【排序算法】(5)基数排序
基数排序
2019-11-10 11:42:38 by冲冲
1、概念
基数排序与本系列前面讲解的七种排序方法都不同,它不需要比较关键字的大小。
它是根据关键字中各位的值,通过对排序的N个元素进行若干趟“分配”与“收集”来实现排序的。
2、基本思想
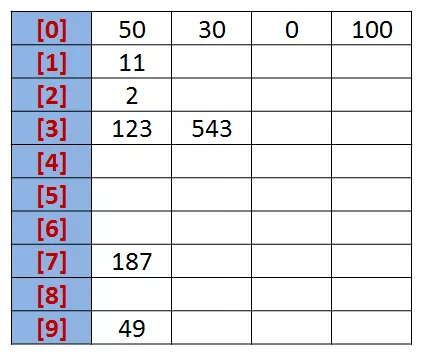
设有一个初始序列为: R {50, 123, 543, 187, 49, 30, 0, 2, 11, 100}。
我们知道,任何一个阿拉伯数,它的各个位数上的基数都是以0~9来表示的。所以我们不妨把0~9视为10个桶。
我们先根据序列的个位数的数字来进行分类,将其分到指定的桶中。例如:R[0] = 50,个位数上是0,将这个数存入编号为0的桶中。分类后,我们在从各个桶中,将这些数按照从编号0到编号9的顺序依次将所有数取出来。这时,得到的序列就是个位数上呈递增趋势的序列。 按照个位数排序: {50, 30, 0, 100, 11, 2, 123, 543, 187, 49}。
接下来,可以对十位数、百位数也按照这种方法进行排序,最后就能得到排序完成的序列。
3、完整代码
1 public class RadixSort { 2 // 获取x这个数的d位数上的数字 3 // 比如获取123的1位数,结果返回3 4 public int getDigit(int x, int d) { 5 int a[] = {1, 1, 10, 100}; // 本实例中的最大数是百位数,所以只要到100就可以了 6 return ((x / a[d]) % 10); 7 } 8 9 public void radixSort(int[] list, int begin, int end, int digit) { 10 final int radix = 10; // 基数 11 int i = 0, j = 0; 12 int[] count = new int[radix]; // 存放各个桶的数据统计个数 13 int[] bucket = new int[end - begin + 1]; 14 // 按照从低位到高位的顺序执行排序过程 15 for (int d = 1; d <= digit; d++) { 16 // 置空各个桶的数据统计 17 for (i = 0; i < radix; i++) { 18 count[i] = 0; 19 } 20 // 统计各个桶将要装入的数据个数 21 for (i = begin; i <= end; i++) { 22 j = getDigit(list[i], d); 23 count[j]++; 24 } 25 // count[i]表示第i个桶的右边界索引 26 for (i = 1; i < radix; i++) { 27 count[i] = count[i] + count[i - 1]; 28 } 29 // 将数据依次装入桶中 30 // 这里要从右向左扫描,保证排序稳定性 31 for (i = end; i >= begin; i--) { 32 j = getDigit(list[i], d); 33 // 求出关键码的第k位的数字, 例如:576的第3位是5 34 bucket[count[j] - 1] = list[i]; 35 // 放入对应的桶中,count[j]-1是第j个桶的右边界索引 36 count[j]--; // 对应桶的装入数据索引减一 37 } 38 // 将已分配好的桶中数据再倒出来,此时已是对应当前位数有序的表 39 for (i = begin, j = 0; i <= end; i++, j++) { 40 list[i] = bucket[j]; 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 45 public int[] sort(int[] list) { 46 radixSort(list, 0, list.length - 1, 3); 47 return list; 48 } 49 50 // 打印完整序列 51 public void printAll(int[] list) { 52 for (int value : list) { 53 System.out.print(value + "\t"); 54 } 55 System.out.println(); 56 } 57 58 public static void main(String[] args) { 59 int[] array = {50, 123, 543, 187, 49, 30, 0, 2, 11, 100}; 60 RadixSort radix = new RadixSort(); 61 System.out.print("排序前:\t\t"); 62 radix.printAll(array); 63 radix.sort(array); 64 System.out.print("排序后:\t\t"); 65 radix.printAll(array); 66 } 67 }
1 排序前: 50 123 543 187 49 30 0 2 11 100 2 排序后: 0 2 11 30 49 50 100 123 187 543

