JDBC基础学习(三)—处理BLOB类型数据
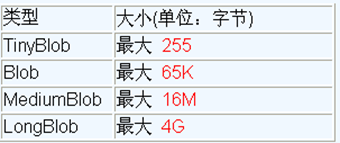
一、BLOB类型介绍
在MySQL中,BLOB是一个二进制的大型对象,可以存储大量数据的容器,它能容纳不同大小的数据。
在MySQL中有四种BLOB类型。
实际使用中根据需要存入的数据大小定义不同的BLOB类型。需要注意的是,如果存储的文件过大,数据库的性能会下降。
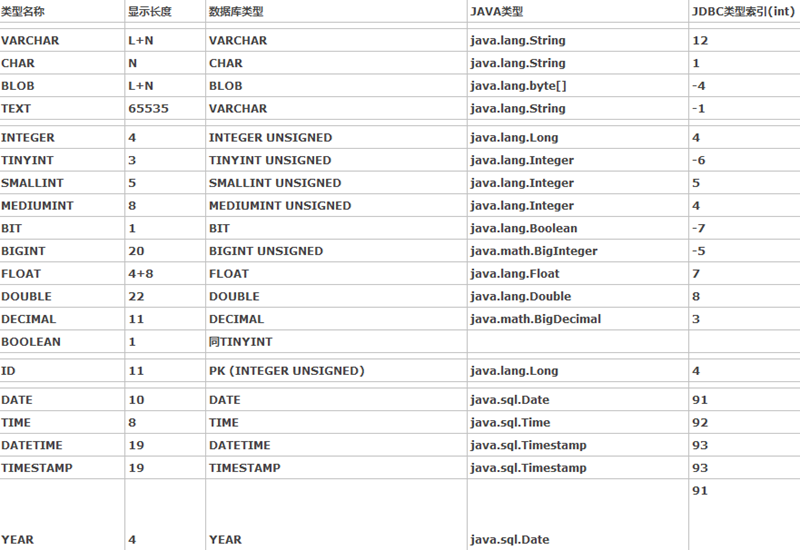
二、Java数据类型与MySQL类型对照表
对于blob,一般用于对图片的数据库存储,原理是把图片打成二进制,然后进行的一种存储方式,在java中对应byte[]数组。
对于boolen类型,在mysql数据库中,个人认为用int类型代替较好,对bit操作不是很方便,尤其是在具有web页面开发的项目中,表示0/1,对应java类型的Integer较好。
三、添加Blob到数据库
Person.java
public class Person{
private int id;
private String name;
private String city;
private int age;
private float salary;
private byte[] head;
public Person(){
super();
}
public Person(int id,String name,String city,int age,float salary,byte[] head){
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.city = city;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
this.head = head;
}
//...get、set方法
}
@Test
public void testAddPerson() throws Exception{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("1.jpg");
byte[] bs = inputStream2Byte(fis);
addPerson(new Person(0,"HeHe2","BJ",23,1300,bs));
}
/*
* 插入数据
*/
public static void addPerson(Person p) throws Exception{
String sql = "insert into person(id,name,city,age,salary,head) values(?,?,?,?,?,?)";
JdbcTools.update(sql,p.getId(),p.getName(),p.getCity(),p.getAge(),p.getSalary(),p.getHead());
}
/*
* 输入流转换为字节数组
* @param inStream
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static byte[] inputStream2Byte(InputStream inStream) throws Exception{
ByteArrayOutputStream outSteam = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while((len = inStream.read(buffer)) != -1){
outSteam.write(buffer,0,len);
}
outSteam.close();
inStream.close();
return outSteam.toByteArray();
}
JdbcTools.update()方法
/*
* 通用的增删改方法
* 执行SQL语句,使用PreparedStatemnt
* @param sql 带占位符的sql语句
* @param args 填写SQL占位符的可变参数
*/
public static void update(String sql,Object...args){
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
con = JdbcTools.getConnection();
ps = con.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i = 0;i < args.length;i++){
ps.setObject(i + 1,args[i]);
}
ps.execute();
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
JdbcTools.releaseResource(con,ps,rs);
}
}
结果:
在最后BLOb中右键另存为图片即可看到。
越努力,越幸运!