面试常见高频算法题总结
一、链表相关
1.链表反转
class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { // base case if(head == null || head.next == null) return head; ListNode first = head; ListNode result = null;//建立一个新的节点用来存放结果 ListNode second = null; while(first != null){ //遍历输入链表,开始处理每一个节点 second = first.next; //先处理第一个节点first,所以需要一个指针来存储first的后继 first.next = result; //将first放到新链表头节点的头部 result = first; //移动新链表的头指针,让它始终指向新链表头部 first = second; //继续处理原链表的节点,即之前指针存放的后继,循环往复 } return result; } }
3.判断链表是否有环
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */ public class Solution { public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {//设置快慢指针,若有环一定会在环里面相遇。否则会有null值 if(head==null) return false; ListNode walker = head; ListNode runner = head; while(runner.next!=null && runner.next.next!=null) { walker = walker.next; runner = runner.next.next; if(walker==runner) return true; } return false; } }
//也可以采用hashmap把每一个节点存储起来,如果地址相同则存在节点
二、数组、字符串巧妙解法相关
1.不使用除法实现除自身外数组元素的乘积(力扣 238)
public class Solution { public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) { int n = nums.length; int[] res = new int[n]; res[0] = 1; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { res[i] = res[i - 1] * nums[i - 1]; } int right = 1; for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) { res[i] *= right; right *= nums[i]; } return res; } }
二、树相关
1.给定一颗二叉搜索树,返回该二叉搜索树第K大的节点
//思路:二叉搜索树按照中序遍历的顺序打印出来正好就是排序好的顺序。 // 所以,按照中序遍历顺序找到第k个结点就是结果。 public class Solution { int index = 0; //计数器 TreeNode KthNode(TreeNode root, int k) { if(root != null){ //中序遍历寻找第k个 TreeNode node = KthNode(root.left,k); if(node != null) return node; index ++; if(index == k) return root; node = KthNode(root.right,k); if(node != null) return node; } return null; } }
2.二叉树最小深度
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ //为什么采用分治的思想而不是求数最大深度思想,因为可能为单链表(链表是特殊树)没法处理 class Solution { public int minDepth(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return 0; int left = minDepth(root.left); int right = minDepth(root.right); return (left == 0 || right == 0) ? left + right + 1//为什么可以写成left + right + 1 : Math.min(left,right) + 1; //因为left 跟right 必有一个为0,所以.. } }
3.二叉树最大深度
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) { return 0; } else{ return 1+ Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)); } } }
三、动态规划相关
1.两个字符串的最长公共子序列长度
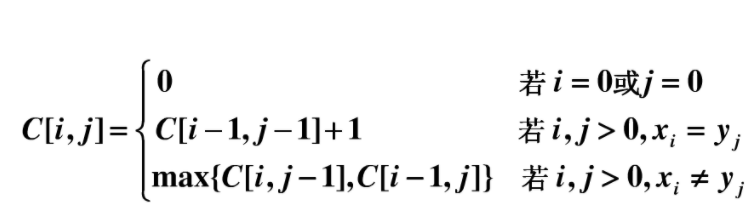
class Solution {
//dp[i][j]表示 0-(i-1) 0-(j-1)之间最长子序列 public int longestCommonSubsequence(String s1, String s2) { int[][] dp = new int[s1.length() + 1][s2.length() + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); ++i) for (int j = 0; j < s2.length(); ++j) if (s1.charAt(i) == s2.charAt(j)) dp[i + 1][j + 1] = 1 + dp[i][j]; else dp[i + 1][j + 1] = Math.max(dp[i][j + 1], dp[i + 1][j]); return dp[s1.length()][s2.length()]; } }
2.求连续子数组的最大和
class Solution { public static int maxSubArray(int[] A) { int maxSoFar=A[0], maxEndingHere=A[0]; for(int i=1;i<A.length;++i){ maxEndingHere = Math.max(A[i], maxEndingHere+A[i]); maxSoFar = Math.max(maxEndingHere, maxSoFar); } return maxSoFar; } }
四、排序
1.快排
public static void quickSort(int[] list, int left, int right) { if (left < right) { // 分割数组,找到分割点 int point = partition(list, left, right); // 递归调用,对左子数组进行快速排序 quickSort(list, left, point - 1); // 递归调用,对右子数组进行快速排序 quickSort(list, point + 1, right); } } /** * 分割数组,找到分割点 */ public static int partition(int[] list, int left, int right) { // 用数组的第一个元素作为基准数 int first = list[left]; while (left < right) { while (left < right && list[right] >= first) { right--; } // 交换 swap(list, left, right); while (left < right && list[left] <= first) { left++; } // 交换 swap(list, left, right); } // 返回分割点所在的位置 return left; } /** * 交换数组中两个位置的元素 */ public static void swap(int[] list, int left, int right) { int temp; if (list != null && list.length > 0) { temp = list[left]; list[left] = list[right]; list[right] = temp; } }
2.二路归并排序
public class MergeSort { /** * 归并排序(Merge Sort)与快速排序思想类似:将待排序数据分成两部分,继续将两个子部分进行递归的归并排序;然后将已经有序的两个子部分进行合并,最终完成排序。 * 其时间复杂度与快速排序均为O(nlogn),但是归并排序除了递归调用间接使用了辅助空间栈,还需要额外的O(n)空间进行临时存储。从此角度归并排序略逊于快速排序,但是归并排序是一种稳定的排序算法,快速排序则不然。 * 所谓稳定排序,表示对于具有相同值的多个元素,其间的先后顺序保持不变。对于基本数据类型而言,一个排序算法是否稳定,影响很小,但是对于结构体数组,稳定排序就十分重要。例如对于student结构体按照关键字score进行非降序排序: */ public static void main(String[] args) { int[] list = {50, 10, 90, 30, 70}; System.out.println("************归并排序************"); System.out.println("排序前:"); display(list); System.out.println("排序后:"); mergeSort(list, new int[list.length], 0, list.length - 1); display(list); } /** * 归并排序算法 * @param list 待排序的列表 * @param tempList 临时列表 * @param head 列表开始位置 * @param rear 列表结束位置 */ public static void mergeSort(int[] list, int[] tempList, int head, int rear) { if (head < rear) { // 取分割位置 int middle = (head + rear) / 2; // 递归划分列表的左序列 mergeSort(list, tempList, head, middle); // 递归划分列表的右序列 mergeSort(list, tempList, middle + 1, rear); // 列表的合并操作 merge(list, tempList, head, middle + 1, rear); } } /** * 合并操作(列表的两两合并) * @param list * @param tempList * @param head * @param middle * @param rear */ public static void merge(int[] list, int[] tempList, int head, int middle, int rear) { // 左指针尾 int headEnd = middle - 1; // 右指针头 int rearStart = middle; // 临时列表的下标 int tempIndex = head; // 列表合并后的长度 int tempLength = rear - head + 1; // 先循环两个区间段都没有结束的情况 while ((headEnd >= head) && (rearStart <= rear)) { // 如果发现右序列大,则将此数放入临时列表 if (list[head] < list[rearStart]) { tempList[tempIndex++] = list[head++]; } else { tempList[tempIndex++] = list[rearStart++]; } } // 判断左序列是否结束 while (head <= headEnd) { tempList[tempIndex++] = list[head++]; } // 判断右序列是否结束 while (rearStart <= rear) { tempList[tempIndex++] = list[rearStart++]; } // 交换数据 for (int i = 0; i < tempLength; i++) { list[rear] = tempList[rear]; rear--; } } /** * 遍历打印 */ public static void display(int[] list) { if (list != null && list.length > 0) { for (int num :list) { System.out.print(num + " "); } System.out.println(""); } } }
五、LRU LFU
1.lru采用双链表+hashmap实现
class LRUCache { int size; Node head,tail; HashMap<Integer,Node> hm; public LRUCache(int capacity) { size=capacity; head=tail=null; hm=new HashMap<>(); } public int get(int key) { if(!hm.containsKey(key)) { return -1; } else { Node ref=hm.get(key); if(ref==head) return ref.val; if(ref!=head && ref!=tail) { ref.Llink.Rlink=ref.Rlink; ref.Rlink.Llink=ref.Llink; } else if(ref!=head && ref==tail) { tail=tail.Llink; tail.Rlink=null; } ref.Llink=null; ref.Rlink=head; head.Llink=ref; head=ref; return ref.val; } } public void put(int key, int value) { if(hm.containsKey(key)) { hm.get(key).val=value; this.get(key); } else { Node temp=new Node(value,key); if(hm.size()<size) { hm.put(key,temp); if(head==null) { head=temp; tail=temp; } else { temp.Rlink=head; head.Llink=temp; head=temp; } } else { if(tail==head) { hm.remove(tail.key); hm.put(key,temp); head=tail=temp; } else { hm.remove(tail.key); hm.put(key,temp); Node help=tail; tail=tail.Llink; tail.Rlink=null; help.Llink=null; temp.Rlink=head; head.Llink=temp; head=temp; } } } } } class Node{ int val; int key; Node Rlink; Node Llink; Node(int val,int key) { this.key=key; this.val=val; Rlink=null; Llink=null; } }
2.lfu



