动手动脑-完成课件中的动手动脑的或需要验证的相关内容
1、运行 TestInherits.java 示例,观察输出,注意总结父类与子类之间构造方法的调用关系修改Parent构造方法的代码,显式调用GrandParent的另一个构造函数,注意这句调用代码是否是第一句。
运行结果: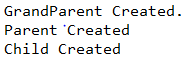
结论:通过 super 调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中的第一个语句。
2、参看ExplorationJDKSource.java示例,此示例中定义了一个类A,它没有任何成员:class A { }示例直接输出这个类所创建的对象 public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(new A());}结果截图:
结果截图:
结果分析:此程序内部调用了String类的valueOf()方法而valueOf方法内部又调用Object.toString方法:public String toString(){return getClass().getName()+”@”+Integer.toHexString(hashCode());}hashCode方法是本地方法,由JVM设计者实现:public native int hashCode()
3、看一段代码,分析运行结果:
代码:
public class Fruit
{
public String toString()
{
return "Fruit toString.";
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Fruit f=new Fruit();
System.out.println("f="+f);
System.out.println("f="+f.toString());
}
}
运行结果:
结果分析:在“+”运算中,当任何一个对象与一个String对象,连接时,会隐式地调用其toString()方法,默认情况下,此方法返回“类名 @ + hashCode”。为了返回有意义的信息,子类可以重写toString()方法。
4、请自行编写代码测试以下特性(动手动脑):在子类中,若要调用父类中被覆盖的方法,可以使用super关键字。源代码:
public class GrandParent
{
public GrandParent()
{
System.out.println("Grandparent Created.");
}
public GrandParent(String string)
{
System.out.println("Grandparent Created.String:"+string);
}
}
class Parent extends GrandParent{
public Parent()
{
super("20163513");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public Child()
{
System.out.println("Child Creatd");
}
}
class AAA{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Child c=new Child();
}
}
5、现在有三个类:class Mammal{}class Dog extends Mammal {}class Cat extends Mammal{}针对每个类定义三个变量并进行初始化 Mammal m=null ; Dog d=new Dog(); Cat c=new Cat();下列语句哪一个将引起编译错误?为什么?哪一个会引起运行时错误?为什么? m=d; d=m; d=(Dog)m; d=c; c=(Cat)m;先进行自我判断,得出结论后,运行TestCast.java实例代码,看看你的判断是否正确。源程序代码:
class Mammal{}
class Dog extends Mammal {}
class Cat extends Mammal{}
public class TestCast
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Mammal m;
Dog d=new Dog();
Cat c=new Cat();
m=d;
//d=m;
d=(Dog)m;
//d=c;
c=(Cat)m;
}
}
运行错误分析:
d=m显示错误:类型不匹配:不能从mammal转换为dog
d=c显示错误:类型不匹配:不能从cat转换为dog
6、请使用javap查看编译器为TestPolymorphism.java生成的字节码指令,然后通过互联网搜索资料,尝试从底层开始理解Java编译器是如何为多态代码生成字节码指令,在程序运行过程中,多态特性又是如何实现的。
class Parent
{
public int value=100;
public void Introduce()
{
System.out.println("I'm father.");
}
}
class Son extends Parent
{
public int value=101;
public void Introduce()
{
System.out.println("I'm son.");
}
}
class Daughter extends Parent
{
public int value=102;
public void Introduce()
{
System.out.println("I'm daughter.");
}
}
public class A {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Parent p=new Parent();
p.Introduce();
System.out.println(p.value);
p=new Son();
p.Introduce();
System.out.println(p.value);
p=new Daughter();
p.Introduce();
System.out.println(p.value);
}
}
多态依赖于类型和实现的分离,多用来把接口和实现分离。
7、运行以下测试代码,回答问题
public class ParentChildTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent=new Parent();
parent.printValue();
Child child=new Child();
child.printValue();
parent=child;
parent.printValue();
parent.myValue++;
parent.printValue();
((Child)parent).myValue++;
parent.printValue();
}
}
class Parent{
public int myValue=100;
public void printValue()
{
System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public int myValue=200;
public void printValue()
{
System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
①左边的程序运行结果是什么

②.你如何解释会得到这样的输出?
a.创建父类对象parent,parent调用父类printValue方法,输出100。
b.创建子类对象child,child调用子类printValue方法,输出200。
c.把子类对象赋值给父类对象,赋值后的parent.printValue();相当于child.printValue();所以输出200。
d.被赋值后的父类对象对数据成员的操作依然是对父类的数据成员进行操作,并没有对子类数据成员进行操作,只是将父类的myValue值+1,而子类的myValue值并没有改变,所以 parent.printValue();输出200。
e.使用了强制类型转换,结果是对子类的myValue+1,而parent已经被子类对象赋值,所以输出201。
③计算机是不会出错的,之所以得到这样的运行结果也是有原因的,那么从这些运行结果中,你能总结出Java的哪些语法特性?
当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。
如果子类与父类有相同的字段,则子类中的字段会代替或隐藏父类的字段,子类方法中访问的是子类中的字段(而不是父类中的字段)。如果子类方法确实想访问父类中被隐藏的同名字段,可以用super关键字来访问它。如果子类被当作父类使用,则通过子类访问的字段是父类的!




