异常
1.为什么需要异常
运行下面的代码,看看有什么问题-> 引出异常和异常处理机制
public class Exception01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 0;//Scanner();
//1. num1 / num2 => 10 / 0
//2. 当执行到 num1 / num2 因为 num2 = 0, 程序就会出现(抛出)异常 ArithmeticException
//3. 当抛出异常后,程序就退出,崩溃了 , 下面的代码就不在执行
//4. 大家想想这样的程序好吗? 不好,不应该出现了一个不算致命的问题,就导致整个系统崩溃
//5. java 设计者,提供了一个叫 异常处理机制来解决该问题
// int res = num1 / num2;
//如果程序员,认为一段代码可能出现异常/问题,可以使用try-catch异常处理机制来解决
//从而保证程序的健壮性
//将该代码块->选中->快捷键 ctrl + alt + t -> 选中 try-catch
//6. 如果进行异常处理,那么即使出现了异常,程序可以继续执行
try {
int res = num1 / num2;
} catch (Exception e) {
//e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("出现异常的原因=" + e.getMessage());//输出异常信息
}
System.out.println("程序继续运行....");
}
}
2.异常介绍
基本概念
Java语言中,将程序执行中发生的不正常情况称为“异常”。(开发过程中的语法错误和逻辑错误不是异常)
执行过程中所发生的异常事件可分为两大类
- Error(错误):Java虚拟机无法解决的严重问题。如:JVM系统内部错误、资源耗尽等严重情况。比如:StackOverflowError[栈溢出]和OOM(out of memory). Error是严重错误,程序会崩溃。
- Exception:其它因编程错误或偶然的外在因素导致的一般性问题,可以使用针对性的代码进行处理。例如空指针访问,试图读取不存在的文件,网络连接中断等等,Exception 分为两大类:运行时异常[程序运行时,发生的异常]和编译时异常[编程时,编译器检查出的异常].
3.异常体系图一览
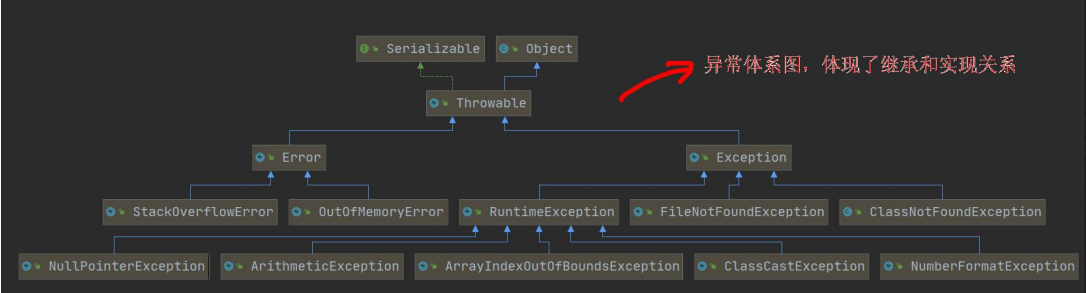
- 异常分为两大类,运行时异常和编译时异常.
- 运行时异常,编译器检查不出来。一般是指编程时的逻辑错误,是程序员应该避免其出现的异常。java.lang.RuntimeException类及它的子类都是运行时异常
- 对于运行时异常,可以不作处理,因为这类异常很普遍,若全处理可能会对程序的可读性和运行效率产生影响
- 编译时异常,是编译器要求必须处置的异常。
public class Exception02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileInputStream fis;
fis = new FileInputStream("d:\\aa.jpg");
int len;
while ((len = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(len);
}
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4.常见的运行时异常
-
NullPointerException 空指针异常
-
ArithmeticException 数学运算异常
-
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 数组下标越界异常
-
ClassCastException 类型转换异常
-
NumberFormatException 数字格式不正确异常[]
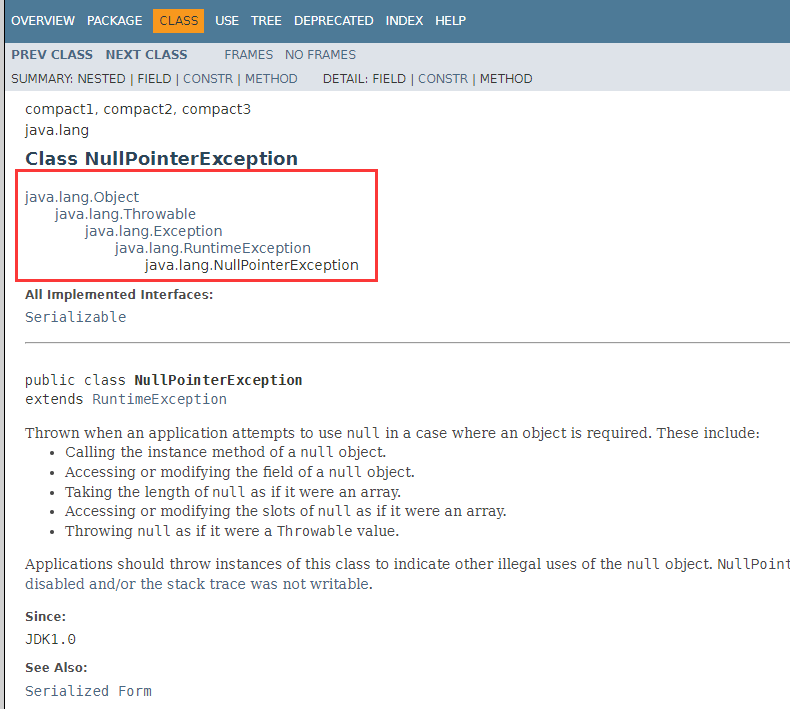
4.1NullPointerException 空指针异常
当应用程序试图在需要对象的地方使用 null 时,抛出该异常.
public class NullPointerException_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = null;
System.out.println(name.length());
}
}
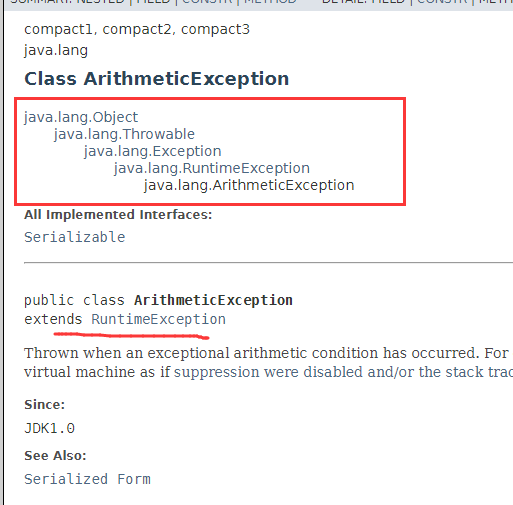
4.2ArithmeticException 数学运算异常
当出现异常的运算条件时,抛出此异常。例如,一个整数“除以零”时,抛出此类的一个实例.
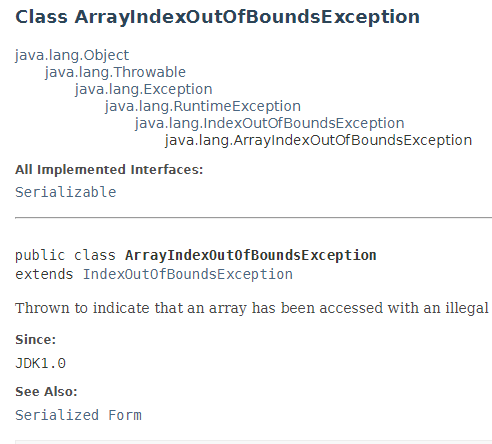
4.3ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 数组下标越界异常
用非法索引访问数组时抛出的异常。如果索引为负或大于等于数组大小,则该索引为非法索引
public class ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,4};
for (int i = 0; i <= arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
4.4ClassCastException 类型转换异常
当试图将对象强制转换为不是实例的子类时,抛出该异常。

public class ClassCastException_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A b = new B(); //向上转型
B b2 = (B)b;//向下转型,这里是OK
C c2 = (C)b;//这里抛出ClassCastException
}
}
class A {}
class B extends A {}
class C extends A {}
4.5NumberFormatException 数字格式不正确异常
当应用程序试图将字符串转换成一种数值类型,但该字符串不能转换为适当格式时,抛出该异常=> 使用异常我们可以确保输入是满足条件数字.
public class NumberFormatException_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "hhhh";
//将String 转成 int
int num = Integer.parseInt(name);//抛出NumberFormatException
System.out.println(num);//1234
}
}
5.编译异常
编译异常是指在编译期间,就必须处理的异常,否则代码不能通过编译。

6.异常处理
异常处理就是当异常发生时,对异常处理的方式。
6.1 异常处理的方式
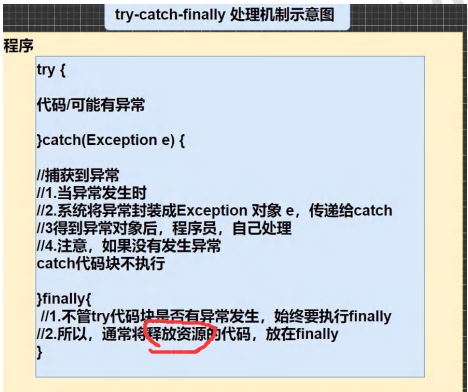
- try-catch-finally
程序员在代码中捕获发生的异常,自行处理
- throws
将发生的异常抛出,交给调用者(方法)来处理,最顶级的处理者就是JVM
6.2try-catch 异常处理

1)如果异常发生了,则异常发生后面的代码不会执行,直接进入到catch块.
2)如果异常没有发生,则顺序执行try的代码块,,不会进入到catch.
3)如果希望不管是否发生异常,都执行某段代码(比如关闭连接,释放资源等)则使用如下代码- finally {}
4)可以有多个catch语句,捕获不同的异常(进行不同的业务处理),要求父类异常在后,子类异常在前,比如(Exception在后,NullPointerException在前),如果发生异常,只会匹配一个catch。
5)可以进行try-finally 配合使用,这种用法相当于没有捕获异常,因此程序会直接崩掉/退出。应用场景,就是执行一段代码,不管是否发生异常,都必须执行某个业务逻辑.
public class TryCatchDetail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ctrl + atl + t
//1. 如果异常发生了,则异常发生后面的代码不会执行,直接进入到catch块
//2. 如果异常没有发生,则顺序执行try的代码块,不会进入到catch
//3. 如果希望不管是否发生异常,都执行某段代码(比如关闭连接,释放资源等)则使用如下代码- finally
try {
String str = "hhh";
int a = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println("数字:" + a);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("异常信息=" + e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("finally代码块被执行...");
}
System.out.println("程序继续...");
}
}
public class TryCatchDetail02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.如果try代码块有可能有多个异常
//2.可以使用多个catch 分别捕获不同的异常,相应处理
//3.要求子类异常写在前面,父类异常写在后面
try {
Person person = new Person();
//person = null;
System.out.println(person.getName());//NullPointerException
int n1 = 10;
int n2 = 0;
int res = n1 / n2;//ArithmeticException
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常=" + e.getMessage());
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("算术异常=" + e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
}
}
}
class Person {
private String name = "jack";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
public class TryCatchDetail03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
可以进行 try-finally 配合使用, 这种用法相当于没有捕获异常,
因此程序会直接崩掉/退出。应用场景,就是执行一段代码,不管是否发生异常,
都必须执行某个业务逻辑
*/
try{
int n1 = 10;
int n2 = 0;
System.out.println(n1 / n2);
}finally {
System.out.println("执行了finally..");
}
System.out.println("程序继续执行..");
}
}
6.3练习
public class TryCatchExercise01 {
}
class Exception01 {
public static int method() {
try {
String[] names = new String[3];//String[]数组
if (names[1].equals("tom")) {//NullPointerException
System.out.println(names[1]);
} else {
names[3] = "hspedu";
}
return 1;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
return 2;
} catch (NullPointerException e) {//捕获
return 3;
} finally { //必须执行
return 4; //返回4
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(method()); //4
}
}
public class TryCatchExercise02 {
}
class Exception02 {
public static int method() {
int i = 1;
try {
i++; //i = 2
String[] names = new String[3];
if (names[1].equals("tom")) {//空指针
System.out.println(names[1]);
} else {
names[3] = "hspedu";
}
return 1;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
return 2;
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
return ++i; //i = 3;不会马上执行
} finally {//必须执行
return ++i; //i = 4
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(method());
}
}

public class TryCatchExercise03 {
}
class ExceptionExe01 {
public static int method() {
int i = 1;//i = 1
try {
i++;// i=2
String[] names = new String[3];
if (names[1].equals("tom")) { //空指针
System.out.println(names[1]);
} else {
names[3] = "hspedu";
}
return 1;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
return 2;
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
return ++i; // i = 3 => 保存临时变量 temp = 3;
} finally {
++i; //i = 4
System.out.println("i=" + i);// i = 4
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(method());// 3
}
}

如果用户输入的不是一个整数,就提示他反复输入,直到输入一个整数为止
public class TryCatchExercise04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//如果用户输入的不是一个整数,就提示他反复输入,直到输入一个整数为止
//思路
//1. 创建Scanner对象
//2. 使用无限循环,去接收一个输入
//3. 然后将该输入的值,转成一个int
//4. 如果在转换时,抛出异常,说明输入的内容不是一个可以转成int的内容
//5. 如果没有抛出异常,则break 该循环
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = 0;
String inputStr = "";
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:"); //
inputStr = scanner.next();
try {
num = Integer.parseInt(inputStr); //这里是可能抛出异常
break;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("你输入的不是一个整数:");
}
}
System.out.println("你输入的值是=" + num);
}
}
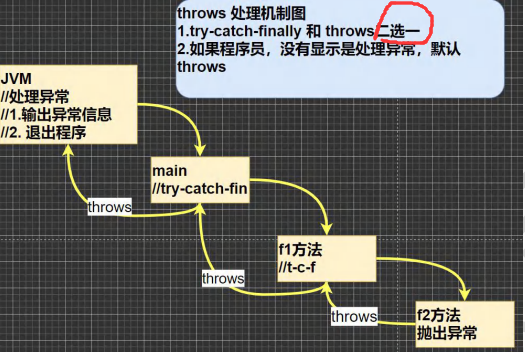
6.4 throws 异常处理
1)如果一个方法(中的语句执行时)可能生成某种异常,但是并不能确定如何处理这种异常,则此方法应显示地声明抛出异常,表明该方法将不对这些异常进行处理,而由该方法的调用者负责处理。
2)在方法声明中用throws语句可以声明抛出异常的列表,throws后面的异常类型可以是方法中产生的异常类型,也可以是它的父类。
public class Throws01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public void f2() throws FileNotFoundException,NullPointerException,ArithmeticException {
//创建了一个文件流对象
//1. 这里的异常是一个FileNotFoundException 编译异常
//2. 使用前面讲过的 try-catch-finally
//3. 使用throws ,抛出异常, 让调用f2方法的调用者(方法)处理
//4. throws后面的异常类型可以是方法中产生的异常类型,也可以是它的父类
//5. throws 关键字后也可以是 异常列表, 即可以抛出多个异常
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d://aa.txt");
}
}
6.5 注意事项
1)对于编译异常,程序中必须处理,比如try-catch或者throws
2)对于运行时异常,程序中如果没有处理,默认就是throws的方式处理
3)子类重写父类的方法时,对抛出异常的规定:子类重写的方法,所抛出的异常类型要么和父类抛出的异常一致,要么为父类抛出的异常的类型的子类型
4)在throws 过程中,如果有方法 try-catch,就相当于处理异常,就可以不必throws
public class ThrowsDetail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
f2();
}
public static void f2() /*throws ArithmeticException*/ {
//1.对于编译异常,程序中必须处理,比如 try-catch 或者 throws
//2.对于运行时异常,程序中如果没有处理,默认就是throws的方式处理
int n1 = 10;
int n2 = 0;
double res = n1 / n2;
}
public static void f1() throws FileNotFoundException {
//这里大家思考问题 调用f3() 报错
//老韩解读
//1. 因为f3() 方法抛出的是一个编译异常
//2. 即这时,就要f1() 必须处理这个编译异常
//3. 在f1() 中,要么 try-catch-finally ,或者继续throws 这个编译异常
f3(); // 抛出异常
}
public static void f3() throws FileNotFoundException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d://aa.txt");
}
public static void f4() {
//老韩解读:
//1. 在f4()中调用方法f5() 是OK
//2. 原因是f5() 抛出的是运行异常
//3. 而java中,并不要求程序员显示处理,因为有默认处理机制
f5();
}
public static void f5() throws ArithmeticException {
}
}
class Father { //父类
public void method() throws RuntimeException {
}
}
class Son extends Father {//子类
//3. 子类重写父类的方法时,对抛出异常的规定:子类重写的方法,
// 所抛出的异常类型要么和父类抛出的异常一致,要么为父类抛出的异常类型的子类型
//4. 在throws 过程中,如果有方法 try-catch , 就相当于处理异常,就可以不必throws
@Override
public void method() throws ArithmeticException {
}
}
7.自定义异常
当程序中出现了某些“错误”,但该错误信息并没有在Throwable子类中描述处理,这个时候可以自己设计异常类,用于描述该错误信息。
7.1自定义异常的步骤
1)定义类:自定义异常类名(程序员自己写)继承Exception或RuntimeException
2)如果继承Exception,属于编译异常
3)如果继承RuntimeException,属于运行异常(一般来说,继承RuntimeException)
当我们接收Person对象年龄时,要求范围在18-120之间,否则抛出一个自定义异常(要求继承RuntimeException),并给出提示信息。
public class CustomException {
public static void main(String[] args) /*throws AgeException*/ {
int age = 180;
//要求范围在 18 – 120 之间,否则抛出一个自定义异常
if(!(age >= 18 && age <= 120)) {
//这里我们可以通过构造器,设置信息
throw new AgeException("年龄需要在 18~120之间");
}
System.out.println("你的年龄范围正确.");
}
}
//自定义一个异常
//1. 一般情况下,我们自定义异常是继承 RuntimeException
//2. 即把自定义异常做成 运行时异常,好处时,我们可以使用默认的处理机制
//3. 即比较方便
class AgeException extends RuntimeException {
public AgeException(String message) {//构造器
super(message);
}
}
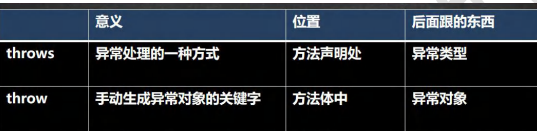
8.throw 和 throws 的区别

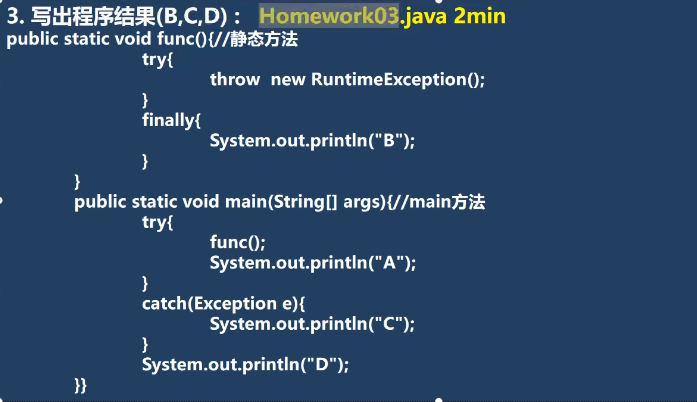
9.异常部分作业
9.1 作业1
a)编写应用程序EcmDef.java,接收命令行的两个参数(整数),计算两数相除。
b)计算两个数相除,要求使用方法cal(int n1, int n2)
c)对数据格式不正确(NumberFormatException)、缺少命令行参数(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException)、除0进行异常处理(ArithmeticException)。
public class Homework01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
编写应用程序EcmDef.java,接收命令行的两个参数(整数),计算两数相除。
计算两个数相除,要求使用方法 cal(int n1, int n2)
对数据格式不正确(NumberFormatException)、缺少命令行参数(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException)、除0 进行异常处理(ArithmeticException)。
*/
try {
//先验证输入的参数的个数是否正确 两个参数
if(args.length != 2) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("参数个数不对");
}
//先把接收到的参数,转成整数
int n1 = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int n2 = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
double res = cal(n1, n2);//该方法可能抛出ArithmeticException
System.out.println("计算结果是=" + res);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("参数格式不正确,需要输出整数");
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("出现了除0的异常");
}
}
//编写cal方法,就是两个数的商
public static double cal(int n1, int n2) {
return n1 / n2;
}
}

public class Homework02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//args.length = 0
//这里发生的是 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
if(args[4].equals("john")){ //可能发生NullPointerException
System.out.println("AA");
}else{
System.out.println("BB");
}
Object o= args[2]; //String->Object ,向上转型
Integer i = (Integer)o; //错误,这里一定会发生 ClassCastException
}
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理