小学四则运算生成器(Java) 刘少允,梁新男
项目相关要求
- 使用 -n 参数控制生成题目的个数。(实现)
- 使用 -r 参数控制题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围。(实现)
- 生成的题目中计算过程不能产生负数。(实现)
- 生成的题目中如果存在形如e1 ÷ e2的子表达式,那么其结果应是真分数。(实现)
- 每道题目中出现的运算符个数不超过3个。(实现)
- 程序一次运行生成的题目不能重复。(实现)
- 在生成题目的同时,计算出所有题目的答案,并存入执行程序的当前目录下的Answers.txt文件。(实现)
- 程序应能支持一万道题目的生成。(实现)
- 程序支持对给定的题目文件和答案文件,判定答案中的对错并进行数量统计。(实现)
效能分析
一开始使用的是ArrayList来存储算式中的数字和符号的,并且整个算式的结构也是一个ArrayList,程序生成10000条算式平均需要4s以上。后来发现在生成优先运算符表中由于过多的修改list的结构导致效率下降,因此后来对于大量用到add和remove操作的地方,把ArrayList换成LinkedList结构,使得生成10000条算式从4s提升到平均1.3s。
使用了链表结构后,生成1000条算式大约需要12ms:
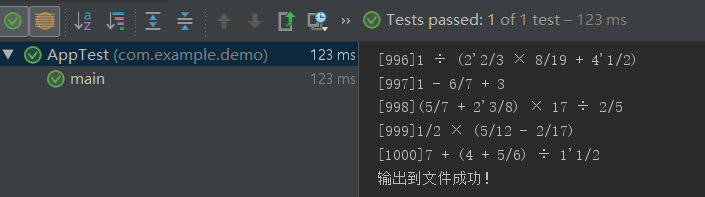
生成10000条算式大约需要1.3s左右
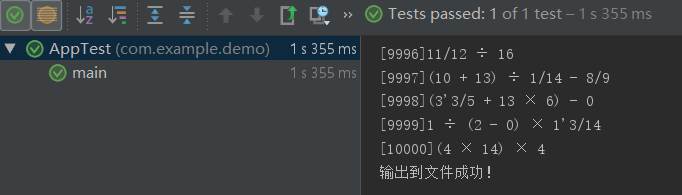
生成100000条算式平均需要1m17s:
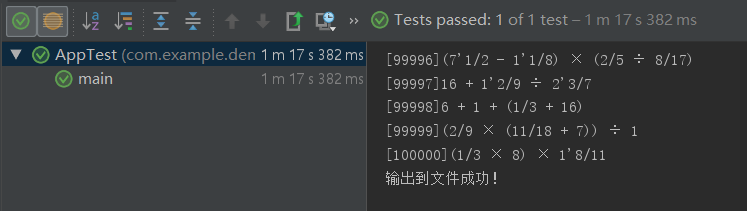
设计实现过程
- 四则运算题目生成
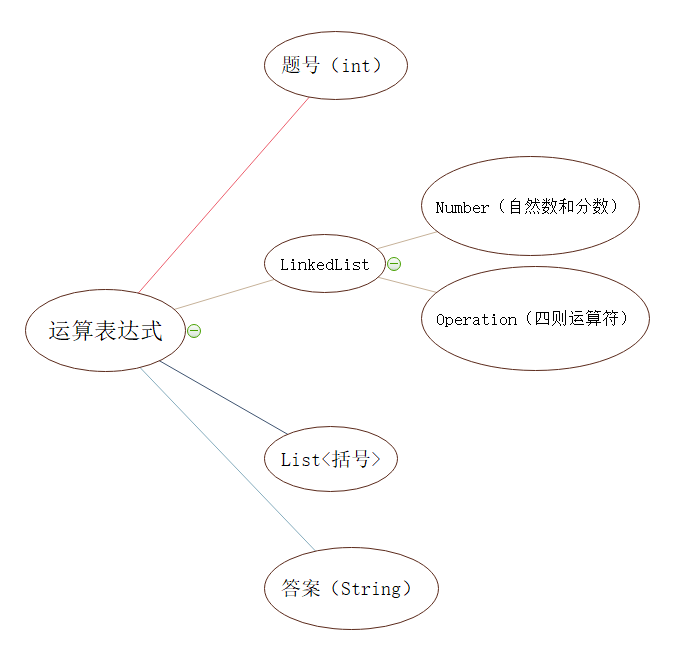
在这个程序中运算式的结构主要由链表构成
整体结构如下图所示:
![]()
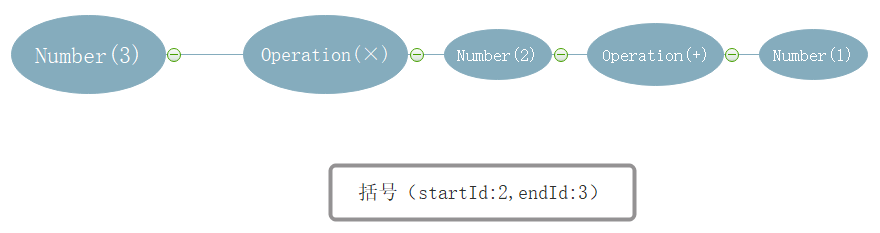
比如3 ×(2+1)的结构:
![]()
数字分为三个部分:带分数的整数部分、分子、分母
如果生成的是整数,则只指对分数的整数部分赋值,分子默认为0,分母默认为1;如果生成的是分数,则三个部分均赋值。
运算题目分为两部分:数字和运算符的链表,括号的链表
运算符数目:通过随机函数随机取1-3 - 负数的避免
运用括号链表,按照计算的顺序,将运算优先级高的部分提前,形成优先计算符链表,再逐次计算每个部分,当出现负数时,舍弃这道题目重新生成 - 真分数的显示
计算时为了方便都是用假分数计算,只有在输出时才显示成真分数 - 判断是否重复
通过括号链表按照计算顺序形成优先计算符链表,按照链表顺序依次比较两个数字以及运算符是否完全相同(或可交换),并依次计算结果覆盖,就可判断是否重复
优先运算符链表:依照正常的计算顺序排列的运算符链表,例如:
3 ×(2 + 1)的优先运算符链表: + -> ×,计算第一个+号后:3 × 3
(1 + 2) × 3的优先运算符链表:+ -> ×,计算第一个+号后:3 × 3
代码说明
生成算式的整体结构:
QuestionService questionService = new QuestionService();
RepeatService repeatService = new RepeatService();
List<Question> questionList = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= questionNumber; i++) {
Question question = questionService.getQuestion(maxRange);
//检查重复题目
\while (question == null || repeatService.isRepeat(questionList, question)) {
question = questionService.getQuestion(maxRange);
}
question.setId(i);
questionList.add(question);
用于生成指定范围的一道题目的class QuestionService:
public class QuestionService {
/**
* 生成指定范围的一道题目
* @param maxRange
* @return 返回一个带运算式和结果的Question
*/
public Question getQuestion(int maxRange) {
Question question = new Question();
Random r = new Random();
int operatorNum = r.nextInt(3) + 1;
List<Operator> operatorList = new LinkedList<>();
List<Char> charList = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < operatorNum; i++) {
//生成运算符
OperatorEnum operatorEnum = OperatorEnum.values()[r.nextInt(4)];
Operator operator = new Operator(i + 1, operatorEnum.getOperator());
operatorList.add(operator);
//生成数字
Number number = createNumber(maxRange, i + 1);
charList.add(number);
charList.add(operator);
}
//生成最后一个数字并加入链表
charList.add(createNumber(maxRange, operatorNum + 1));
//生成括号
List<Parentheses> parenthesesList = new LinkedList<>();
getParenthesesList(1, operatorList.size() + 1, parenthesesList);
//构造运算符优先处理链
List<Operator> buildList = QuestionUtil.buildLink(operatorList, parenthesesList);
//计算结果
List<Char> tempList = new LinkedList<>();
tempList.addAll(charList);
for(int i = 0; i < buildList.size(); i++) {
Operator o = buildList.get(i);
int temp = tempList.indexOf(o);
Number n1 = (Number)tempList.get(temp - 1);
Number n2 = (Number)tempList.get(temp + 1);
Number n = MathUtil.calculate(n1, o, n2);
//返回null表示为减法得出是负数或被除数为0,题目无效返回
if (n == null) {
return null;
}
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
tempList.remove(temp - 1);
}
tempList.add(temp - 1, n);
if (tempList.size() == 1) {
question.setResult(n.getOutput());
}
}
question.setCharList(charList);
question.setParenthesesList(parenthesesList);
return question;
}
private Number createNumber(int maxRange, int nid) {
Random r = new Random();
NumberTypeEnum numberTypeEnum = NumberTypeEnum.values()[r.nextInt(2)];
if (numberTypeEnum.equals(NumberTypeEnum.NATURAL_NUMBER)) {
return new Number(nid, NumberTypeEnum.NATURAL_NUMBER.getCode(), r.nextInt(maxRange));
} else {
CalculateFraction cf = MathUtil.reduction(r.nextInt(maxRange - 1) + 1, r.nextInt(maxRange - 1) + 1);
Number number = cf.getNumber();
number.setNId(nid);
return number;
}
}
public void getParenthesesList(int startNid, int endNid, List<Parentheses> parenthesesList) {
if (endNid - startNid > 1) {
Random r = new Random();
Parentheses p = null;
for (int i = startNid; i <= endNid - 1; i++) {
if (p != null && i == endNid - 1) {
if (p.getStartNId() == startNid) {
break;
}
p.setEndNId(i + 1);
parenthesesList.add(p);
getParenthesesList(p.getStartNId(), p.getEndNId(), parenthesesList);
break;
}
boolean flag = r.nextBoolean();
if (p != null || !flag) {
if (!flag) {
p = new Parentheses();
p.setStartNId(i);
}
if (flag || r.nextBoolean()) {
p.setEndNId(i + 1);
parenthesesList.add(p);
getParenthesesList(p.getStartNId(), p.getEndNId(), parenthesesList);
p = null;
i = i + 1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
用于验证题目是否重复的class RepeatService:
public class RepeatService {
/**
* 检查题目是否与已有题目重复
* @param questionList
* @param question
* @return
*/
public boolean isRepeat(List<Question> questionList, Question question) {
for (Question origin: questionList) {
//先检查题目答案是否相同再进行下一步
if (origin.getResult().equals(question.getResult())) {
//检查运算符的个数和种类是否相同
if (isOperatorRepeat(QuestionUtil.fatherListToSonList(origin.getCharList(), Operator.class), QuestionUtil.fatherListToSonList(question.getCharList(), Operator.class))) {
//只有一个运算符说明重复
if (QuestionUtil.fatherListToSonList(question.getCharList(), Operator.class).size() == 1) {
return true;
}
//构建运算符优先链表
List<Operator> o1 = QuestionUtil.buildLink(QuestionUtil.fatherListToSonList(origin.getCharList(), Operator.class), origin.getParenthesesList());
List<Operator> o2 = QuestionUtil.buildLink(QuestionUtil.fatherListToSonList(question.getCharList(), Operator.class), question.getParenthesesList());
//比较运算符优先链表是否相同
for (int i = 0; i < o1.size(); i++) {
if (!o1.get(i).getOperator().equals(o2.get(i).getOperator())) {
return false;
}
}
//根据优先链表逐一比较
List<Char> charList1 = new LinkedList<>();
List<Char> charList2 = new LinkedList<>();
charList1.addAll(origin.getCharList());
charList2.addAll(question.getCharList());
List<String> stringList1 = new LinkedList<>();
List<String> stringList2 = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < o1.size() - 1; i ++) {
int index1 = charList1.indexOf(o1.get(i));
int index2 = charList2.indexOf(o2.get(i));
stringList1.add(((Number)charList1.get(index1 - 1)).getOutput());
stringList1.add(((Number)charList1.get(index1 + 1)).getOutput());
stringList2.add(((Number)charList2.get(index2 - 1)).getOutput());
stringList2.add(((Number)charList2.get(index2 + 1)).getOutput());
if (!QuestionUtil.isListEqual(stringList1, stringList2)) {
return false;
}
stringList1.clear();
stringList2.clear();
Number n = MathUtil.calculate((Number)charList1.get(index1 - 1), o1.get(i), (Number)charList1.get(index1 + 1));
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
charList1.remove(index1 - 1);
charList2.remove(index2 - 1);
}
charList1.add(index1 - 1, n);
charList2.add(index2 - 1, n);
}
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean isOperatorRepeat(List<Operator> operatorList1, List<Operator> operatorList2) {
if (!(operatorList1.size() == operatorList2.size())) {
return false;
}
List<String> stringList1 = operatorList1.stream().map(Operator::getOperator).collect(Collectors.toList());
List<String> stringList2 = operatorList2.stream().map(Operator::getOperator).collect(Collectors.toList());
return QuestionUtil.isListEqual(stringList1, stringList2);
}
}
其中用于生成优先运算符链表的方法:
/**
* 构建运算符优先运算链表
* @param operatorList
* @param pList
* @return
*/
public static List<Operator> buildLink(List<Operator> operatorList, List<Parentheses> pList) {
if (operatorList.size() == 1) {
return operatorList;
}
List<Operator> originList = new LinkedList<>(operatorList);
List<Parentheses> parenthesesList = new LinkedList<>(pList);
List<Operator> calculateList = new LinkedList<>();
//如果有括号,找到最优先的括号
Parentheses priorityParentheses;
if (parenthesesList.size() != 0) {
priorityParentheses = parenthesesList.get(0);
for (int i = 1; i < parenthesesList.size(); i++) {
Parentheses p = parenthesesList.get(i);
if (p.getEndNId() - p.getStartNId() < priorityParentheses.getEndNId() - priorityParentheses.getStartNId()) {
priorityParentheses = p;
} else if (p.getEndNId() - p.getStartNId() == priorityParentheses.getEndNId() - priorityParentheses.getStartNId() && p.getStartNId() < priorityParentheses.getStartNId()) {
priorityParentheses = p;
}
}
parenthesesList.remove(priorityParentheses);
int start = priorityParentheses.getStartNId();
int end = priorityParentheses.getEndNId() - 1;
operatorList = QuestionUtil.findCharById(operatorList, start, end);
}
List<Operator> tempOs = new LinkedList<>();
for (Operator o: operatorList) {
if (o.getOperator().equals(OperatorEnum.MULTIPLICATION.getOperator()) || o.getOperator().equals(OperatorEnum.DIVISION.getOperator())) {
((LinkedList<Operator>) calculateList).addLast(o);
} else {
((LinkedList<Operator>) tempOs).addLast(o);
}
}
for (Operator o: tempOs) {
((LinkedList<Operator>) calculateList).addLast(o);
}
//删除已添加到链表的运算符
for (Operator o: calculateList) {
originList.remove(o);
}
if (originList.size() == 0) {
return calculateList;
} else {
calculateList.addAll(buildLink(originList, parenthesesList));
return calculateList;
}
}
通用于各部分的四则运算运算方法(传入两个数和运算符可返回计算结果)
public static Number calculate(Number n1, Operator o, Number n2) {
CalculateFraction cf1 = n1.getCalculate();
CalculateFraction cf2 = n2.getCalculate();
//如果是加法或减法
if (o.getOperator().equals(OperatorEnum.PLUS.getOperator()) || o.getOperator().equals(OperatorEnum.SUBTRACTION.getOperator())) {
//最小公倍数
int lcm = lcm(cf1.getDenominator(), cf2.getDenominator());
int a1 = cf1.getNumerator() * (lcm / cf1.getDenominator());
int a2 = cf2.getNumerator() * (lcm / cf2.getDenominator());
if (o.getOperator().equals(OperatorEnum.PLUS.getOperator())) {
Number n = reduction(a1 + a2, lcm).getNumber();
n.setNId(o.getOid());
return n;
} else {
//如果是负数,返回null
if (a1 < a2) {
return null;
}
Number n = reduction(a1 - a2, lcm).getNumber();
n.setNId(o.getOid());
return n;
}
}
//如果是乘法
if (o.getOperator().equals(OperatorEnum.MULTIPLICATION.getOperator())) {
Number n = reduction(cf1.getNumerator() * cf2.getNumerator(), cf1.getDenominator() * cf2.getDenominator()).getNumber();
n.setNId(o.getOid());
return n;
}
//如果是除法
if (cf2.getNumerator() == 0) {//如果被除数是0,返回null
return null;
}
Number n = reduction(cf1.getNumerator() * cf2.getDenominator(), cf1.getDenominator() * cf2.getNumerator()).getNumber();
n.setNId(o.getOid());
return n;
}
测试运行
生成10个四则运算:
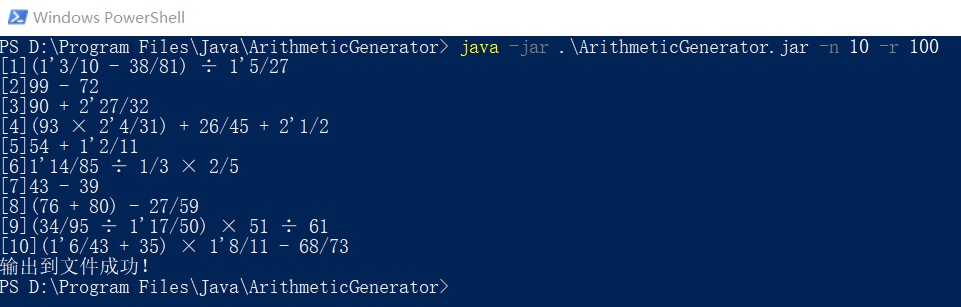
输出到文件的结果:
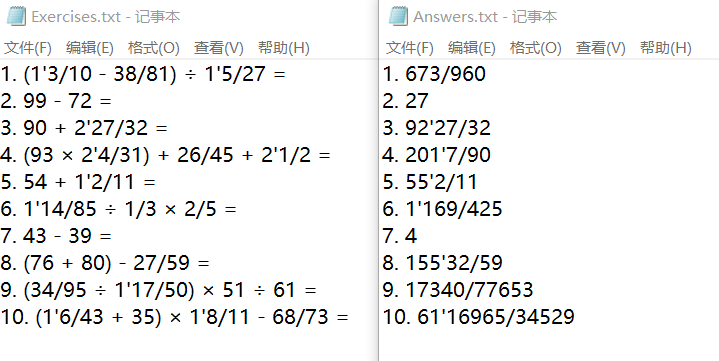
验证答案对错功能:
在第1、6、7题填上正确的答案,其他题填错误的答案或者不填
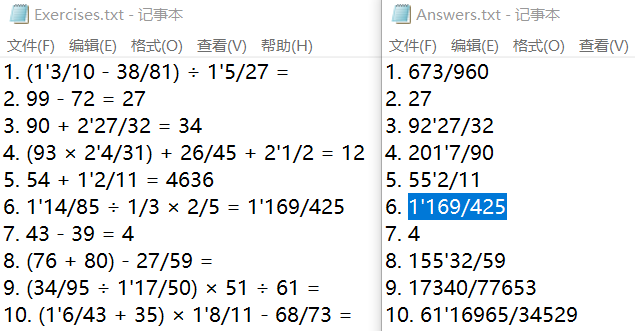
运行结果:
生成代码时,如果没有输入-r参数,报错:

生成更多的题目:
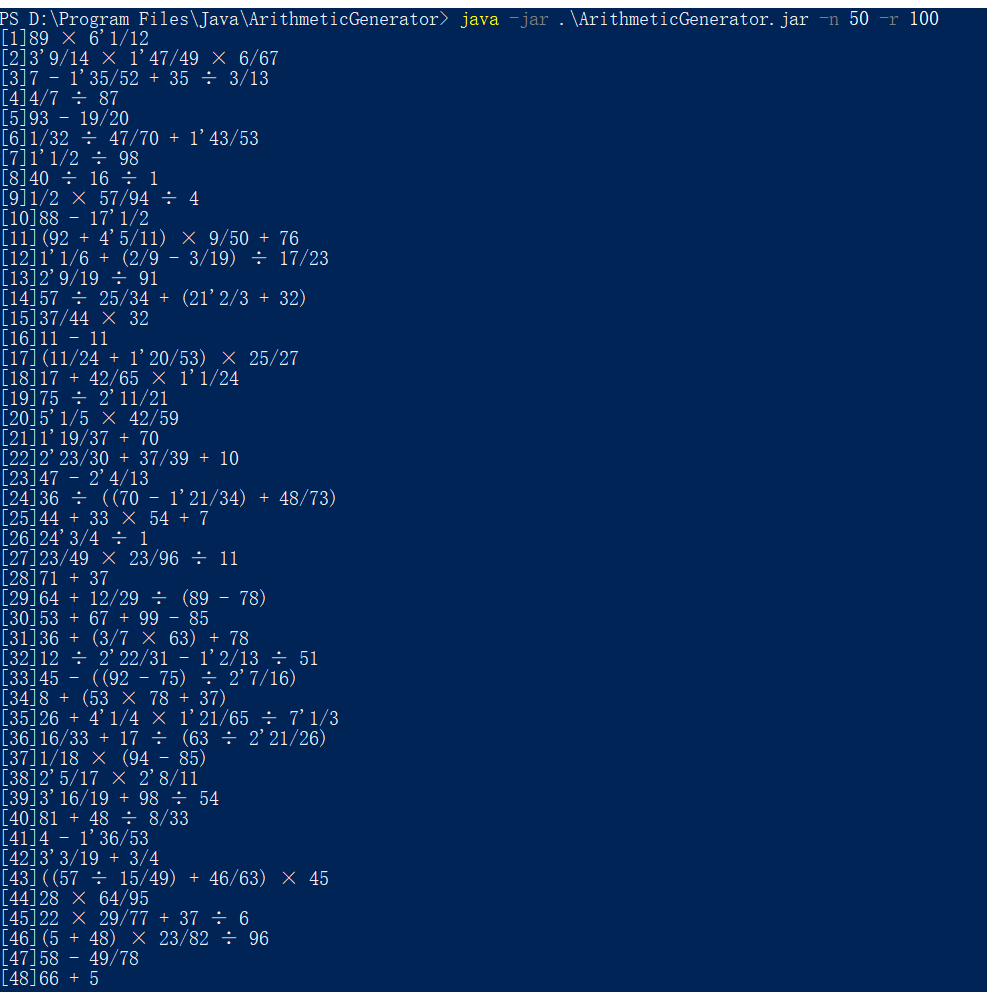
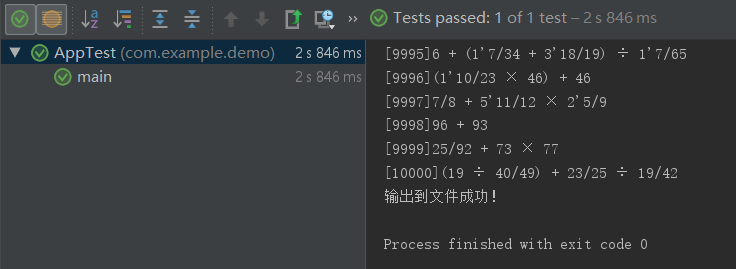
生成10000道题目,平均用时2s多:
由于题目过多,这里给出链接:
题目
答案
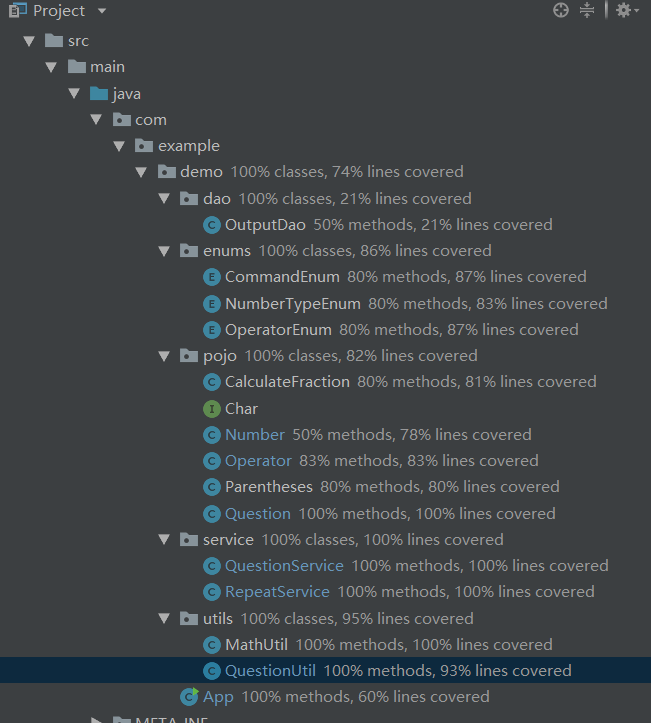
代码覆盖率:
PSP
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 30 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 30 |
| Development | 开发 | 1010 | 1375 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 30 | 30 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 20 | 20 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 60 | 80 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 30 | 45 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 180 | 300 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 480 | 600 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 150 | 180 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | 120 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 135 | 155 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 90 | 100 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 15 | 15 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 40 |
| 合计 | 1175 | 1560 |
项目小结
这次结对编程中,我主要负责代码编写,梁新男同学负责代码复审,我们两人首先分析了项目的需求,然后一起讨论项目各功能的实现,完成代码的设计文档和整体的结构设计,并对设计进行多次的探讨修改。在一开始的结构设计中,我们对于表达式的存储结构思考了很久,最终选择了效率与直观性并存的链表存储结构。在我写代码的过程中,两个人的交流确实比一个人考虑地更全面。比如在减法产生负数这个问题,一开始想着是要交换两个数字,后来经过我们的讨论发现这样会让题目重复的概率增大,也违反了随机的理念,于是最终做法是舍弃这道题重新生成。在这次磨合过程中,通过互相学习,掌握了更加高效的编程技巧。而在之后的代码复审中,梁新男同学发现了很多编程时没有注意到的细节问题,比如没有生成0的问题和没有产生嵌套括号的问题,从而很好地避免了bug的产生,增加了代码的健壮性,也让我们了解到别人的思维方式,从而提高了编程的质量。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号