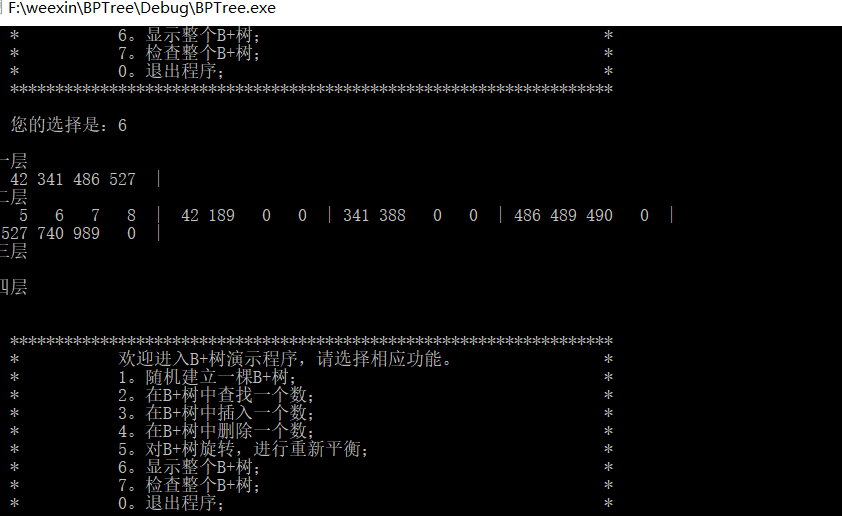
代码如下
BPulsTree.h
/* BPlusTree.h B+树定义文件,本程序实行一个简单的B+树 Definition (from http://www.seanster.com/BplusTree/BplusTree.html ): (1) A B+ tree of order v consists of a root, internal nodes and leaves. (2) The root my be either leaf or node with two or more children. (3) Internal nodes contain between v and 2v keys, and a node with k keys has k + 1 children. (4) Leaves are always on the same level. (5) If a leaf is a primary index, it consists of a bucket of records, sorted by search key. If it is a secondary index, it will have many short records consisting of a key and a pointer to the actual record. (1) 一个v阶的B+树由根结点、内部结点和叶子结点组成。 (2) 根结点可以是叶子结点,也可以是有两个或更多子树的内部结点。 (3) 每个内部结点包含v - 2v个键。如果一个内部结点包含k个键,则有且只有k+1个指向子树的指针。 (4) 叶子结点总是在树的同一层上。 (5) 如果叶子结点是主索引,它包含一组按键值排序的记录;如果叶子结点是从索引,它包含一组短记录,每个短记录包含一个键以及指向实际记录的指针。 (6) 内部结点的键值和叶子结点的数据值都是从小到大排序的。 (7) 在中间结点中,每个键的左子树中的所有的键都小于这个键,每个键的右子树中的所有的键都大于等于这个键。 */ /* B+ 树的阶,即内部结点中键的最小数目v。 也有些人把阶定义为内部结点中键的最大数目,即2v。 一般而言,叶子结点中最大数据个数和内部结点中最大键个数是一样的,也是2v。(我想这样做的目的是为了把内部结点和叶子结点统一到同一个结构中吧) */ #define ORDER_V 2 /* 为简单起见,把v固定为2,实际的B+树v值应该是可配的。这里的v是内部节点中键的最小值 */ #define MAXNUM_KEY (ORDER_V * 2) /* 内部结点中最多键个数,为2v */ #define MAXNUM_POINTER (MAXNUM_KEY + 1) /* 内部结点中最多指向子树的指针个数,为2v */ #define MAXNUM_DATA (ORDER_V * 2) /* 叶子结点中最多数据个数,为2v */ /* 键值的类型*/ typedef int KEY_TYPE; /* 为简单起见,定义为int类型,实际的B+树键值类型应该是可配的 */ /*备注: 为简单起见,叶子结点的数据也只存储键值*/ /* 结点类型 */ enum NODE_TYPE { NODE_TYPE_ROOT = 1, // 根结点 NODE_TYPE_INTERNAL = 2, // 内部结点 NODE_TYPE_LEAF = 3, // 叶子结点 }; #define NULL 0 #define INVALID 0 #define FLAG_LEFT 1 #define FLAG_RIGHT 2 /* 结点数据结构,为内部结点和叶子结点的父类 */ class CNode { public: CNode(); virtual ~CNode(); //获取和设置结点类型 NODE_TYPE GetType() { return m_Type; } void SetType(NODE_TYPE type) {m_Type = type;} // 获取和设置有效数据个数 int GetCount() { return m_Count;} void SetCount(int i) { m_Count = i; } // 获取和设置某个元素,对中间结点指键值,对叶子结点指数据 virtual KEY_TYPE GetElement(int i) {return 0;} virtual void SetElement(int i, KEY_TYPE value) { } // 获取和设置某个指针,对中间结点指指针,对叶子结点无意义 virtual CNode* GetPointer(int i) {return NULL;} virtual void SetPointer(int i, CNode* pointer) { } // 获取和设置父结点 CNode* GetFather() { return m_pFather;} void SetFather(CNode* father) { m_pFather = father; } // 获取一个最近的兄弟结点 CNode* GetBrother(int& flag); // 删除结点 void DeleteChildren(); protected: NODE_TYPE m_Type; // 结点类型,取值为NODE_TYPE类型 int m_Count; // 有效数据个数,对中间结点指键个数,对叶子结点指数据个数 CNode* m_pFather; // 指向父结点的指针,标准B+树中并没有该指针,加上是为了更快地实现结点分裂和旋转等操作 }; /* 内部结点数据结构 */ class CInternalNode : public CNode { public: CInternalNode(); virtual ~CInternalNode(); // 获取和设置键值,对用户来说,数字从1开始,实际在结点中是从0开始的 KEY_TYPE GetElement(int i) { if ((i > 0 ) && (i <= MAXNUM_KEY)) { return m_Keys[i - 1]; } else { return INVALID; } } void SetElement(int i, KEY_TYPE key) { if ((i > 0 ) && (i <= MAXNUM_KEY)) { m_Keys[i - 1] = key; } } // 获取和设置指针,对用户来说,数字从1开始 CNode* GetPointer(int i) { if ((i > 0 ) && (i <= MAXNUM_POINTER)) { return m_Pointers[i - 1]; } else { return NULL; } } void SetPointer(int i, CNode* pointer) { if ((i > 0 ) && (i <= MAXNUM_POINTER)) { m_Pointers[i - 1] = pointer; } } // 在结点pNode上插入键value bool Insert(KEY_TYPE value, CNode* pNode); // 删除键value bool Delete(KEY_TYPE value); // 分裂结点 KEY_TYPE Split(CInternalNode* pNode, KEY_TYPE key); // 结合结点(合并结点) bool Combine(CNode* pNode); // 从另一结点移一个元素到本结点 bool MoveOneElement(CNode* pNode); protected: KEY_TYPE m_Keys[MAXNUM_KEY]; // 键数组 CNode* m_Pointers[MAXNUM_POINTER]; // 指针数组 }; /* 叶子结点数据结构 */ class CLeafNode : public CNode { public: CLeafNode(); virtual ~CLeafNode(); // 获取和设置数据 KEY_TYPE GetElement(int i) { if ((i > 0 ) && (i <= MAXNUM_DATA)) { return m_Datas[i - 1]; } else { return INVALID; } } void SetElement(int i, KEY_TYPE data) { if ((i > 0 ) && (i <= MAXNUM_DATA)) { m_Datas[i - 1] = data; } } // 获取和设置指针,对叶子结点无意义,只是实行父类的虚函数 CNode* GetPointer(int i) { return NULL; } // 插入数据 bool Insert(KEY_TYPE value); // 删除数据 bool Delete(KEY_TYPE value); // 分裂结点 KEY_TYPE Split(CNode* pNode); // 结合结点 bool Combine(CNode* pNode); public: // 以下两个变量用于实现双向链表 CLeafNode* m_pPrevNode; // 前一个结点 CLeafNode* m_pNextNode; // 后一个结点 protected: KEY_TYPE m_Datas[MAXNUM_DATA]; // 数据数组 }; /* B+树数据结构 */ class BPlusTree { public: BPlusTree(); virtual ~BPlusTree(); // 查找指定的数据 bool Search(KEY_TYPE data, char* sPath); // 插入指定的数据 bool Insert(KEY_TYPE data); // 删除指定的数据 bool Delete(KEY_TYPE data); // 清除树 void ClearTree(); // 打印树 void PrintTree(); // 旋转树 BPlusTree* RotateTree(); // 检查树是否满足B+树的定义 bool CheckTree(); void PrintNode(CNode* pNode); // 递归检查结点及其子树是否满足B+树的定义 bool CheckNode(CNode* pNode); // 获取和设置根结点 CNode* GetRoot() { return m_Root; } void SetRoot(CNode* root) { m_Root = root; } // 获取和设置深度 int GetDepth() { return m_Depth; } void SetDepth(int depth) { m_Depth = depth; } // 深度加一 void IncDepth() { m_Depth = m_Depth + 1; } // 深度减一 void DecDepth() { if (m_Depth > 0) { m_Depth = m_Depth - 1; } } public: // 以下两个变量用于实现双向链表 CLeafNode* m_pLeafHead; // 头结点 CLeafNode* m_pLeafTail; // 尾结点 protected: // 为插入而查找叶子结点 CLeafNode* SearchLeafNode(KEY_TYPE data); //插入键到中间结点 bool InsertInternalNode(CInternalNode* pNode, KEY_TYPE key, CNode* pRightSon); // 在中间结点中删除键 bool DeleteInternalNode(CInternalNode* pNode, KEY_TYPE key); CNode* m_Root; // 根结点 int m_Depth; // 树的深度 };
BPulsTree.cpp
----------------------------------------------
#include "BPlusTree.h" #include "stdio.h" #include "stdlib.h" CNode::CNode() { m_Type = NODE_TYPE_LEAF; m_Count = 0; m_pFather = NULL; } CNode::~CNode() { DeleteChildren(); } // 获取一个最近的兄弟结点 CNode* CNode::GetBrother(int& flag) { CNode* pFather = GetFather(); //获取其父结点指针 if (NULL == pFather) { return NULL; } CNode* pBrother = NULL; for (int i = 1; i <= pFather->GetCount() + 1; i++) //GetCount()表示获取数据或关键字数,要比指针数小1。 { // 找到本结点的位置 if (pFather->GetPointer(i) == this) { if (i == (pFather->GetCount() + 1)) //表示其为父结点的最右边孩子。 { pBrother = pFather->GetPointer(i - 1); // 本身是最后一个指针,只能找前一个指针 flag = FLAG_LEFT; } else { pBrother = pFather->GetPointer(i + 1); // 优先找后一个指针 flag = FLAG_RIGHT; } } } return pBrother; } // 递归删除子结点 void CNode::DeleteChildren() // 疑问:这里的指针下标是否需要从0开始 { for (int i = 1; i <= GetCount(); i++) //GetCount()为返回结点中关键字即数据的个数 { CNode * pNode = GetPointer(i); if (NULL != pNode) // 叶子结点没有指针 { pNode->DeleteChildren(); } delete pNode; } } //将内部节点的关键字和指针分别初始化为0和空 CInternalNode::CInternalNode() { m_Type = NODE_TYPE_INTERNAL; int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < MAXNUM_KEY; i++) { m_Keys[i] = INVALID; } for (i = 0; i < MAXNUM_POINTER; i++) { m_Pointers[i] = NULL; } } CInternalNode::~CInternalNode() { for (int i = 0; i < MAXNUM_POINTER; i++) { m_Pointers[i] = NULL; } } // 在中间结点中插入键。 /*疑问:中间结点需要插入值吗?在插入值时,通常都是先找到在叶子结点中的位置,然后再插入。 中间结点通常当叶子结点需要分裂时将分裂后的两个孩子结点插入其中*/ bool CInternalNode::Insert(KEY_TYPE value, CNode* pNode) { int i; // 如果中间结点已满,直接返回失败 if (GetCount() >= MAXNUM_KEY) { return false; } int j = 0; // 找到要插入键的位置 for (i = 0; (value > m_Keys[i]) && ( i < m_Count); i++) { } // 当前位置及其后面的键依次后移,空出当前位置 for (j = m_Count; j > i; j--) { m_Keys[j] = m_Keys[j - 1]; } // 当前位置及其后面的指针依次后移 for (j = m_Count + 1; j > i + 1; j--) { m_Pointers[j] = m_Pointers[j - 1]; } // 把键和指针存入当前位置 m_Keys[i] = value; m_Pointers[i + 1] = pNode; // 注意是第i+1个指针而不是第i个指针 pNode->SetFather(this); // 非常重要 该函数的意思是插入关键字value及其所指向子树 m_Count++; // 返回成功 return true; } // 在中间结点中删除键,以及该键后的指针 bool CInternalNode::Delete(KEY_TYPE key) { int i,j,k; for (i = 0; (key >= m_Keys[i]) && (i < m_Count); i++) { } for (j = i - 1; j < m_Count - 1; j++) { m_Keys[j] = m_Keys[j + 1]; } m_Keys[j] = INVALID; for (k = i; k < m_Count; k++) { m_Pointers[k] = m_Pointers[k + 1]; } m_Pointers[k] = NULL; m_Count--; return true; } /* 分裂中间结点 分裂中间结点和分裂叶子结点完全不同,因为中间结点不仅有2V键,还有2V+1指针,如果单纯地一分为2,指针将无法分 配。 因此根据http://www.seanster.com/BplusTree/BplusTree.html ,分裂中 间结点的算法是: 根据要插入的键key判断: (1)如果key小于第V个键,则把第V个键提出来,其左右的键分别分到两个结点中 (2) 如果key大于第V+1个键,则把第V+1个键提出来,其左右的键分别分到两个结点中 (3)如果key介于第V和V+1个键之间,则把key作为 要提出的键,原来的键各分一半到两个结点中 提出来的RetKey作用是便于后续插入到祖先结点 */ KEY_TYPE CInternalNode::Split(CInternalNode* pNode, KEY_TYPE key) //key是新插入的值,pNode是分裂结点 { int i = 0, j = 0; // 如果要插入的键值在第V和V+1个键值中间,需要翻转一下,因此先处理此情况 if ((key > this->GetElement(ORDER_V)) && (key < this->GetElement(ORDER_V + 1))) { // 把第V+1 -- 2V个键移到指定的结点中 for (i = ORDER_V + 1; i <= MAXNUM_KEY; i++) { j++; pNode->SetElement(j, this->GetElement(i)); this->SetElement(i, INVALID); } // 把第V+2 -- 2V+1个指针移到指定的结点中 j = 0; for (i = ORDER_V + 2; i <= MAXNUM_POINTER; i++) { j++; this->GetPointer(i)->SetFather(pNode); // 重新设置子结点的父亲 pNode->SetPointer(j, this->GetPointer(i)); this->SetPointer(i, INVALID); } // 设置好Count个数 this->SetCount(ORDER_V); pNode->SetCount(ORDER_V); // 把原键值返回 return key; } // 以下处理key小于第V个键值或key大于第V+1个键值的情况 // 判断是提取第V还是V+1个键 int position = 0; if (key < this->GetElement(ORDER_V)) { position = ORDER_V; } else { position = ORDER_V + 1; } // 把第position个键提出来,作为新的键值返回 KEY_TYPE RetKey = this->GetElement(position); // 把第position+1 -- 2V个键移到指定的结点中 j = 0; for (i = position + 1; i <= MAXNUM_KEY; i++) { j++; pNode->SetElement(j, this->GetElement(i)); this->SetElement(i, INVALID); } // 把第position+1 -- 2V+1个指针移到指定的结点中(注意指针比键多一个) j = 0; for (i = position + 1; i <= MAXNUM_POINTER; i++) { j++; this->GetPointer(i)->SetFather(pNode); // 重新设置子结点的父亲 pNode->SetPointer(j, this->GetPointer(i)); this->SetPointer(i, INVALID); } // 清除提取出的位置 this->SetElement(position, INVALID); // 设置好Count个数 this->SetCount(position - 1); pNode->SetCount(MAXNUM_KEY - position); return RetKey; } //结合结点,把指定中间结点的数据全部剪切到本中间结点 bool CInternalNode::Combine(CNode* pNode) { // 参数检查 if (this->GetCount() + pNode->GetCount() + 1> MAXNUM_DATA) // 预留一个新键的位置 { return false; } // 取待合并结点的第一个孩子的第一个元素作为新键值 KEY_TYPE NewKey = pNode->GetPointer(1)->GetElement(1); //疑问:感觉应该改为KEY_TYPE NewKey = pNode->GetElement(1); m_Keys[m_Count] = NewKey; m_Count++; m_Pointers[m_Count] = pNode->GetPointer(1); //疑问:感觉应该为m_Pointers[m_Count+1] = pNode->GetPointer(1); for (int i = 1; i <= pNode->GetCount(); i++) { m_Keys[m_Count] = pNode->GetElement(i); m_Count++; m_Pointers[m_Count] = pNode->GetPointer(i+1); } return true; } // 从另一结点移一个元素到本结点 bool CInternalNode::MoveOneElement(CNode* pNode) { // 参数检查 if (this->GetCount() >= MAXNUM_DATA) { return false; } int i,j; // 兄弟结点在本结点左边 if (pNode->GetElement(1) < this->GetElement(1)) { // 先腾出位置 for (i = m_Count; i > 0; i--) { m_Keys[i] = m_Keys[i -1]; } for (j = m_Count + 1; j > 0; j--) { m_Pointers[j] = m_Pointers[j -1]; } // 赋值 // 第一个键值不是兄弟结点的最后一个键值,而是本结点第一个子结点的第一个元素的值 m_Keys[0] = GetPointer(1)->GetElement(1); // 第一个子结点为兄弟结点的最后一个子结点 m_Pointers[0] = pNode->GetPointer(pNode->GetCount() + 1); // 修改兄弟结点 pNode->SetElement(pNode->GetCount(), INVALID); pNode->SetPointer(pNode->GetCount() + 1, INVALID); } else // 兄弟结点在本结点右边 { // 赋值 // 最后一个键值不是兄弟结点的第一个键值,而是兄弟结点第一个子结点的第一个元素的值 m_Keys[m_Count] = pNode->GetPointer(1)->GetElement(1); // 最后一个子结点为兄弟结点的第一个子结点 m_Pointers[m_Count + 1] = pNode->GetPointer(1); // 修改兄弟结点 for (i = 1; i < pNode->GetCount() - 1; i++) { pNode->SetElement(i, pNode->GetElement(i + 1)); } for (j = 1; j < pNode->GetCount(); j++) { pNode->SetPointer(j, pNode->GetPointer(j + 1)); } } // 设置数目 this->SetCount(this->GetCount() + 1); pNode->SetCount(pNode->GetCount() - 1); return true; } // 清除叶子结点中的数据 CLeafNode::CLeafNode() { m_Type = NODE_TYPE_LEAF; for (int i = 0; i < MAXNUM_DATA; i++) { m_Datas[i] = INVALID; } m_pPrevNode = NULL; m_pNextNode = NULL; } CLeafNode::~CLeafNode() { } // 在叶子结点中插入数据 bool CLeafNode::Insert(KEY_TYPE value) { int i,j; // 如果叶子结点已满,直接返回失败 if (GetCount() >= MAXNUM_DATA) { return false; } // 找到要插入数据的位置 for (i = 0; (value > m_Datas[i]) && ( i < m_Count); i++) { } // 当前位置及其后面的数据依次后移,空出当前位置 for (j = m_Count; j > i; j--) { m_Datas[j] = m_Datas[j - 1]; } // 把数据存入当前位置 m_Datas[i] = value; m_Count++; // 返回成功 return true; } bool CLeafNode::Delete(KEY_TYPE value) { int i,j; bool found = false; for (i = 0; i < m_Count; i++) { if (value == m_Datas[i]) { found = true; break; } } // 如果没有找到,返回失败 if (false == found) { return false; } // 后面的数据依次前移 for (j = i; j < m_Count - 1; j++) { m_Datas[j] = m_Datas[j + 1]; } m_Datas[j] = INVALID; m_Count--; // 返回成功 return true; } // 分裂叶子结点,把本叶子结点的后一半数据剪切到指定的叶子结点中 KEY_TYPE CLeafNode::Split(CNode* pNode) { // 把本叶子结点的后一半数据移到指定的结点中 int j = 0; for (int i = ORDER_V + 1; i <= MAXNUM_DATA; i++) { j++; pNode->SetElement(j, this->GetElement(i)); this->SetElement(i, INVALID); } // 设置好Count个数 this->SetCount(this->GetCount() - j); pNode->SetCount(pNode->GetCount() + j); // 返回新结点的第一个元素作为键 return pNode->GetElement(1); } // 结合结点,把指定叶子结点的数据全部剪切到本叶子结点 bool CLeafNode::Combine(CNode* pNode) { // 参数检查 if (this->GetCount() + pNode->GetCount() > MAXNUM_DATA) { return false; } for (int i = 1; i <= pNode->GetCount(); i++) { this->Insert(pNode->GetElement(i)); } return true; } BPlusTree::BPlusTree() { m_Depth = 0; m_Root = NULL; m_pLeafHead = NULL; m_pLeafTail = NULL; } BPlusTree::~BPlusTree() { ClearTree(); } // 在树中查找数据 bool BPlusTree::Search(KEY_TYPE data, char* sPath) { int i = 0; int offset = 0; if (NULL != sPath) { (void)sprintf(sPath+offset, "The serach path is:"); offset+=19; } CNode * pNode = GetRoot(); // 循环查找对应的叶子结点 while (NULL != pNode) { // 结点为叶子结点,循环结束 if (NODE_TYPE_LEAF == pNode->GetType()) { break; } // 找到第一个键值大于等于key的位置 for (i = 1; (data >= pNode->GetElement(i) )&& (i <= pNode->GetCount()); i++) { } if (NULL != sPath) { (void)sprintf(sPath+offset, " %3d -->", pNode->GetElement(1)); offset+=8; } pNode = pNode->GetPointer(i); } // 没找到 if (NULL == pNode) { return false; } if (NULL != sPath) { (void)sprintf(sPath+offset, "%3d", pNode->GetElement(1)); offset+=3; } // 在叶子结点中继续找 bool found = false; for (i = 1; (i <= pNode->GetCount()); i++) { if (data == pNode->GetElement(i)) { found = true; } } if (NULL != sPath) { if (true == found) { (void)sprintf(sPath+offset, " ,successed."); } else { (void)sprintf(sPath+offset, " ,failed."); } } return found; } /* 在B+树中插入数据 插入数据首先要找到理论上要插入的叶子结点,然后分三种情况: (1) 叶子结点未满。直接在该结点中插入即可; (2) 叶子结点已满,且无父结点(即根结点是叶子结点),需要首先把叶子结点分裂,然后选择插入原结点或新结点,然后新生成根节点; (3) 叶子结点已满,但其父结点未满。需要首先把叶子结点分裂,然后选择插入原结点或新结点,再修改父结点的指针; (4) 叶子结点已满,且其父结点已满。需要首先把叶子结点分裂,然后选择插入原结点或新结点,接着把父结点分裂,再修改祖父结点的指针。 因为祖父结点也可能满,所以可能需要一直递归到未满的祖先结点为止。 */ bool BPlusTree::Insert(KEY_TYPE data) // { // 检查是否重复插入 bool found = Search(data, NULL); if (true == found) { return false; } // for debug //if (289 == data) //{ // printf("\n%d,check failed!",data); //} // 查找理想的叶子结点 CLeafNode* pOldNode = SearchLeafNode(data); // 如果没有找到,说明整个树是空的,生成根结点 if (NULL == pOldNode) { pOldNode = new CLeafNode; m_pLeafHead = pOldNode; m_pLeafTail = pOldNode; SetRoot(pOldNode); } // 叶子结点未满,对应情况1,直接插入 if (pOldNode->GetCount() < MAXNUM_DATA) { return pOldNode->Insert(data); } // 原叶子结点已满,新建叶子结点,并把原结点后一半数据剪切到新结点 CLeafNode* pNewNode = new CLeafNode; KEY_TYPE key = INVALID; key = pOldNode->Split(pNewNode); // 在双向链表中插入结点 CLeafNode* pOldNext = pOldNode->m_pNextNode; pOldNode->m_pNextNode = pNewNode; pNewNode->m_pNextNode = pOldNext; pNewNode->m_pPrevNode = pOldNode; if (NULL == pOldNext) { m_pLeafTail = pNewNode; } else { pOldNext->m_pPrevNode = pNewNode; } // 判断是插入到原结点还是新结点中,确保是按数据值排序的 if (data < key) { pOldNode->Insert(data); // 插入原结点 } else { pNewNode->Insert(data); // 插入新结点 } // 父结点 CInternalNode* pFather = (CInternalNode*)(pOldNode->GetFather()); // 如果原结点是根节点,对应情况2 if (NULL == pFather) { CNode* pNode1 = new CInternalNode; pNode1->SetPointer(1, pOldNode); // 指针1指向原结点 pNode1->SetElement(1, key); // 设置键 pNode1->SetPointer(2, pNewNode); // 指针2指向新结点 pOldNode->SetFather(pNode1); // 指定父结点 pNewNode->SetFather(pNode1); // 指定父结点 pNode1->SetCount(1); SetRoot(pNode1); // 指定新的根结点 return true; } // 情况3和情况4在这里实现 bool ret = InsertInternalNode(pFather, key, pNewNode); return ret; } /* 删除某数据 删除数据的算法如下: (1) 如果删除后叶子结点填充度仍>=50%,只需要修改叶子结点,如果删除的是父结点的键,父结点也要相应修改; (2) 如果删除后叶子结点填充度<50%,需要先找到一个最近的兄弟结点(左右均可),然后分两种情况: A. 如果该兄弟结点填充度>50%,把该兄弟结点的最近一个数据剪切到本结点,父结点的键值也要相应修改。 B. 如果该兄弟结点的填充度=50%,则把两个结点合并,父结点键也相应合并。(如果合并后父结点的填充度<50%,则需要递归) */ bool BPlusTree::Delete(KEY_TYPE data) { // 查找理想的叶子结点 CLeafNode* pOldNode = SearchLeafNode(data); // 如果没有找到,返回失败 if (NULL == pOldNode) { return false; } // 删除数据,如果失败一定是没有找到,直接返回失败 bool success = pOldNode->Delete(data); if (false == success) { return false; } // 获取父结点 CInternalNode* pFather = (CInternalNode*)(pOldNode->GetFather()); if (NULL == pFather) { // 如果一个数据都没有了,删除根结点(只有根节点可能出现此情况) if (0 == pOldNode->GetCount()) { delete pOldNode; m_pLeafHead = NULL; m_pLeafTail = NULL; SetRoot(NULL); } return true; } // 删除后叶子结点填充度仍>=50%,对应情况1 if (pOldNode->GetCount() >= ORDER_V) { for (int i = 1; (data >= pFather->GetElement(i)) && (i <= pFather->GetCount()); i++) { // 如果删除的是父结点的键值,需要更改该键 if (pFather->GetElement(i) == data) { pFather->SetElement(i, pOldNode->GetElement(1)); // 更改为叶子结点新的第一个元素 } } return true; } // 找到一个最近的兄弟结点(根据B+树的定义,除了叶子结点,总是能找到的) int flag = FLAG_LEFT; CLeafNode* pBrother = (CLeafNode*)(pOldNode->GetBrother(flag)); // 兄弟结点填充度>50%,对应情况2A KEY_TYPE NewData = INVALID; if (pBrother->GetCount() > ORDER_V) { if (FLAG_LEFT == flag) // 兄弟在左边,移最后一个数据过来 { NewData = pBrother->GetElement(pBrother->GetCount()); } else // 兄弟在右边,移第一个数据过来 { NewData = pBrother->GetElement(1); } pOldNode->Insert(NewData); pBrother->Delete(NewData); // 修改父结点的键值 if (FLAG_LEFT == flag) { for (int i = 1; i <= pFather->GetCount() + 1; i++) { if (pFather->GetPointer(i) == pOldNode && i > 1) { pFather->SetElement(i - 1 , pOldNode->GetElement(1)); // 更改本结点对应的键 } } } else { for (int i = 1; i <= pFather->GetCount() + 1; i++) { if (pFather->GetPointer(i) == pOldNode && i > 1) { pFather->SetElement(i - 1, pOldNode->GetElement(1)); // 更改本结点对应的键 } if (pFather->GetPointer(i) == pBrother && i > 1) { pFather->SetElement(i - 1 , pBrother->GetElement(1)); // 更改兄弟结点对应的键 } } } return true; } // 情况2B // 父结点中要删除的键 KEY_TYPE NewKey = NULL; // 把本结点与兄弟结点合并,无论如何合并到数据较小的结点,这样父结点就无需修改指针 if (FLAG_LEFT == flag) { (void)pBrother->Combine(pOldNode); NewKey = pOldNode->GetElement(1); CLeafNode* pOldNext = pOldNode->m_pNextNode; pBrother->m_pNextNode = pOldNext; // 在双向链表中删除结点 if (NULL == pOldNext) { m_pLeafTail = pBrother; } else { pOldNext->m_pPrevNode = pBrother; } // 删除本结点 delete pOldNode; } else { (void)pOldNode->Combine(pBrother); NewKey = pBrother->GetElement(1); CLeafNode* pOldNext = pBrother->m_pNextNode; pOldNode->m_pNextNode = pOldNext; // 在双向链表中删除结点 if (NULL == pOldNext) { m_pLeafTail = pOldNode; } else { pOldNext->m_pPrevNode = pOldNode; } // 删除本结点 delete pBrother; } return DeleteInternalNode(pFather, NewKey); } // 清除整个树,删除所有结点 void BPlusTree::ClearTree() { CNode* pNode = GetRoot(); if (NULL != pNode) { pNode->DeleteChildren(); delete pNode; } m_pLeafHead = NULL; m_pLeafTail = NULL; SetRoot(NULL); } // 旋转以重新平衡,实际上是把整个树重构一下,结果不理想,待重新考虑 BPlusTree* BPlusTree::RotateTree() { BPlusTree* pNewTree = new BPlusTree; int i = 0; CLeafNode * pNode = m_pLeafHead; while (NULL != pNode) { for (int i = 1; i <= pNode->GetCount(); i ++) { (void)pNewTree->Insert(pNode->GetElement(i)); } pNode = pNode->m_pNextNode; } return pNewTree; } // 检查树是否满足B+树的定义 bool BPlusTree::CheckTree() { CLeafNode * pThisNode = m_pLeafHead; CLeafNode * pNextNode = NULL; while (NULL != pThisNode) { pNextNode = pThisNode->m_pNextNode; if (NULL != pNextNode) { if (pThisNode->GetElement(pThisNode->GetCount()) > pNextNode->GetElement(1)) { return false; } } pThisNode = pNextNode; } return CheckNode(GetRoot()); } // 递归检查结点及其子树是否满足B+树的定义 bool BPlusTree::CheckNode(CNode* pNode) { if (NULL == pNode) { return true; } int i = 0; bool ret = false; // 检查是否满足50%的填充度 if ((pNode->GetCount() < ORDER_V) && (pNode != GetRoot())) { return false; } // 检查键或数据是否按大小排序 for (i = 1; i < pNode->GetCount(); i++) { if (pNode->GetElement(i) > pNode->GetElement(i + 1)) { return false; } } if (NODE_TYPE_LEAF == pNode->GetType()) { return true; } // 对中间结点,递归检查子树 for (i = 1; i <= pNode->GetCount() + 1; i++) { ret = CheckNode(pNode->GetPointer(i)); // 只要有一个不合法就返回不合法 if (false == ret) { return false; } } return true; } // 打印整个树 void BPlusTree::PrintTree() { CNode* pRoot = GetRoot(); if (NULL == pRoot) return; CNode* p1, *p2, *p3; int i, j, k; int total = 0; printf("\n第一层\n | "); PrintNode(pRoot); total = 0; printf("\n第二层\n | "); for (i = 1; i <= MAXNUM_POINTER; i++) { p1 = pRoot->GetPointer(i); if (NULL == p1) continue; PrintNode(p1); total++; if (total%4 == 0) printf("\n | "); } total = 0; printf("\n第三层\n | "); for (i = 1; i <= MAXNUM_POINTER; i++) { p1 = pRoot->GetPointer(i); if (NULL == p1) continue; for (j = 1; j <= MAXNUM_POINTER; j++) { p2 = p1->GetPointer(j); if (NULL == p2) continue; PrintNode(p2); total++; if (total%4 == 0) printf("\n | "); } } total = 0; printf("\n第四层\n | "); for (i = 1; i <= MAXNUM_POINTER; i++) { p1 = pRoot->GetPointer(i); if (NULL == p1) continue; for (j = 1; j <= MAXNUM_POINTER; j++) { p2 = p1->GetPointer(j); if (NULL == p2) continue; for (k = 1; k <= MAXNUM_POINTER; k++) { p3 = p2->GetPointer(k); if (NULL == p3) continue; PrintNode(p3); total++; if (total%4 == 0) printf("\n | "); } } } } // 打印某结点 void BPlusTree::PrintNode(CNode* pNode) { if (NULL == pNode) { return; } for (int i = 1; i <= MAXNUM_KEY; i++) { printf("%3d ", pNode->GetElement(i)); if (i >= MAXNUM_KEY) { printf(" | "); } } } // 查找对应的叶子结点 CLeafNode* BPlusTree::SearchLeafNode(KEY_TYPE data) { int i = 0; CNode * pNode = GetRoot(); // 循环查找对应的叶子结点 while (NULL != pNode) { // 结点为叶子结点,循环结束 if (NODE_TYPE_LEAF == pNode->GetType()) { break; } // 找到第一个键值大于等于key的位置 for (i = 1; i <= pNode->GetCount(); i++) { if (data < pNode->GetElement(i)) { break; } } pNode = pNode->GetPointer(i); } return (CLeafNode*)pNode; } //递归函数:插入键到中间结点 bool BPlusTree::InsertInternalNode(CInternalNode* pNode, KEY_TYPE key, CNode* pRightSon) { if (NULL == pNode || NODE_TYPE_LEAF ==pNode->GetType()) { return false; } // 结点未满,直接插入 if (pNode->GetCount() < MAXNUM_KEY) { return pNode->Insert(key, pRightSon); } CInternalNode* pBrother = new CInternalNode; //C++中new 类名表示分配一个类需要的内存空间,并返回其首地址; KEY_TYPE NewKey = INVALID; // 分裂本结点 NewKey = pNode->Split(pBrother, key); if (pNode->GetCount() < pBrother->GetCount()) { pNode->Insert(key, pRightSon); } else if (pNode->GetCount() > pBrother->GetCount()) { pBrother->Insert(key, pRightSon); } else // 两者相等,即键值在第V和V+1个键值中间的情况,把字节点挂到新结点的第一个指针上 { pBrother->SetPointer(1,pRightSon); pRightSon->SetFather(pBrother); } CInternalNode* pFather = (CInternalNode*)(pNode->GetFather()); // 直到根结点都满了,新生成根结点 if (NULL == pFather) { pFather = new CInternalNode; pFather->SetPointer(1, pNode); // 指针1指向原结点 pFather->SetElement(1, NewKey); // 设置键 pFather->SetPointer(2, pBrother); // 指针2指向新结点 pNode->SetFather(pFather); // 指定父结点 pBrother->SetFather(pFather); // 指定父结点 pFather->SetCount(1); SetRoot(pFather); // 指定新的根结点 return true; } // 递归 return InsertInternalNode(pFather, NewKey, pBrother); } // 递归函数:在中间结点中删除键 bool BPlusTree::DeleteInternalNode(CInternalNode* pNode, KEY_TYPE key) { // 删除键,如果失败一定是没有找到,直接返回失败 bool success = pNode->Delete(key); if (false == success) { return false; } // 获取父结点 CInternalNode* pFather = (CInternalNode*)(pNode->GetFather()); if (NULL == pFather) { // 如果一个数据都没有了,把根结点的第一个结点作为根结点 if (0 == pNode->GetCount()) { SetRoot(pNode->GetPointer(1)); delete pNode; } return true; } // 删除后结点填充度仍>=50% if (pNode->GetCount() >= ORDER_V) { for (int i = 1; (key >= pFather->GetElement(i)) && (i <= pFather->GetCount()); i++) { // 如果删除的是父结点的键值,需要更改该键 if (pFather->GetElement(i) == key) { pFather->SetElement(i, pNode->GetElement(1)); // 更改为叶子结点新的第一个元素 } } return true; } //找到一个最近的兄弟结点(根据B+树的定义,除了根结点,总是能找到的) int flag = FLAG_LEFT; CInternalNode* pBrother = (CInternalNode*)(pNode->GetBrother(flag)); // 兄弟结点填充度>50% KEY_TYPE NewData = INVALID; if (pBrother->GetCount() > ORDER_V) { pNode->MoveOneElement(pBrother); // 修改父结点的键值 if (FLAG_LEFT == flag) { for (int i = 1; i <= pFather->GetCount() + 1; i++) { if (pFather->GetPointer(i) == pNode && i > 1) { pFather->SetElement(i - 1 , pNode->GetElement(1)); // 更改本结点对应的键 } } } else { for (int i = 1; i <= pFather->GetCount() + 1; i++) { if (pFather->GetPointer(i) == pNode && i > 1) { pFather->SetElement(i - 1, pNode->GetElement(1)); // 更改本结点对应的键 } if (pFather->GetPointer(i) == pBrother && i > 1) { pFather->SetElement(i - 1 , pBrother->GetElement(1)); // 更改兄弟结点对应的键 } } } return true; } // 父结点中要删除的键:兄弟结点都不大于50,则需要合并结点,此时父结点需要删除键 KEY_TYPE NewKey = NULL; // 把本结点与兄弟结点合并,无论如何合并到数据较小的结点,这样父结点就无需修改指针 if (FLAG_LEFT == flag) { (void)pBrother->Combine(pNode); NewKey = pNode->GetElement(1); delete pNode; } else { (void)pNode->Combine(pBrother); NewKey = pBrother->GetElement(1); delete pBrother; } // 递归 return DeleteInternalNode(pFather, NewKey); }
---------------------------------------
-Demo.cpp
#include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> #include "BPlusTree.h" // 随机建立一棵树 void Test1(BPlusTree* pTree, int count) { pTree->ClearTree(); //srand( (unsigned)time( NULL ) );//这是一个种子,如果不要随机功能,请把此句话注释掉 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { int x = rand()%999 + 1; (void)pTree->Insert(x); } printf("successed!\n"); } // 在树中查找某数据 void Test2(BPlusTree* pTree, int data) { char sPath[255] = {0, }; (void)pTree->Search(data, sPath); printf("\n%s", sPath); } // 在树中插入某数据 void Test3(BPlusTree* pTree, int data) { bool success = pTree->Insert(data); if (true == success) { printf("\nsuccessed!\n"); } else { printf("\nfailed!\n"); } } // 在树中删除某数据 void Test4(BPlusTree* pTree, int data) { bool success = pTree->Delete(data); if (true == success) { printf("\nsuccessed!\n"); } else { printf("\nfailed!\n"); } } // 对树进行旋转 BPlusTree* Test5(BPlusTree* pTree) { BPlusTree* pNewTree = pTree->RotateTree(); delete pTree; printf("\nsuccessed!\n"); return pNewTree; } // 打印 void Test6(BPlusTree* pTree) { pTree->PrintTree(); } // 对树进行检查 void Test7(BPlusTree* pTree) { bool success = pTree->CheckTree(); if (true == success) { printf("\nsuccessed!\n"); } else { printf("\nfailed!\n"); } } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { BPlusTree* pTree = new BPlusTree; int x = 1; int y = 0; while (0 != x) { printf("\n\n"); printf(" *******************************************************************\n"); printf(" * 欢迎进入B+树演示程序,请选择相应功能。 *\n"); printf(" * 1。随机建立一棵B+树; *\n"); printf(" * 2。在B+树中查找一个数; *\n"); printf(" * 3。在B+树中插入一个数; *\n"); printf(" * 4。在B+树中删除一个数; *\n"); printf(" * 5。对B+树旋转,进行重新平衡; *\n"); printf(" * 6。显示整个B+树; *\n"); printf(" * 7。检查整个B+树; *\n"); printf(" * 0。退出程序; *\n"); printf(" *******************************************************************\n"); printf("\n 您的选择是:"); scanf("%d", &x); switch (x) { case 1: printf("请输入数据个数(10-150):"); scanf("%d", &y); Test1(pTree, y); break; case 2: printf("请输入要查找的数值:"); scanf("%d", &y); Test2(pTree, y); break; case 3: printf("请输入要插入的数值:"); scanf("%d", &y); Test3(pTree, y); break; case 4: printf("请输入要删除的数值:"); scanf("%d", &y); Test4(pTree, y); break; case 5: pTree = Test5(pTree); break; case 6: Test6(pTree); break; case 7: Test7(pTree); break; case 0: delete pTree; return 0; break; default: break; } } delete pTree; return 0; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号