libtorch 常用api函数示例(史上最全、最详细)
pytorch/libtorch qq群2群:302984355
pytorch/libtorch qq群: 1041467052(一群满了)
其实pytorch的函数libtorch都有,只是写法上有些出入。
libtorch的官方文档链接
class tensor
只是官方文档只是类似与函数申明,没有告诉干嘛的,只能通过函数名字猜了。比如我要一个一个函数和已知的一个torch::Tensor变量形状一样,只是填充指定的数值,我记得在哪里看到过的有个full开头的函数,然后我就搜素full,然后找到一个函数full_like好像是我需要的。(见0)
- pytorch/libtorch qq群2群:302984355
- 调试技巧:
- CMakeLists.txt
- 0.torch::full_like
- 1.创建与初始化tensor 1.1 torch::rand 1.2 torch::empty 1.3 torch::ones 1.4 torch::Tensor keep = torch::zeros({scores.size(0)}).to(torch::kLong).to(scores.device()); 1.5 torch::Tensor num_out = torch::full({ 2,3 }, -2, torch::dtype(torch::kLong));torch::full创建tensor指定形 1.6 torch::Tensor a = torch::ones({3,2}).fill_(-8).to(torch::kCUDA); 1.7. torch::full_like(见0)创建一个和已知tensor形状一样的 状并填充指定val的
- 2.拼接tensor torch::cat 以及vector 和cat的融合操作
- 3.torch的切片操作 【select(浅拷贝)】【index_select 深拷贝)】【index 深拷贝】【slice 浅拷贝】 narrow,narrow_copy
- 4.squeeze() unsqueeze()
- 5.torch::nonzero 输出非0的坐标
- 6.访问tensor值 a.item
()就把1*1 的 tensor的a转为float - 7.opencv Mat类型转tensor 或者其他的vector或者数组数据转tensor
- 8.tensor 的size sizes() numel()
- 9.torch::sort
- 10.clamp 把数值控制在min max之间,小于min的就为min,大于max的就为max
- 11.大于> 小于< 运算
- 12.转置Tensor::transpose
- 13.expand_as
- 14.乘 mul_ 除div 减sub_
- 15.加载模型
- 16.模型forward出来的结果
- 17.resize_ zero_
- 18.meshgrid 把tens变成方阵
- 19.flatten 展平tensor
- 20.fill_ tensor填充某个值 就地操作,填充当前tensor
- 21.torch::stack
- 22.reshape
- 23. view
- 24.argmax argmin
- 25.where
- 26.accessor
- 27. torch::max torch::min 同max
- 28.masked_select 与 masked_fill
- 29.libtorch综合操作1
- 30.pytorch nms <---------> libtorch nms
- 31.数据类型很重要! .to(torch::kByte);
- 32.指针访问Tensor数据
- 33 PyTorch内Tensor按索引赋值的方法比较
- 44 输出多个tensor(pytorch端)以及取出多个tensor(libtorch端)
- 45. torch::Tensor作为函数参数,不管是引用还是不引用,函数内部对形参操作都会影响本来的tensor,即都是引用
- 46. 实现pytorch下标神操作
- 47.pytorch libtorch的tensor验证精度
- 48. 其他--颜色映射
- 49.torch.gather
- 50. torch::argsort(libtorch1.0没有这个函数) torch::sort
- 51. 判断tensor是否为空 ind_mask.sizes().empty()
- 52.pytorch代码 out = aim[ind_mask],用libtorch写出来。
- 53. pytorch代码a4 = arr[...,3,0] 用libtorch如何表达出来 masked_select运用!
- 54.再次强调一下类型很重要!!有时候需要强制写下 kernel = kernel.toType(torch::kByte);
- 小弟不才,同时谢谢友情赞助!
调试技巧:
torch::Tensor box_1 = torch::rand({5,4});
std::cout<<box_1<<std::endl; //可以打印出数值
box_1.print();//可以打印形状
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0 FATAL_ERROR)
project(main)
SET(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Debug")
set(CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH "/data_2/everyday/0429/pytorch/torch")
find_package(Torch REQUIRED)
set(CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH "/home/yhl/software_install/opencv3.2")
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
add_executable(main main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(main "${TORCH_LIBRARIES}")
target_link_libraries(main ${OpenCV_LIBS})
set_property(TARGET main PROPERTY CXX_STANDARD 11)
CMakeLists.txt 样例2,不用find_package自动找库,手动设定库路径:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.6)
project(libtorch_lstm_1.1.0)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug CACHE STRING "set build type to debug")
#add_definitions(-std=c++11)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)
option(CUDA_USE_STATIC_CUDA_RUNTIME OFF)
#set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug)
# cuda10.0
include_directories(${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/3rdparty/cuda/include)
link_directories(${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/3rdparty/cuda/lib64)
###libtorch1.1.0
set(TORCH_ROOT ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/3rdparty/libtorch)
set(CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/3rdparty/libtorch)
include_directories(${TORCH_ROOT}/include)
include_directories(${TORCH_ROOT}/include/torch/csrc/api/include)
link_directories(${TORCH_ROOT}/lib)
#OpenCv3.4.10
set(OPENCV_ROOT ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/3rdparty/opencv-3.4.10)
include_directories(${OPENCV_ROOT}/include)
link_directories(${OPENCV_ROOT}/lib)
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=c++11 -Wall -Ofast -Wfatal-errors -D_MWAITXINTRIN_H_INCLUDED")
add_executable(libtorch_lstm ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/lstm.cpp)
target_link_libraries(libtorch_lstm opencv_calib3d opencv_core opencv_imgproc opencv_highgui opencv_imgcodecs)
target_link_libraries(libtorch_lstm torch c10 caffe2)
target_link_libraries(libtorch_lstm nvrtc cuda)
#target_link_libraries(crnn c10 c10_cuda torch torch_cuda torch_cpu "-Wl,--no-as-needed -ltorch_cuda")
add_definitions(-O2 -pthread)
0.torch::full_like
static Tensor at::full_like(const Tensor &self, Scalar fill_value, const TensorOptions &options = {}, c10::optional
然后就自己试:
#include <iostream>
#include "torch/script.h"
#include "torch/torch.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
torch::Tensor tmp_1 = torch::rand({2,3});
torch::Tensor tmp_2 = torch::full_like(tmp_1,1);
cout<<tmp_1<<endl;
cout<<tmp_2<<endl;
}
打印的结果如下:
0.8465 0.5771 0.4404
0.9805 0.8665 0.7807
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
1 1 1
1 1 1
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
1.创建与初始化tensor 1.1 torch::rand 1.2 torch::empty 1.3 torch::ones 1.4 torch::Tensor keep = torch::zeros({scores.size(0)}).to(torch::kLong).to(scores.device()); 1.5 torch::Tensor num_out = torch::full({ 2,3 }, -2, torch::dtype(torch::kLong));torch::full创建tensor指定形 1.6 torch::Tensor a = torch::ones({3,2}).fill_(-8).to(torch::kCUDA); 1.7. torch::full_like(见0)创建一个和已知tensor形状一样的 状并填充指定val的
1.1 torch::rand
torch::Tensor input = torch::rand({ 1,3,2,3 });
(1,1,.,.) =
0.5943 0.4822 0.6663
0.7099 0.0374 0.9833
(1,2,.,.) =
0.4384 0.4567 0.2143
0.3967 0.4999 0.9196
(1,3,.,.) =
0.2467 0.5066 0.8654
0.7873 0.4758 0.3718
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{1,3,2,3} ]
1.2 torch::empty
torch::Tensor a = torch::empty({2, 4});
std::cout << a << std::endl;
7.0374e+22 5.7886e+22 6.7120e+22 6.7331e+22
6.7120e+22 1.8515e+28 7.3867e+20 9.2358e-01
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,4} ]
1.3 torch::ones
torch::Tensor a = torch::ones({2, 4});
std::cout << a<< std::endl;
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,4} ]
1.4 torch::zeros
torch::Tensor scores;
torch::Tensor keep = torch::zeros({scores.size(0)}).to(torch::kLong).to(scores.device());
1.5 torch::full
inline at::Tensor full(at::IntArrayRef size, at::Scalar fill_value, c10::optional
inline at::Tensor full(at::IntArrayRef size, at::Scalar fill_value, const at::TensorOptions & options = {})
torch::Tensor num_out = torch::full({ 2,3 }, -2, torch::dtype(torch::kLong));
std::cout<<num_out<<std::endl;
1.6 torch::Tensor a = torch::ones({3,2}).fill_(-8).to(torch::kCUDA);
torch::Tensor a = torch::ones({3,2}).fill_(-8).to(torch::kCUDA);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
-8 -8
-8 -8
-8 -8
[ Variable[CUDAFloatType]{3,2} ]
2.拼接tensor torch::cat 以及vector 和cat的融合操作
2.1 按列拼接
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
torch::Tensor b = torch::rand({2,1});
torch::Tensor cat_1 = torch::cat({a,b},1);//按列拼接--》》前提是行数需要一样
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
std::cout<<cat_1<<std::endl;
0.3551 0.7215 0.3603
0.1188 0.4577 0.2201
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0.5876
0.3040
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,1} ]
0.3551 0.7215 0.3603 0.5876
0.1188 0.4577 0.2201 0.3040
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,4} ]
注意:如果行数不一样会报如下错误
terminate called after throwing an instance of 'std::runtime_error'
what(): invalid argument 0: Sizes of tensors must match except in dimension 1. Got 2 and 4 in dimension 0 at /data_2/everyday/0429/pytorch/aten/src/TH/generic/THTensor.cpp:689
2.2 按行拼接
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
torch::Tensor b = torch::rand({1,3});
torch::Tensor cat_1 = torch::cat({a,b},0);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
std::cout<<cat_1<<std::endl;
0.0004 0.7852 0.4586
0.1612 0.6524 0.7655
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0.5999 0.5445 0.2152
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{1,3} ]
0.0004 0.7852 0.4586
0.1612 0.6524 0.7655
0.5999 0.5445 0.2152
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{3,3} ]
2.3 其他例子
torch::Tensor box_1 = torch::rand({5,4});
torch::Tensor score_1 = torch::rand({5,1});
torch::Tensor label_1 = torch::rand({5,1});
torch::Tensor result_1 = torch::cat({box_1,score_1,label_1},1);
result_1.print();
[Variable[CPUFloatType] [5, 6]]
2.4 vector 和cat的融合操作
torch::Tensor xs_t0 = xs - wh_0 / 2;
torch::Tensor ys_t0 = ys - wh_1 / 2;
torch::Tensor xs_t1 = xs + wh_0 / 2;
torch::Tensor ys_t1 = ys + wh_1 / 2;
xs_t0.print();
ys_t0.print();
xs_t1.print();
ys_t1.print();
vector<torch::Tensor> abce = {xs_t0,ys_t0,xs_t1,ys_t1};
torch::Tensor bboxes = torch::cat(abce,2);
std::cout<<"-----cat shape---"<<std::endl;
bboxes.print();
while(1);
打印如下:
[Variable[CUDAType] [1, 100, 1]]
[Variable[CUDAType] [1, 100, 1]]
[Variable[CUDAType] [1, 100, 1]]
[Variable[CUDAType] [1, 100, 1]]
[Variable[CUDAType] [1, 100, 4]]
-----cat shape---
也可以一句话搞定:
torch::Tensor bboxes = torch::cat({xs_t0,ys_t0,xs_t1,ys_t1},2);
3.torch的切片操作 【select(浅拷贝)】【index_select 深拷贝)】【index 深拷贝】【slice 浅拷贝】 narrow,narrow_copy
select【浅拷贝】只能指定取某一行或某一列
index【深拷贝】只能指定取某一行
index_select【深拷贝】可以按行或按列,指定多行或多列
slice【浅拷贝】 连续的行或列
narrow,narrow_copy
当是浅拷贝,又不想影响之前的结果的时候,可以加个clone(),比如:
torch::Tensor x1 = boxes.select(1,0).clone();
3.1 inline Tensor Tensor::select(int64_t dim, int64_t index) ;好像只能整2维的。第一个参数是维度,0是取行,1是取 列,第二个参数是索引的序号
3.1.1 select//按行取
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor b = a.select(0,1);//按行取
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
0.6201 0.7021 0.1975
0.3080 0.6304 0.1558
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0.3080
0.6304
0.1558
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{3} ]
3.1.2 select//按列取
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor b = a.select(1,1);
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
0.8295 0.9871 0.1287
0.8466 0.7719 0.2354
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0.9871
0.7719
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2} ]
注意:这里是浅拷贝,就是改变b,同时a的值也会同样的改变
3.1.3 select浅拷贝
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor b = a.select(1,1);
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
b[0] = 0.0;
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
0.0938 0.2861 0.0089
0.3481 0.5806 0.3711
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0.2861
0.5806
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2} ]
0.0938 0.0000 0.0089
0.3481 0.5806 0.3711
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0.0000
0.5806
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2} ]
可以看到,b[0] = 0.0;然后a,b的对应位置都为0了。浅拷贝!!
3.2 inline Tensor Tensor::index_select(Dimname dim, const Tensor & index) //同样的,dim0表示按行,1表示按列 index表示取的行号或者列号,这里
比较奇怪,index一定要是toType(torch::kLong)这种类型的。还有一个奇怪的地方是我准备用数组导入tensor的,发现idx全是0,原因未知
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,6});
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
slice
torch::Tensor idx = torch::empty({4}).toType(torch::kLong);
idx[0]=0;
idx[1]=2;
idx[2]=4;
idx[3]=1;
// int idx_data[4] = {1,3,2,4};
// torch::Tensor idx = torch::from_blob(idx_data,{4}).toType(torch::kLong);//idx全是0 ?????????????????
std::cout<<idx<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor b = a.index_select(1,idx);
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
0.4956 0.5028 0.0863 0.9464 0.6714 0.5348
0.3523 0.2245 0.0924 0.7088 0.6913 0.2237
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,6} ]
0
2
4
1
[ Variable[CPULongType]{4} ]
0.4956 0.0863 0.6714 0.5028
0.3523 0.0924 0.6913 0.2245
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,4} ]
3.2.2 index_select深拷贝
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,6});
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor idx = torch::empty({4}).toType(torch::kLong);
idx[0]=0;
idx[1]=2;
idx[2]=4;
idx[3]=1;
// int idx_data[4] = {1,3,2,4};
// torch::Tensor idx = torch::from_blob(idx_data,{4}).toType(torch::kLong);
std::cout<<idx<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor b = a.index_select(1,idx);
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
b[0][0]=0.0;
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
0.6118 0.6078 0.5052 0.9489 0.6201 0.8975
0.0901 0.2040 0.1452 0.6452 0.9593 0.7454
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,6} ]
0
2
4
1
[ Variable[CPULongType]{4} ]
0.6118 0.5052 0.6201 0.6078
0.0901 0.1452 0.9593 0.2040
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,4} ]
0.6118 0.6078 0.5052 0.9489 0.6201 0.8975
0.0901 0.2040 0.1452 0.6452 0.9593 0.7454
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,6} ]
0.0000 0.5052 0.6201 0.6078
0.0901 0.1452 0.9593 0.2040
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,4} ]
3.3 index inline Tensor Tensor::index(TensorList indices)
这个函数实验下来,只能按行取,且是深拷贝
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,6});
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor idx_1 = torch::empty({2}).toType(torch::kLong);
idx_1[0]=0;
idx_1[1]=1;
torch::Tensor bb = a.index(idx_1);
bb[0][0]=0;
std::cout<<bb<<std::endl;
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
0.1349 0.8087 0.2659 0.3364 0.0202 0.4498
0.4785 0.4274 0.9348 0.0437 0.6732 0.3174
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,6} ]
0.0000 0.8087 0.2659 0.3364 0.0202 0.4498
0.4785 0.4274 0.9348 0.0437 0.6732 0.3174
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,6} ]
0.1349 0.8087 0.2659 0.3364 0.0202 0.4498
0.4785 0.4274 0.9348 0.0437 0.6732 0.3174
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,6} ]
3.4 slice inline Tensor Tensor::slice(int64_t dim, int64_t start, int64_t end, int64_t step) //dim0表示按行取,1表示按列取,从start开始,到end(不含)结束
可以看到结果,是浅拷贝!!!
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,6});
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor b = a.slice(0,0,1);
torch::Tensor c = a.slice(1,0,3);
b[0][0]=0.0;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
std::cout<<c<<std::endl;
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
0.8270 0.7952 0.3743 0.7992 0.9093 0.5945
0.3764 0.8419 0.7977 0.4150 0.8531 0.9207
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,6} ]
0.0000 0.7952 0.3743 0.7992 0.9093 0.5945
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{1,6} ]
0.0000 0.7952 0.3743
0.3764 0.8419 0.7977
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0.0000 0.7952 0.3743 0.7992 0.9093 0.5945
0.3764 0.8419 0.7977 0.4150 0.8531 0.9207
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,6} ]
3.5 narrow narrow_copy
inline Tensor Tensor::narrow(int64_t dim, int64_t start, int64_t length) const
inline Tensor Tensor::narrow_copy(int64_t dim, int64_t start, int64_t length) const
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({4,6});
torch::Tensor b = a.narrow(0,1,2);
torch::Tensor c = a.narrow_copy(0,1,2);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
std::cout<<c<<std::endl;
0.9812 0.4205 0.4169 0.2412 0.8769 0.9873
0.8052 0.0312 0.9901 0.5065 0.6344 0.3408
0.0182 0.6933 0.9375 0.8675 0.5201 0.9521
0.5119 0.3880 0.1117 0.5413 0.8203 0.4163
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{4,6} ]
0.8052 0.0312 0.9901 0.5065 0.6344 0.3408
0.0182 0.6933 0.9375 0.8675 0.5201 0.9521
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,6} ]
0.8052 0.0312 0.9901 0.5065 0.6344 0.3408
0.0182 0.6933 0.9375 0.8675 0.5201 0.9521
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,6} ]
4.squeeze() unsqueeze()
inline Tensor Tensor::squeeze() const//不加参数的,把所有为1的维度都压缩
inline Tensor Tensor::squeeze(int64_t dim)const//加参数的,指定哪个维度压缩
inline Tensor & Tensor::squeeze_() const //暂时不知道啥区别
inline Tensor & Tensor::squeeze_(int64_t dim) const //暂时不知道啥区别
4.1 squeeze()
(1,.,.) =
0.5516 0.6561 0.3603
0.7555 0.1048 0.2016
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{1,2,3} ]
0.5516 0.6561 0.3603
0.7555 0.1048 0.2016
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
(1,.,.) =
0.7675 0.5439 0.5162
(2,.,.) =
0.6103 0.1925 0.1222
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,1,3} ]
0.7675 0.5439 0.5162
0.6103 0.1925 0.1222
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
(1,1,.,.) =
0.9875
0.1980
(2,1,.,.) =
0.6973
0.3272
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,1,2,1} ]
0.9875 0.1980
0.6973 0.3272
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,2} ]
4.2 squeeze(int64_t dim) 指定压缩哪个维度
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({1,1,3});
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor b = a.squeeze();
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor c = a.squeeze(0);
std::cout<<c<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor d = a.squeeze(1);
std::cout<<d<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor e = a.squeeze(2);
std::cout<<e<<std::endl;
(1,.,.) =
0.8065 0.1287 0.8073
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{1,1,3} ]
0.8065
0.1287
0.8073
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{3} ]
0.8065 0.1287 0.8073
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{1,3} ]
0.8065 0.1287 0.8073
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{1,3} ]
(1,.,.) =
0.8065 0.1287 0.8073
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{1,1,3} ]
4.3. unsqueeze
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor b = a.unsqueeze(0);
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor bb = a.unsqueeze(1);
std::cout<<bb<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor bbb = a.unsqueeze(2);
std::cout<<bbb<<std::endl;
0.7945 0.0331 0.1666
0.7821 0.3359 0.0663
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
(1,.,.) =
0.7945 0.0331 0.1666
0.7821 0.3359 0.0663
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{1,2,3} ]
(1,.,.) =
0.7945 0.0331 0.1666
(2,.,.) =
0.7821 0.3359 0.0663
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,1,3} ]
(1,.,.) =
0.7945
0.0331
0.1666
(2,.,.) =
0.7821
0.3359
0.0663
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3,1} ]
5.torch::nonzero 输出非0的坐标
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
a[0][1] = 0;
a[1][2] = 0;
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor b = torch::nonzero(a);
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
0.4671 0.0000 0.3360
0.9320 0.9246 0.0000
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0 0
0 2
1 0
1 1
[ Variable[CPULongType]{4,2} ]
6.访问tensor值 a.item()就把1*1 的 tensor的a转为float
取出tensor的某个值 为int或者float ===》》》auto bbb = a[1][1].item().toFloat();
一般情况下取出tensor某个值可以直接下标索引即可。比如a[0][1],但是这个值还是tensor类型的,要想为c++的int或者float的,如下:
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
auto bbb = a[1][1].item().toFloat();
std::cout<<bbb<<std::endl;
0.7303 0.6608 0.0024
0.5917 0.0145 0.6472
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0.014509
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{} ]
0.014509
另外的例子:
torch::Tensor scores = torch::rand({10});
std::tuple<torch::Tensor,torch::Tensor> sort_ret = torch::sort(scores.unsqueeze(1), 0, 1);
torch::Tensor v = std::get<0>(sort_ret).squeeze(1).to(scores.device());
torch::Tensor idx = std::get<1>(sort_ret).squeeze(1).to(scores.device());
std::cout<<scores<<std::endl;
std::cout<<v<<std::endl;
std::cout<<idx<<std::endl;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
int idx_1 = idx[i].item<int>();
float s = v[i].item<float>();
std::cout<<idx_1<<" "<<s<<std::endl;
}
0.1125
0.9524
0.7033
0.3204
0.7907
0.8486
0.7783
0.3215
0.0378
0.7512
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{10} ]
0.9524
0.8486
0.7907
0.7783
0.7512
0.7033
0.3215
0.3204
0.1125
0.0378
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{10} ]
1
5
4
6
9
2
7
3
0
8
[ Variable[CPULongType]{10} ]
1 0.952351
5 0.848641
4 0.790685
6 0.778329
9 0.751163
2 0.703278
7 0.32146
3 0.320435
0 0.112517
8 0.0378203
7.opencv Mat类型转tensor 或者其他的vector或者数组数据转tensor
7.1
Mat m_out = imread(path);
//[320,320,3]
input_tensor = torch::from_blob(
m_out.data, {m_SIZE_IMAGE, m_SIZE_IMAGE, 3}).toType(torch::kFloat32);//torch::kByte //大坑
//[3,320,320]
input_tensor = input_tensor.permute({2,0,1});
input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0);
input_tensor = input_tensor.to(torch::kFloat).to(m_device);
这里需要注意,因为上面图片被我预处理减均值过的,导致m_out像素值有负数,如果torch::kByte这种格式,会把负数变成正数,所以需要torch::kFloat32类型的。
permute({2,0,1});
之前是opencv Mat是
0 1 2
[320,320,3]
经过了permute({2,0,1}),表示把对应位置换一下,就变成了[3,320,320]
7.2
std::vector<float> region_priors;
//region_priors.push_back(num) region_priors的size是6375 × 4
torch::Tensor m_prior = torch::from_blob(region_priors.data(),{6375,4}).cuda();
8.tensor 的size sizes() numel()
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
auto aa = a.size(0);
auto bb = a.size(1);
auto a_size = a.sizes();
std::cout<<aa<<std::endl;
std::cout<<bb<<std::endl;
std::cout<<a_size<<std::endl;
int num_ = a.numel();
std::cout<<num_<<std::endl;
0.6522 0.0480 0.0009
0.1185 0.4639 0.0386
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
2
3
[2, 3]
6
8.2
有个问题就是当torch::Tensor a;直接定义一个tensor的时候,再访问
torch::Tensor a;
auto a_size = a.sizes();
就会报错
terminate called after throwing an instance of 'c10::Error'
what(): sizes() called on undefined Tensor (sizes at /data_2/everyday/0429/pytorch/c10/core/UndefinedTensorImpl.cpp:12)
frame #0: c10::Error::Error(c10::SourceLocation, std::__cxx11::basic_string<char, std::char_traits
frame #1: c10::UndefinedTensorImpl::sizes() const + 0x258 (0x7f83b56362b8 in /data_2/everyday/0429/pytorch/torch/lib/libc10.so)
frame #2: at::Tensor::sizes() const + 0x27 (0x405fc9 in /data_2/everyday/0516/build-libtorch- syntax-unknown-Default/main)
frame #3: main + 0x30 (0x405d06 in /data_2/everyday/0516/build-libtorch- syntax-unknown-Default/main)
frame #4: __libc_start_main + 0xf0 (0x7f83b4d12830 in /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6)
frame #5: _start + 0x29 (0x405c09 in /data_2/everyday/0516/build-libtorch- syntax-unknown-Default/main)
程序异常结束。
用numel()就没有问题
torch::Tensor a;
int num_ = a.numel();
std::cout<<num_<<std::endl;
8.3 获取维度大小,比如[1,5,8,2],我需要得到维度4
auto aaa = img_poly.sizes();
int len_ = aaa.size();
9.torch::sort
static inline std::tuple<Tensor,Tensor> sort(const Tensor & self, Dimname dim, bool descending)
dim0表示按行,1表示按列
descending=false表示升序,true表示降序
返回的是元组,第一个表示排序后的值,第二个表示排序之后对应之前的索引。
torch::Tensor scores = torch::rand({10});
std::tuple<torch::Tensor,torch::Tensor> sort_ret = torch::sort(scores.unsqueeze(1), 0, 1);
torch::Tensor v = std::get<0>(sort_ret).squeeze(1).to(scores.device());
torch::Tensor idx = std::get<1>(sort_ret).squeeze(1).to(scores.device());
std::cout<<scores<<std::endl;
std::cout<<v<<std::endl;
std::cout<<idx<<std::endl;
0.8355
0.1386
0.7910
0.0988
0.2607
0.7810
0.7855
0.5529
0.5846
0.1403
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{10} ]
0.8355
0.7910
0.7855
0.7810
0.5846
0.5529
0.2607
0.1403
0.1386
0.0988
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{10} ]
0
2
6
5
8
7
4
9
1
3
[ Variable[CPULongType]{10} ]
10.clamp 把数值控制在min max之间,小于min的就为min,大于max的就为max
inline Tensor Tensor::clamp(c10::optional
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
a[0][0] = 20;
a[0][1] = 21;
a[0][2] = 22;
a[1][0] = 23;
a[1][1] = 24;
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor b = a.clamp(21,22);
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
20.0000 21.0000 22.0000
23.0000 24.0000 0.4792
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
21 21 22
22 22 21
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
在工程中,一般要取tensor里面的值,还有有时候就只限制一边,比如只限制min,如下:
xx1 = xx1.clamp(x1[i].item().toFloat(),INT_MAX*1.0);
11.大于> 小于< 运算
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor b = a > 0.5;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
0.3526 0.0321 0.7098
0.9794 0.6531 0.9410
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0 0 1
1 1 1
[ Variable[CPUBoolType]{2,3} ]
12.转置Tensor::transpose
inline Tensor Tensor::transpose(Dimname dim0, Dimname dim1) const
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor b = a.transpose(1,0);
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
0.4039 0.3568 0.9978
0.6895 0.7258 0.5576
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0.4039 0.6895
0.3568 0.7258
0.9978 0.5576
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{3,2} ]
13.expand_as
inline Tensor Tensor::expand_as(const Tensor & other) const
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});;
// torch::Tensor b = torch::ones({2,2});
torch::Tensor b = torch::ones({2,1});
torch::Tensor c = b.expand_as(a);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
std::cout<<c<<std::endl;
0.6063 0.4150 0.7665
0.8663 0.9563 0.7461
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
1
1
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,1} ]
1 1 1
1 1 1
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
注意维度有一定要求,我这么写torch::Tensor b = torch::ones({2,2});torch::Tensor b = torch::ones({2});都会报错:
terminate called after throwing an instance of 'c10::Error'
what(): The expanded size of the tensor (3) must match the existing size (2) at non-singleton dimension 1. Target sizes: [2, 3]. Tensor sizes: [2, 2] (inferExpandGeometry at /data_2/everyday/0429/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/ExpandUtils.cpp:76)
frame #0: c10::Error::Error(c10::SourceLocation, std::__cxx11::basic_string<char, std::char_traits
frame #1: at::inferExpandGeometry(c10::ArrayRef
frame #2: at::native::expand(at::Tensor const&, c10::ArrayRef
frame #3:
frame #4:
frame #5:
frame #6:
frame #7:
frame #8: at::native::expand_as(at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&) + 0x39 (0x7f6a4a1e4d49 in /data_2/everyday/0429/pytorch/torch/lib/libtorch.so)
frame #9:
frame #10:
frame #11:
frame #12: at::Tensor c10::KernelFunction::callUnboxed<at::Tensor, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&>(at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&) const + 0xb0 (0x433e06 in /data_2/everyday/0516/build-libtorch- syntax-unknown-Default/main)
frame #13: at::Tensor c10::impl::OperatorEntry::callUnboxed<at::Tensor, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&>(c10::TensorTypeId, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&) const::{lambda(c10::DispatchTable const&)#1}::operator()(c10::DispatchTable const&) const + 0x79 (0x432525 in /data_2/everyday/0516/build-libtorch- syntax-unknown-Default/main)
frame #14: std::result_of<at::Tensor c10::impl::OperatorEntry::callUnboxed<at::Tensor, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&>(c10::TensorTypeId, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&) const::{lambda(c10::DispatchTable const&)#1} (c10::DispatchTable const&)>::type c10::LeftRightc10::DispatchTable::read<at::Tensor c10::impl::OperatorEntry::callUnboxed<at::Tensor, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&>(c10::TensorTypeId, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&) const::{lambda(c10::DispatchTable const&)#1}>(at::Tensor c10::impl::OperatorEntry::callUnboxed<at::Tensor, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&>(c10::TensorTypeId, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&) const::{lambda(c10::DispatchTable const&)#1}&&) const + 0x11c (0x4340ba in /data_2/everyday/0516/build-libtorch- syntax-unknown-Default/main)
frame #15: at::Tensor c10::impl::OperatorEntry::callUnboxed<at::Tensor, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&>(c10::TensorTypeId, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&) const + 0x5f (0x4325a5 in /data_2/everyday/0516/build-libtorch- syntax-unknown-Default/main)
frame #16: at::Tensor c10::Dispatcher::callUnboxed<at::Tensor, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&>(c10::OperatorHandle const&, c10::TensorTypeId, at::Tensor const&, at::Tensor const&) const + 0x85 (0x42fd5d in /data_2/everyday/0516/build-libtorch- syntax-unknown-Default/main)
frame #17: at::Tensor::expand_as(at::Tensor const&) const + 0x1a5 (0x42ba47 in /data_2/everyday/0516/build-libtorch- syntax-unknown-Default/main)
frame #18: main + 0xbd (0x427c97 in /data_2/everyday/0516/build-libtorch- syntax-unknown-Default/main)
frame #19: __libc_start_main + 0xf0 (0x7f6a47ee8830 in /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6)
frame #20: _start + 0x29 (0x426999 in /data_2/everyday/0516/build-libtorch- syntax-unknown-Default/main)
14.乘 mul_ 除div 减sub_
boxes_my.select(1,0).mul_(width);
boxes_my.select(1,1).mul_(height);
boxes_my.select(1,2).mul_(width);
boxes_my.select(1,3).mul_(height);
prediction.select(2, 3).div(2);
input_tensor[0][0] = input_tensor[0][0].sub_(0.485).div_(0.229);
input_tensor[0][1] = input_tensor[0][1].sub_(0.456).div_(0.224);
input_tensor[0][2] = input_tensor[0][2].sub_(0.406).div_(0.225);
15.加载模型
torch::Device m_device(torch::kCUDA);
torch::jit::script::Module m_model = torch::jit::load(path_pt);
m_model.to(m_device);
m_model.eval();
16.模型forward出来的结果
当模型有几个东东输出来的时候
auto output = m_model.forward({input_tensor});
auto tpl = output.toTuple();
auto arm_loc = tpl->elements()[0].toTensor();
// arm_loc.print();
// std::cout<<arm_loc[0]<<std::endl;
auto arm_conf = tpl->elements()[1].toTensor();
//arm_conf.print();
auto odm_loc = tpl->elements()[2].toTensor();
//odm_loc.print();
// std::cout<<odm_loc[0]<<std::endl;
auto odm_conf = tpl->elements()[3].toTensor();
// odm_conf.print();
17.resize_ zero_
Tensor & resize_(IntArrayRef size) const;
Tensor & zero_() const;
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({1,3,2,2});
const int batch_size = a.size(0);
const int depth = a.size(1);
const int image_height = a.size(2);
const int image_width = a.size(3);
torch::Tensor crops = torch::rand({1,3,2,2});
// torch::Tensor crops;
crops.resize_({ batch_size, depth, image_height, image_width });
crops.zero_();
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<crops<<std::endl;
(1,1,.,.) =
0.7889 0.3291
0.2541 0.8283
(1,2,.,.) =
0.0209 0.1846
0.2528 0.2755
(1,3,.,.) =
0.0294 0.6623
0.2736 0.3376
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{1,3,2,2} ]
(1,1,.,.) =
0 0
0 0
(1,2,.,.) =
0 0
0 0
(1,3,.,.) =
0 0
0 0
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{1,3,2,2} ]
注意:这里如果只定义 torch::Tensor crops;//torch::Tensor crops = torch::rand({1,3,2,2});就会报错,感觉还是要先初始化一下才会分配内存,要不然就会报错!
terminate called after throwing an instance of '
c10::Error'
what(): There were no tensor arguments to this function (e.g., you passed an empty list of Tensors), but no fallback function is registered for schema aten::resize_. This usually means that this function requires a non-empty list of Tensors. Available functions are [CUDATensorId, QuantizedCPUTensorId, CPUTensorId, VariableTensorId] (lookup_ at /data_2/everyday/0429/pytorch/torch/include/ATen/core/dispatch/DispatchTable.h:243)
frame #0: c10::Error::Error(c10::SourceLocation, std::cxx11::basic_string<char, std::char_traits
frame #1: c10::KernelFunction const& c10::DispatchTable::lookup
frame #2: c10::DispatchTable::lookup(c10::TensorTypeId) const + 0x3a (0x42acf4 in /data_2/everyday/0516/build-libtorch- syntax-unknown-Default/main)
frame #3: at::Tensor& c10::impl::OperatorEntry::callUnboxedOnly<at::Tensor&, at::Tensor&, c10::ArrayRef
frame #4: std::result_of<at::Tensor& c10::impl::OperatorEntry::callUnboxedOnly<at::Tensor&, at::Tensor&, c10::ArrayRef
frame #5: at::Tensor& c10::impl::OperatorEntry::callUnboxedOnly<at::Tensor&, at::Tensor&, c10::ArrayRef
frame #6: at::Tensor& c10::Dispatcher::callUnboxedOnly<at::Tensor&, at::Tensor&, c10::ArrayRef
frame #7: at::Tensor::resize
frame #8: main + 0x134 (0x42798f in /data_2/everyday/0516/build-libtorch- syntax-unknown-Default/main)
frame #9: __libc_start_main + 0xf0 (0x7fa2f5618830 in /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6)
frame #10: _start + 0x29 (0x426719 in /data_2/everyday/0516/build-libtorch- syntax-unknown-Default/main)
18.meshgrid 把tens变成方阵
static inline std::vector
torch::Tensor scales = torch::ones({2});
torch::Tensor ratios = torch::ones({2});
ratios += 2;
std::cout<<scales<<std::endl;
std::cout<<ratios<<std::endl;
std::vector<torch::Tensor> mesh = torch::meshgrid({ scales, ratios });
torch::Tensor scales_1 = mesh[0];
torch::Tensor ratios_1 = mesh[1];
std::cout<<scales_1<<std::endl;
std::cout<<ratios_1<<std::endl;
1
1
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2} ]
3
3
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2} ]
1 1
1 1
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,2} ]
3 3
3 3
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,2} ]
19.flatten 展平tensor
Tensor flatten(int64_t start_dim=0, int64_t end_dim=-1) const;
Tensor flatten(int64_t start_dim, int64_t end_dim, Dimname out_dim) const;
Tensor flatten(Dimname start_dim, Dimname end_dim, Dimname out_dim) const;
Tensor flatten(DimnameList dims, Dimname out_dim) const;
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
torch::Tensor b = a.flatten();
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
0.9953 0.1461 0.0084
0.6169 0.4037 0.7685
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0.9953
0.1461
0.0084
0.6169
0.4037
0.7685
20.fill_ tensor填充某个值 就地操作,填充当前tensor
Tensor & fill_(Scalar value) const;
Tensor & fill_(const Tensor & value) const;
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
torch::Tensor b = a.fill_(4);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
4 4 4
4 4 4
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
4 4 4
4 4 4
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
21.torch::stack
static inline Tensor stack(TensorList tensors, int64_t dim)
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({3});
torch::Tensor b = torch::rand({3});
torch::Tensor c = torch::stack({a,b},1);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
std::cout<<c<<std::endl;
0.6776
0.5610
0.2835
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{3} ]
0.6846
0.3753
0.3873
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{3} ]
0.6776 0.6846
0.5610 0.3753
0.2835 0.3873
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{3,2} ]
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({3});
torch::Tensor b = torch::rand({3});
torch::Tensor c = torch::stack({a,b},0);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
std::cout<<c<<std::endl;
0.7129
0.1650
0.6764
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{3} ]
0.8035
0.1807
0.8100
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{3} ]
0.7129 0.1650 0.6764
0.8035 0.1807 0.8100
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
22.reshape
inline Tensor Tensor::reshape(IntArrayRef shape) const
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,4});
torch::Tensor b = a.reshape({-1,2});
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
0.3782 0.6390 0.6919 0.8298
0.3872 0.5923 0.4337 0.9634
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,4} ]
0.3782 0.6390
0.6919 0.8298
0.3872 0.5923
0.4337 0.9634
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{4,2} ]
23. view
inline Tensor Tensor::view(IntArrayRef size) const
需要先contiguous
a.contiguous().view({-1, 4});
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
torch::Tensor b = a.contiguous().view({ -1, 6 });
torch::Tensor c = a.contiguous().view({ 3, 2 });
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
std::cout<<c<<std::endl;
0.2069 0.8814 0.8506
0.6451 0.0107 0.7591
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0.2069 0.8814 0.8506 0.6451 0.0107 0.7591
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{1,6} ]
0.2069 0.8814
0.8506 0.6451
0.0107 0.7591
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{3,2} ]
注意这里和转置不一样
24.argmax argmin
static inline Tensor argmax(const Tensor & self, c10::optional<int64_t> dim=c10::nullopt, bool keepdim=false);
static inline Tensor argmin(const Tensor & self, c10::optional<int64_t> dim=c10::nullopt, bool keepdim=false);
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
auto b = torch::argmax(a, 0);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
0.9337 0.7443 0.1323
0.6514 0.5068 0.5052
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0
0
1
[ Variable[CPULongType]{3} ]
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
auto b = torch::argmax(a, 1);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
0.0062 0.3846 0.4844
0.9555 0.2844 0.4025
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
2
0
[ Variable[CPULongType]{2} ]
25.where
static inline Tensor where(const Tensor & condition, const Tensor & self, const Tensor & other);
static inline std::vector
torch::Tensor d = torch::where(a>0.5,b,c);
说明:在a大于0.5的位置设为pos,d的pos位置上用b的pos位置上面值填充,其余的位置上值是c的值
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
torch::Tensor b = torch::ones({2,3});
torch::Tensor c = torch::zeros({2,3});
torch::Tensor d = torch::where(a>0.5,b,c);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
std::cout<<c<<std::endl;
std::cout<<d<<std::endl;
0.7301 0.8926 0.9570
0.0979 0.5679 0.4473
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
1 1 1
1 1 1
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0 0 0
0 0 0
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
1 1 1
0 1 0
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
另外的例子:
auto b = torch::where(a>0.5);
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
auto b = torch::where(a>0.5);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
0.3439 0.1622 0.7149
0.4845 0.5982 0.9443
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0
1
1
[ Variable[CPULongType]{3} ]
2
1
2
[ Variable[CPULongType]{3} ]
26.accessor
TensorAccessor<T,N> accessor() const&
auto result_data = result.accessor<float, 2>(); //2代表二维
示例1:
torch::Tensor one = torch::randn({9,6});
auto foo_one=one.accessor<float,2>();
for(int i=0,sum=0;i<foo_one.size(0);i++)
for(int j=0;j<foo_one.size(1);j++)
sum+=foo_one[i][j];
示例2:
torch::Tensor result;
for(int i=1;i<m_num_class;i++)
{
//...
if(0 == result.numel())
{
result = result_.clone();
}else
{
result = torch::cat({result,result_},0);//按行拼接
}
}
result =result.cpu();
auto result_data = result.accessor<float, 2>();
cv::Mat img_draw = img.clone();
for(int i=0;i<result_data.size(0);i++)
{
float score = result_data[i][4];
if(score < 0.4) { continue;}
int x1 = result_data[i][0];
int y1 = result_data[i][1];
int x2 = result_data[i][2];
int y2 = result_data[i][3];
int id_label = result_data[i][5];
cv::rectangle(img_draw,cv::Point(x1,y1),cv::Point(x2,y2),cv::Scalar(255,0,0),3);
cv::putText(img_draw,label_map[id_label],cv::Point(x1,y2),CV_FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,1,cv::Scalar(255,0,55));
}
27. torch::max torch::min 同max
static inline std::tuple<Tensor,Tensor> max(const Tensor & self, Dimname dim, bool keepdim=false);
static inline Tensor max(const Tensor & self);
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({4,2});
std::tuple<torch::Tensor, torch::Tensor> max_test = torch::max(a,1);
auto max_val = std::get<0>(max_test);
// index
auto index = std::get<1>(max_test);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<max_val<<std::endl;
std::cout<<index<<std::endl;
0.1082 0.7954
0.3099 0.4507
0.2447 0.5169
0.8210 0.3141
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{4,2} ]
0.7954
0.4507
0.5169
0.8210
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{4} ]
1
1
1
0
[ Variable[CPULongType]{4} ]
另外一个例子:全局max
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({4,2});
torch::Tensor max_test = torch::max(a);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<max_test<<std::endl;
0.1904 0.9493
0.6521 0.5788
0.9216 0.5997
0.1758 0.7384
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{4,2} ]
0.94929
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{} ]
28.masked_select 与 masked_fill
28.1 Tensor masked_select(const Tensor & mask) const;
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
torch::Tensor c = (a>0.25);
torch::Tensor d = a.masked_select(c);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<c<<std::endl;
std::cout<<d<<std::endl;
0.0667 0.3812 0.3810
0.3558 0.8628 0.6329
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
0 1 1
1 1 1
[ Variable[CPUBoolType]{2,3} ]
0.3812
0.3810
0.3558
0.8628
0.6329
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{5} ]
28.2 Tensor masked_fill(const Tensor & mask, Scalar value) const;
Tensor & masked_fill_(const Tensor & mask, const Tensor & value) const;
Tensor masked_fill(const Tensor & mask, const Tensor & value) const;
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({2,3});
torch::Tensor aa = a.clone();
aa.masked_fill_(aa>0.5,-2);
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<aa<<std::endl;
0.8803 0.2387 0.8577
0.8166 0.0730 0.4682
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
-2.0000 0.2387 -2.0000
-2.0000 0.0730 0.4682
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3} ]
28.3 masked_fill_ 带下划线的都是就地操作
有个需求是Tensor score表示得分,Tensor label表示标签,他们都是同大小的。后处理就是当label=26并且label=26的分数小于0.5,那么就把label相应位置置1
float index[] = {3,2,3,3,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16};
float score[] = {0.1,0.1,0.9,0.9,0.9,0.1,0.1,0.1,0.1,0.1,0.8,0.8,0.8,0.8,0.8,0.8};
torch::Tensor aa = torch::from_blob(index, {4,4}).toType(torch::kFloat32);
torch::Tensor bb = torch::from_blob(score, {4,4}).toType(torch::kFloat32);
std::cout<<aa<<std::endl;
std::cout<<bb<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor tmp = (aa == 3);
torch::Tensor tmp_2 = (bb >= 0.9);
std::cout<<tmp<<std::endl;
std::cout<<tmp_2<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor condition_111 = tmp * tmp_2;
std::cout<<condition_111<<std::endl;
aa.masked_fill_(condition_111,-1);
std::cout<<aa<<std::endl;
输出如下:
3 2 3 3
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{4,4} ]
0.1000 0.1000 0.9000 0.9000
0.9000 0.1000 0.1000 0.1000
0.1000 0.1000 0.8000 0.8000
0.8000 0.8000 0.8000 0.8000
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{4,4} ]
1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
[ Variable[CPUByteType]{4,4} ]
0 0 1 1
1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
[ Variable[CPUByteType]{4,4} ]
0 0 1 1
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
[ Variable[CPUByteType]{4,4} ]
3 2 -1 -1
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{4,4} ]
29.libtorch综合操作1
torch::jit::script::Module module = torch::jit::load(argv[1]);
std::cout << "== Switch to GPU mode" << std::endl;
// to GPU
module.to(at::kCUDA);
if (LoadImage(file_name, image)) {
auto input_tensor = torch::from_blob(
image.data, {1, kIMAGE_SIZE, kIMAGE_SIZE, kCHANNELS});
input_tensor = input_tensor.permute({0, 3, 1, 2});
input_tensor[0][0] = input_tensor[0][0].sub_(0.485).div_(0.229);
input_tensor[0][1] = input_tensor[0][1].sub_(0.456).div_(0.224);
input_tensor[0][2] = input_tensor[0][2].sub_(0.406).div_(0.225);
// to GPU
input_tensor = input_tensor.to(at::kCUDA);
torch::Tensor out_tensor = module.forward({input_tensor}).toTensor();
auto results = out_tensor.sort(-1, true);
auto softmaxs = std::get<0>(results)[0].softmax(0);
auto indexs = std::get<1>(results)[0];
for (int i = 0; i < kTOP_K; ++i) {
auto idx = indexs[i].item<int>();
std::cout << " ============= Top-" << i + 1
<< " =============" << std::endl;
std::cout << " Label: " << labels[idx] << std::endl;
std::cout << " With Probability: "
<< softmaxs[i].item<float>() * 100.0f << "%" << std::endl;
}
}
30.pytorch nms <---------> libtorch nms
pytorch nms
比如:
boxes [1742,4]
scores [1742]
def nms(boxes, scores, overlap=0.5, top_k=200):
"""Apply non-maximum suppression at test time to avoid detecting too many
overlapping bounding boxes for a given object.
Args:
boxes: (tensor) The location preds for the img, Shape: [num_priors,4].
scores: (tensor) The class predscores for the img, Shape:[num_priors].
overlap: (float) The overlap thresh for suppressing unnecessary boxes.
top_k: (int) The Maximum number of box preds to consider.
Return:
The indices of the kept boxes with respect to num_priors.
"""
keep = scores.new(scores.size(0)).zero_().long()
if boxes.numel() == 0:
return keep
x1 = boxes[:, 0]
y1 = boxes[:, 1]
x2 = boxes[:, 2]
y2 = boxes[:, 3]
area = torch.mul(x2 - x1, y2 - y1)
v, idx = scores.sort(0) # sort in ascending order
# I = I[v >= 0.01]
idx = idx[-top_k:] # indices of the top-k largest vals
xx1 = boxes.new()
yy1 = boxes.new()
xx2 = boxes.new()
yy2 = boxes.new()
w = boxes.new()
h = boxes.new()
# keep = torch.Tensor()
count = 0
while idx.numel() > 0:
i = idx[-1] # index of current largest val
# keep.append(i)
keep[count] = i
count += 1
if idx.size(0) == 1:
break
idx = idx[:-1] # remove kept element from view
# load bboxes of next highest vals
torch.index_select(x1, 0, idx, out=xx1)
torch.index_select(y1, 0, idx, out=yy1)
torch.index_select(x2, 0, idx, out=xx2)
torch.index_select(y2, 0, idx, out=yy2)
# store element-wise max with next highest score
xx1 = torch.clamp(xx1, min=x1[i])
yy1 = torch.clamp(yy1, min=y1[i])
xx2 = torch.clamp(xx2, max=x2[i])
yy2 = torch.clamp(yy2, max=y2[i])
w.resize_as_(xx2)
h.resize_as_(yy2)
w = xx2 - xx1
h = yy2 - yy1
# check sizes of xx1 and xx2.. after each iteration
w = torch.clamp(w, min=0.0)
h = torch.clamp(h, min=0.0)
inter = w*h
# IoU = i / (area(a) + area(b) - i)
rem_areas = torch.index_select(area, 0, idx) # load remaining areas)
union = (rem_areas - inter) + area[i]
IoU = inter/union # store result in iou
# keep only elements with an IoU <= overlap
idx = idx[IoU.le(overlap)]
return keep, count
libtorch nms
bool nms(const torch::Tensor& boxes, const torch::Tensor& scores, torch::Tensor &keep, int &count,float overlap, int top_k)
{
count =0;
keep = torch::zeros({scores.size(0)}).to(torch::kLong).to(scores.device());
if(0 == boxes.numel())
{
return false;
}
torch::Tensor x1 = boxes.select(1,0).clone();
torch::Tensor y1 = boxes.select(1,1).clone();
torch::Tensor x2 = boxes.select(1,2).clone();
torch::Tensor y2 = boxes.select(1,3).clone();
torch::Tensor area = (x2-x1)*(y2-y1);
// std::cout<<area<<std::endl;
std::tuple<torch::Tensor,torch::Tensor> sort_ret = torch::sort(scores.unsqueeze(1), 0, 0);
torch::Tensor v = std::get<0>(sort_ret).squeeze(1).to(scores.device());
torch::Tensor idx = std::get<1>(sort_ret).squeeze(1).to(scores.device());
int num_ = idx.size(0);
if(num_ > top_k) //python:idx = idx[-top_k:]
{
idx = idx.slice(0,num_-top_k,num_).clone();
}
torch::Tensor xx1,yy1,xx2,yy2,w,h;
while(idx.numel() > 0)
{
auto i = idx[-1];
keep[count] = i;
count += 1;
if(1 == idx.size(0))
{
break;
}
idx = idx.slice(0,0,idx.size(0)-1).clone();
xx1 = x1.index_select(0,idx);
yy1 = y1.index_select(0,idx);
xx2 = x2.index_select(0,idx);
yy2 = y2.index_select(0,idx);
xx1 = xx1.clamp(x1[i].item().toFloat(),INT_MAX*1.0);
yy1 = yy1.clamp(y1[i].item().toFloat(),INT_MAX*1.0);
xx2 = xx2.clamp(INT_MIN*1.0,x2[i].item().toFloat());
yy2 = yy2.clamp(INT_MIN*1.0,y2[i].item().toFloat());
w = xx2 - xx1;
h = yy2 - yy1;
w = w.clamp(0,INT_MAX);
h = h.clamp(0,INT_MAX);
torch::Tensor inter = w * h;
torch::Tensor rem_areas = area.index_select(0,idx);
torch::Tensor union_ = (rem_areas - inter) + area[i];
torch::Tensor Iou = inter * 1.0 / union_;
torch::Tensor index_small = Iou < overlap;
auto mask_idx = torch::nonzero(index_small).squeeze();
idx = idx.index_select(0,mask_idx);//pthon: idx = idx[IoU.le(overlap)]
}
return true;
}
31.数据类型很重要! .to(torch::kByte);
31.1
//[128,512]
torch::Tensor b = torch::argmax(output_1, 2).cpu();
// std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
b.print();
cv::Mat mask(T_height, T_width, CV_8UC1, (uchar*)b.data_ptr());
imshow("mask",mask*255);
waitKey(0);
[Variable[CPULongType] [128, 512]]
如上!得到的b是分割图[128, 512]。可是死活不能显示!!然后我检测b的值和pytorch的对比,发现是一致的。可是上面的就是死活得不到想要的分割图,全是黑的,为0.可是我把值打出来有不为0的啊!
之前工程也是这么写的啊,哎。。。然后我就github上面找psenet libtorch的实现,发现人家也是类似的写法
cv::Mat tempImg = Mat::zeros(T_height, T_width, CV_8UC1);
memcpy((void *) tempImg.data, b.data_ptr(), sizeof(torch::kU8) * b.numel());
我也这么写,发现还是不行!!!2个小时过去了,没有办法,我准备把128*512的数据保存在els里面查看。漫无目的的实验了一下
cout<<b[0][0].item().toFloat()<<endl;
这样可以打印出值,一定要加.toFloat()才行。漫无目的的编写循环
for(int i=0;i<128;i++)
for(int j=0;j<512;j++)
{
}
可是不服啊!哪里有问题呢,值都是对的就是显示不出来?
发现刚刚上面b[0][0].item().toFloat()必须加.toFloat(),那么我的b是什么类型的呢,是tensor类型的,具体什么类型呢,看到打印的[Variable[CPULongType] [128, 512]],long类型的。
哦,那我转一下类型看看。翻看之前的转类型的,发现只需要在tensor后面加.to(torch::kFloat32);类似的
因为我需要int的,我就先int一下,
torch::Tensor b = torch::argmax(output_1, 2).cpu().to(torch::kInt);
试了一下还是不行,
.to(torch::kFloat32); 试了一下还是不行,
我在敲torch::k的时候编译器会自动弹出k开头的东西。其中第一个就是kByte.然后试了下:
torch::Tensor b = torch::argmax(output_1, 2).cpu().to(torch::kByte);
!!!!
可以了!出来了我想要的分割图。
搞死我了,数据类型的问题。至少整了2个小时!
31.2
要把中间处理的图片转为tensor
Mat m_tmp = grayMat.clone();
torch::Tensor label_deal = torch::from_blob(
m_tmp.data, {grayMat.rows, grayMat.cols}).toType(torch::kByte).to(m_device);
// label_deal = label_deal.to(m_device);
auto aaa = torch::max(label_deal);
std::cout<<label_deal<<std::endl;
std::cout<<aaa<<std::endl;
while(1);
又是一个大坑啊!!!一开始认为就这么就ok了,然后后面的处理结果不对,就一步步排查哪里出问题,然后定位到这里,m_tmp的像素值在tensor里面压根就对不上啊!!!我知道m_tmp最大像素值34,可是打出来的tensor最大255!!!哎,是torch::kByte类型啊!没办法,再换成kFloat32还是不行,值更离谱还有nan的。。呃呃呃。然后发现.toType(torch::kByte)还有.to(torch::kByte)这个写法的,到底用哪个还是一样?然后继续实验还是一样有问题,然后把.to(m_device);单独拎出来还是不行,因为根据之前的经验,torch::Tensor tmp = tmp.cpu();好像是需要单独写,要不然会有问题。那这边啥问题呢?像素值就是不能正确放到tensor!!!咋回事呢???
然后郁闷良久,那么Mat的类型是不是也要转。
Mat m_tmp = grayMat.clone();
m_tmp.convertTo(m_tmp,CV_32FC1);/////又是个大坑 图片要先转float32啊
torch::Tensor label_deal = torch::from_blob(
m_tmp.data, {grayMat.rows, grayMat.cols}).toType(torch::kByte).to(m_device);
这样就可以了!!!呃呃呃,一定要转CV_32FC1吗?可能是吧!
32.指针访问Tensor数据
torch::Tensor output = m_model->forward({input_tensor}).toTensor()[0];
torch::Tensor output_cpu = output.cpu();
//output_cpu Variable[CPUFloatType] [26, 480, 480]]
output_cpu.print();
void *ptr = output_cpu.data_ptr();
//std::cout<<(float*)ptr[0]<<std::endl;
只能用void 或者auto来定义,否则会报错。比如我用float ptr = output_cpu.data_ptr();会报错:
error: invalid conversion from ‘void’ to ‘float’ [-fpermissive]
float *ptr = output_cpu.data_ptr();
那么void *编译通过了,我需要用指针访问tensor里面的数据啊!
torch::Tensor output = m_model->forward({input_tensor}).toTensor()[0];
torch::Tensor output_cpu = output.cpu();
//output_cpu Variable[CPUFloatType] [26, 480, 480]]
output_cpu.print();
void *ptr = output_cpu.data_ptr();
std::cout<<(float*)ptr<<std::endl;
如上这么写,输出:
[Variable[CPUFloatType] [26, 480, 480]]
0x7fab195ee040
输出来的是个地址,那怎么访问数据呢,自然而然的就这么写:
std::cout<<(float)ptr[0]<<std::endl;
这么写又报错!!!!
: error: ‘void’ is not a pointer-to-object type,然后又这么写:
std::cout<<(float*)ptr[0][0][0]<<std::endl;还是报一样的错误!。没有办法,然后Google了一下,发现有报错和我一样的,以及解决方案:

果真!解决了!
void *ptr = output_cpu.data_ptr();
// std::cout<<*((float*)ptr[0][0][0])<<std::endl;
// std::cout<<(float*)ptr[0][0][0]<<std::endl;
std::cout<<*((float*)(ptr+2))<<std::endl;
还有一种写法:
const float* result = reinterpret_cast<const float *>(output_cpu.data_ptr());
还有刚刚的那种写法:
void *ptr = output_cpu.data_ptr();
const float* result = (float*)ptr;
33 PyTorch内Tensor按索引赋值的方法比较
PyTorch内Tensor按索引赋值的方法比较[https://www.jianshu.com/p/e568213c8501]
44 输出多个tensor(pytorch端)以及取出多个tensor(libtorch端)
pytorch端的输出:
def forward(self, x, batch=None):
output, cnn_feature = self.dla(x)
return (output['ct_hm'],output['wh'],cnn_feature)
对应的libtorch端
auto out = m_model->forward({input_tensor});
auto tpl = out.toTuple();
auto out_ct_hm = tpl->elements()[0].toTensor();
out_ct_hm.print();
auto out_wh = tpl->elements()[1].toTensor();
out_wh.print();
auto out_cnn_feature = tpl->elements()[2].toTensor();
out_cnn_feature.print();
如果输出单个tensor,就是
at::Tensor output = module->forward(inputs).toTensor();
45. torch::Tensor作为函数参数,不管是引用还是不引用,函数内部对形参操作都会影响本来的tensor,即都是引用
void test_tensor(torch::Tensor a)
{
a[0][0] = -100;
}
int main(int argc, const char* argv[])
{
torch::Tensor p = torch::rand({2,2});
std::cout<<p<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"~~~~#########~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~"<<std::endl;
test_tensor(p);
std::cout<<p<<std::endl;
while (1);
}
输出如下:
0.0509 0.3509
0.8019 0.1350
[ Variable[CPUType]{2,2} ]
~~~~#########~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
-100.0000 0.3509
0.8019 0.1350
[ Variable[CPUType]{2,2} ]
可以看出,函数void test_tensor(torch::Tensor a),虽然不是引用,但是经过了这个函数之后值改变了!
46. 实现pytorch下标神操作
比如在pytorch端,写法如下:
c=b[a]
其中,a的形状是[1,100], b的形状是[1,100,40,2],所以,大家猜c的形状是什么。。哦,还有一个已知条件是a相当于一个掩模,a里面的值只有0或者1,假设a的前5个值是1,其余为0
得到的c的形状是[5,40,2],大概也能猜到就是把为1的那些行取出,其余的不要! 那么,libtorch端如何优雅的实现呢?
呃呃呃,暂时没有想到什么好法子,因为libtorch端不支持下标操作。。很麻烦。。。然后自己写的循环实现的:
为了方便看数值,只假设10个。
// aim [1,10,2,2] ind_mask_ [1,10] 比如前5个是1余都是0 得到的结果形状是[5,40,2] 即pytorch里面的操作 aim = aim[ind_mask]
torch::Tensor deal_mask_index22(torch::Tensor aim_,torch::Tensor ind_mask_)
{
torch::Tensor aim = aim_.clone().squeeze(0);//[1,100,40,2] -->> [100,40,2]
torch::Tensor ind_mask = ind_mask_.clone().squeeze(0);////[1,100] -->> [100]
int row = ind_mask.size(0);
int cnt = 0;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
if(ind_mask[i].item().toInt())
{
cnt += 1;
}
}
torch::Tensor out = torch::zeros({cnt,aim.size(1),aim.size(2)});
int index_ = 0;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
if(ind_mask[i].item().toInt())
{
out[index_++] = aim[i];
// std::cout<<i<<std::endl;
}
}
std::cout<<"##############################################"<<std::endl;
std::cout<<out<<std::endl;
return out;
}
int main(int argc, const char* argv[])
{
torch::Tensor ind_mask = torch::ones({1,10});
ind_mask[0][0] = 0;
ind_mask[0][1] = 0;
ind_mask[0][2] = 0;
ind_mask[0][4] = 0;
torch::Tensor aim = torch::rand({1,10,2,2});
std::cout<<aim<<std::endl;
deal_mask_index22(aim,ind_mask);
while (1);
}
47.pytorch libtorch的tensor验证精度
[pytorch libtorch的tensor验证精度](pytorch libtorch的tensor验证精度)
https://www.cnblogs.com/yanghailin/p/13669046.html
48. 其他--颜色映射
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
auto t1 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
// static torch::Tensor tensor_m0 = torch::zeros({m_height,m_width}).to(torch::kByte).to(torch::kCPU);
// static torch::Tensor tensor_m1 = torch::zeros({m_height,m_width}).to(torch::kByte).to(torch::kCPU);
// static torch::Tensor tensor_m2 = torch::zeros({m_height,m_width}).to(torch::kByte).to(torch::kCPU);
static torch::Tensor tensor_m0 = torch::zeros({m_height,m_width}).to(torch::kByte);
static torch::Tensor tensor_m1 = torch::zeros({m_height,m_width}).to(torch::kByte);
static torch::Tensor tensor_m2 = torch::zeros({m_height,m_width}).to(torch::kByte);
tensor_m0 = tensor_m0.to(torch::kCUDA);
tensor_m1 = tensor_m1.to(torch::kCUDA);
tensor_m2 = tensor_m2.to(torch::kCUDA);
for(int i=1;i<m_color_cnt;i++)
{
tensor_m0.masked_fill_(index==i,colormap[i * 3]);
tensor_m1.masked_fill_(index==i,colormap[i * 3 + 1]);
tensor_m2.masked_fill_(index==i,colormap[i * 3 + 2]);
}
torch::Tensor tensor_m00 = tensor_m0.cpu();
torch::Tensor tensor_m11 = tensor_m1.cpu();
torch::Tensor tensor_m22 = tensor_m2.cpu();
cv::Mat m0 = cv::Mat(m_height, m_width, CV_8UC1, (uchar*)tensor_m00.data_ptr());
cv::Mat m1 = cv::Mat(m_height, m_width, CV_8UC1, (uchar*)tensor_m11.data_ptr());
cv::Mat m2 = cv::Mat(m_height, m_width, CV_8UC1, (uchar*)tensor_m22.data_ptr());
std::vector<cv::Mat> channels = {m0,m1,m2};
cv::Mat mergeImg;
cv::merge(channels, mergeImg);
mergeImg = mergeImg.clone();
auto ttt1 = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>
(std::chrono::steady_clock::now() - t1).count();
std::cout << "merge time="<<ttt1<<"ms"<<std::endl;
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
用cpu需要35ms左右,gpu2-3ms,下面的代码实现功能一样也是2-3ms
auto t0 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
for (int i = 0; i<labelMat.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j<labelMat.cols; j++)
{
int id = labelMat.at<uchar>(i,j);
if(0 == id)
{
continue;
}
colorMat.at<cv::Vec3b>(i, j)[0] = colormap[id * 3];
colorMat.at<cv::Vec3b>(i, j)[1] = colormap[id * 3 + 1];
colorMat.at<cv::Vec3b>(i, j)[2] = colormap[id * 3 + 2];
}
}
auto ttt = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>
(std::chrono::steady_clock::now() - t0).count();
std::cout << "consume time="<<ttt<<"ms"<<std::endl;
49.torch.gather
纯pytorch端的: (转载于https://www.jianshu.com/p/5d1f8cd5fe31)
torch.gather(input, dim, index, out=None) → Tensor
沿给定轴 dim ,将输入索引张量 index 指定位置的值进行聚合.
对一个 3 维张量,输出可以定义为:
out[i][j][k] = input[index[i][j][k]][j][k] # if dim == 0
out[i][j][k] = input[i][index[i][j][k]][k] # if dim == 1
out[i][j][k] = input[i][j][index[i][j][k]] # if dim == 2
Parameters:
input (Tensor) – 源张量
dim (int) – 索引的轴
index (LongTensor) – 聚合元素的下标(index需要是torch.longTensor类型)
out (Tensor, optional) – 目标张量
例子:
dim = 1
import torch
a = torch.randint(0, 30, (2, 3, 5))
print(a)
#tensor([[[ 18., 5., 7., 1., 1.],
# [ 3., 26., 9., 7., 9.],
# [ 10., 28., 22., 27., 0.]],
# [[ 26., 10., 20., 29., 18.],
# [ 5., 24., 26., 21., 3.],
# [ 10., 29., 10., 0., 22.]]])
index = torch.LongTensor([[[0,1,2,0,2],
[0,0,0,0,0],
[1,1,1,1,1]],
[[1,2,2,2,2],
[0,0,0,0,0],
[2,2,2,2,2]]])
print(a.size()==index.size())
b = torch.gather(a, 1,index)
print(b)
#True
#tensor([[[ 18., 26., 22., 1., 0.],
# [ 18., 5., 7., 1., 1.],
# [ 3., 26., 9., 7., 9.]],
# [[ 5., 29., 10., 0., 22.],
# [ 26., 10., 20., 29., 18.],
# [ 10., 29., 10., 0., 22.]]])
dim =2
c = torch.gather(a, 2,index)
print(c)
#tensor([[[ 18., 5., 7., 18., 7.],
# [ 3., 3., 3., 3., 3.],
# [ 28., 28., 28., 28., 28.]],
# [[ 10., 20., 20., 20., 20.],
# [ 5., 5., 5., 5., 5.],
# [ 10., 10., 10., 10., 10.]]])
dim = 0
index2 = torch.LongTensor([[[0,1,1,0,1],
[0,1,1,1,1],
[1,1,1,1,1]],
[[1,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0],
[1,1,0,0,0]]])
d = torch.gather(a, 0,index2)
print(d)
#tensor([[[ 18., 10., 20., 1., 18.],
# [ 3., 24., 26., 21., 3.],
# [ 10., 29., 10., 0., 22.]],
# [[ 26., 5., 7., 1., 1.],
# [ 3., 26., 9., 7., 9.],
# [ 10., 29., 22., 27., 0.]]])
这里我之前看过然后再看到的时候又是一头雾水,然后记录在此!主要是这个
out[i][j][k] = input[i][index[i][j][k]][k] # if dim == 1
可是这个gather函数可以干什么呢?直观上就是output和input的形状是一样的,自己推导一两个看看,比如dim=1
output[0][0][0] = input[0] [index[0][0][0]] [0],然后先查找index找到index[0][0][0]=0,然后再查找input[0][0][0]
流程就是这样,所以,index是下标索引,其值不能超过dim的维度!
直观上就是在某个维度整了个新的映射规则得到output,关键还在于index!这个就是规则。
50. torch::argsort(libtorch1.0没有这个函数) torch::sort
用1.1写好的一个libtorch工程,由于项目是用1.0的,然后把写好的1.1转1.0.然后提示说:
error: ‘argsort’ is not a member of ‘torch’
恩,我知道了,就是由于版本问题导致函数名对不上,可是我去哪里找argsort啊,然后,看到之前的max好像有记录索引的,然后又看到sort,然后实验了一下,和argsort结果一样!
//pytorch1.1
torch::Tensor edge_idx_sort2 = torch::argsort(edge_num, 2, true);
//pytorch1.0
std::tupletorch::Tensor,torch::Tensor sort_ret = torch::sort(edge_num, 2, true);
// torch::Tensor v = std::get<0>(sort_ret);
torch::Tensor edge_idx_sort = std::get<1>(sort_ret);
51. 判断tensor是否为空 ind_mask.sizes().empty()
int row = ind_mask.size(0);
如果ind_mask是空代码就会奔溃报错,
terminate called after throwing an instance of 'c10::Error'
what(): dimension specified as 0 but tensor has no dimensions (maybe_wrap_dim at /data_1/leon_develop/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/core/WrapDimMinimal.h:9)
frame #0: c10::Error::Error(c10::SourceLocation, std::__cxx11::basic_string<char, std::char_traits<char>, std::allocator<char> > const&) + 0x6a (0x7f4cf0a4af5a in /data_2/project_202009/chejian/3rdparty/libtorch/lib/libc10.so)
frame #1: <unknown function> + 0x48a74f (0x7f4d010af74f in /data_2/project_202009/chejian/3rdparty/libtorch/lib/libcaffe2.so)
frame #2: at::native::size(at::Tensor const&, long) + 0x20 (0x7f4d010afac0 in /data_2/project_202009/chejian/3rdparty/libtorch/lib/libcaffe2.so)
frame #3: at::Tensor::size(long) const + 0x36 (0x467fba in /data_2/project_202009/libtorch/snake_libtorch_cuda8/cmake-build-debug/example-app)
frame #4: deal_mask_index(at::Tensor, at::Tensor) + 0x1a7 (0x45a83e in /data_2/project_202009/libtorch/snake_libtorch_cuda8/cmake-build-debug/example-app)
frame #5: get_gcn_feature(at::Tensor, at::Tensor, at::Tensor, int, int) + 0x4f3 (0x45e092 in /data_2/project_202009/libtorch/snake_libtorch_cuda8/cmake-build-debug/example-app)
frame #6: init_poly(std::shared_ptr<torch::jit::script::Module> const&, std::shared_ptr<torch::jit::script::Module> const&, at::Tensor const&, std::tuple<at::Tensor, at::Tensor, at::Tensor> const&) + 0x168 (0x45e777 in /data_2/project_202009/libtorch/snake_libtorch_cuda8/cmake-build-debug/example-app)
frame #7: main + 0xaee (0x463ab5 in /data_2/project_202009/libtorch/snake_libtorch_cuda8/cmake-build-debug/example-app)
frame #8: __libc_start_main + 0xf0 (0x7f4ced29c840 in /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6)
frame #9: _start + 0x29 (0x456b89 in /data_2/project_202009/libtorch/snake_libtorch_cuda8/cmake-build-debug/example-app)
所以,有必要判断tensor是否为空,可是:
ind_mask.numel() //返回总个数,但是为空的时候返回1
ind_mask.sizes()// 返回类似python list的东东,[1, 100, 40, 2] [1, 40, 2]
ind_mask.sizes()然后我跟到sizes()libtorch函数定义里面是IntList类型的,然后再跟踪,using IntList = ArrayRef<int64_t>;然后再跟踪,ArrayRef,然后看这个类,找到
/// empty - Check if the array is empty.
constexpr bool empty() const {
return Length == 0;
}
所以,说明有判断为空的成员函数可以调用!
if(ind_mask.sizes().empty())
{
}
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
我也太难了吧!
本来以为搞定了的!
if(ind_mask.sizes().empty())
{
torch::Tensor tmp;
return tmp;
}
当判断一个tensor为空,我就创建一个tensor退出,因为函数返回是torch::Tensor类型的。
但是直接创建的这个tensor访问sizes也会报错!!!
如下:
torch::Tensor tmp;
tmp.print(); //打印[UndefinedTensor]
if(tmp.sizes().empty())
{
}
[UndefinedTensor]
terminate called after throwing an instance of 'c10::Error'
what(): sizes() called on undefined Tensor (sizes at /data_1/leon_develop/pytorch/aten/src/ATen/core/UndefinedTensorImpl.cpp:12)
frame #0: c10::Error::Error(c10::SourceLocation, std::__cxx11::basic_string<char, std::char_traits<char>, std::allocator<char> > const&) + 0x6a (0x7f35f1b21f5a in /data_2/project_202009/chejian/3rdparty/libtorch/lib/libc10.so)
frame #1: at::UndefinedTensorImpl::sizes() const + 0x77 (0x7f360217d6b7 in /data_2/project_202009/chejian/3rdparty/libtorch/lib/libcaffe2.so)
frame #2: at::Tensor::sizes() const + 0x27 (0x45e921 in /data_2/project_202009/libtorch/snake_libtorch_cuda8/cmake-build-debug/example-app)
frame #3: main + 0x55 (0x45bcaa in /data_2/project_202009/libtorch/snake_libtorch_cuda8/cmake-build-debug/example-app)
frame #4: __libc_start_main + 0xf0 (0x7f35ee373840 in /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6)
frame #5: _start + 0x29 (0x44f889 in /data_2/project_202009/libtorch/snake_libtorch_cuda8/cmake-build-debug/example-app)
但是这个时候:
torch::Tensor tmp;
tmp.print();
std::cout<<tmp.numel()<<std::endl; // 输出为0
!!!!
所以,直接定义tensor,这个时候的.numel()为0.
52.pytorch代码 out = aim[ind_mask],用libtorch写出来。
pytorch代码
out = aim[ind_mask]
其中,形状如下:
aim [21, 40, 2]
ind_mask [21] #元素非0即1,比如有12个1
out输出形状是[12,40,2]
#####################################
以上pytorch代码out = aim[ind_mask]
如何用libtorch代码表示出来
torch::Tensor a = torch::rand({5,3,2});
torch::Tensor idx = torch::zeros({5}).toType(torch::kLong);
idx[3] = 1;
idx[1] = 1;
torch::Tensor abc = torch::nonzero(idx);
torch::Tensor b = a.index_select(0,abc.squeeze());
std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
std::cout<<abc<<std::endl;
std::cout<<b<<std::endl;
输出如下:
(1,.,.) =
0.1767 0.8695
0.3779 0.3531
0.3413 0.3734
(2,.,.) =
0.9664 0.7723
0.8640 0.7289
0.8395 0.6344
(3,.,.) =
0.9043 0.2671
0.9901 0.2966
0.0347 0.1650
(4,.,.) =
0.1457 0.1169
0.7983 0.5157
0.6405 0.2213
(5,.,.) =
0.7977 0.4066
0.6691 0.7191
0.5897 0.7400
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{5,3,2} ]
1
3
[ Variable[CPULongType]{2,1} ]
(1,.,.) =
0.9664 0.7723
0.8640 0.7289
0.8395 0.6344
(2,.,.) =
0.1457 0.1169
0.7983 0.5157
0.6405 0.2213
[ Variable[CPUFloatType]{2,3,2} ]
53. pytorch代码a4 = arr[...,3,0] 用libtorch如何表达出来 masked_select运用!
>>> import numpy as np
>>> arr = np.arange(40).reshape(1,5,4,2)
>>> arr
array([[[[ 0, 1],
[ 2, 3],
[ 4, 5],
[ 6, 7]],
[[ 8, 9],
[10, 11],
[12, 13],
[14, 15]],
[[16, 17],
[18, 19],
[20, 21],
[22, 23]],
[[24, 25],
[26, 27],
[28, 29],
[30, 31]],
[[32, 33],
[34, 35],
[36, 37],
[38, 39]]]])
>>> a1 = arr[...,0,1]
>>> a2 = arr[...,1,0]
>>> a3 = arr[...,2,1]
>>> a4 = arr[...,3,0]
>>> print(a1)
[[ 1 9 17 25 33]]
>>> print(a2)
[[ 2 10 18 26 34]]
>>> print(a3)
[[ 5 13 21 29 37]]
>>> print(a4)
[[ 6 14 22 30 38]]
>>>
一开始折腾好久,好像没有什么好办法,然后用for循环完成的,
//ex shape[1,5,4,2] ex[..., 0, 1] -->>[1,5]
torch::Tensor index_tensor_3(const torch::Tensor &ex,const int &idx1,const int &idx2)
{
// ex.print();
int dim_ = ex.size(1);
torch::Tensor out = torch::empty({1,dim_}).to(ex.device());
int size_ = ex.size(1);
for(int i=0;i<size_;i++)
{
auto a = ex[0][i][idx1][idx2];
out[0][i] = a;
// std::cout<<a<<std::endl;
}
return out;
}
然后优化,用纯libtorch函数完成:
//ex shape[1,5,4,2] ex[..., 0, 1] -->>[1,5]
torch::Tensor index_tensor_3(const torch::Tensor &ex,const int &idx1,const int &idx2)
{
const int dim0 = ex.size(0);
const int dim1 = ex.size(1);
const int dim2 = ex.size(2);
const int dim3 = ex.size(3);
std::vector<int> v_index(ex.numel());//初始化:ex.numel() 个0
int offset = dim2 * dim3;
for(int i=0;i<dim1;i++)
{
int index_ = idx1 * dim3 + idx2;
v_index[i * offset + index_] = 1;
}
torch::Tensor index = torch::tensor(v_index).to(ex.device());
index = index.reshape(ex.sizes()).toType(torch::kByte);//这里需要kByte类型
// std::cout<<index<<std::endl;
torch::Tensor selete = ex.masked_select(index).unsqueeze(0);
return selete;
}
接上函数,大概累计调用这个函数10次,第一种需要耗时15ms,而下面的耗时5ms
54.再次强调一下类型很重要!!有时候需要强制写下 kernel = kernel.toType(torch::kByte);
今天一个需求是用libtorch1.8的跑libtorch1.0的pt模型,稍微改改语法,旧版本的就可以在高版本编译通过,并且可以运行,但是运行的结果不对。这个挺麻烦的。
因为不知道问题出在哪里。首先值得怀疑的是不支持。为了验证这个问题,就是首先是用高版本的和旧版本输入都一样跑推理,看看模型出来的结果是否一致。当然这个也挺费事的,因为pytorch高版本的
需要跑低版本的,需要改挺多东西的。没办法,我改了,各种报错啊,我是psenet,这东东是运行在cuda8,python2.7上面的,不单单是print,还有其他各种各样的问题,原因在于各种数据处理需要用到各种库,后来我不管三七二十一全删了,
因为我发现跑推理就是
out = model(img)
这句话,我只要准备同样的img就可以了。很长很长的test.py文件就被我浓缩为如下:
#encoding=utf-8
import os
import cv2
import sys
import time
import collections
import torch
import argparse
import numpy as np
import models
#import util
def test(args):
# Setup Model
if args.arch == "resnet50":
model = models.resnet50(pretrained=True, num_classes=7, scale=args.scale)
elif args.arch == "resnet101":
model = models.resnet101(pretrained=True, num_classes=7, scale=args.scale)
elif args.arch == "resnet152":
model = models.resnet152(pretrained=True, num_classes=7, scale=args.scale)
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
model = model.cuda()
if args.resume is not None:
if os.path.isfile(args.resume):
print("Loading model and optimizer from checkpoint '{}'".format(args.resume))
checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume)
# model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
d = collections.OrderedDict()
for key, value in checkpoint['state_dict'].items():
tmp = key[7:]
d[tmp] = value
model.load_state_dict(d)
print("Loaded checkpoint '{}' (epoch {})"
.format(args.resume, checkpoint['epoch']))
sys.stdout.flush()
else:
print("No checkpoint found at '{}'".format(args.resume))
sys.stdout.flush()
model.eval()
img_tmp = torch.rand(1, 3, 963, 1280).cuda()
traced_script_module = torch.jit.trace(model, img_tmp)
traced_script_module.save("./myfile/22.pt")
init_seed = 1 #设置同样的种子确保产生一样的随机数
torch.manual_seed(init_seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed(init_seed)
img_tmp = torch.rand(1, 3, 64, 64).cuda()
out = model(img_tmp)
print(img_tmp)
print(out)
print("save pt ok!")
return 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Hyperparams')
parser.add_argument('--arch', nargs='?', type=str, default='resnet50')
parser.add_argument('--resume', nargs='?', type=str, default="./myfile/checkpoint.pth.tar",
help='Path to previous saved model to restart from')
parser.add_argument('--binary_th', nargs='?', type=float, default=1.0,
help='Path to previous saved model to restart from')
parser.add_argument('--kernel_num', nargs='?', type=int, default=3,
help='Path to previous saved model to restart from')
parser.add_argument('--scale', nargs='?', type=int, default=1,
help='Path to previous saved model to restart from')
parser.add_argument('--long_size', nargs='?', type=int, default=1280,
help='Path to previous saved model to restart from')
parser.add_argument('--min_kernel_area', nargs='?', type=float, default=10.0,
help='min kernel area')
parser.add_argument('--min_area', nargs='?', type=float, default=300.0,
help='min area')
parser.add_argument('--min_score', nargs='?', type=float, default=0.93,
help='min score')
args = parser.parse_args()
test(args)
这里很重要:
init_seed = 1 #设置同样的种子确保产生一样的随机数
torch.manual_seed(init_seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed(init_seed)
因为我同时需要在torch1.0和torch1.8上面验证模型精度,需要控制输入一样的,所以设置同样的种子确保产生一样的随机数。print打印出来验证是一致的。
然后我发现out是有差别的,但是只是小数点后面3位不同,前面几位一样,所以我感觉高版本加载低版本权重运行是ok的!但是libtorch里面结果相差很大,为啥呢?
这个就需要仔细看libtorch的代码了!!!
然后漫无目的的实验,打印。。这里说一下打印很重要!!!
我先在我的低版本的libtorch打印的部分内容如下:
[ Variable[CPUByteType]{7,703,1280} ]
[Variable[CPUByteType] [7, 703, 1280]]
[Variable[CPUByteType] [3, 703, 1280]]
kernel_size=3
[Variable[CPUByteType] [3, 703, 1280]]
然后高版本的打印的如下:
[CUDAFloatType [1, 7, 703, 1280]]
[CPUFloatType [7, 703, 1280]]
[CPUFloatType [3, 703, 1280]]
kernel_size=3
[CPUFloatType [3, 703, 1280]]
额,看到没有,数据类型不一样啊,为啥不一样啊,所以我就知道了又是哪里数据类型的问题。
然后加了这句话,
kernel = kernel.toType(torch::kByte);
完美解决!
就是一些操作低版本默认是CPUByteType类型,但是到了高版本就是CPUFloatType类型了。
看似简单的一句话,耗费我大半天!
所以总结起来,上面就是我查找问题的思路流程并且完美解决问题。总结起来就是需要不断查找定位问题并不断实验解决问题。
然后再发一个最近遇到的opencv的Mat的一个数据类型的问题。
Mat convertTo3Channels_2(const Mat& binImg)
{
Mat three_channel = Mat::zeros(binImg.rows,binImg.cols,CV_8UC3);
vector<Mat> channels;
for (int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
channels.push_back(binImg);
}
merge(channels,three_channel);
three_channel.convertTo(three_channel,CV_8UC3); //重要,还要再写一次!!
return three_channel;
}
看代码,
我一开始声明的CV_8UC3这个类型的, Mat three_channel = Mat::zeros(binImg.rows,binImg.cols,CV_8UC3);。因为函数传出去我就是需要uint类型的。
three_channel.convertTo(three_channel,CV_8UC3); //重要,还要再写一次!!
这里,这里还需要再写一次,要不然传出去的不是这个类型的,Mat不知道如何查看或者打印出这个类型,但是我是通过我的调试器gdb imagewatch看这张图片,下面会显示类型。
我去复现了一下并截图了,我在
merge(channels,three_channel);这句话下面打断点我的gdb imagewatch显示如下类型
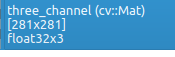
看到没有,我明明初始化的是Mat three_channel = Mat::zeros(binImg.rows,binImg.cols,CV_8UC3);
CV_8UC3类型,这个应该是uint类型的,可是merge之后就是float类型的了,可能就是merge这个函数给我改变类型了的吧。
导致函数传出去的后面的一些操作很奇怪,也不知道问题出在哪里。
然后再强制转一下就可以。
three_channel.convertTo(three_channel,CV_8UC3); //重要,还要再写一次!!
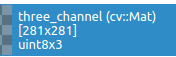
总结:
类型很重要
类型很重要
类型很重要
重要的事情说三遍。
小弟不才,同时谢谢友情赞助!