java并发编程——CompletableFuture
简介
Java的java.util.concurrent包中提供了并发相关的接口和类,本文将重点介绍CompletableFuture并发操作类
JDK1.8新增CompletableFuture该类
Class CompletableFuture<T>
java.lang.Object
java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture<T>
All Implemented Interfaces:
CompletionStage <T>, Future <T>
可见源码中,CompletableFuture是个泛型类,意味着,肯定有地方能够传入或返回所指定的泛型类对象,在java8源码中
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> {
volatile Object result; // Either the result or boxed AltResult
volatile Completion stack; // Top of Treiber stack of dependent actions
...//部分源代码省略
}
在JDK1.8的源码中,我们看见,在类定义下,最前面两个代码,定义了两个volatile的变量,我们都知道volatile变量,主要有两个作用
1.保证变量在不同线程之间的可见性,修改该变量系统会及时刷新到主内存,各线程读取的时候从主内存中读取;
2.禁止指令重排序,通过内存屏障的方式禁止指令被编译优化后的重排序。
它所实现的两个接口:Future
1.Future接口
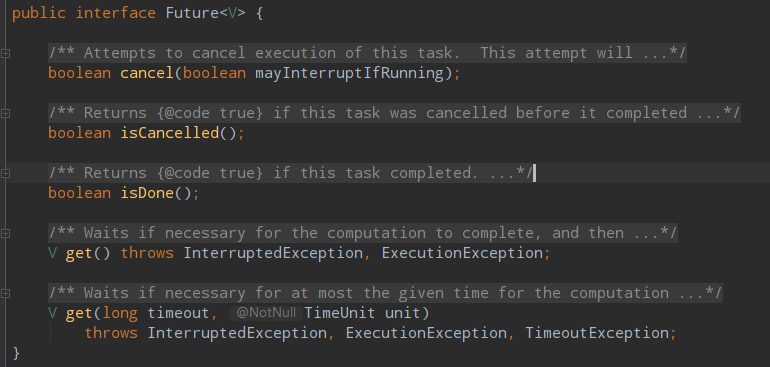
Future接口,在java多线程编程中用到很多,综合来看主要有两个方向上会用到
1.通过另外一个线程运行,并带返回值,通过future的方式传回返回值
2.程序在主线程中新建并运行新的线程后,主线程需要拿到结果,可以通过future.get阻塞的方式等待线程运行结束并拿回结果。
2.CompletionStage接口
这个主要提供异步线程任务提交、运行的管理,future主要是异步线程运行结果的管理。
综合来看CompletableFuture
1.创建任务
由于CompletableFuture中JDK8版本出来的,所以对JDK8有了非常好的支持
runAsync(Runnable)
supplyAsync(Supplier)
等等
2.获取任务结果
get()方法,获取返回值的时候,如果任务没有运行完成,则阻塞并一直等到任务结束并返回结果,而在这中间,如果持有这个completableFutre对象可以通过completableFuture.compleate(T)来手动地将结果返回get,并唤醒调用get()线程,任务线程即使运行完再返回去也接受不到了,因为已经被compleate提前返回结果了。
getNow(T vluaeIfAbsent),当调用此方法的时候,如果任务已经完成,则直接拿到返回值,如果没有则获取预设定的值,而线程运行状态不会发生改变
实例
get和getNow的区别
get阻塞代码,只到任务运行完成返回结果或者直到有人调用compleate(T)
public static void main(String[] args) {
//通过这种方式来创建一个复杂的Student并返回
CompletableFuture<Student> studentCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//为了模拟复杂情行
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new Student("yan", 50);
});
//如果任务没有结束,就调用getNow的话,则返回getNow方法传入的内容
Student student = studentCompletableFuture.getNow(new Student("wang",20));
System.out.println(student.getAge());//输出20
try {
Thread.sleep(6000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
student = studentCompletableFuture.getNow(new Student("wang",20));
System.out.println(student.getAge());//输出50
}
get和compleate(T)使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
//通过这种方式来创建一个复杂的Student并返回
CompletableFuture<Student> studentCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//为了模拟复杂情行
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("我能不能运行到?");
return new Student("yan", 50);
});
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
executorService.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
studentCompletableFuture.complete(new Student("wang", 25));
});
executorService.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Student student = studentCompletableFuture.get();
System.out.println(student.getAge());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Student student = studentCompletableFuture.get();
System.out.println(student.getAge());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
执行输出结果
ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-2
25
我能不能运行到?
main
25


