(四)SpringBoot与Web开发
1.简介
使用SpringBoot;
1.创建SpringBoot应用,选中我们需要的模块
2.SpringBoot已经默认将这些场景配置好了,只需要在配置文件中指定少量配置就可以运行起来
3.自己编写业务代码
自动配置原理?
这个场景SpringBoot帮我们配置了什么?能不能修改?能修改哪些配置?能不能扩展?
1 xxxAutoConfiguration:帮我们给容器中自动配置组件 2 xxxProperties:配置类来封装配置文件的内容
//可以设置和静态资源有关的参数,缓存时间
2.SpringBoot对静态资源的映射规则;
1 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false) 2 public class ResourceProperties implements ResourceLoaderAware { 3 //可以设置和静态资源有关的参数,缓存时间等
1 @Override 2 public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) { 3 if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) { 4 logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled"); 5 return; 6 } 7 Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod(); 8 CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache() 9 .getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl(); 10 if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) { 11 customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry 12 .addResourceHandler("/webjars/**") 13 .addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/") 14 .setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)) 15 .setCacheControl(cacheControl)); 16 } 17 String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(); 18 if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) { 19 customizeResourceHandlerRegistration( 20 registry.addResourceHandler(staticPathPattern) 21 .addResourceLocations(getResourceLocations( 22 this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations())) 23 .setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)) 24 .setCacheControl(cacheControl)); 25 } 26 }
1.所有/webjars/**,都去classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjar/找资源;
webjars:以jar包的方式引入静态资源
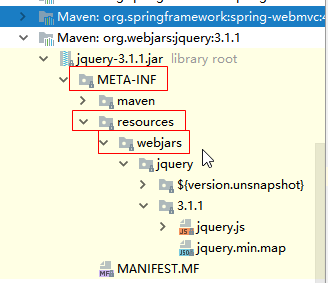
localhost:8080/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.js
<!-- 引入jquery-webjar -->在访问的时候只需要写webjars下面资源的名称即可 <dependency> <groupId>org.webjars</groupId> <artifactId>jquery</artifactId> <version>3.3.1</version> </dependency>
2."/**"访问当前项目的任何资源,(静态资源的文件夹)
1 "classpath:/META-INF/resources/", 2 "classpath:/resources/", 3 "classpath:/static/", 4 "classpath:/public/" 5 "/":当前项目的根路径
localhost:8080/abc ===> 去静态资源文件夹里面找abc
3.欢迎页;静态资源文件夹下的所有index.html页面;被"/**"映射;
localhost:8080/ 找index页面
4.所有的**/favicon.ico 都是在静态资源文件夹找
3.模板引擎
jsp、Velocity、Thymeleaf
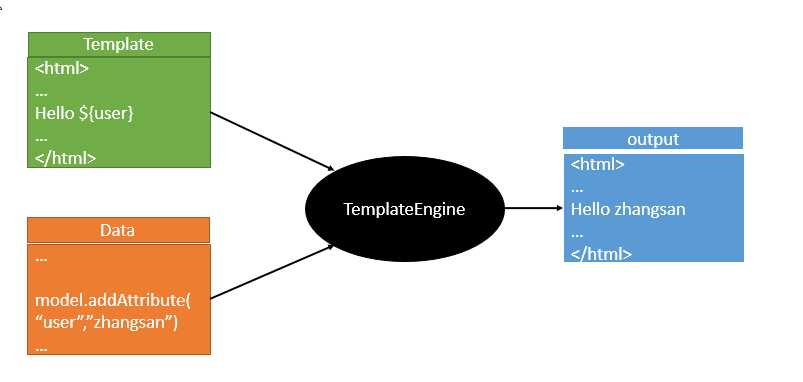
SpringBoot推荐的Thymeleaf
语法更简单,功能更强大
1.引入thymeleaf
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> 4 </dependency>
切换thymeleaf版本
<thymeleaf.version>3.0.9.RELEASE</thymeleaf.version> <!-- 布局功能的支持程序 thymeleaf3主程序 layout2以上版本 --> <!-- thymeleaf2 layout1 --> <thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>2.2.2</thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>
2.Thymeleaf使用&语法
1 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.thymeleaf") 2 public class ThymeleafProperties { 3 4 private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING = StandardCharsets.UTF_8; 5 6 public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/"; 7 8 public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
只要我们把HTML页面放在classpath:/templates/,thymeleaf就能自动渲染
使用:
1.导入thymeleaf的名称空间
1 <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
2.使用thymeleaf语法
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <h1>成功!</h1> 9 <!-- th:text 将div里面的文本内容设置为 --> 10 <div th:text="${hello}"></div> 11 </body> 12 </html>
3.语法规则
1.th:text;改变当前元素里面的文本内容
th:任意html属性;来替换原生属性的值
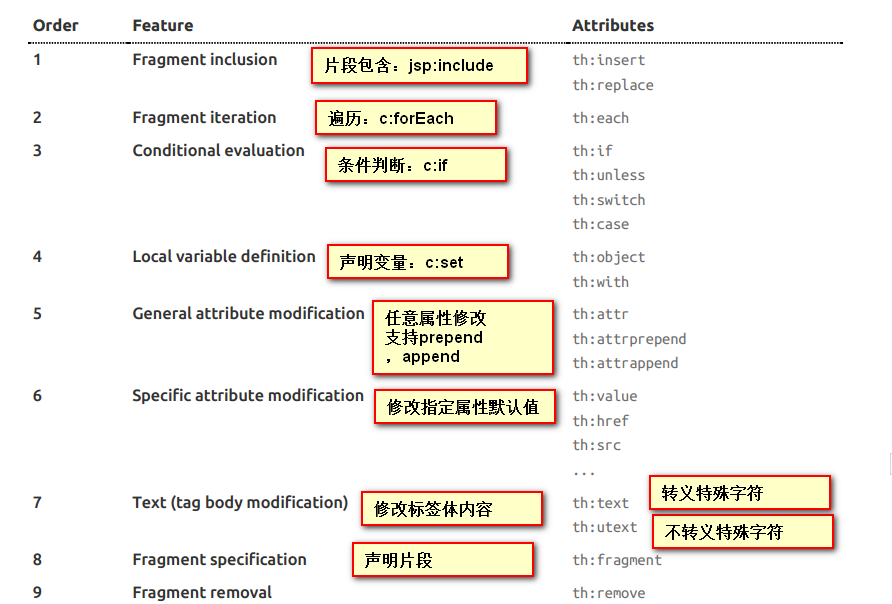
2.表达式
1 Simple expressions:(表达式语法) 2 Variable Expressions: ${...}:获取变量值;OGNL; 3 1)、获取对象的属性、调用方法 4 2)、使用内置的基本对象: 5 #ctx : the context object. 6 #vars: the context variables. 7 #locale : the context locale. 8 #request : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletRequest object. 9 #response : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletResponse object. 10 #session : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpSession object. 11 #servletContext : (only in Web Contexts) the ServletContext object. 12 13 ${session.foo} 14 3)、内置的一些工具对象: 15 #execInfo : information about the template being processed. 16 #messages : methods for obtaining externalized messages inside variables expressions, in the same way as they would be obtained using #{…} syntax. 17 #uris : methods for escaping parts of URLs/URIs 18 #conversions : methods for executing the configured conversion service (if any). 19 #dates : methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc. 20 #calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects. 21 #numbers : methods for formatting numeric objects. 22 #strings : methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc. 23 #objects : methods for objects in general. 24 #bools : methods for boolean evaluation. 25 #arrays : methods for arrays. 26 #lists : methods for lists. 27 #sets : methods for sets. 28 #maps : methods for maps. 29 #aggregates : methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections. 30 #ids : methods for dealing with id attributes that might be repeated (for example, as a result of an iteration). 31 32 Selection Variable Expressions: *{...}:选择表达式:和${}在功能上是一样; 33 补充:配合 th:object="${session.user}: 34 <div th:object="${session.user}"> 35 <p>Name: <span th:text="*{firstName}">Sebastian</span>.</p> 36 <p>Surname: <span th:text="*{lastName}">Pepper</span>.</p> 37 <p>Nationality: <span th:text="*{nationality}">Saturn</span>.</p> 38 </div> 39 40 Message Expressions: #{...}:获取国际化内容 41 Link URL Expressions: @{...}:定义URL; 42 @{/order/process(execId=${execId},execType='FAST')} 43 Fragment Expressions: ~{...}:片段引用表达式 44 <div th:insert="~{commons :: main}">...</div> 45 46 Literals(字面量) 47 Text literals: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,… 48 Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,… 49 Boolean literals: true , false 50 Null literal: null 51 Literal tokens: one , sometext , main ,… 52 Text operations:(文本操作) 53 String concatenation: + 54 Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}| 55 Arithmetic operations:(数学运算) 56 Binary operators: + , - , * , / , % 57 Minus sign (unary operator): - 58 Boolean operations:(布尔运算) 59 Binary operators: and , or 60 Boolean negation (unary operator): ! , not 61 Comparisons and equality:(比较运算) 62 Comparators: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le ) 63 Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne ) 64 Conditional operators:条件运算(三元运算符) 65 If-then: (if) ? (then) 66 If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else) 67 Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue) 68 Special tokens: 69 No-Operation: _
4.SpringMVC自动配置
1. Spring MVC auto-configuration
Spring Boot自动配置好了SpringMVC
以下是SpringBoot对SpringMVC的默认:
A.Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans
自动配置了ViewResolver(视图解析器:根据方法的返回值得到视图对象(View),视图对象决定如何渲染(转发?重定向))
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver :组合所有的视图解析器的;
如何定制:我们可以自己给容器中添加一个视图解析器;自动的将其组合进来
B.Support for serving static resource,including support for Webjars(see below).静态资源文件家路径webjars
C.Static index.html support.静态首页访问
D.Custom Fvicon support(see below).favicon.ico
E.自动注册了 Converter,GenericConverter,Formatter beans
Converter:转换器;public String hello(User user):类型转换使用Converter
Formatter:格式化器;2017-12-17===Date;
@Bean @Override public FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService() { WebConversionService conversionService = new WebConversionService( this.mvcProperties.getDateFormat()); addFormatters(conversionService); return conversionService; }
自己添加的格式化器转换器,我们只需要放在容器中即可
F.Support for HttpMessageConverters(see below).
HttpMessageConverter:SpirngMVC用来转换Http请求和响应的;User---json;
HttpMessageConverters是从容器中确定;获取所有的HttpMessageConverter;
自己给容器中添加HttpMessageConverter,只需要将自己的组件注册容器中(@Bean,@Component)
G.MessageCodesResolver
定义错误代码生成规则
H.ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer
我们可以配置一个ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer来替换默认的;(添加到容器)
1 初始化WebDataBinder;
2 请求数据=====JavaBean;
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web:web的所有自动场景;
2. 扩展SpringMVC
<mvc:view-controller path="/hello" view-name="success"/> <mvc:interceptors> <mvc:interceptor> <mvc:mapping path="/hello"/> <bean></bean> </mvc:interceptor> </mvc:interceptors>
编写一个配置类(@Configuration),是WebMvcConfigurerAdapter类型;不能标注@EnableWebMvc
即保留了所有的自动配置,也能用我们扩展的配置
1 //使用WebMvcConfigurerAdapter可以扩展SpringMVC的功能 2 @Configuration 3 public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { 4 5 @Override 6 public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { 7 //super.addViewControllers(registry); 8 //浏览器发送 /young 请求,来到success页面 9 registry.addViewController("/young").setViewName("success"); 10 } 11 }
原理:
1.WebMvcAutoConfiguration是SpingMVC的自动配置类
2.在做其他自动配置时会导入:@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
1 @Configuration 2 public static class EnableWebMvcConfiguration extends DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration { 3 private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite(); 4 5 //从容器中获取所有的WebMvcConfigurer 6 @Autowired(required = false) 7 public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) { 8 if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) { 9 this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers); 10 //一个参考实现;将所有的WebMvcConfigurer相关配置都来一起调用; 11 @Override 12 // public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { 13 // for (WebMvcConfigurer delegate : this.delegates) { 14 // delegate.addViewControllers(registry); 15 // } 16 } 17 } 18 }
3.容器中所有的WebMvcConfigurer 都会一起起作用
4.我们的配置类也会被调用
效果:SpringMVC的自动配置和我们的扩展配置都会起作用
3. 全面接管SpringMVC
SpringBoot对SpringMVC的自动配置不需要了,所有都是我们自己配;所有的SpringMVC的自动配置都失效了
我们需要在配置类中添加@EnableWebMvc即可;
1 //使用WebMvcConfigurerAdapter可以扩展SpringMVC的功能 2 @EnableWebMvc 3 @Configuration 4 public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { 5 6 @Override 7 public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { 8 //super.addViewControllers(registry); 9 //浏览器发送 /young 请求,来到success页面 10 registry.addViewController("/young").setViewName("success"); 11 } 12 }
原理:
为什么@EnableWebMvc自动配置就失效了?
1.EnableWebMvc的核心
1 @Import(DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class) 2 public @interface EnableWebMvc { 3 }
2.
1 @Configuration 2 public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
3.
1 @Configuration 2 @ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET) 3 @ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class }) 4 //容器中没有这个组件的时候,这个自动配置类才生效 5 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class) 6 @AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10) 7 @AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, 8 ValidationAutoConfiguration.class }) 9 public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
4.@EnableWebMvc将WebMvcConfigurationSupport这个组件导入进来了;
5.导入的WebMvcConfigurationSupport只是SpringMVC最基本的功能;
5.如何修改SpringBoot的默认配置
模式:
1.SpringBoot在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(@Bean、@Component)如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有,才自动配置;如果有些组件可以有多个(ViewResolver)将用户配置的和自己默认的组合起来;
2.在SpringBoot中会有非常多的xxxConfigurer帮助我们进行扩展配置
3.在SpringBoot中会有很多的xxxCustomizer帮助我们进行定制配置
6.RestfulCRUD
1.默认访问首页
1 //使用WebMvcConfigurerAdapter可以来扩展SpringMVC的功能 2 //@EnableWebMvc 不要接管SpringMVC 3 @Configuration 4 public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { 5 6 @Override 7 public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { 8 // super.addViewControllers(registry); 9 //浏览器发送 /atguigu 请求来到 success 10 registry.addViewController("/atguigu").setViewName("success"); 11 } 12 13 //所有的WebMvcConfigurerAdapter组件都会一起起作用 14 @Bean //将组件注册在容器 15 public WebMvcConfigurerAdapter webMvcConfigurerAdapter(){ 16 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter adapter = new WebMvcConfigurerAdapter() { 17 @Override 18 public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { 19 registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("login"); 20 registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("login"); 21 } 22 }; 23 return adapter; 24 } 25 }
2.国际化
1.编写国际化配置文件
2.使用ResourceBundleMessageSource管理国际化资源文件
3.在页面使用fmt:message取出国家化内容
步骤:
1.编写国家化配置文件,抽取页面需要显示的国家化消息
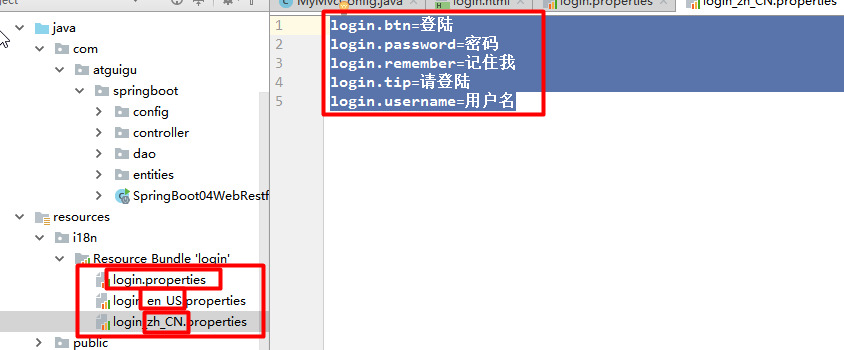
2.SpringBoot自动配置好了管理国际化资源文件的组件
1 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.messages") 2 public class MessageSourceAutoConfiguration { 3 4 /** 5 * Comma-separated list of basenames (essentially a fully-qualified classpath 6 * location), each following the ResourceBundle convention with relaxed support for 7 * slash based locations. If it doesn't contain a package qualifier (such as 8 * "org.mypackage"), it will be resolved from the classpath root. 9 */ 10 private String basename = "messages"; 11 //我们的配置文件可以直接放在类路径下叫messages.properties; 12 13 @Bean 14 public MessageSource messageSource() { 15 ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource(); 16 if (StringUtils.hasText(this.basename)) { 17 //设置国际化资源文件的基础名(去掉语言国家代码的) 18 messageSource.setBasenames(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray( 19 StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(this.basename))); 20 } 21 if (this.encoding != null) { 22 messageSource.setDefaultEncoding(this.encoding.name()); 23 } 24 messageSource.setFallbackToSystemLocale(this.fallbackToSystemLocale); 25 messageSource.setCacheSeconds(this.cacheSeconds); 26 messageSource.setAlwaysUseMessageFormat(this.alwaysUseMessageFormat); 27 return messageSource; 28 }
3.去页面获取国际化的值
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> 3 <head> 4 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> 5 <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no"> 6 <meta name="description" content=""> 7 <meta name="author" content=""> 8 <title>Signin Template for Bootstrap</title> 9 <!-- Bootstrap core CSS --> 10 <link href="asserts/css/bootstrap.min.css" th:href="@{/webjars/bootstrap/4.0.0/css/bootstrap.css}" rel="stylesheet"> 11 <!-- Custom styles for this template --> 12 <link href="asserts/css/signin.css" th:href="@{/asserts/css/signin.css}" rel="stylesheet"> 13 </head> 14 15 <body class="text-center"> 16 <form class="form-signin" action="dashboard.html"> 17 <img class="mb-4" th:src="@{/asserts/img/bootstrap-solid.svg}" src="asserts/img/bootstrap-solid.svg" alt="" width="72" height="72"> 18 <h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal" th:text="#{login.tip}">Please sign in</h1> 19 <label class="sr-only" th:text="#{login.username}">Username</label> 20 <input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="Username" th:placeholder="#{login.username}" required="" autofocus=""> 21 <label class="sr-only" th:text="#{login.password}">Password</label> 22 <input type="password" class="form-control" placeholder="Password" th:placeholder="#{login.password}" required=""> 23 <div class="checkbox mb-3"> 24 <label> 25 <input type="checkbox" value="remember-me"/> [[#{login.remember}]] 26 </label> 27 </div> 28 <button class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" type="submit" th:text="#{login.btn}">Sign in</button> 29 <p class="mt-5 mb-3 text-muted">© 2017-2018</p> 30 <a class="btn btn-sm">中文</a> 31 <a class="btn btn-sm">English</a> 32 </form> 33 34 </body> 35 36 </html>
效果:根据浏览器语言设置的信息切换了国际化
原理:
国际化Locale(区域信息对象);LocaleResolver(获取区域信息对象)
1 @Bean 2 @ConditionalOnMissingBean 3 @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc", name = "locale") 4 public LocaleResolver localeResolver() { 5 if (this.mvcProperties 6 .getLocaleResolver() == WebMvcProperties.LocaleResolver.FIXED) { 7 return new FixedLocaleResolver(this.mvcProperties.getLocale()); 8 } 9 AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver localeResolver = new AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver(); 10 localeResolver.setDefaultLocale(this.mvcProperties.getLocale()); 11 return localeResolver; 12 }//默认的就是根据请求头带来的区域信息获取Locale进行国家化
4.点击链接切换国际化
1 /** 2 * 可以在连接上携带区域信息 3 */ 4 public class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver { 5 6 @Override 7 public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) { 8 String l = request.getParameter("l"); 9 Locale locale = Locale.getDefault(); 10 if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(l)){ 11 String[] split = l.split("_"); 12 locale = new Locale(split[0],split[1]); 13 } 14 return locale; 15 } 16 17 @Override 18 public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) { 19 20 } 21 } 22 23 24 @Bean 25 public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){ 26 return new MyLocaleResolver(); 27 } 28 }
3.登陆
开发期间模板引擎页面修改以后,要实时生效
1.禁用模板引擎的缓存
1 # 禁用缓存 2 spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
2.页面修改完成以后ctrl+F9,重新编译
登陆错误消息的显示
1 <!-- 判断 --> 2 <p style="color: red;" th:text="${msg}" th:if="${not #strings.isEmpty(msg)}"></p>
3.连接器进行登陆检查
1 /** 2 * 登陆检查 3 */ 4 public class LoginHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { 5 6 //目标方法执行之前 7 @Override 8 public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { 9 Object user = request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser"); 10 if(user == null){ 11 //未登陆,返回登陆页面 12 request.setAttribute("msg","没有权限请先登陆"); 13 request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html").forward(request,response); 14 return false; 15 }else{ 16 //已登录,放行请求 17 return true; 18 } 19 } 20 21 }
4.注册拦截器
//所有的WebMvcConfigurerAdapter组件都会一起其作用 @Bean//将组件注册在容器中 public WebMvcConfigurerAdapter webMvcConfigurerAdapter(){ WebMvcConfigurerAdapter webMvcConfigurerAdapter = new WebMvcConfigurerAdapter(){ @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("login"); registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("login"); registry.addViewController("/main.html").setViewName("dashboard"); } //注册拦截器 @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { //静态资源: *.css,*.js //SpringBoot已经做好了静态资源映射 registry.addInterceptor(new LoginHandlerInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**") .excludePathPatterns("/index.html","/","/user/login"); } }; return webMvcConfigurerAdapter; }
5.员工列表-CRUD
要求:
1.RestfulCRUD:CRUD满足Rest风格;
URI:/资源名称/资源标识 HTTP请求方式区分对资源CRUD操作
| 普通CRUD(uri来区分操作) | RestfulCRUD:CRUD | |
| 查询 | getEmp | emp---GET |
| 添加 | addEMP?xxx | emp---POST |
| 修改 | updateEmp?id=xxx&xxx=xxx | emp/{id}---PUT |
| 删除 | deleteEmp?id=1 | emp/{id}---DELETE |
2.实验请求架构
| 请求URI | 请求方式 | |
| 查询所有员工 | emps | GET |
| 查询某个员工(来到修改页面) | emp/{id} | GET |
| 来到添加页面 | emp | GET |
| 添加员工 | emp | POST |
| 来到修改页面(查出员工进行信息回显) | emp/{id} | GET |
| 修改员工 | emp | PUT |
| 删除员工 | emp/{id} | DELETE |
3.员工列表:
thymeleaf公共页面元素抽取
1 1、抽取公共片段 2 <div th:fragment="copy"> 3 © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery 4 </div> 5 6 2、引入公共片段 7 <div th:insert="~{footer :: copy}"></div> 8 ~{templatename::selector}:模板名::选择器 9 ~{templatename::fragmentname}:模板名::片段名 10 11 3、默认效果: 12 insert的公共片段在div标签中 13 如果使用th:insert等属性进行引入,可以不用写~{}: 14 行内写法可以加上:[[~{}]];[(~{})];
三种引入公共片段的th属性:
a.th:insert,将公共片段整个插入到声明引入的元素中
b.th:replace,将声明引入的元素替换为公共片段
c.th:include,将被引入的片段的内容包含进这个标签中
1 <footer th:fragment="copy"> 2 © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery 3 </footer> 4 5 引入方式 6 <div th:insert="footer :: copy"></div> 7 <div th:replace="footer :: copy"></div> 8 <div th:include="footer :: copy"></div> 9 10 效果 11 <div> 12 <footer> 13 © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery 14 </footer> 15 </div> 16 17 <footer> 18 © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery 19 </footer> 20 21 <div> 22 © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery 23 </div>
7.错误处理机制
1)、SpringBoot默认的错误处理机制
默认效果:
1)、返回一个默认的错误页面
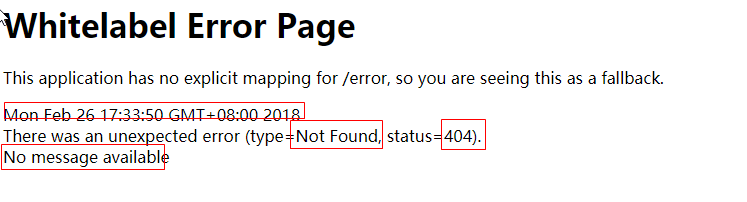
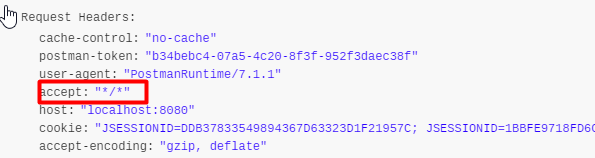
浏览器发送请求的请求头:
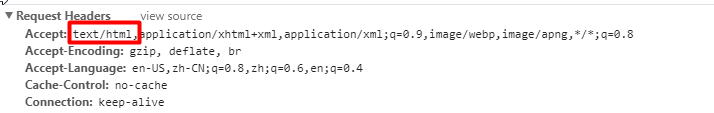
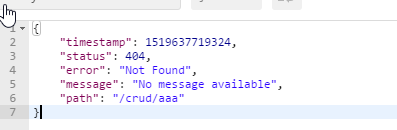
2)、如果是其他客户端,默认响应一个json数据
原理:
可以参照ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration;错误处理的自动配置;
给容器中添加了一下组件
1、DefaultErrorAttributes;
帮我们在页面共享信息; @Override public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(RequestAttributes requestAttributes,boolean includeStackTrace) { Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>(); errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date()); addStatus(errorAttributes, requestAttributes); addErrorDetails(errorAttributes, requestAttributes, includeStackTrace); addPath(errorAttributes, requestAttributes); return errorAttributes; }
2、BasicErrorController;处理默认/error请求
1 @Controller 2 @RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}") 3 public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
1 @RequestMapping(produces = "text/html")//产生html类型的数据,浏览器发送的请求来到这个方法处理 2 public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, 3 HttpServletResponse response) { 4 HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); 5 Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes( 6 request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML))); 7 response.setStatus(status.value());
//去哪个页面作为错误页面;包含页面地址和页面内容 8 ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model); 9 return (modelAndView != null ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model)); 10 } 11 12 @RequestMapping 13 @ResponseBody //产生json数据,其他客户端来到这个方法处理 14 public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) { 15 Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, 16 isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL)); 17 HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); 18 return new ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>>(body, status); 19 }
3、ErrorPageCustomizer;
1 @Value("${error.path:/error}") 2 private String path = "/error";系统出现错误以后来到error请求进行处理;()web.xml注册的错误页面规则)
4、DefaultErrorViewResolver;
1 @Override 2 public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, 3 Map<String, Object> model) { 4 ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status), model); 5 if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) { 6 modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model); 7 } 8 return modelAndView; 9 } 10 11 private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) { 12 //默认SpringBoot可以去找到一个页面? error/404 13 String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName; 14 15 //模板引擎可以解析这个页面地址就用模板引擎解析 16 TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders 17 .getProvider(errorViewName, this.applicationContext); 18 if (provider != null) { 19 //模板引擎可用的情况下返回到errorViewName指定的视图地址 20 return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model); 21 } 22 模板引擎不可以用,就在静态资源文件夹下找errorViewName对应的页面 error/404 23 return resolveResource(errorViewName, model); 24 }
步骤:
一旦系统出现4xx或者5xx之类的错误:ErrorPageCustomizer就会生效(定制错误的响应规则);就会来到/error请求;就会被BasicErrorController处理;
1)、响应页面;去哪个页面是由DefaultErrorViewResolver解析得到的
1 protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, 2 HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) { 3 //所有的ErrorViewResolver得到ModelAndView 4 for (ErrorViewResolver resolver : this.errorViewResolvers) { 5 ModelAndView modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model); 6 if (modelAndView != null) { 7 return modelAndView; 8 } 9 } 10 return null; 11 }
2)、如何定制错误响应:
1)、如何定制错误的页面;
1)、有模板引擎的情况下;error/状态码;【将错误页面命名为 错误状态码.html放在模板引起文件夹里面的error文件下】,发生此状态码的错误就会来到对应的页面;
我们可以使用4xx和5xx作为错误页面的文件夹名来匹配这种类型的所有错误,精确优先(优先寻找精确的状态码.html)
页面能获取的信息;
timestamp:时间戳
status:状态码
error:错误提示
exception:异常对象
message:异常消息
errors:JSR303数据
2)、没有模板引擎(模板引擎找不到这个错误页面),静态资源文件夹下找;
3)、以上都没有错误页面,就是默认来到SpringBoot默认的错误提示页面
2)、如何定制错误的json数据;
1)、自定义异常处理&返回定制json数据;
1 @ControllerAdvice 2 public class MyExceptionHandler { 3 4 @ResponseBody 5 @ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class) 6 public Map<String,Object> handleException(Exception e){ 7 8 Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); 9 map.put("code","user.notexist"); 10 map.put("message",e.getMessage()); 11 12 return map; 13 } 14 15 }//没有自适应效果...
2)、转发到/error进行自适应响应效果处理
1 @ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class) 2 public String handleException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request){ 3 4 Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); 5 //传入我们自己的错误状态码 4xx 5xx,否则就不会进入定制错误页面的解析流程 6 /* 7 Integer statusCode = (Integer) request 8 .getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code"); 9 */ 10 request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code",500); 11 map.put("code","user.notexist"); 12 map.put("message",e.getMessage()); 13 //转发到/error 14 return "forward:/error"; 15 } 16 17 }
3)、将我们的定制数据携带出去;
出现错误以后,会来到/error请求,会被BasicErrorController处理,响应出去可以获取的数据是由getErrorAttributes得到的(是AbstractErrorController(ErrorController)规定的方法);
1)、完全来编写一个ErrorController的实现类(或者是编写AbstractErrorController的子类),放在容器中;
2)、页面上能用的数据,或者是json返回能用的数据都是通过errorAttributes.getErrorAttributes得到;容器中DefaultErrorAtrributes.getErrorAttributes默认进行数据处理的;
自定义ErrorAttributes
1 //给容器中加入我们自己定义的ErrorAttributes 2 @Component 3 public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes{ 4 5 @Override 6 public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(RequestAttributes requestAttributes, boolean includeStackTrace) { 7 Map<String, Object> map = super.getErrorAttributes(requestAttributes, includeStackTrace); 8 map.put("company","youngyoung"); 9 return map; 10 } 11 }
最终的效果:响应是自适应的,可以通过定制ErrorAttributes改变需要返回的内容
8、配置嵌入式Servlet
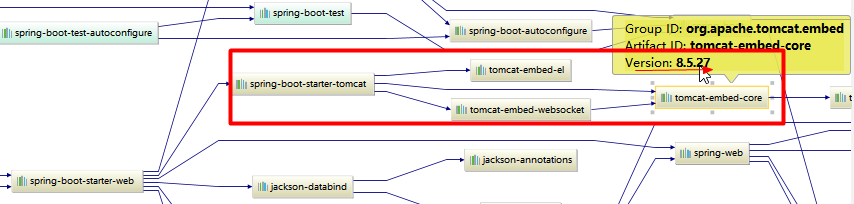
SpringBoot默认使用Tomcat作为嵌入式的Servlet容器
问题?
1)、如何定制和修改Servlet容器的相关配置;
1、修改和server有关的配置(ServerProperties【也是EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer】)
1 server.port=8081 2 server.context-path=/young 3 4 server.tomcat.uri-encoding=utf-8 5 6 //通用的Servlet容器设置 7 server.xxx 8 //Tomcat的设置 9 server.tomcat.xxx
2、编写一个EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer:嵌入式的Servlet容器的定制器;来修改Servlet容器的配置
1 @Bean 2 public EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer embeddedServletContainerCustomizer(){ 3 return new EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer() { 4 5 //定制嵌入式的Servlet容器相关的规则 6 @Override 7 public void customize(ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer container) { 8 container.setPort(8083); 9 } 10 }; 11 }
2)、注册Servlet三大组件【Servlet、Filter、Listener】
由于SpringBoot默认是以jar包的方式启动嵌入式的Servlet容器来启动SpringBoot的web应用,没有web.xml文件.
注册三大组件用以下方式
ServletRegistrationBean
1 @Bean 2 public ServletRegistrationBean myServlet(){ 3 ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new MyServlet(),"/myServlet"); 4 return registrationBean; 5 }
FilterRegistrationBean
1 @Bean 2 public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter(){ 3 FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean(); 4 filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(new MyFilter()); 5 filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/hello","/myservlet")); 6 return filterRegistrationBean; 7 }
ServletListenerRegistrationBean
1 @Bean 2 public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener(){ 3 ServletListenerRegistrationBean<MyListener> registrationBean = new ServletListenerRegistrationBean<>(new MyListener()); 4 registrationBean.setListener(new MyListener()); 5 return registrationBean; 6 }
SpringBoot帮我们自动SpringMVC的时候,自动的注册SpringMVC的前端控制器;DispatcherServlet;
1 @Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME) 2 @ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME) 3 public ServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistration( 4 DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet) { 5 ServletRegistrationBean registration = new ServletRegistrationBean( 6 dispatcherServlet, this.serverProperties.getServletMapping()); 7 //默认拦截: / 所有请求;包静态资源,但是不拦截jsp请求; /*会拦截jsp 8 //可以通过server.servletPath来修改SpringMVC前端控制器默认拦截的请求路径 9 10 registration.setName(DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME); 11 registration.setLoadOnStartup( 12 this.webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup()); 13 if (this.multipartConfig != null) { 14 registration.setMultipartConfig(this.multipartConfig); 15 } 16 return registration; 17 }
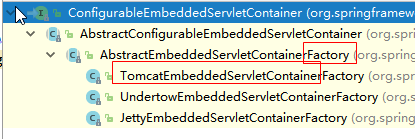
3)、替换为其他嵌入式Servlet容器
默认支持:
Tomcat(默认使用)
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 4 引入web模块默认就是使用嵌入式的Tomcat作为Servlet容器; 5 </dependency>
Jetty
1 <!-- 引入web模块 --> 2 <dependency> 3 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 4 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 5 <exclusions> 6 <exclusion> 7 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> 8 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 9 </exclusion> 10 </exclusions> 11 </dependency> 12 13 <!--引入其他的Servlet容器--> 14 <dependency> 15 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId> 16 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 17 </dependency>
Undertow
1 <!-- 引入web模块 --> 2 <dependency> 3 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 4 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 5 <exclusions> 6 <exclusion> 7 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> 8 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 9 </exclusion> 10 </exclusions> 11 </dependency> 12 13 <!--引入其他的Servlet容器--> 14 <dependency> 15 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId> 16 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 17 </dependency>
4)、嵌入式Servlet容器自动配置原理
EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration:嵌入式的Servlet容器自动配置?
1 @AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE) 2 @Configuration 3 @ConditionalOnWebApplication 4 @Import(BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class) 5 //导入BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar:Spring注解版;给容器中导入一些组件 6 //导入了EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor: 7 //后置处理器:bean初始化前后(创建完对象,还没赋值赋值)执行初始化工作 8 public class EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration { 9 10 @Configuration 11 @ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Tomcat.class })//判断当前是否引入了Tomcat依赖; 12 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EmbeddedServletContainerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)//判断当前容器没有用户自己定义EmbeddedServletContainerFactory:嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂;作用:创建嵌入式的Servlet容器 13 public static class EmbeddedTomcat { 14 15 @Bean 16 public TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory tomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory() { 17 return new TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory(); 18 } 19 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * Nested configuration if Jetty is being used. 24 */ 25 @Configuration 26 @ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Server.class, Loader.class, 27 WebAppContext.class }) 28 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EmbeddedServletContainerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) 29 public static class EmbeddedJetty { 30 31 @Bean 32 public JettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory jettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory() { 33 return new JettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory(); 34 } 35 36 } 37 38 /** 39 * Nested configuration if Undertow is being used. 40 */ 41 @Configuration 42 @ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Undertow.class, SslClientAuthMode.class }) 43 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EmbeddedServletContainerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) 44 public static class EmbeddedUndertow { 45 46 @Bean 47 public UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory undertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory() { 48 return new UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory(); 49 } 50 51 }
1)、EmbeddedServletContainerFactory(嵌入式Servlet容器工厂)
1 public interface EmbeddedServletContainerFactory { 2 3 /** 4 * Gets a new fully configured but paused {@link EmbeddedServletContainer} instance. 5 * Clients should not be able to connect to the returned server until 6 * {@link EmbeddedServletContainer#start()} is called (which happens when the 7 * {@link ApplicationContext} has been fully refreshed). 8 * @param initializers {@link ServletContextInitializer}s that should be applied as 9 * the container starts 10 * @return a fully configured and started {@link EmbeddedServletContainer} 11 * @see EmbeddedServletContainer#stop() 12 */ 13 EmbeddedServletContainer getEmbeddedServletContainer(//获取嵌入式的Servlet容器 14 ServletContextInitializer... initializers); 15 16 }
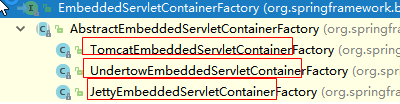
2)、EmbeddedServletContainer(嵌入式的Servlet容器)
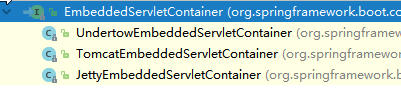
3)、以TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory为例
1 @Override 2 public EmbeddedServletContainer getEmbeddedServletContainer( 3 ServletContextInitializer... initializers) { 4 //创建一个Tomcat 5 Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat(); 6 7 //配置Tomcat的基本环节 8 File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory 9 : createTempDir("tomcat")); 10 tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath()); 11 Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol); 12 tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector); 13 customizeConnector(connector); 14 tomcat.setConnector(connector); 15 tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false); 16 configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine()); 17 for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) { 18 tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector); 19 } 20 prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers); 21 22 //将配置好的Tomcat传入进去,返回一个EmbeddedServletContainer;并且启动Tomcat服务器 23 return getTomcatEmbeddedServletContainer(tomcat); 24 }
4)、我们对嵌入式容器的配置修改是怎么生效的?
1 ServerProperties、EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer
EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer:定制器帮我们修改了Servlet容器的配置?
怎么修改的原理?
5)、容器中导入了EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor
1 //初始化之前 2 @Override 3 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) 4 throws BeansException { 5 //如果当前初始化的是一个ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer类型的组件 6 if (bean instanceof ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer) { 7 // 8 postProcessBeforeInitialization((ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer) bean); 9 } 10 return bean; 11 } 12 13 private void postProcessBeforeInitialization( 14 ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer bean) { 15 //获取所有的定制器,调用每一个定制器的customize方法来给Servlet容器进行属性赋值; 16 for (EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer customizer : getCustomizers()) { 17 customizer.customize(bean); 18 } 19 } 20 21 private Collection<EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer> getCustomizers() { 22 if (this.customizers == null) { 23 // Look up does not include the parent context 24 this.customizers = new ArrayList<EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer>( 25 this.beanFactory 26 //从容器中获取所有这葛类型的组件:EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer 27 //定制Servlet容器,给容器中可以添加一个EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer类型的组件 28 .getBeansOfType(EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer.class, 29 false, false) 30 .values()); 31 Collections.sort(this.customizers, AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE); 32 this.customizers = Collections.unmodifiableList(this.customizers); 33 } 34 return this.customizers; 35 } 36 37 ServerProperties也是定制器
步骤:
1)、SpringBoot根据导入的依赖情况,给容器中添加相应的EmbeddedServletContainerFactory【TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory】
2)、容器中某个组件要创建对象就会惊动后置处理器;EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor;
只要是嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂,后置处理器就工作
3)、后置处理器,从容器中获取所有的EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer,调用定制器的定制方法
5)、嵌入式Servlet容器启动原理;
什么时候创建嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂?什么时候获取嵌入式的Servlet容器并启动Tomcat;
获取嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂:
1)、SpringBoot应用启动运行run方法
2)、refreshContext(context);SpringBoot刷新IOC容器【创建IOC容器对象,并初始化容器,创建容器中的每一个组件】;如果是web应用创建AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext,否则创建AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext
3)、refresh(context)刷新刚才创建好的Ioc容器
1 public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { 2 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { 3 // Prepare this context for refreshing. 4 prepareRefresh(); 5 6 // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. 7 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); 8 9 // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. 10 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); 11 12 try { 13 // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. 14 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); 15 16 // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. 17 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); 18 19 // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. 20 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); 21 22 // Initialize message source for this context. 23 initMessageSource(); 24 25 // Initialize event multicaster for this context. 26 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); 27 28 // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. 29 onRefresh(); 30 31 // Check for listener beans and register them. 32 registerListeners(); 33 34 // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. 35 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); 36 37 // Last step: publish corresponding event. 38 finishRefresh(); 39 } 40 41 catch (BeansException ex) { 42 if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { 43 logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + 44 "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); 45 } 46 47 // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. 48 destroyBeans(); 49 50 // Reset 'active' flag. 51 cancelRefresh(ex); 52 53 // Propagate exception to caller. 54 throw ex; 55 } 56 57 finally { 58 // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we 59 // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... 60 resetCommonCaches(); 61 } 62 } 63 }
4)、onRefresh();web的ioc容器重写了onRefresh方法
5)、webioc容器会创建嵌入式的Servlet容器;createEmbeddedServletContainer();
6)、获取嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂:
EmbeddedServletContainerFactory containerFactory = getEmbeddedServletContainerFactory();
从IOC容器中获取EmbeddedServletContainerFactory 组件;
TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory创建对象,后置处理器一看是这个对象,就获取所有的定制器来先定制Servlet容器的相关配置;
7)、使用容器工厂获取嵌入式的Servlet容器:
this.embeddedServletContainer = containerFactory.getEmbeddedServletContainer(getSelfInitializer());
8)、嵌入式的Servlet容器创建对象并启动Servlet容器;
先启动嵌入式的Servlet容器,再将ioc容器中剩下没有创建出的对象获取出来;
IOC容器启动创建嵌入式的Servlet容器
9、使用外置的Servlet容器
嵌入式Servlet容器:应用打成可执行的jar
优点:简单、便携;
缺点:默认不支持JSP、优化定制比较复杂(使用定制器【ServerProperties、自定义EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer】,自己编写嵌入式Servlet容器的创建工厂【EmbeddedServletContainerFactory】);
外置的Servlet容器:外面安装Tomcat---应用war包的方式打包;
步骤:
1)、必须创建一个war项目;(利用idea创建好目录结构)
2)、将嵌入式的Tomact指定为provided;
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId><scope>provided</scope></dependency>
3)、必须编写一个SpringBootServletInitializer的子类,并调用configure方法
1 public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer { 2 3 @Override 4 protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) { 5 return application.sources(SpringBoot04WebJspApplication.class);//需要传入SpringBoot应用的主程序 6 } 7 8 }
4)、启动服务器就可以使用;
原理
jar包:执行SpringBoot主类的main方法,启动ioc容器,再来创建嵌入式的Servlet容器;
war包:启动服务器,服务器启动SpringBoot应用【SpringBootServletInitializer 】,启动ioc容器;
servlet3.0:
规则:
1)、服务器启动(web应用启动)会创建当前web应用里面每一个jar包里面ServletContainerInitializer实例;
2)、ServletContainerInitializer的实现放在jar包的META-INF/services文件夹下,有一个名为javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer的文件,内容就是ServletContainerInitializer的实现类的全类名
3)、还可以使用@HandlesTypes,在应用启动的时候加载我们感兴趣的类;
流程:
1)、启动Tomcat
2)、org\springframework\spring-web\4.3.18.RELEASE\spring-web-4.3.18.RELEASE.jar!\META-INF\services\javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer
Spring的web模块里面有个这个文件:org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
3)、ServletContainerInitializer将@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)标注的所有类型的类都传入到onStartup放发的Set<Class<?>>;为这些WebApplicationInitializer类型的类创建实例;
4)、每一个WebApplicationInitializer都调用自己的onStartup;
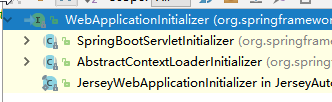
5)、相当于我们的SpringBootServletInitializer的类会被创建对象,并执行onStartup方法
6)、SpringBootServletInitializer实例执行onStartup的时候会创建createRootApplicationContext;创建容器
1 protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext( 2 ServletContext servletContext) { 3 //1、创建SpringApplicationBuilder 4 SpringApplicationBuilder builder = createSpringApplicationBuilder(); 5 StandardServletEnvironment environment = new StandardServletEnvironment(); 6 environment.initPropertySources(servletContext, null); 7 builder.environment(environment); 8 builder.main(getClass()); 9 ApplicationContext parent = getExistingRootWebApplicationContext(servletContext); 10 if (parent != null) { 11 this.logger.info("Root context already created (using as parent)."); 12 servletContext.setAttribute( 13 WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, null); 14 builder.initializers(new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(parent)); 15 } 16 builder.initializers( 17 new ServletContextApplicationContextInitializer(servletContext)); 18 builder.contextClass(AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext.class); 19 20 //调用configure方法,子类重写了这个方法,将SpringBoot的主程序类传入了进来 21 builder = configure(builder); 22 23 //使用builder创建一个Spring应用 24 SpringApplication application = builder.build(); 25 if (application.getSources().isEmpty() && AnnotationUtils 26 .findAnnotation(getClass(), Configuration.class) != null) { 27 application.getSources().add(getClass()); 28 } 29 Assert.state(!application.getSources().isEmpty(), 30 "No SpringApplication sources have been defined. Either override the " 31 + "configure method or add an @Configuration annotation"); 32 // Ensure error pages are registered 33 if (this.registerErrorPageFilter) { 34 application.getSources().add(ErrorPageFilterConfiguration.class); 35 } 36 //启动Spring应用 37 return run(application); 38 }
7)、Spring的应用就启动并且创建IOC容器
1 public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { 2 StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); 3 stopWatch.start(); 4 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; 5 FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null; 6 configureHeadlessProperty(); 7 SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); 8 listeners.starting(); 9 try { 10 ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments( 11 args); 12 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, 13 applicationArguments); 14 Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); 15 context = createApplicationContext(); 16 analyzers = new FailureAnalyzers(context); 17 prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, 18 printedBanner); 19 20 //刷新IOC容器 21 refreshContext(context); 22 afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); 23 listeners.finished(context, null); 24 stopWatch.stop(); 25 if (this.logStartupInfo) { 26 new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass) 27 .logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); 28 } 29 return context; 30 } 31 catch (Throwable ex) { 32 handleRunFailure(context, listeners, analyzers, ex); 33 throw new IllegalStateException(ex); 34 } 35 }
启动Servlet容器,再启动SpringBoot应用


