Spring 二:Spring Bean装配之XMl配置
概要
Bean中的装配,重点是:Bean配置项、Bean作用域、Bean生命周期、Bean的自动装配、Resources&ResourceLoader。
常用的配置项是:Id(IOC容器中的唯一标识)、Class(具体要实例化的类)、Scope(作用范围)、Constructor arguments(构造器参数)、Properties(属性)、Autowiring mode(自动装配模式)、lazy-initalization mode(懒初始化模式)、Initalization/destruction method(初始化/销毁方法)。
Bean作用域
singleton:单列模式,指每个容器只存在一份。
prototype:每次请求创建新的实例,destroy方式不生效
request:每次http请求创建一个实例只在当前的request有效。
session:同上,只是作用域不同。
global session:基于portlet的web有效,如果同web中同session。
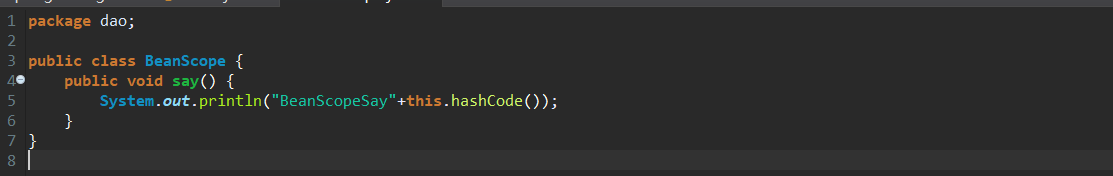
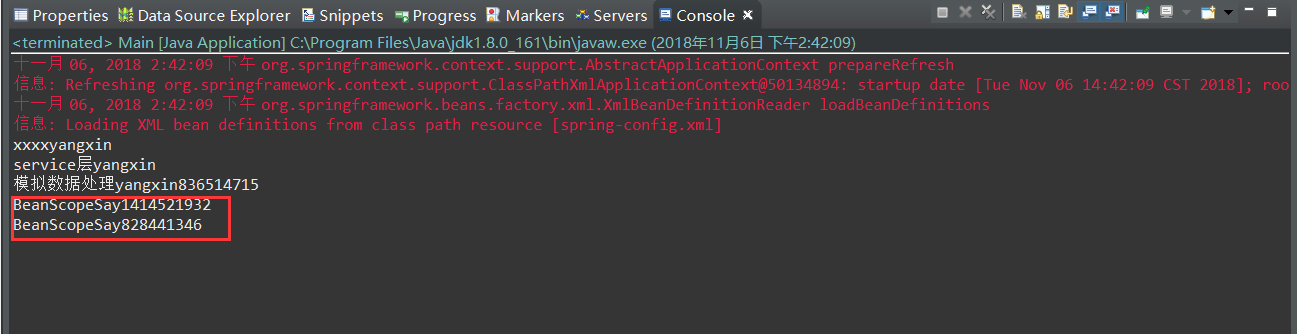
创建一个BeanScope类,输出hashCode,验证是不是新的实例。
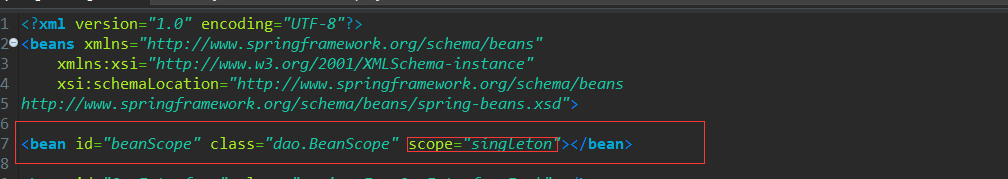
配置Spring-config.xml中的Bean,并设置scope为singleton
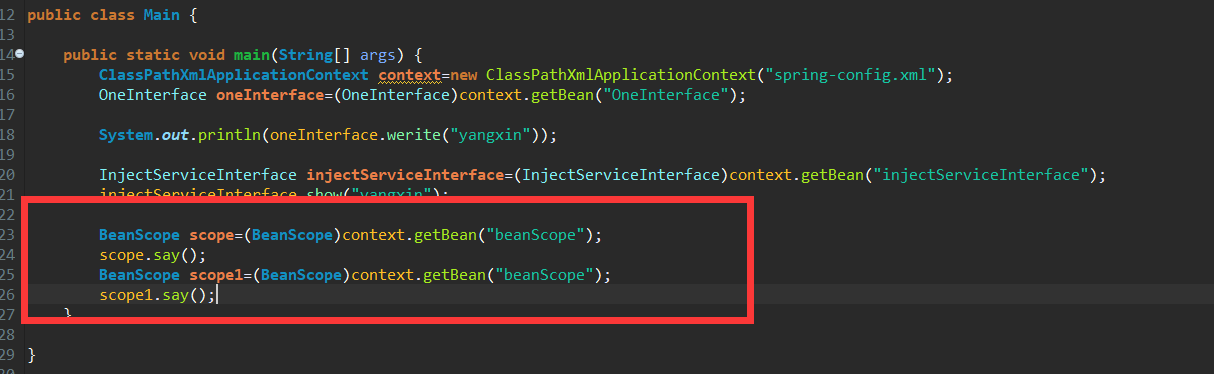
因为每个实例有一个确定的hashcode,所以我们验证两个实例的hashcode是不是相同,来确定singleton是不是有效的。
运行结果
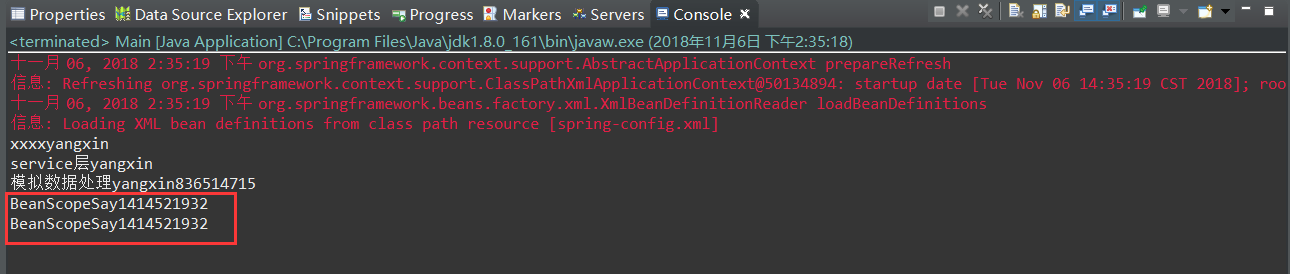
将Bean的Scope改成prototype后运行结果如下
Bean的生命周期
分为定义、初始化、使用、销毁;我们接下来值分析初始化和销毁。
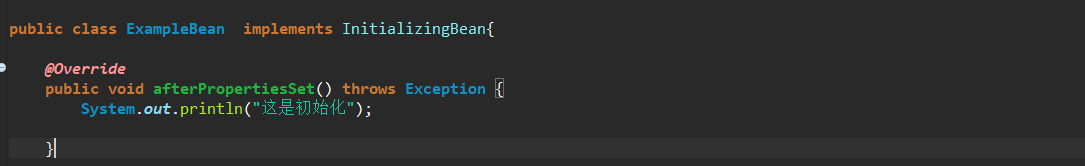
初始化
- 实现InitializingBean接口,覆盖他的afterPropertiesSet方法
- 配置init-method


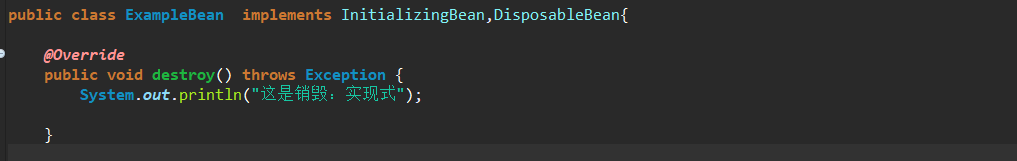
销毁
- 实现DisposableBean接口,覆盖destory方法
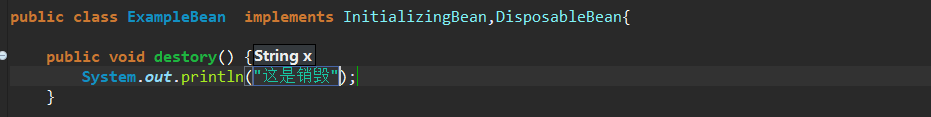
-
配置destory-method方法。

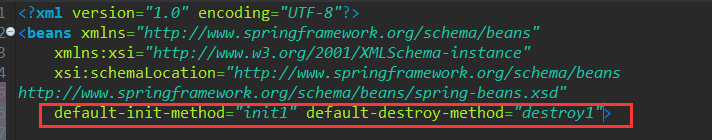
配置全局默认初始化、销毁方法
1 public class Main {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
5 /* OneInterface oneInterface=(OneInterface)context.getBean("OneInterface");
6
7 System.out.println(oneInterface.werite("yangxin"));
8
9 InjectServiceInterface injectServiceInterface=(InjectServiceInterface)context.getBean("injectServiceInterface");
10 injectServiceInterface.show("yangxin");
11
12 BeanScope scope=(BeanScope)context.getBean("beanScope");
13 scope.say();
14 BeanScope scope1=(BeanScope)context.getBean("beanScope");
15 scope1.say();*/
16
17 ExampleBean bean=(ExampleBean)context.getBean("exampleBean");
18
19 }
20
21 }
运行结果
这是初始化:实现式
这是初始化
结论:继承方式的先运行,配置init-method和destroy-method运行在后面,在一个Bean中只要实现了其中一种方式,全局默认初始销毁就不会执行。
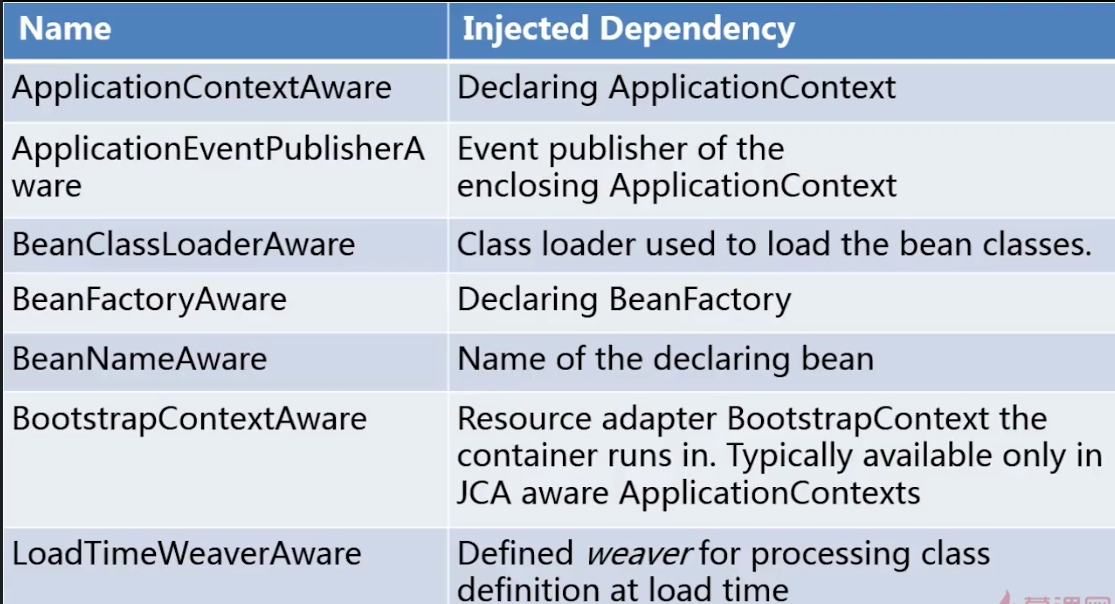
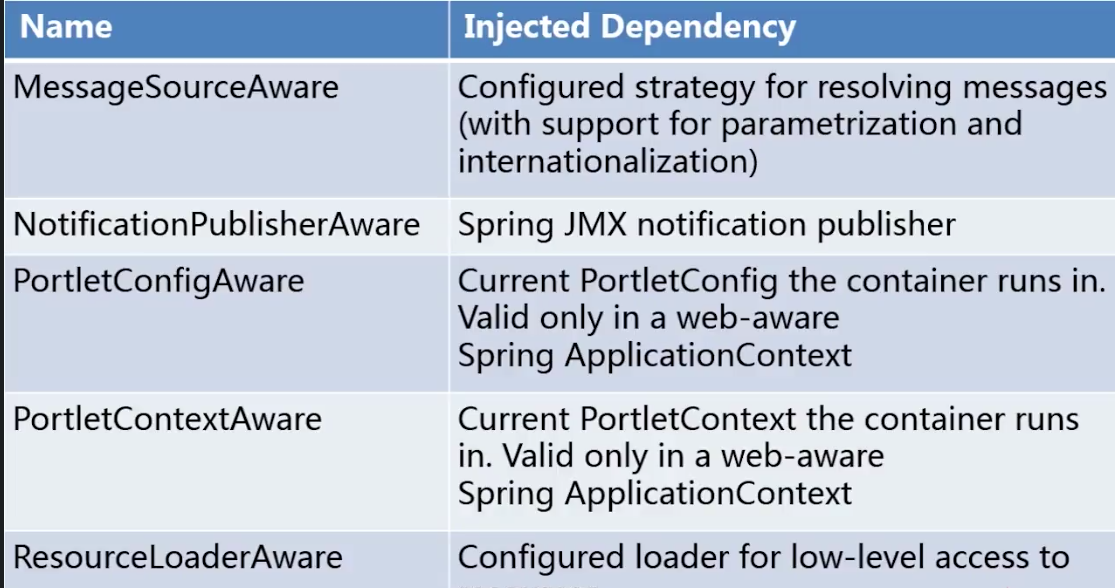
Aware
spring中提供一些Aware结尾的接口,实现了Aware接口的Bean在初始化之后,可以获得相应的资源。通过实现Aware接口,可以对Spring相应的资源进行操作(操作一定要慎重,随意改动有可能会出现灾难性的后果)。为Spring进行简单的扩展提供了方便的入口。
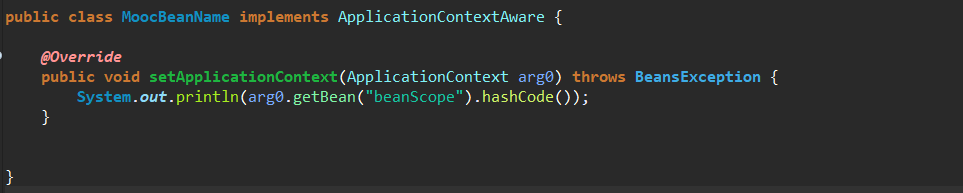
ApplicationContextAware,向实现了这个接口的Bean提供ApplicationContext实现这个接口的Bean配置到Spring的配置中去,并且由Spring容器去加载,这样才能实现这种效果,
BeanNameAware:和上述一样,只是提供的BeanName的资源。
例子:


Bean的自动装入
No:不做任何操作
byName:根据属性名自动装配。此选项将检查容器并根据名字查找属性完全一致的Bean,并将其与属性自动装配。
byType:如果容器存在一个与指定属性类型相同的bean,那么将与该属性自动装配,如果存在多个该类型的bean,将抛出异常,并指出不能使用byType自动装配;如果没有找到相应的Type什么事都不会发生。
Constructor:与byType类似,不同的是在于它应用于构造器参数,如果容器没有找到与构造器参数类型一致的bean会抛出异常。
用例
1 package dao; 2 3 public class AutowiringDao { 4 public void say(String str) { 5 System.out.println("Autowiring say"+str); 6 } 7 } 8 9 10 ////////////////////////////////////////////// 11 ////////////////////////////////////////////// 12 ////////////////////////////////////////////// 13 package service; 14 15 import dao.AutowiringDao; 16 17 public class AutowiringService { 18 19 private AutowiringDao dao; 20 21 public AutowiringService(AutowiringDao dao) { 22 this.dao=dao; 23 } 24 25 public void setDao(AutowiringDao dao) { 26 this.dao = dao; 27 } 28 29 30 31 public void say(String str) { 32 dao.say(str); 33 } 34 }
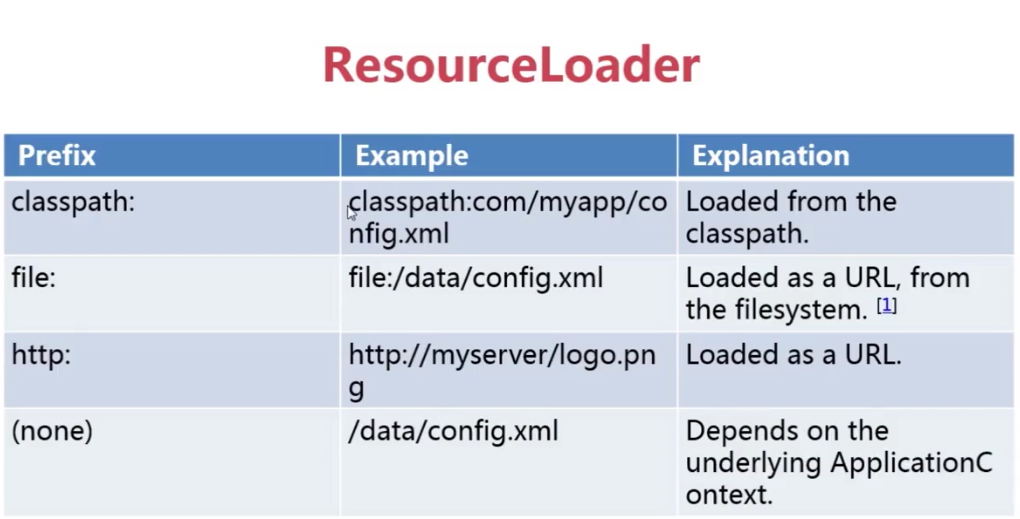
Resources
UrlResource:URL对应的资源,根据一个URL地址即可构建。
ClassPathResource:获取类路径下的资源文件。
FileSystemResource:获取文件系统里的资源。
ServletContextResource:ServletContext封装的资源,用于访问ServletContext环境下的资源。
InputStreamResource:针对输入流封装的资源。
ByteArrayResource:针对于字节数组封装的资源。
ResourceLoader:对Resource加载的类,IOC容器中,所有的ApplicationText都实现在这个家口中。
用例
1 package spring_Ioc;
2
3
4
5 import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
6 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
7 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
8 import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
9
10 public class Proresource implements ApplicationContextAware {
11 private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
12 @Override
13 public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext arg0) throws BeansException {
14 this.applicationContext=arg0;
15
16 }
17
18 public void resource() {
19 //Resource resource=(Resource) applicationContext.getResource("classpath:spring-config.xml");
20 Resource resource=(Resource) applicationContext.getResource("url:http://spring.io/projects/spring-framework");
21 System.out.println(resource.getFilename());
22 System.out.println(resource.getDescription());
23 }
24
25 }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
default-init-method="init1" default-destroy-method="destory1"
default-autowire="constructor">
<bean id="proResource" class="spring_Ioc.Proresource"></bean>
<bean id="dao" class="dao.AutowiringDao"></bean>
<bean id="autowiringService" class="service.AutowiringService"></bean>
<bean id="BeanName" class="dao.MoocBeanName"></bean>
<bean id="exampleBean" class="dao.ExampleBean" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory"></bean>
<bean id="beanScope" class="dao.BeanScope" scope="prototype"></bean>
<bean id="OneInterface" class="spring_Ioc.OneInterfaceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="injectDaoInterface" class="dao.InjectDaoInterfaceImpl"></bean>
<!-- <bean id="injectServiceInterface" class="service.InjectServiceInterfaceImpl">
<property name="injectDaoInterface" ref="injectDaoInterface"></property>
</bean>
-->
<bean id="injectServiceInterface" class="service.InjectServiceInterfaceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="injectDaoInterface" ref="injectDaoInterface"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
1 package test_class;
2
3 import org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContext;
4 import org.eclipse.jdt.internal.compiler.ast.SuperReference;
5 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
6
7 import dao.BeanScope;
8 import dao.ExampleBean;
9 import dao.MoocBeanName;
10 import service.AutowiringService;
11 import service.InjectServiceInterface;
12 import spring_Ioc.OneInterface;
13 import spring_Ioc.OneInterfaceImpl;
14 import spring_Ioc.Proresource;
15
16 public class Main {
17
18 public static void main(String[] args) {
19 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
20 /* OneInterface oneInterface=(OneInterface)context.getBean("OneInterface");
21
22 System.out.println(oneInterface.werite("yangxin"));
23
24 InjectServiceInterface injectServiceInterface=(InjectServiceInterface)context.getBean("injectServiceInterface");
25 injectServiceInterface.show("yangxin");
26
27 BeanScope scope=(BeanScope)context.getBean("bean-Scope");
28 scope.say();
29 BeanScope scope1=(BeanScope)context.getBean("beanScope");
30 scope1.say();*/
31
32 /* ExampleBean bean=(ExampleBean)context.getBean("exampleBean");
33
34 MoocBeanName name=(MoocBeanName)context.getBean("BeanName");*/
35
36 AutowiringService service=(AutowiringService)context.getBean("autowiringService");
37 service.say("bendan");
38
39 Proresource rProresource=(Proresource)context.getBean("proResource");
40 rProresource.resource();
41 }
42
43 }

