实验1 Python开发环境使用和编程初体验作业
实验任务一:
task1_1:
print('hey, u') print('hey', ' u') x,y,z = 1,2,3 print(x, y, z) print('x = %d, y = %d, z = %d' %(x,y,z)) print('x = {}, y = {}, z = {}'.format(x,y,z)) print(f'x = {x}, y = {y}, z = {z}') print(x) print(y) print(z) print(x, end=' ') print(y, end=' ') print(z)
task1_1运行结果: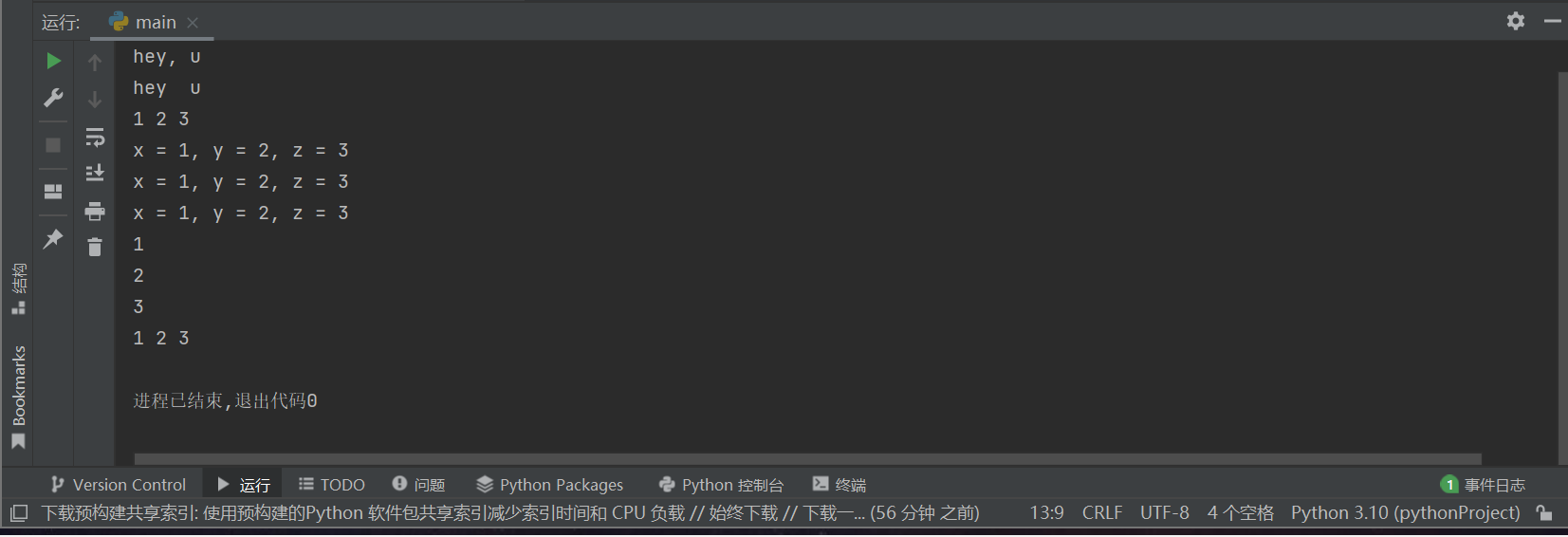
task1_2:
x1, y1 = 1.2, 3.57 x2, y2 = 2.26, 8.7 print('{:-^40}'.format('输出1')) print('x1 = {}, y1 = {}'.format(x1, y1)) print('x2 = {}, y2 = {}'.format(x2, y2)) print('{:-^40}'.format('输出2')) print('x1 = {:.1f}, y1 = {:.1f}'.format(x1, y1)) print('x2 = {:.1f}, y2 = {:.1f}'.format(x2, y2)) print('{:-^40}'.format('输出3')) print('x1 = {:<15.1f}, y1 = {:<15.1f}'.format(x1, y1)) print('x2 = {:<15.1f}, y2 = {:<15.1f}'.format(x2, y2)) print('{:-^40}'.format('输出3')) print('x1 = {:>15.1f}, y1 = {:>15.1f}'.format(x1, y1)) print('x2 = {:>15.1f}, y2 = {:>15.1f}'.format(x2, y2))
task1_2运行结果
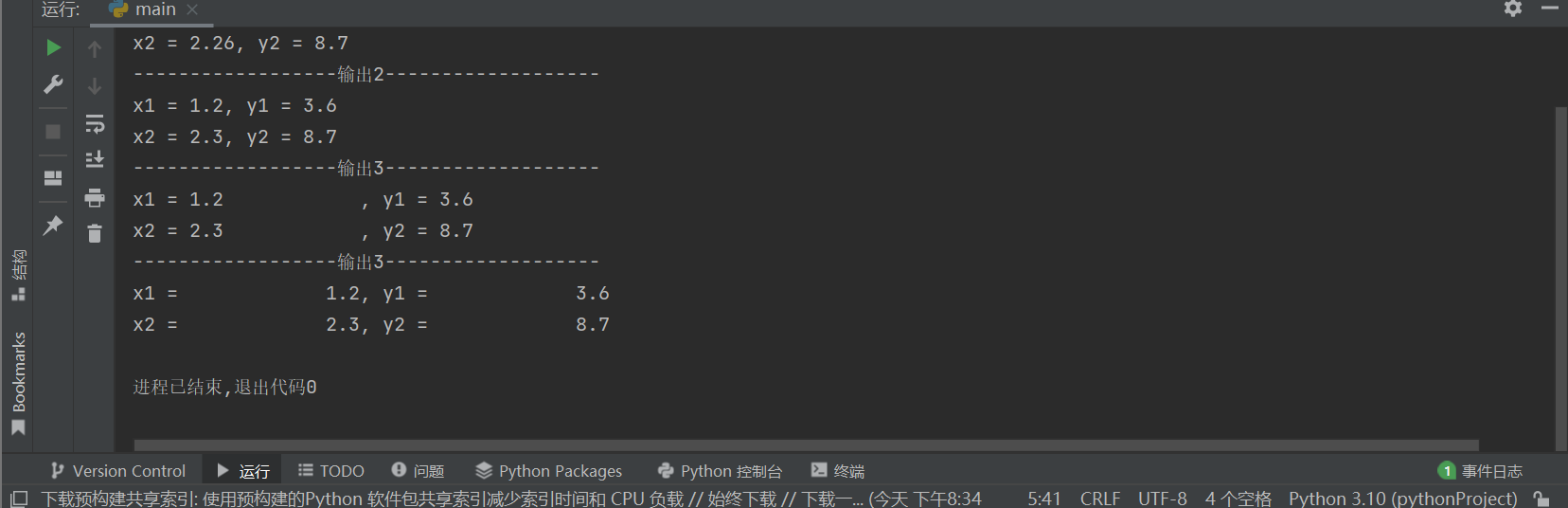
task1_3:
name1, age1 = 'Bill', 19 name2, age2 = 'Hellen', 18 title = 'Personnel Information' print(f'{title:=^40}') print(f'name: {name1:10}, age: {age1:3}') print(f'name: {name2:10}, age: {age2:3}') print(40*'=')
task1_3运行结果
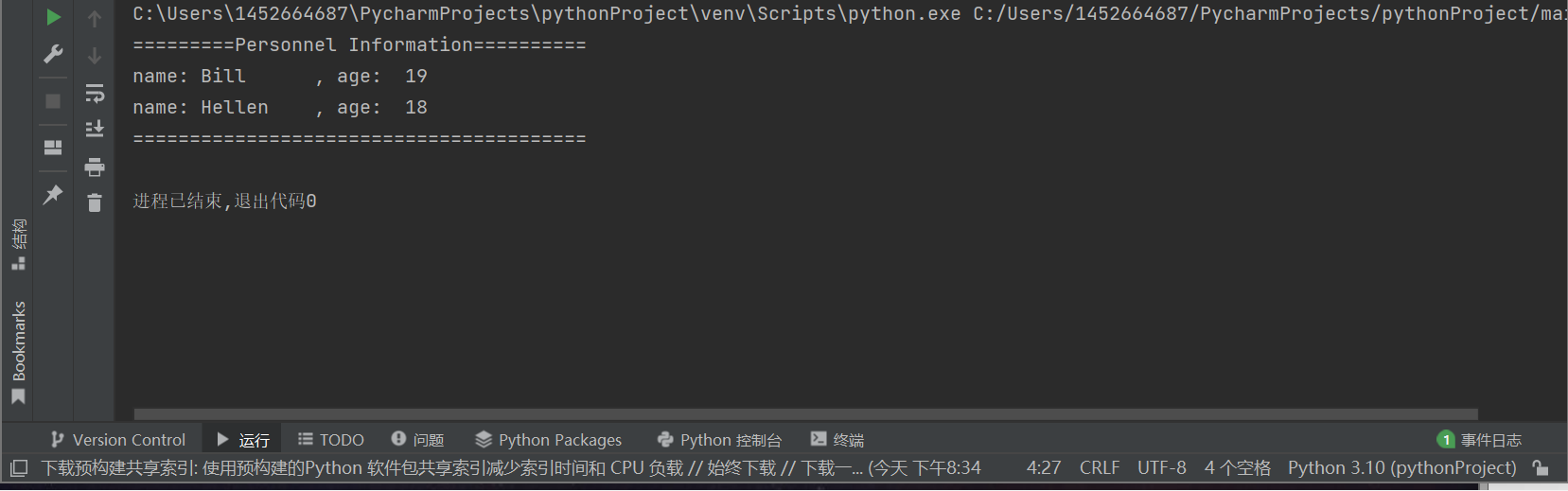
总结:用法1:用于输出单个字符串或单个变量
用法2: 用于输出多个数据项,用逗号分隔
用法3: 用户混合字符串和变量值
方式1: 传统c风格
方式2: s.format()方法
方式3: f-string方式
实验任务二
task2_1
r1 = eval('1 + 2') print(type(r1), r1) r2 = eval('[1, 6, 7.5]') print(type(r2), r2) r3 = eval('"python"') print(type(r3), r3) r4 = eval('7, 42') print(type(r4), r4)
task2_1运行结果
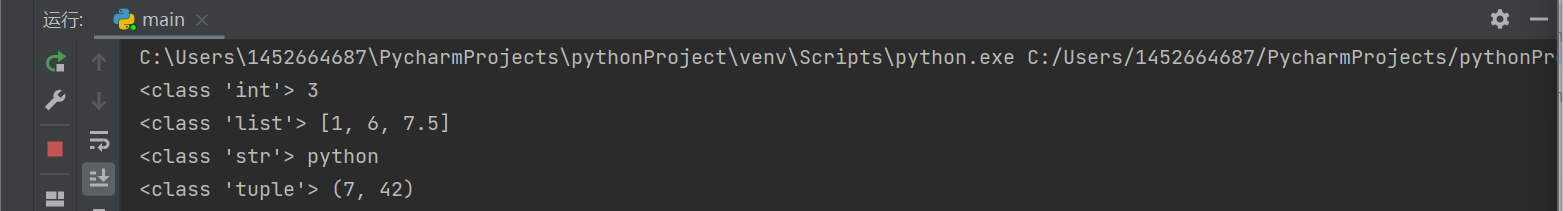
task2_2
a = 0
while a < 3 :
x, y = eval(input('Enter two oprands: '))
ans = x + y
print(f'{x} + {y} = {ans}')
print(f'{type(x)} + {type(y)} = {type(ans)}')
a += 1
else:
print("程序结束")
task2_2运行结果
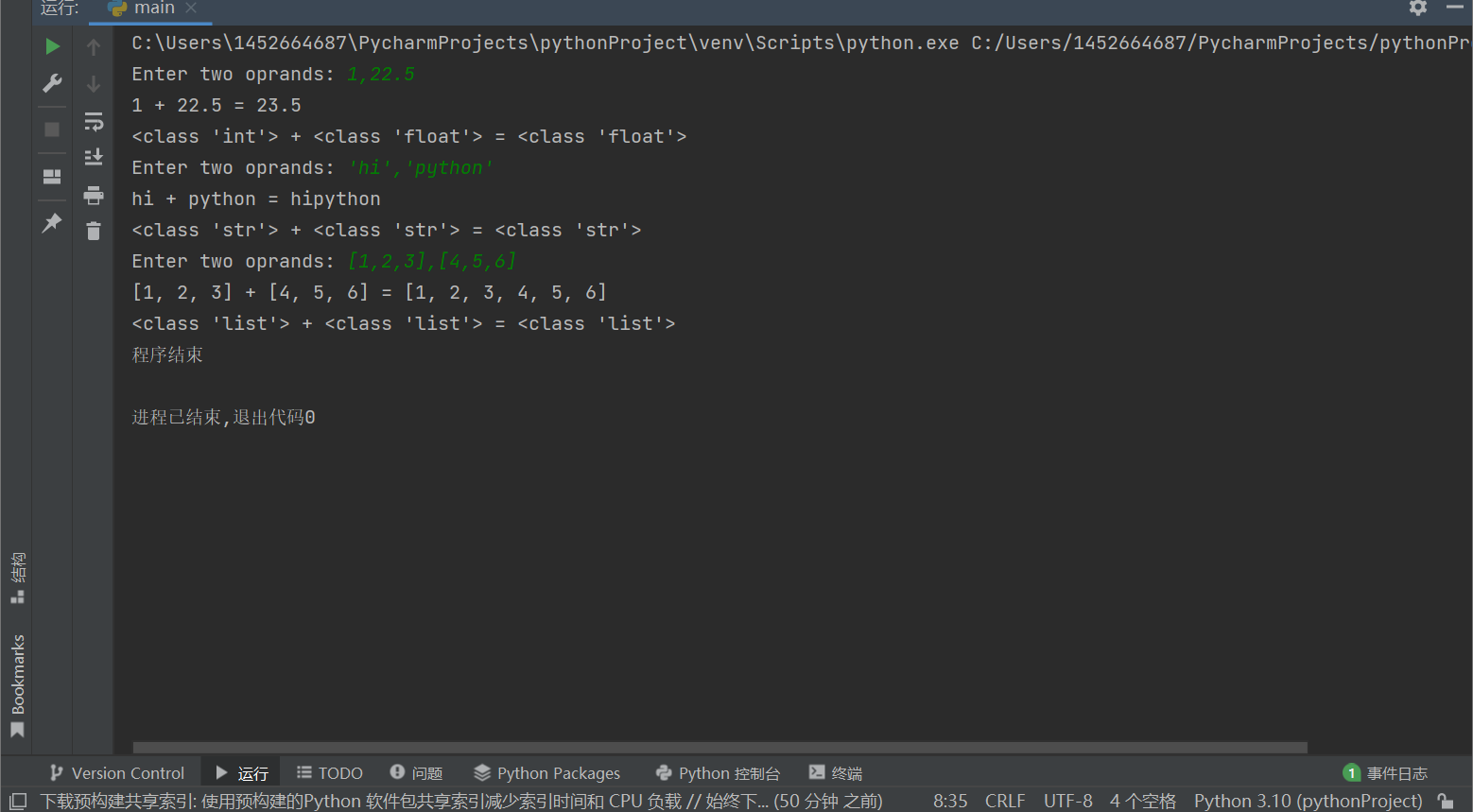
总结:eval()函数的作用是去掉字符串最外侧的引号,并按照Python的语法执行去掉引号后的字符内容
实验任务三
ans1 = 0.1 + 0.2 print(f'0.1 + 0.2 = {ans1}') from decimal import Decimal ans2 = Decimal('0.1') + Decimal('0.2') print(f'0.1 + 0.2 = {ans2}')
运行结果
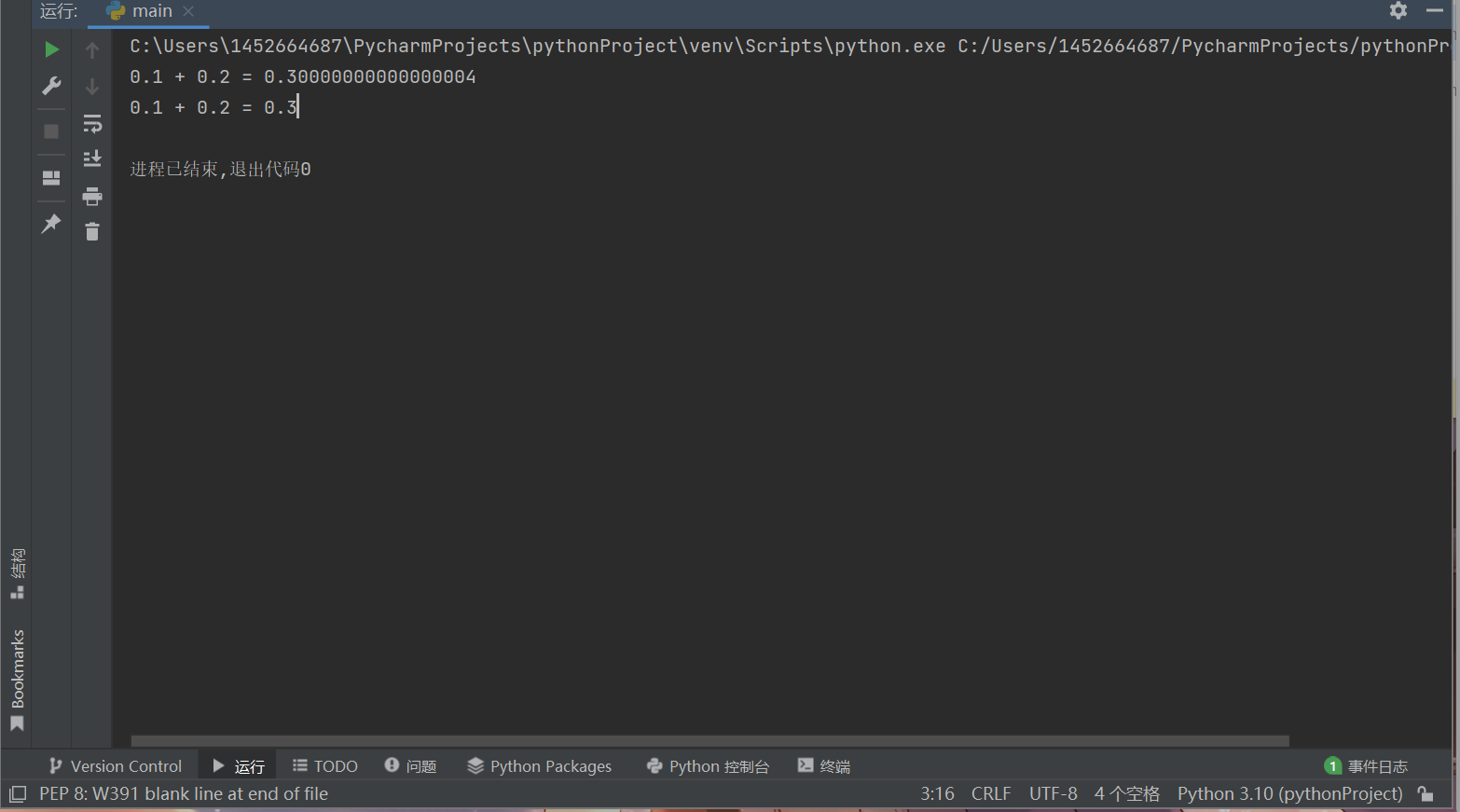
总结:0.1,0.2在二进制浮点中没有精确的表达
Decimal()是将数字舍到十进制下的位数然后再进行运算
实验任务四
print(chr(0x1f601), end = " ") print(chr(0x1f602), end = " ") print(chr(0x1f603), end = " ") print(chr(0x1f604)) print(chr(10000), end=" ") print(chr(0x025b), end=" ") print(chr(0x2708), end=" ") print(chr(0x00A5), end=" ") print(chr(0x266b)) print(ord('a'), end = " ") print(ord('b'), end = " ") print(ord('c')) print(ord('A'), end = " ") print(ord('B'), end = " ") print(ord('C')) print(ord('0'), end = " ") print(ord('1'), end = " ") print(ord('2'))
运行结果
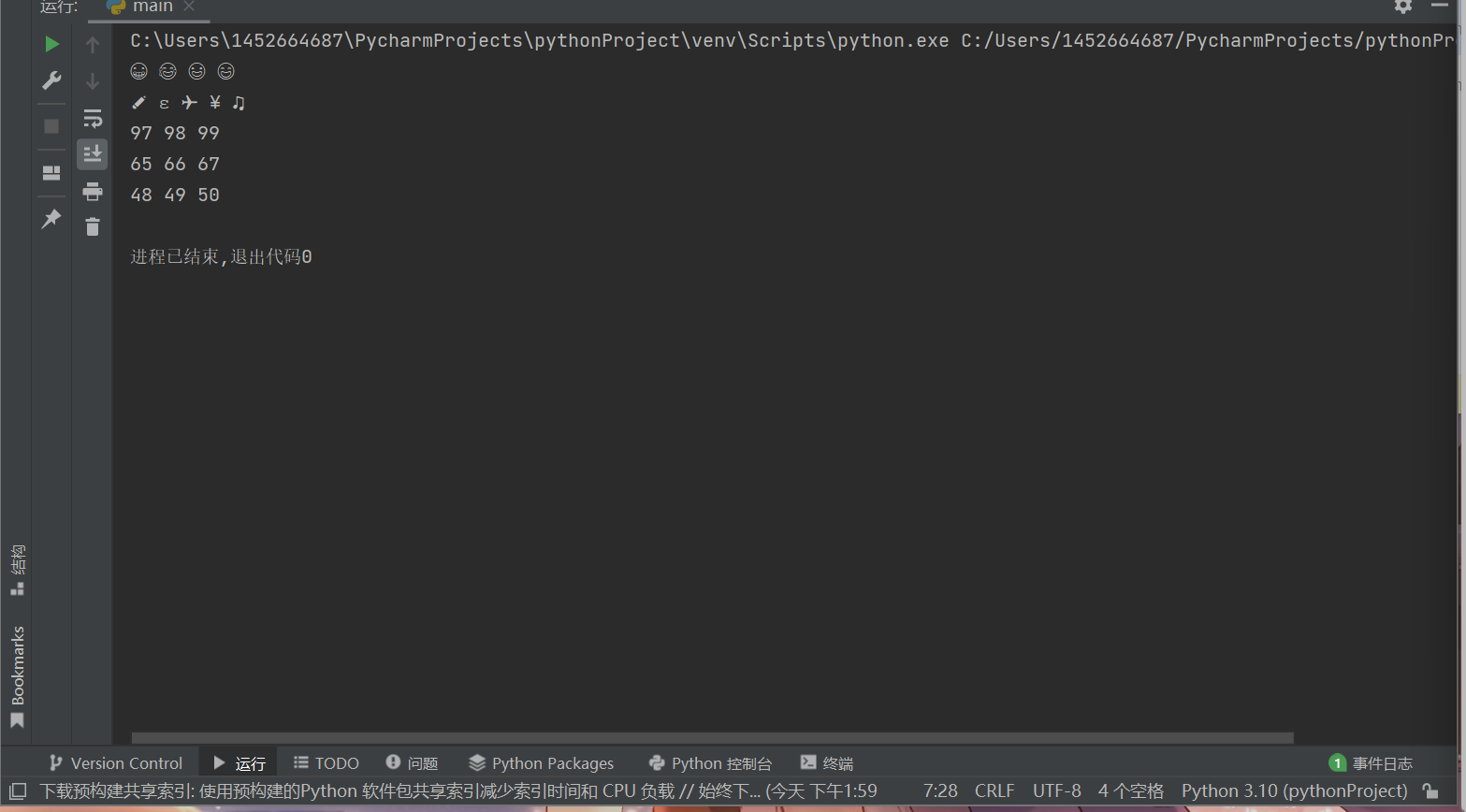
总结: chr()转换成整数对应的ASCII字符
ord()转换成ASCII字符对应的整数
实验任务五
task5_1
from math import sqrt n = float(input('输入一个数:')) ans1 = sqrt(n) ans2 = n**0.5 print('%.2f的平方根是: %.2f' %(n, ans1)) print('{:.2f}的平方根是: {:.2f}'.format(n, ans2)) print(f'{n:.2f}的平方根是: {ans2:.2f}')
task5_1运行结果

task5_2
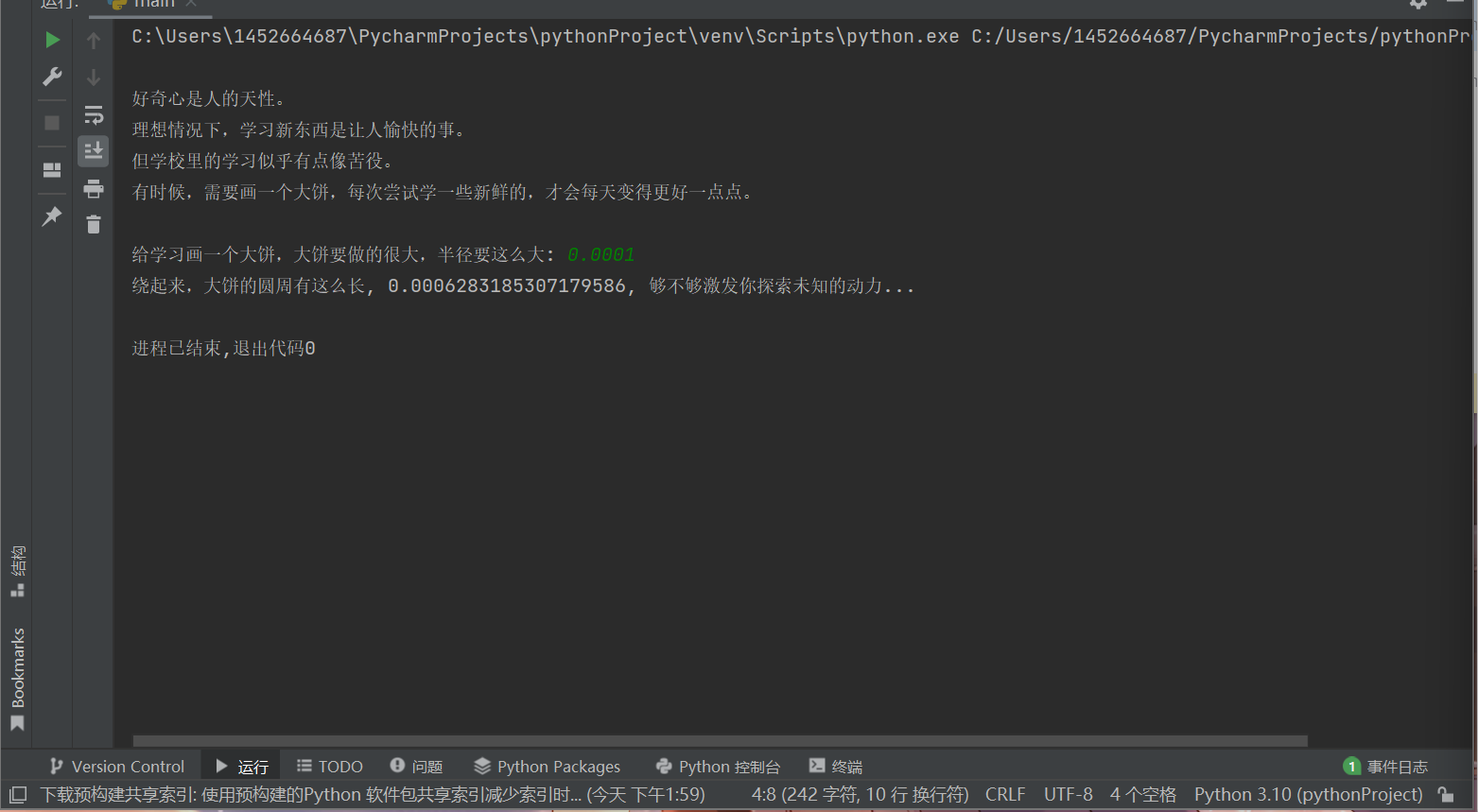
from math import pi text = ''' 好奇心是人的天性。 理想情况下,学习新东西是让人愉快的事。 但学校里的学习似乎有点像苦役。 有时候,需要画一个大饼,每次尝试学一些新鲜的,才会每天变得更好一点点。 ''' print(text) r = float(input('给学习画一个大饼,大饼要做的很大,半径要这么大: ')) circle = 2*pi*r print(f'绕起来,大饼的圆周有这么长, {circle}, 够不够激发你探索未知的动力...')
task5_2运行结果
实验任务六
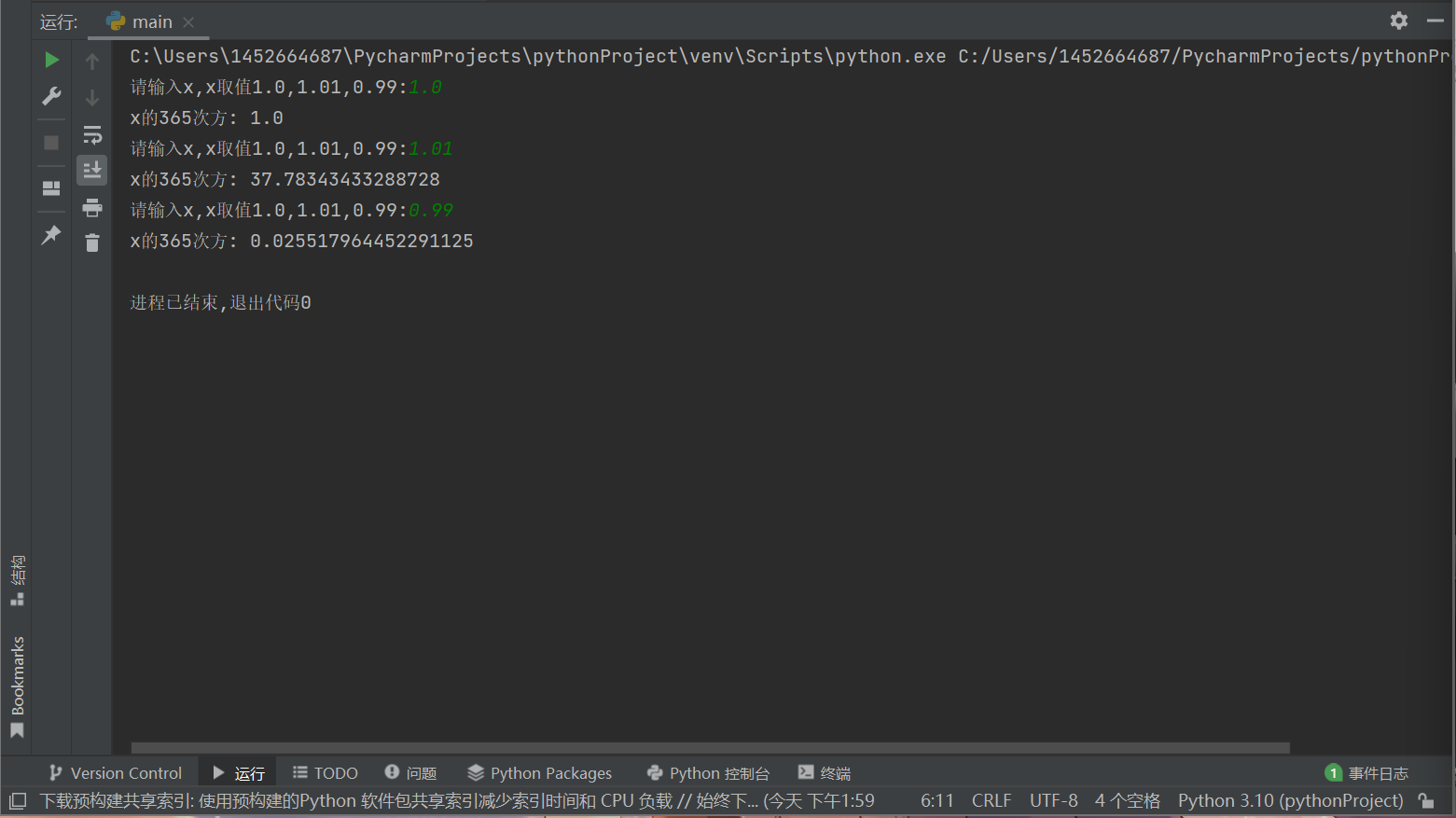
a = 0 while a<3: x = eval(input("请输入x,x取值1.0,1.01,0.99:")) y = x ** 365 print("x的365次方:",y) a += 1
运行结果
实验任务七
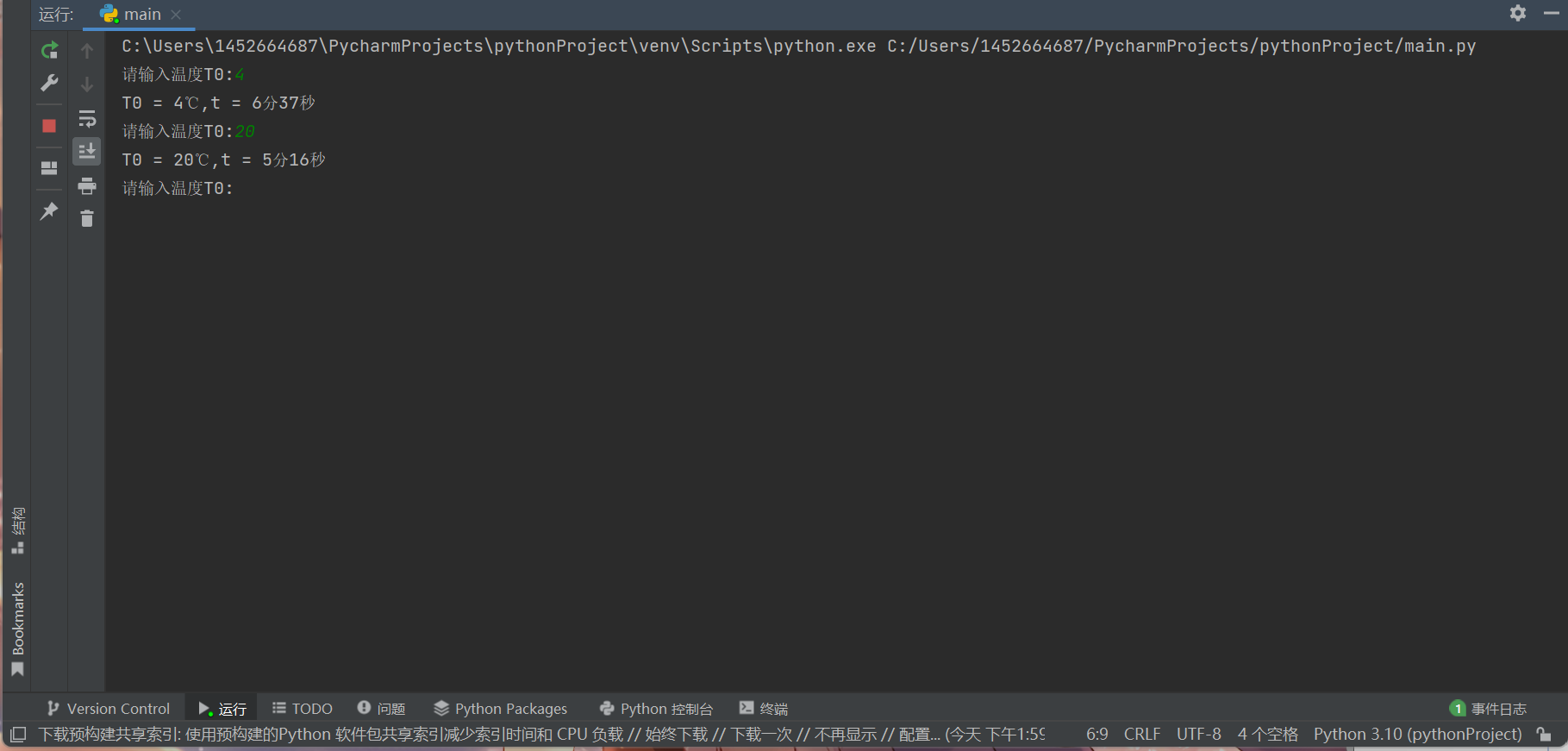
while 1==1: import math T0 = eval(input("请输入温度T0:")) ρ = 1.038 c = 3.7 K = 5.4*(10**(-3)) Tw = 100 Ty = 70 M = 67 t=((M**(2/3)*c*ρ**(1/3))/(K*math.pi**2*(4*math.pi/3)**(2/3)))*math.log(0.76*(T0-Tw)/(Ty-Tw)) m=math.floor(math.ceil(t)/60) s=math.ceil(t)-m*60 print(f'T0 = {T0}℃,t = {m}分{s}秒')
运行结果
作业总结:本次实验主要了解了Python的输出方法,Python中字符串的用法,Python中模块的导入以及数据运算等。
从中得到的经验是:多看书,书上都有,远比搜索引擎靠谱,主要是不能懒。
建议放弃不切实际的幻想,把时间花在行动上。


