java 8 常用功能实践整理
1. 对象排序
void java.util.List.sort(Comparator<? super Apple> c);
int compare(T o1, T o2);
public static <T, U extends Comparable<? super U>> Comparator<T> comparing(
Function<? super T, ? extends U> keyExtractor);
default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action);
List<Apple> inventory = Arrays.asList(new Apple(80,"green"), new Apple(155, "green"), new Apple(120, "red")); //集合排序(倒序) inventory.sort((Apple a1,Apple a2) -> a2.getWeight().compareTo(a1.getWeight()));
//顺序排序
inventory.sort(Comparator.comparing(Apple::getWeight));
inventory.forEach(n -> System.out.println(n.toString()));
2. 集合过滤
//集合过滤 List<Apple> apples = inventory.stream().filter((Apple a) -> a.getColor().equals("green")).collect(Collectors.toList());
3. 修改集合元素内容
apples.forEach(n -> {//if(n.getWeight() == 120)
n.setWeight(333);
});
4. 读取文件
//中文问题 %e6%9d%a8%e9%a3%9e System.out.println(ExecuteAround.class.getClassLoader().getResource("lambdasinaction/chap3/data.txt").getPath()); System.out.println(ExecuteAround.class.getClassLoader().getResource("lambdasinaction/chap3/data.txt").toURI().getPath()); String result = processFileLimited(); System.out.println(result); System.out.println("---"); /** * lambda表达式用在函数式接口作为参数的方法中,用来替代函数式接口中的唯一的一个抽象方法,抽象方法签名和lambda表达式签名一致 */ String oneLine = processFile((BufferedReader b) -> b.readLine()); System.out.println(oneLine); String twoLines = processFile((BufferedReader b) -> b.readLine() + b.readLine()); System.out.println(twoLines); public static String processFileLimited() throws IOException, URISyntaxException { try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(ExecuteAround.class.getClassLoader().getResource("lambdasinaction/chap3/data.txt").toURI().getPath()))) { return br.readLine(); } } public static String processFile(BufferedReaderProcessor p) throws IOException, URISyntaxException { try(BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(ExecuteAround.class.getClassLoader().getResource("lambdasinaction/chap3/data.txt").toURI().getPath()))){ return p.process(br); } } public interface BufferedReaderProcessor{ public String process(BufferedReader b) throws IOException; }
5. 方法引用解析(不仅仅用于单参数lambda)
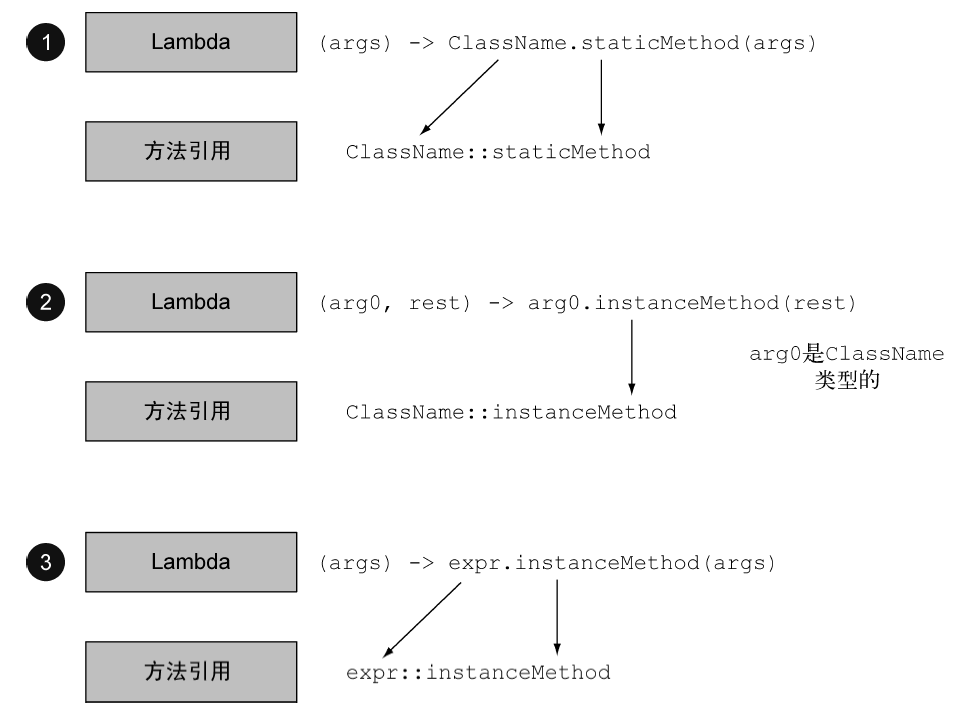
方法引用可以被看作仅仅调用特定方法的Lambda的一种快捷写法,如果一个Lambda代表的只是“直接调用这个方法”,那最好还是用名称来调用它,而不是去描述如何调用它.方法引用就是让你根据已有的方法实现来创建Lambda表达式,使用方法引用时,目标引用放在分隔符::前,方法的名称放在后面.
例如,Apple::getWeight就是引用了Apple类中定义的方法getWeight,方法引用就是Lambda表达式(Apple a) -> a.getWeight()的快捷写法。
方法引用其实和lambda是对应的,参数对应目标引用类型,返回值对应方法返回值.

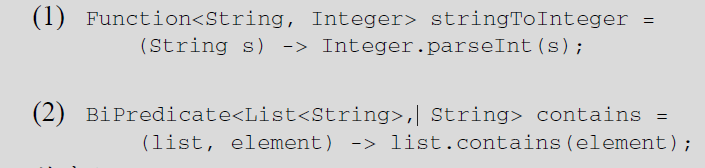
6. list 转 map java8分组
List<AttachPO> list = attachDao.findByTarget(toIds); Map<Long, List<Attach>> ret = new HashMap<>(); //list.stream().map(n -> BeanMapUtils.copy(n)).collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Attach::getId)); list.forEach(po -> { Attach a = BeanMapUtils.copy(po); List<Attach> ats = ret.get(a.getToId()); if (ats == null) { ats = new ArrayList<>(); ret.put(a.getToId(), ats); } ats.add(a); });
常用方式 代码如下: public Map<Long, String> getIdNameMap(List<Account> accounts) { return accounts.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Account::getId, Account::getUsername)); } 收集成实体本身map 代码如下: public Map<Long, Account> getIdAccountMap(List<Account> accounts) { return accounts.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Account::getId, account -> account)); } account -> account是一个返回本身的lambda表达式,其实还可以使用Function接口中的一个默认方法代替,使整个方法更简洁优雅: public Map<Long, Account> getIdAccountMap(List<Account> accounts) { return accounts.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Account::getId, Function.identity())); } 重复key的情况 代码如下: public Map<String, Account> getNameAccountMap(List<Account> accounts) { return accounts.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Account::getUsername, Function.identity())); } 这个方法可能报错(java.lang.IllegalStateException: Duplicate key),因为name是有可能重复的。toMap有个重载方法,可以传入一个合并的函数来解决key冲突问题: public Map<String, Account> getNameAccountMap(List<Account> accounts) { return accounts.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Account::getUsername, Function.identity(), (key1, key2) -> key2)); } 这里只是简单的使用后者覆盖前者来解决key重复问题。 指定具体收集的map toMap还有另一个重载方法,可以指定一个Map的具体实现,来收集数据: public Map<String, Account> getNameAccountMap(List<Account> accounts) { return accounts.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Account::getUsername, Function.identity(), (key1, key2) -> key2, LinkedHashMap::new)); }



