ubus应用-第二篇ubus代码应用
本文写作目的是方便以后查询使用,以实用为主。前期完全不会ubus使用的时候看了一些文章,确实是很详尽的,但是我很难一下子进行应用(本人水平有限),在经过一些时间的使用之后逐渐了解其中的使用方法,希望这篇文章能够总结的很容易懂,能够帮到最开始接触ubus的人。
关于ubus的基本使用机制可以参看我之前的一篇文章(https://www.cnblogs.com/y-c-y/p/12187422.html),本篇更注重于代码使用。
ubus server
在本文中假设您已经对object等ubus基本概念已经有所了解了(如果没有可以参见我之前的文章),本次代码讲解将围绕以下两个表格进行讲解。
作为ubus server进程实现以下两个表格的功能:
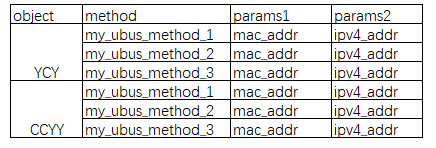

根据以上两个表格,可以得出以下这些命令是本ubus server 进程支持的:
ubus call YCY my_ubus_method_1 '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.2.1.2"}'
ubus call YCY my_ubus_method_2 '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.2.1.2"}'
ubus call YCY my_ubus_method_3 '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.2.1.2"}'
ubus call CCYY my_ubus_method_1 '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.2.1.2"}'
ubus call CCYY my_ubus_method_2 '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.2.1.2"}'
ubus call CCYY my_ubus_method_3 '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.2.1.2"}'
ubus send my_notify '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.2.1.2"}'
ubus send my_notify_1 '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.2.1.2"}'
PS:
1.ubus call YCY my_ubus_method_1 '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.2.1.2"}'
ubus :指的是ubus命令,所有代码中实现的ubus命令都可以通过ubus -v list查看到,或者是ubus list -v 。
call:指的是call调用,ubus调用方法还有另外的send。
YCY:指的是ubus object
my_ubus_method_1:指的是ubus method
'{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.22.1.2"}':指的是ubus call method需要使用的参数,其实如果对应的method要用到这些是需要传送的,如果有些method不需要参数(例如代码中的method2和method3)就算传了参数也没有关系,ubus不会判定语法出错,只不过是对应method并不会解析这些参数而已。
2.ubus send my_notify '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.2.1.2"}'
ubus :指的是ubus命令,所有代码中实现的ubus命令都可以通过ubus -v list查看到,或者是ubus list -v 。
send :指的是send调用
'{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.22.1.2"}':指的是ubus send需要使用的参数,具体同上。
3.其实从表格上也可以看出对于ubus call和ubus send两种命令的使用差别,ubus call是需要有明确调用对象的,类似于单播命令,而ubus send是没有明确调用对象的,是对所有的ubus进程发送notify消息,类似于广播命令;而所有接收到这个notify的ubus client进程,如果注册了这个notify,ubus client进程就会触发回调函数处理这个notify,ubus client进程没有注册这个notify的就无视它。
ubus server代码
注意事项(我想还是把注意事项写在代码前面为好,正确使用代码比使用代码更为重要,可以避免很多不必要的错误):
1.同一个ubus进程可以注册多个ubus object,例如 ubus call CCYY my_ubus_method_1 '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.22.1.2"}' 。
2.policy注意不能是NULL。
#define MY_UBUS_OBJECT_NAME "YCY"
#define MY_UBUS_OBJECT_NAME_1 "CCYY"
#define MY_UBUS_NOTIFY_EVENT "my_notify"
#define MY_UBUS_NOTIFY_EVENT_1 "my_notify_1"
#define MY_UBUS_METHOD_1 "my_ubus_method_1"
#define MY_UBUS_METHOD_2 "my_ubus_method_2"
#define MY_UBUS_METHOD_3 "my_ubus_method_3"
#define MY_UBUS_PARAM_NAME_1 "mac_addr"
#define MY_UBUS_PARAM_NAME_2 "ipv4_addr"
typedef (void *)my_ubus_event_handler(struct ubus_context *ctx, struct ubus_event_handler *ev, const char *type, struct blob_attr *msg);
/* global variables */
struct ubus_context *g_ubus_ctx;
struct blob_buf g_ubus_buf;
struct ubud_event_handler g_ubus_notify;
struct ubud_event_handler g_ubus_notify_1;
/* method function declare */
int my_ubus_method_1(struct ubus_context *ctx, struct ubus_object *obj,
struct ubus_request_data *req, const char *method,
struct blob_attr *msg);
int my_ubus_method_2(struct ubus_context *ctx, struct ubus_object *obj,
struct ubus_request_data *req, const char *method,
struct blob_attr *msg);
int my_ubus_method_3(struct ubus_context *ctx, struct ubus_object *obj,
struct ubus_request_data *req, const char *method,
struct blob_attr *msg);
void my_wifi_notify_handler(struct ubus_context *ctx, struct ubus_event_handler *ev,
const char *type, struct blob_attr *msg);
/* policy */
enum
{
PARAM_MAC_ADDR,
PARAM_IP4_ADDR,
PARAM_MAX
}
static const struct blobmsg_policy my_ubus_policy[PARAM_MAX] =
{
[PARAM_MAC_ADDR] = {.name = MY_UBUS_PARAM_NAME_1, .type = BLOBMSG_TYPE_STRING},
[PARAM_IP4_ADDR] = {.name = MY_UBUS_PARAM_NAME_2, .type = BLOBMSG_TYPE_STRING},
};
static const struct ubus_method g_ubus_methods[] =
{
UBUS_METHOD(MY_UBUS_METHOD_1, my_ubus_method_1, my_ubus_policy),//注意这里的policy绝对不能是NULL,程序运行会出错
UBUS_METHOD(MY_UBUS_METHOD_2, my_ubus_method_2, my_ubus_policy),
UBUS_METHOD(MY_UBUS_METHOD_3, my_ubus_method_3, my_ubus_policy),
};
static struct ubus_object_type g_ubus_type = UBUS_OBJECT_TYPE(MY_UBUS_OBJECT_NAME, g_ubus_methods);
struct ubus_object g_ubus_object =
{
.name = MY_UBUS_OBJECT_NAME,
.type = &g_ubus_type,
.methods = g_ubus_methods,
.n_methods = ARRAY_SIZE(g_ubus_methods)
};
static struct ubus_object_type g_ubus_type_1 = UBUS_OBJECT_TYPE(MY_UBUS_OBJECT_NAME_1, g_ubus_methods);/* g_ubus_methods 可以是其他的,这里是为了去掉重复代码简便使用 */
struct ubus_object g_ubus_object_1 =
{
.name = MY_UBUS_OBJECT_NAME_1,
.type = &g_ubus_type_1,
/* g_ubus_methods 可以是其他的,这里是为了去掉重复代码简便使用 */
.methods = g_ubus_methods,
.n_methods = ARRAY_SIZE(g_ubus_methods)
};
int my_ubus_add_object()
{
int ret = 0;
ret = ubus_add_object(g_ubus_ctx, &g_ubus_object);
if (ret != 0)
{
printf("failed to add object to ubus\n");
return -1;
}
ret = ubus_add_object(g_ubus_ctx, &g_ubus_object_1);
if (ret != 0)
{
printf("failed to add object to ubus\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int my_ubus_register_event(struct ubus_context ctx, struct ubud_event_handler *notify, my_ubus_event_handler fun, char *notify_event)
{
int ret = 0;
memset(notify, 0, sizeof(struct ubus_event_handler));
notify->cb = fun;
ret = ubus_register_event_handler(ctx, notify, notify_event);
if (ret != 0)
{
printf("Failed to register wifi notify event to ubus server %s\n", ubus_strerror(ret));
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int my_ubus_register_event_all()
{
int ret = 0;
ret = my_ubus_register_event(g_ubus_ctx, &g_ubus_notify, my_wifi_notify_handler, MY_UBUS_NOTIFY_EVENT);
/* your own handler function */
ret = my_ubus_register_event(g_ubus_ctx, &g_ubus_notify_1, my_wifi_notify_handler, MY_UBUS_NOTIFY_EVENT_1);
return ret;
}
int my_ubus_start(void)
{
int ret = 0;
int i = 0;
printf("wifison ubus start\n");
uloop_init();
g_ubus_ctx = ubus_connect(NULL);
if (g_ubus_ctx == NULL)
{
printf("failed to connect to ubus\n");
return -1;
}
ubus_add_uloop(g_ubus_ctx);
/* ubus add objects */
ret = my_ubus_add_object();
if (ret != 0)
{
printf("failed to add object to ubus\n");
return -1;
}
/* ubus register events */
my_ubus_register_event_all();
if (ret != 0)
{
printf("failed to register event to ubus\n");
return -1;
}
uloop_run();//loop
/* unregister ubus event */
ret = ubus_unregister_event_handler(g_ubus_ctx, &g_ubus_notify);
if(ret != 0)
{
printf("Failed to unregister notify event to ubus server %s\n", ubus_strerror(ret));
return -1;
}
/* free resource */
ubus_free(g_ubus_ctx);
uloop_done();
printf("return out of uloop_run\n");
return 0;
}
int main()
{
my_ubus_start();
return 0;
}
void my_wifi_notify_handler(struct ubus_context *ctx, struct ubus_event_handler *ev, const char *type, struct blob_attr *msg)
{
struct blob_attr *tb[PARAM_MAX] = {NULL};
char mac_addr[32] = {0};
char ipv4_addr[32] = {0};
if (!msg)
{
printf(" input msg is NULL\n");
return;
}
/* 这个函数按照my_ubus_policy规则解析收到的ubus参数,然后保存在tb临时变量中 */
blobmsg_parse(my_ubus_policy, PARAM_MAX, tb, blob_data(msg), blob_len(msg));
//macaddr
if( NULL != tb[PARAM_MAC_ADDR] )
{
strcpy(mac_addr, blobmsg_get_string(tb[PARAM_IP4_ADDR]));
}
//ipv4_addr
if( NULL != tb[PARAM_IP4_ADDR] )
{
strcpy(ipv4_addr, blobmsg_get_string(tb[PARAM_IP4_ADDR]));
}
/* TO DO */
}
static int my_ubus_method_1(struct ubus_context *ctx, struct ubus_object *obj,
struct ubus_request_data *req, const char *method,
struct blob_attr *msg)
{
json_object *this_wifison_all_info = NULL;
json_object *this_cap_sys_info = NULL;
struct blob_attr *tb[PARAM_MAX] = {NULL};
char mac_addr[32] = {0};
char ipv4_addr[32] = {0};
if (!msg)
{
printf(" input msg is NULL\n");
return;
}
/* 这个函数按照my_ubus_policy规则解析收到的ubus参数,然后保存在tb临时变量中 */
blobmsg_parse(my_ubus_policy, PARAM_MAX, tb, blob_data(msg), blob_len(msg));
//macaddr
if( NULL != tb[PARAM_MAC_ADDR] )
{
strcpy(mac_addr, blobmsg_get_string(tb[PARAM_IP4_ADDR]));
}
//ipv4_addr
if( NULL != tb[PARAM_IP4_ADDR] )
{
strcpy(ipv4_addr, blobmsg_get_string(tb[PARAM_IP4_ADDR]));
}
this_wifison_all_info = json_object_new_object();
this_cap_sys_info = json_object_new_object();
json_object_object_add(this_wifison_all_info, "sys_info", this_cap_sys_info);
json_object_object_add(this_cap_sys_info, "other_mac", json_object_new_string(g_wifison_info.cap_info.sys_info.sn));
json_object_object_add(this_cap_sys_info, "other_ipv4", json_object_new_string(g_wifison_info.cap_info.sys_info.model));
blob_buf_init(&g_ubus_buf, 0);
blobmsg_add_object(&g_ubus_buf, this_wifison_all_info);
ubus_send_reply(ctx, req, g_ubus_buf.head);
json_object_put(this_cap_sys_info);
json_object_put(this_wifison_all_info);
return 0;
}
static int my_ubus_method_2(struct ubus_context *ctx, struct ubus_object *obj,
struct ubus_request_data *req, const char *method,
struct blob_attr *msg)
{
/* TO DO */
return 0;
}
static int my_ubus_method_3(struct ubus_context *ctx, struct ubus_object *obj,
struct ubus_request_data *req, const char *method,
struct blob_attr *msg)
{
/* TO DO */
return 0;
}
ubus cleint
在这一部代码中主要实现以下两条命令:
ubus call YCY my_ubus_method_1 '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.2.1.2"}'
ubus send my_notify '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.2.1.2"}'
ubus client代码
注意事项:
1.在命令行可以使用ubus call这样的命令,那么代码中如何调用另外进程的objetc的某个method是使用ubus_invoke函数,本例中将这个函数再进行了一层封装方便使用。
2.在命令行可以使用ubus send这样的命令,那么代码中如何发送event是使用ubus_send_event函数,本例中将这个函数再进行了一层封装方便使用。
3.请注意,在这个进程中,因为没有常驻的ubus进程,所以可以将ubus call和ubus send这样封装成独立的函数使用,如果本身这个ubus client也另外作为一个server运行了ubus常驻进程,就不可以按照我这里的封装之后的函数使用,因为每个封装之后的函数都有ctx的创建和free,这显然和常驻进程的概念出现了冲突。
/* ubus send notify */
#define MY_UBUS_PARAM_NAME_1 "mac_addr"
#define MY_UBUS_PARAM_NAME_2 "ipv4_addr"
#define MY_UBUS_NOTIFY_EVENT "my_notify"
#define MY_UBUS_NOTIFY_EVENT_1 "my_notify_1"
#define MY_UBUS_RETURN_STATUS "status"
#define MY_UBUS_RETURN_ERR_STR "err_str"
struct ubus_context *g_ubus_ctx;
struct blob_buf g_ubus_buf;
struct ubud_event_handler g_ubus_notify;
enum
{
RETURN_STATUS,
RETURN_ERR_STR,
RETURN_MAX,
}
enum
{
PARAM_MAC_ADDR,
PARAM_IP4_ADDR,
PARAM_MAX
}
static const struct blobmsg_policy my_ubus_policy[PARAM_MAX] =
{
[PARAM_MAC_ADDR] = {.name = MY_UBUS_PARAM_NAME_1, .type = BLOBMSG_TYPE_STRING},
[PARAM_IP4_ADDR] = {.name = MY_UBUS_PARAM_NAME_2, .type = BLOBMSG_TYPE_STRING},
};
static const struct blobmsg_policy my_ubus_return_policy[PARAM_MAX] =
{
[RETURN_STATUS] = {.name = MY_UBUS_RETURN_STATUS, .type = BLOBMSG_TYPE_INT32},
[RETURN_ERR_STR] = {.name = MY_UBUS_RETURN_ERR_STR, .type = BLOBMSG_TYPE_STRING},
};
static int my_ubus_call_method(struct ubus_context *ubus_ctx,
char *ubus_name,
char *ubus_method,
struct blob_buf b_buf,
ubus_data_handler_t cb)
{
unsigned int id = 0;
int ret;
ret = ubus_lookup_id(ubus_ctx, ubus_name, &id);
if (0 != ret)
{
printf("Error. Can't find %s\n", ubus_name);
}
return ubus_invoke(ubus_ctx, id, ubus_method, b_buf.head, cb, NULL, 0);
}
static int my_invoke_ubus_init(struct ubus_context **ctx)
{
uloop_init();
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
*ctx = ubus_connect(NULL);
if (NULL == *ctx)
{
printf("ubus connect failed\n");
return -1;
}
ubus_add_uloop(*ctx);
return 0;
}
static void my_ubus_ctx_exit(struct ubus_context **ctx)
{
if (*ctx)
ubus_free(*ctx);
}
static void cb_reply_status(struct ubus_request *req, int type, struct blob_attr *msg)
{
struct blob_attr *tb[RETURN_MAX];
int status = 0;
char err_str[128] = {0};
blobmsg_parse(return_policy1, RETURN_MAX, tb, blob_data(msg), blob_len(msg));
if(tb[RETURN_STATUS] != NULL)
{
status = blobmsg_get_u32(tb[RETURN_STATUS]);
}
else
{
printf("cb_reply_status :status can't pick out\n");
}
if(status == 0)//success
{
/* TO DO with status */
printf("%d\n", status);
return ;
}
else
{
if(tb[RETURN_ERR_STR] != NULL)
{
strlcpy(err_str, blobmsg_get_string(tb[RETURN_ERR_STR]), 32);
}
else
{
printf("cb_reply_status :err_str can't pick out\n");
}
}
}
int ubus_call_object_method_with_params(char *macaddr, char *ipv4_addr)
{
int ret = -1;
ret = my_invoke_ubus_init(&g_ubus_ctx);
if (0 != ret)
{
printf("ubus init failed\n");
return -1;
}
/* add params */
blob_buf_init(&g_ubus_buf, 0);
blobmsg_add_string(&g_ubus_buf, MY_UBUS_PARAM_NAME_1, macaddr);
blobmsg_add_string(&g_ubus_buf, MY_UBUS_PARAM_NAME_2, ipv4_addr);
/* ubus call YCY my_ubus_method_1 */
my_ubus_call_method(g_ubus_ctx, MY_UBUS_OBJECT_NAME, MY_UBUS_METHOD_1, g_ubus_buf, cb_reply_status);
my_ubus_ctx_exit(&g_ubus_ctx);
return 0;
}
int ubus_send_event_with_params(char *macaddr, char *ipv4_addr)
{
int ret = -1;
ret = my_invoke_ubus_init(&g_ubus_ctx);
if (0 != ret)
{
printf("ubus init failed\n");
return -1;
}
/* add params */
blob_buf_init(&g_ubus_buf, 0);
blobmsg_add_string(&g_ubus_buf, MY_INVOKE_PARAMS_1, macaddr);
blobmsg_add_string(&g_ubus_buf, MY_INVOKE_PARAMS_2, ipv4_addr);
/* ubus send my_notify */
ubus_send_event(g_ubus_ctx, MY_UBUS_NOTIFY_EVENT, g_ubus_buf.head);
my_ubus_ctx_exit(&g_ubus_ctx);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
char macaddr[] = "60:03:4f:a0:52:51",
char ipv4_addr[] = "192.22.1.2",
/* ubus call YCY my_ubus_method_1 '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.2.1.2"}' */
ubus_call_object_method_with_params(macaddr, ipv4_addr);
/* ubus send my_notify '{"mac_addr":"60:03:4f:a0:52:51","ipv4_addr":"192.2.1.2"}' */
ubus_send_event_with_params(macaddr, ipv4_addr);
return 0;
}
ubus传输过程使用的blob数据我认为也有必要弄清楚一下,在下一篇文章中总结。
以上结束,这两种使用法已经基本涵盖了日常使用的部分。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步