二叉排序数
1.为什么要用二叉排序树
- 使用数组
- 数组未排序,优点:直接在数组尾添加,速度快。 缺点:查找速度慢.
- 数组排序,优点:可以使用二分查找,查找速度快,缺点:为了保证数组有序,在添加新数据时,找到插入位置后,后面的数据需整体移动,速度慢。
- 使用链式存储-链表
- 不管链表是否有序,查找速度都慢,添加数据速度比数组快,不需要数据整体移动。
2.二叉排序树介绍
二叉排序树:BST: (Binary Sort(Search) Tree), 对于二叉排序树的任何一个非叶子节点,要求左子节点的值比当前节点的值小,右子节点的值比当前节点的值大。
特别说明:如果有相同的值,可以将该节点放在左子节点或右子节点
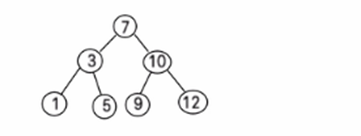
比如针对前面的数据 (7,3, 10, 12, 5, 1, 9) ,对应的二叉排序树为:
3.二叉排序数创建和遍历
一个数组创建成对应的二叉排序树,并使用中序遍历二叉排序树,
比如: 数组为 Array(7, 3, 10, 12, 5, 1, 9) ,
创建成对应的二叉排序树为 :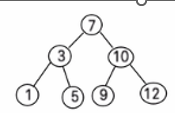
3.1代码实现
//第二,创建二叉排序树
class BinarySortTree{
Node root;
// 添加结点方法
public void add(Node node){
if (root == null) {
root = node;
} else {
root.add(node);
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder(){
if (root != null) {
root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉排序树为空,不能遍历");
}
}
}
//第一,创建结点信息
class Node{
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int value) {
super();
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [value=" + value + "]";
}
// 编写中序遍历方法(前序,后序遍历复习前面的)
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
System.out.println(this);
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
//编写增加结点的方法
public void add(Node node){
if (node == null) {
return;
}
//判断当前结点与左右子树值的大小关系
if (node.value < this.value ) {
//左子树的值小,向左子树增加
if (this.left == null) {
// 左子树为空,直接添加
this.left = node;
} else {
// 左子树不为空,向左子树增加
this.left.add(node);
}
} else {
//传入的node结点的值大于当前结点,增加到右子树
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = node;
} else {
//递归增加到右子树
this.right.add(node);
}
}
}
}
3.2测试代码
public class BinarySortTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {7,3,10,12,5,1,9};
BinarySortTree binarySortTree = new BinarySortTree();
//循环的增加结点到二叉排序树
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){
binarySortTree.add(new Node(arr[i]));
}
//中序遍历二叉排序树
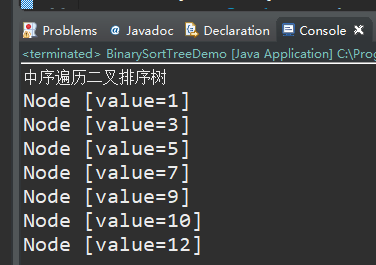
System.out.println("中序遍历二叉排序树");
binarySortTree.infixOrder();
}
}
输出是有序的
4.二叉排序树删除结点
4.1删除情况分析
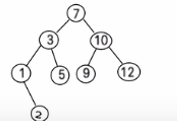
二叉排序树的删除情况比较复杂,有下面三种情况需要考虑
- 删除叶子节点 (比如:2, 5,9, 12)
- 删除只有一颗子树的节点 (比如:1)
- 删除有两颗子树的节点. (比如:7, 3,10 )
第一种情况:删除叶子节点
(1) 需求先去找到要删除的结点 targetNode
(2) 找到targetNode 的 父结点 parent
(3) 确定 targetNode 是 parent的左子结点 还是右子结点
(4) 根据前面的情况来对应删除
左子结点 parent.left = null
右子结点 parent.right = null;
第二种情况:删除只有一颗子树的节点
(1) 需求先去找到要删除的结点 targetNode
(2) 找到targetNode 的 父结点 parent
(3) 确定targetNode 的子结点是左子结点还是右子结点
(4) targetNode 是 parent 的左子结点还是右子结 点
(5) 如果targetNode 有左子结点
5. 1 如果 targetNode 是 parent 的左子结点 parent.left = targetNode.left;
5.2 如果 targetNode 是 parent 的右子结点 parent.right = targetNode.left;
(6) 如果targetNode 有右子结点
6.1 如果 targetNode 是 parent 的左子结点 parent.left = targetNode.right;
6.2 如果 targetNode 是 parent 的右子结点 parent.right = targetNode.right
第三种情况:删除有两颗子树的节点
(1) 需求先去找到要删除的结点 targetNode
(2) 找到targetNode 的 父结点 parent
(3) 从targetNode 的右子树找到最小的结点
3.1用一个临时变量,将 最小结点的值保存 temp = 12
3.2删除该最小结点
3.3targetNode.value = temp
或者
(4) 从targetNode 的左子树找到最大的结点
4.1用一个临时变量,将 最大结点的值保存 temp = 9
4.2删除该最大结点
43targetNode.value = temp
小结
都有的共性:
1.都需要找到要删除的结点
2.都需要找到需要删除结点的父结点
5.问题
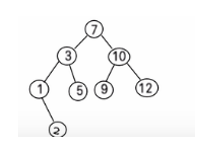
先删除10,再删除1会出现空指针异常
为什么会出错呢
最后只有两个结点的时候不知道谁是根结点
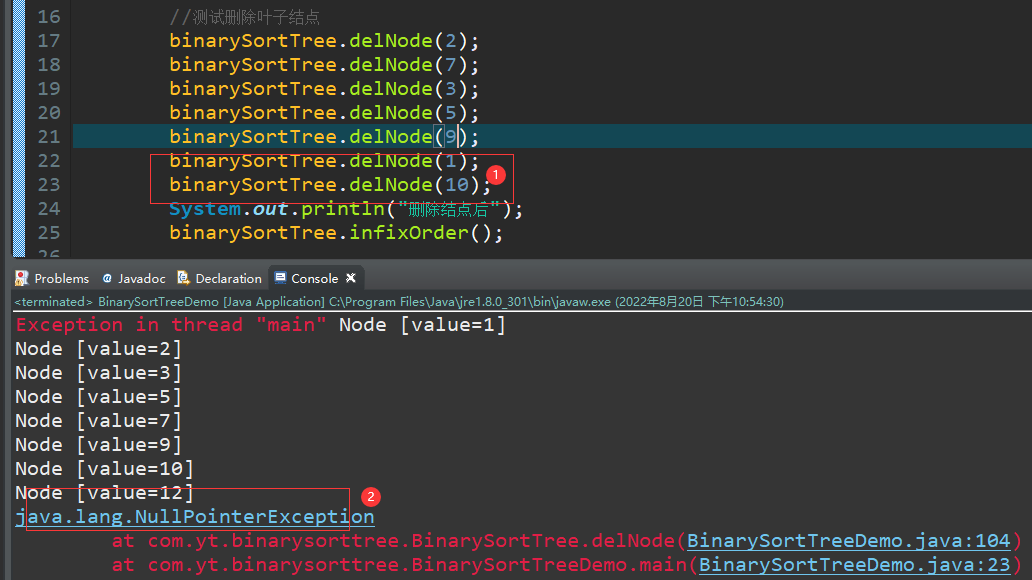
修改代码
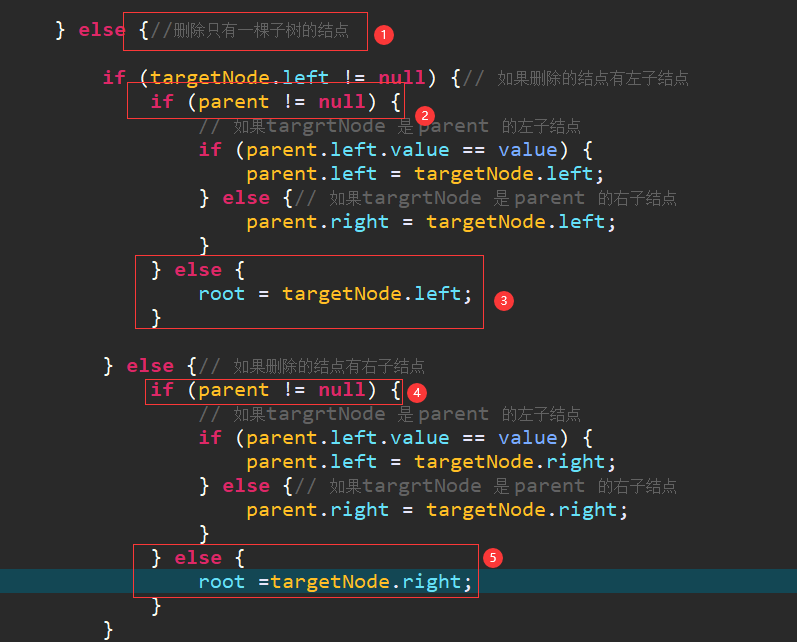
测试
6.代码总结
public class BinarySortTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {7,3,10,12,5,1,9,2};
BinarySortTree binarySortTree = new BinarySortTree();
//循环的增加结点到二叉排序树
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){
binarySortTree.add(new Node(arr[i]));
}
//中序遍历二叉排序树
System.out.println("中序遍历二叉排序树");
binarySortTree.infixOrder();
//测试删除叶子结点
binarySortTree.delNode(2);
binarySortTree.delNode(7);
binarySortTree.delNode(3);
binarySortTree.delNode(5);
binarySortTree.delNode(9);
binarySortTree.delNode(1);
binarySortTree.delNode(10);
binarySortTree.delNode(12);
System.out.println("删除结点后");
binarySortTree.infixOrder();
}
}
//第二,创建二叉排序树
class BinarySortTree{
Node root;
//编写一个返回要删除结点右子树的最大值
/**
*
* @param node 传入的结点(当做二叉排序树的根结点)
* @return 返回以node为根结点的二叉排序树的最小结点的值
*/
public int delRightTreeMin(Node node){
Node target = node;
// 循环的查找左子结点,就会找到最小值
while (target.left != null) {
target = target.left;
}
//找到最小值之后,删除最小值
delNode(target.value);
//此时target还是指向最小值结点的
return target.value;
}
//删除结点
public void delNode(int value){
if (root == null) {
return;
} else {
//1.先查找要删除的结点
Node targetNode = search(value);
// 如果没有找到要删除的结点
if (targetNode == null) {
return;
}
//如果发现当前这棵二叉排序树只有一个结点(特例,只有更结点)
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
root = null;
return;
}
//2.找到targetNode的父结点
Node parent = searchParent(value);
//如果删除的结点是子结点
if (targetNode.left == null && targetNode.right == null) {
//判断targetNode是父结点的左子结点还是右子结点
if (parent.left != null && parent.left.value == value) {
//是左子结点
parent.left = null;
} else if (parent.right != null && parent.right.value == value) {
//是右子结点
parent.right = null;
}
} else if (targetNode.right != null && targetNode.left != null) {
//删除有两棵子树的结点
int minVal = delRightTreeMin(targetNode.right);
targetNode.value = minVal;
} else {//删除只有一棵子树的结点
if (targetNode.left != null) {// 如果删除的结点有左子结点
if (parent != null) {
// 如果targrtNode 是 parent 的左子结点
if (parent.left.value == value) {
parent.left = targetNode.left;
} else {// 如果targrtNode 是 parent 的右子结点
parent.right = targetNode.left;
}
} else {
root = targetNode.left;
}
} else {// 如果删除的结点有右子结点
if (parent != null) {
// 如果targrtNode 是 parent 的左子结点
if (parent.left.value == value) {
parent.left = targetNode.right;
} else {// 如果targrtNode 是 parent 的右子结点
parent.right = targetNode.right;
}
} else {
root =targetNode.right;
}
}
}
}
}
// 查找要删除的结点
public Node search(int value){
if (root == null) {
return null;
} else {
return root.search(value);
}
}
//查找要删除结点的父结点
public Node searchParent(int value){
if (root== null) {
return null;
} else {
return root.searchParent(value);
}
}
// 添加结点方法
public void add(Node node){
if (root == null) {
root = node;
} else {
root.add(node);
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder(){
if (root != null) {
root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉排序树为空,不能遍历");
}
}
}
//第一,创建结点信息
class Node{
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int value) {
super();
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [value=" + value + "]";
}
//编写查找需要删除结点的父结点
/**
*
* @param value 要查找的结点值
* @return 返回的是要删除结点的父结点,如果没有就返回null
*/
public Node searchParent(int value){
//如果当前结点就是要删除结点的父结点,返回该结点
if ((this.left != null && this.left.value == value)
|| (this.right != null && this.right.value == value)) {
return this;
} else {
//如果查找的值小于当前结点的值,并且当前结点的左子结点不为空
if (value < this.value && this.left != null) {
return this.left.searchParent(value);//向左子树递归查找
} else if (value >= this.value && this.right != null) {
return this.right.searchParent(value);
} else {
return null;//没有找到父结点
}
}
}
// 编写查找要删除的结点
/**
*
* @param value 需要删除的结点
* @return 如果找到则返回该结点,否则返回null
*/
public Node search(int value){
if (this.value == value) {
//找到删除的结点,返回
return this;
} else if (value < this.value) {
//如果查找的结点值小于当前结点,向左子树递归查找
//注意,判断左子结点是否为空
if (this.left == null) {
return null;//没有找到
}
return this.left.search(value);
} else {
//如果查找的结点值大于当前结点,向右子树递归查找
// 注意,判断右子结点是否为空
if (this.right == null) {
return null;//没有找到
}
return this.right.search(value);
}
}
// 编写中序遍历方法(前序,后序遍历复习前面的)
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
System.out.println(this);
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
//编写增加结点的方法
public void add(Node node){
if (node == null) {
return;
}
//判断当前结点与左右子树值的大小关系
if (node.value < this.value ) {
//左子树的值小,向左子树增加
if (this.left == null) {
// 左子树为空,直接添加
this.left = node;
} else {
// 左子树不为空,向左子树增加
this.left.add(node);
}
} else {
//传入的node结点的值大于当前结点,增加到右子树
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = node;
} else {
//递归增加到右子树
this.right.add(node);
}
}
}
}

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号