opencv 旋转 点旋转 以及 逆旋转
#include"opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include"opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void CalcRotateMatrix(const cv::Mat& img, float degree, cv::Mat& trans_mat, cv::Size& dst_size){
degree = fmod(degree + 360.0f, 360.0f);
double angle = degree * CV_PI / 180.;
int width = img.cols;
int height = img.rows;
double a = sin(angle), b = cos(angle);
int widthRotate = int(height * fabs(a) + width * fabs(b));
int heightRotate = int(width * fabs(a) + height * fabs(b));
// int widthRotate = width;
// int heightRotate = height;
// [ m0 m1 m2 ] ===> [ A11 A12 b1 ]
// [ m3 m4 m5 ] ===> [ A21 A22 b2 ]
trans_mat.create(2, 3, CV_32F);
float *map = (float *)trans_mat.ptr<float>();
CvPoint2D32f center = cvPoint2D32f(width / 2.0f, height / 2.0f);
CvMat mapMatrix = trans_mat;
cv2DRotationMatrix(center, degree, 1.0f, &mapMatrix);
map[2] += (widthRotate - width) / 2.0f;
map[5] += (heightRotate - height) / 2.0f;
dst_size = cv::Size(widthRotate, heightRotate);
}
std::vector<cv::Point> PointAffine(const std::vector<cv::Point>& points, const cv::Mat& trans_mat){
float *m = (float *)trans_mat.ptr<float>();
vector<Point> transPoints;
for(size_t i = 0; i < points.size(); i++)
{
Point p = points[i];
int x = p.x * m[0] + p.y * m[1] + m[2];
int y = p.x * m[3] + p.y * m[4] + m[5];
transPoints.push_back(Point(x, y));
}
return transPoints;
}
int main()
{
Mat img = imread("/data_2/everyday/1228/plane.png");
Point pt(285,67);
circle(img,pt,13,Scalar(0,0,255),2);
float angle = 32.5;
Mat M;
Mat img_rot, img_roi;
Size dst_size;
vector<Point> rot_points;
CalcRotateMatrix(img, angle, M, dst_size);
warpAffine(img, img_rot, M, dst_size, 1, 0, 0);
std::vector<cv::Point> points,points_rot;
points.push_back(pt);
points_rot = PointAffine(points, M);
Point pt_rot = points_rot[0];
circle(img_rot,pt_rot,13,Scalar(255,0,255),2);
imshow("img",img);
imshow("img_rot",img_rot);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
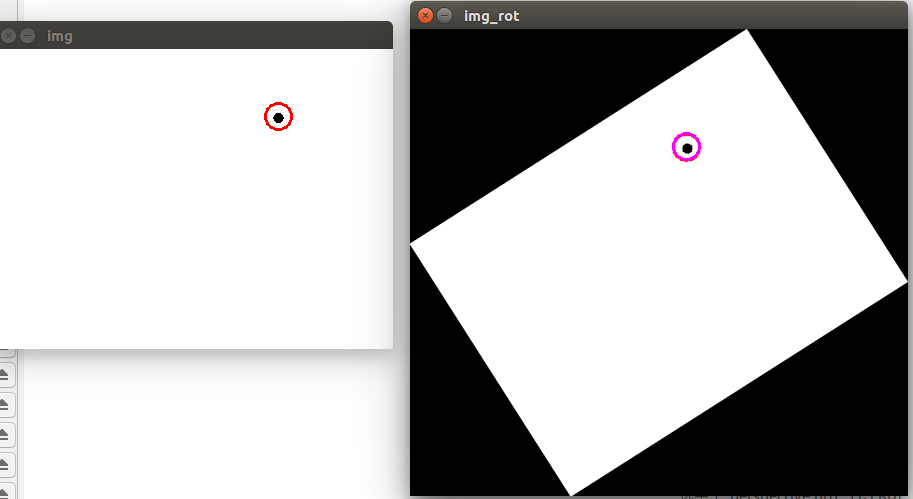
通过旋转角度可以求得旋转矩阵,然后原图中的一个点通过旋转矩阵可以对应到旋转之后的图。但是问题来了,已知旋转矩阵,旋转后的图上的一个点,能对应到原图上面去吗???
经过分析原图上面点通过防射变换矩阵旋转到旋转之后的图上,这段代码如下:
Point p = points[i];
int x = p.x * m[0] + p.y * m[1] + m[2];
int y = p.x * m[3] + p.y * m[4] + m[5];
我们现在是已知旋转矩阵,旋转后的图上的一个点,即x,y已知,所有m已知,要求的是p.x,p.y,二元一次方程组可以求出来。所以代码如下:
float *m = (float *)M.ptr<float>();
int xx = (m[4]*pt_rot.x-m[2]*m[4]-m[1]*pt_rot.y+m[1]*m[5])*1.0/MAX((m[0]*m[4]-m[1]*m[3]),0.01);
int yy = (pt_rot.y-m[5]-m[3]*xx)*1.0/MAX(m[4],0.01);
#include"opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include"opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void CalcRotateMatrix(const cv::Mat& img, float degree, cv::Mat& trans_mat, cv::Size& dst_size){
degree = fmod(degree + 360.0f, 360.0f);
double angle = degree * CV_PI / 180.;
int width = img.cols;
int height = img.rows;
double a = sin(angle), b = cos(angle);
int widthRotate = int(height * fabs(a) + width * fabs(b));
int heightRotate = int(width * fabs(a) + height * fabs(b));
// int widthRotate = width;
// int heightRotate = height;
// [ m0 m1 m2 ] ===> [ A11 A12 b1 ]
// [ m3 m4 m5 ] ===> [ A21 A22 b2 ]
trans_mat.create(2, 3, CV_32F);
float *map = (float *)trans_mat.ptr<float>();
CvPoint2D32f center = cvPoint2D32f(width / 2.0f, height / 2.0f);
CvMat mapMatrix = trans_mat;
cv2DRotationMatrix(center, degree, 1.0f, &mapMatrix);
map[2] += (widthRotate - width) / 2.0f;
map[5] += (heightRotate - height) / 2.0f;
dst_size = cv::Size(widthRotate, heightRotate);
}
std::vector<cv::Point> PointAffine(const std::vector<cv::Point>& points, const cv::Mat& trans_mat){
float *m = (float *)trans_mat.ptr<float>();
vector<Point> transPoints;
for(size_t i = 0; i < points.size(); i++)
{
Point p = points[i];
int x = p.x * m[0] + p.y * m[1] + m[2];
int y = p.x * m[3] + p.y * m[4] + m[5];
transPoints.push_back(Point(x, y));
}
return transPoints;
}
int main()
{
Mat img = imread("/data_2/everyday/1228/plane.png");
Point pt(285,67);
circle(img,pt,13,Scalar(0,0,255),2);
float angle = 32.5;
Mat M;
Mat img_rot, img_roi;
Size dst_size;
vector<Point> rot_points;
CalcRotateMatrix(img, angle, M, dst_size);
warpAffine(img, img_rot, M, dst_size, 1, 0, 0);
std::vector<cv::Point> points,points_rot;
points.push_back(pt);
points_rot = PointAffine(points, M);
Point pt_rot = points_rot[0];
circle(img_rot,pt_rot,13,Scalar(255,0,255),2);
float *m = (float *)M.ptr<float>();
int xx = (m[4]*pt_rot.x-m[2]*m[4]-m[1]*pt_rot.y+m[1]*m[5])*1.0/MAX((m[0]*m[4]-m[1]*m[3]),0.01);
int yy = (pt_rot.y-m[5]-m[3]*xx)*1.0/MAX(m[4],0.01);
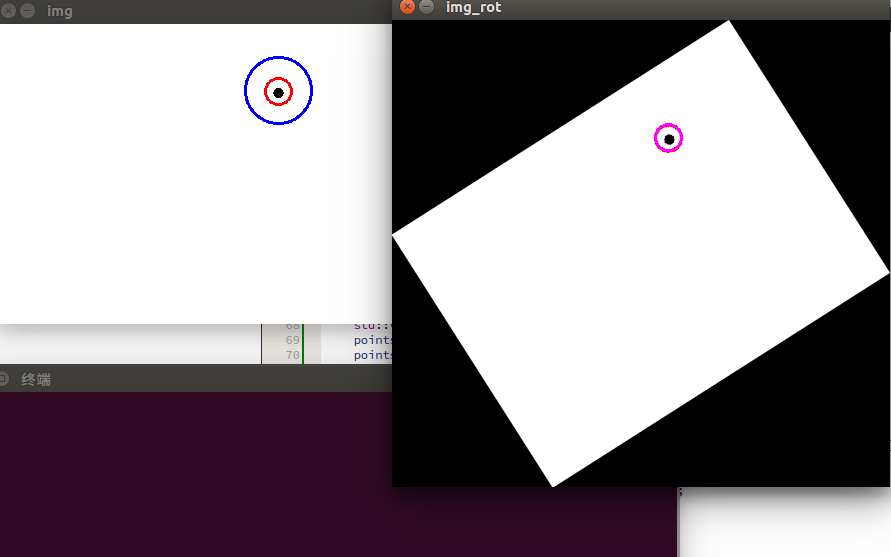
circle(img,Point(xx,yy),33,Scalar(255,0,0),2);
imshow("img",img);
imshow("img_rot",img_rot);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
好记性不如烂键盘---点滴、积累、进步!




