SpringMVC(中)
一、传值方式
(1)Map
Controller
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("first")
public String show(Map map){
// 把数据写到 request 域
map.put("name","大白");
map.put("age",20);
return "/result.jsp";
}
}
结果页
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>结果页</h3>
${requestScope.name}
${requestScope.age}
</body>
</html>
(2)ModelMap
ModelMap 对象主要用于传递控制方法处理数据到结果页面,也就是说我们把结果页面上需要的数据放到ModelMap 对象中即可。
把数据写到 request 域。request对象的setAttribute方法的作用: 用来在一个请求过程中传递处理的数据。
使用方法与model一样。
(3)Model
Model 和 ModelMap 的实例都是 spirng mvc 框架来自动创建并作为控制器方法参数传入,用户无需自己创建
可以简单地将model的实现类理解成一个Map,Request级别的模型数据。
Model 是一个接口, 其实现类为 ExtendedModelMap,继承了ModelMap类。
方法介绍
① asMap
Map<String, Object> asMap();
将当前的 model 转换成 Map
发送请求页
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/first">发送请求</a>
</body>
</html>
结果页
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>结果页</h3>
${requestScope.name}
</body>
</html>
Controller
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("first")
public String show(Model model){
// 把数据写到 request 域
model.addAttribute("name","Hello World");
System.out.println(model.asMap());
return "/result.jsp";
}
}
② addAttribute
// 添加键值属性对
Model addAttribute(String attributeName, Object attributeValue);
// 以属性的类型为键添加属性
Model addAttribute(Object attributeValue);
注意:
① addAttribute(Object attributeValue) 默认的key是属性的类型首字母小写
② 如果model存在相同key,会被覆盖
请求页和 ① asMap 一样
结果页
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>结果页</h3>
${requestScope.dog}
</body>
</html>
Controller
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("first")
public String show(Model model){
// 把数据写到 request 域
Dog mydog = new Dog();
mydog.setName("WC");
mydog.setColor("白色");
model.addAttribute("dogs",mydog);
// model.addAttribute(mydog); 相当于 model.addAttribute("dog",mydog);
model.addAttribute(mydog);
System.out.println(model.asMap());
return "/result.jsp";
}
}
③ addAllAttributes
// 将attributes中的内容复制到当前的model中,如果当前model存在相同内容,会被覆盖
Model addAllAttributes(Map<String, ?> attributes);
// 以集合中数据的类型首字母小写做为key,将所提供的Collection中的所有属性复制到这个Map中,如果有同类型会存在覆盖现象
Model addAllAttributes(Collection<?> attributeValues);
Controller
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("first")
public String show(Model model){
// 把数据写到 request 域
model.addAttribute("name","旺财");
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","大白");
map.put("age",20);
model.addAllAttributes(map);
System.out.println(model.asMap());
// output:{name=大白, age=20}
ArrayList<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("小白");
list.add(20);
model.addAllAttributes(list);
System.out.println(model.asMap());
// output:{name=大白, age=20, string=小白, integer=20}
return "/result.jsp";
}
}
④ mergeAttributes
// 将attributes中的内容复制到当前的model中,如果当前model存在相同内容,不会被覆盖
Model mergeAttributes(Map<String, ?> attributes);
Controller
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("first")
public String show(Model model){
// 把数据写到 request 域
model.addAttribute("name","旺财");
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","大白");
map.put("age",20);
model.mergeAttributes(map);
System.out.println(model.asMap());
// output:{name=旺财, age=20}
return "/result.jsp";
}
}
⑤ containsAttribute
// 判断是否包含键为attributeName的值
boolean containsAttribute(String attributeName);
(4)ModelAndView
需要自己创建,既包含模型也包含视图
Controller
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("first")
public ModelAndView show(){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
// 把数据写到 request 域
modelAndView.addObject("name","大白");
modelAndView.addObject("age",20);
System.out.println(modelAndView.getModel());
modelAndView.setViewName("/result.jsp");
return modelAndView;
}
}
结果页
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>结果页</h3>
${requestScope.name}
${requestScope.age}
</body>
</html>
(5)@SessionAttributes注解
将模型中的某个属性暂存到 HttpSession 中,以便多个请求之间可以共享这个属性,@SessionAttributes是标注在类上的。
value :通过指定key将model数据放到session域当中
type :把指定类型的模型数据放到session域当中
@Controller
@SessionAttributes(value = {"name","age"},types = String.class)
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("first")
public String show(Model model){
// 把数据写到 request 域
model.addAttribute("name","大白");
model.addAttribute("age",20);
return "/result.jsp";
}
}
结果页
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>结果页</h3>
${requestScope.name}
${requestScope.age}
${sessionScope.name}
${sessionScope.age}
</body>
</html>
(6)@SessionAttribute注解
使用 @SessionAttribute 来访问预先存在的全局会话属性
请求发送页
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/first">发送请求</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/second">获取Session</a>
</body>
</html>
Controller
@Controller
@SessionAttributes(value = {"name","age"},types = String.class)
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("first")
public String show(Model model){
model.addAttribute("name","大白");
model.addAttribute("age",20);
return "/result.jsp";
}
@RequestMapping("second")
public String get(@SessionAttribute("name") String name, @SessionAttribute("age") Integer age){
// 把数据写到 request 域
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
return "/result.jsp";
}
}
(7)@ModelAttribute
① @ModelAttribute 修饰方法参数:修改处理方法的参数时,自动把该参数放到model当中
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("first")
// 使用JavaBean接收参数,如果方法参数中有 Model model,会自动的把JavaBean添加到 model中去
// 默认键名为JavaBean类型首字母小写,键名可以用@ModelAttribute设置
public String show(@ModelAttribute("mydog") Dog mydog, Model model){
// 把数据写到 request 域
System.out.println(model.asMap());
return "/result.jsp";
}
}
② @ModelAttribute 修饰方法
@ModelAttribute 修饰的方法,在对应的 @RequestMapping 映射方法执行之前,会自动调用,并且会自动的把model传入这个方法,允许提前传入一些model信息。
请求发送页
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/first">发送请求</a>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/first" method="post">
<p>name : <input type="text" name="name" value="小白"></p>
<p>color : <input type="text" name="color" value="白色"></p>
<p><input type="submit" value="提交"></p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Controller
@ModelAttribute 修饰的方法,在对应的 @RequestMapping 映射方法执行之前,允许提前传入一些model信息
@Controller
public class MyController {
@ModelAttribute
public void init(Model model){
System.out.println("@ModelAttribute 自动调用");
model.addAttribute("age",5);
}
@RequestMapping("first")
public String show(@ModelAttribute("mydog") Dog mydog, Model model){
System.out.println(model.asMap());
return "/result.jsp";
}
}
注意:
@ModelAttribute 修饰的方法中设置的 key 和 @RequestMapping 修饰的方法参数中的 key值相同时 @ModelAttribute中的会被“属性”覆盖。即 同名的属性名覆盖。
请求发送页不变,Controller如下
@Controller
public class MyController {
@ModelAttribute
public void init(Model model){
System.out.println("@ModelAttribute 自动调用");
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.setName("initName");
dog.setColor("initColor");
dog.setAge(20);
model.addAttribute("mydog",dog);
}
@RequestMapping("first")
public String show(@ModelAttribute("mydog") Dog mydog, Model model){
System.out.println(model.asMap());
// outPut:{mydog=Dog{name='小白', color='白色', age=20}, ……}
return "/result.jsp";
}
}
注意:
@ModelAttribute 修饰的方法中,model 传进来之前,会把session域里的数据放到model中。
在 @ModelAttribute 里写的内容会覆盖session里的同名内容(“对象”覆盖)
请求发送
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/session">发送请求</a>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/first" method="post">
<p>name : <input type="text" name="name" value="小白"></p>
<p>color : <input type="text" name="color" value="白色"></p>
<p><input type="submit" value="提交"></p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Controller
@Controller
@SessionAttributes(value = "")
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("session")
public String session(Model model){
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.setName("sessionName");
dog.setColor("sessionColor");
dog.setAge(10);
model.addAttribute("dogs",dog);
return "/result.jsp";
}
// model 传进来之前,会把session域里的数据放到model中。
// 在 @ModelAttribute 里写的内容会覆盖session里的同名内容(“对象”覆盖)
@ModelAttribute
public void init(Model model){
System.out.println("@ModelAttribute 自动调用");
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.setName("initName");
dog.setColor("initColor");
model.addAttribute("dogs",dog);
}
@RequestMapping("first")
public String show(@ModelAttribute("mydog") Dog mydog, Model model){
System.out.println(model.asMap());
// outPut:{dogs=Dog{name='initName', color='initColor', age=null}, mydog=Dog{name='小白', color='白色', age=null},……}
return "/result.jsp";
}
}
二、mvc:view-controller
当我们发送一个请求时,如果没有找到对应的mapping,则会对配置文件当中匹配 mvc:view-controller
请求发送页
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/session">发送请求</a>
</body>
</html>
Controller
@Controller
public class MyController {
}
springmvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--注解扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ssm"/>
<mvc:view-controller path="session" view-name="/result.jsp"/>
</beans>
注意点
使用时要添加:
<mvc:annotation-driven/>如果没有添加,@Controller 中的 @RequestMapping 将不能使用。
请求发送页
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/session">发送请求</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/first">发送请求</a>
</body>
</html>
Controller
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("first")
public String view(){
return "/result.jsp";
}
}
springmvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--注解扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ssm"/>
<mvc:view-controller path="session" view-name="/result.jsp"/>
</beans>
点击第二个发送请求时,会报404错误
(1)默认情况下(不写 mvc:view-controller),DispatcherServlet (前端控制器)会自动注册以下三个类
0 = {HttpRequestHandlerAdapter@8252}
1 = {SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter@8253}
2 = {RequestMappingHandlerAdapter@8254}RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 就是处理 @RequestMapping 的。
(2)写了 mvc:view-controller 后,DispatcherServlet (前端控制器)只会自动注册以下两个类
0 = {HttpRequestHandlerAdapter@8255}
1 = {SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter@8256}缺少了 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter ,所以发送 @RequestMapping 的请求会报 404 未找到错误。
(3)添加了 <mvc:annotation-driven/> 后会自动注册那三个类。
三、mvc:annotation-driven
<mvc:annotation-driven /> 是一种简写形式
会自动注册三个Bean
- RequestMappingHandlerMapping
- RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
- ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
并提供了:
- 数据绑定支持,
- @NumberFormatannotation支持,
- @DateTimeFormat支持,
- @Valid支持,读写XML的支持(JAXB),
- 读写JSON的支持(Jackson)。
所以,一般我们都加上 <mvc:annotation-driven /> 。
四、SpringMVC 中的 form标签
简介
在使用SpringMVC的时候我们可以使用Spring封装的一系列表单标签,这些标签都可以访问到 ModelMap 中的内容。
作用
第一是它会自动的绑定来自Model中的一个属性值到当前form对应的实体对象;第二是它支持我们在提交表单的时候使用除GET和POST之外的其他方法进行提交,包括DELETE和PUT等
使用场景
当编辑时, 跳转到form表单页,传统模式要在跳转前先到数据库查询数据,然后进行表单数据回显。
使用form之前一定要保证有对应的bean,没有对应的bean时, 会自动以command为key到 request域中查询,当找不到的时候, 会报异常。
使用方式
User
package com.ssm.domain;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Setter @Getter
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String gender;
private Integer age;
private String[] hobby;
private Pet pet;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", hobby=" + Arrays.toString(hobby) +
", pet=" + pet +
'}';
}
}
Pet
package com.ssm.domain;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Setter @Getter
public class Pet {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Pet() {
}
public Pet(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Pet{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
发送请求
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/edit/2">发送更新请求</a>
</body>
</html>
处理请求
@RequestMapping("edit/{id}")
public String view(@PathVariable Integer id, Model model){
System.out.println(id);
/* 模拟数据库查询,准备数据 */
ArrayList<String> hobbyList = new ArrayList<>();
hobbyList.add("篮球");
hobbyList.add("足球");
hobbyList.add("排球");
hobbyList.add("乒乓球");
model.addAttribute("hobbys", hobbyList);
ArrayList<Pet> petList = new ArrayList<>();
petList.add(new Pet(1,"狗"));
petList.add(new Pet(2,"猫"));
petList.add(new Pet(3,"鸟"));
petList.add(new Pet(4,"猪"));
model.addAttribute("pets",petList);
User user = new User();
// 文本框
user.setId(id);
user.setUsername("user1");
user.setPassword("145263");
user.setAge(20);
// 单选框
user.setGender("男");
// 复选框
String[] hobby = new String[]{"篮球","足球","排球"};
user.setHobby(hobby);
// 下拉框
user.setPet(new Pet(2,"猫"));
model.addAttribute("user",user);
return "/update.jsp";
}
创建表单页,引入标签库
引入标签库
<%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" prefix="fm" %>
update.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" prefix="fm" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>更新界面</h1>
<fm:form modelAttribute="user" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/update">
<p>用户Id : <fm:input path="id"/></p>
<p>用户名 : <fm:input path="username"/></p>
<p>密码 : <fm:input path="password"/></p>
<p>年龄 : <fm:input path="age"/></p>
<p>性别 : <fm:radiobutton path="gender" value="男" label="男"/>
<fm:radiobutton path="gender" value="女" label="女"/></p>
<p>爱好 : <fm:checkboxes path="hobby" items="${hobbys}"/></p>
<p>宠物 : <fm:select path="pet.id" items="${pets}" itemValue="id" itemLabel="name"/></p>
<p><input type="submit" value="更新"></p>
</fm:form>
</body>
</html>
处理请求
@RequestMapping("update")
public String update(User user){
System.out.println(user);
return "result.jsp";
}
result.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>结果页</h3>
${requestScope.user}
</body>
</html>
五、服务器表单校验
为什么后端要做表单的校验,如果只使用前端校验的话,当浏览器把JS给禁用掉,就校验不了啦
JSR
JSR 303 是 Java 为 Bean 数据合法性校验提供的标准框架,它已经包含在 JavaEE 6.0 中 ,JSR 303 通过在 Bean 属性上标注类似于 @NotNull、@Max 等标准的注解,指定校验规则,并通过标准的验证接口对 Bean 进行验证。
Hibernate Validator
Hibernate Validator 是 JSR 303 的一个参考实现,除支持所有标准的校验注解外,它还支持其它的扩展注解。
使用时需要导入jar包
+ Hibernate-Validator
- classmate.jar
- hibernate-validator-5.jar
- hibernate-validator-annotation-processor-5.jar
- jboss-logging-3.1.1.jar
- validation-api-1.1.0.jar
常用校验规则
Bean Validation 中内置的约束
| 约束注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @Null | 被注释的元素必须为 null |
| @NotNull | 被注释的元素必须不为 null |
| @AssertTrue | 被注释的元素必须为 true |
| @AssertFalse | 被注释的元素必须为 false |
| @Min(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @Max(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @DecimalMin(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @DecimalMax(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @Size(max=, min=) | 被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内 |
| @Digits (integer, fraction) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内 |
| @Past | 被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期 |
| @Future | 被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期 |
| @Pattern(regex=,flag=) | 被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式 |
Hibernate Validator 附加的约束
| 约束注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @NotBlank(message =) | 验证字符串非null,且长度必须大于0 |
| 被注释的元素必须是电子邮箱地址 | |
| @Length(min=,max=) | 被注释的字符串的大小必须在指定的范围内 |
| @NotEmpty | 被注释的字符串的必须非空 |
| @Range(min=,max=,message=) | 被注释的元素必须在合适的范围内 |
使用
① 导入jar包,在配置文件当中写上
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
② 在模型当中添加对应的校验规则
package com.ssm.domain;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotBlank;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Setter @Getter
public class User {
@NotNull(message = "ID不能为空")
private Integer id;
@NotBlank(message = "用户名不能为空")
private String username;
@NotBlank(message = "密码不能为空")
private String password;
private String gender;
@Max(value = 200, message = "年龄不正确")
@Min(value = 0, message = "年龄不正确")
private Integer age;
private String[] hobby;
private Pet pet;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", hobby=" + Arrays.toString(hobby) +
", pet=" + pet +
'}';
}
}
③ 在处理器方法的参数标记@valid注解即可
@RequestMapping("update")
public String update(@Valid User user, BindingResult result) {
System.out.println(user);
List<FieldError> fieldErrors = result.getFieldErrors();
for (FieldError fieldError : fieldErrors) {
System.out.println(fieldError.getField() + " : " + fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
}
return "result.jsp";
}
④ 错误信息页面回显
(1)使用form标签
<fm:errors path=""/>
请求发送页
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/edit/2">发送更新请求</a>
</body>
</html>
user
package com.ssm.domain;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotBlank;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Setter @Getter
public class User {
@NotNull(message = "ID不能为空")
private Integer id;
@NotBlank(message = "用户名不能为空")
private String username;
@NotBlank(message = "密码不能为空")
private String password;
private String gender;
@Max(value = 200, message = "年龄不正确")
@Min(value = 0, message = "年龄不正确")
private Integer age;
private String[] hobby;
private Pet pet;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", hobby=" + Arrays.toString(hobby) +
", pet=" + pet +
'}';
}
}
Controller
package com.ssm.web.controller;
import com.ssm.domain.Pet;
import com.ssm.domain.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.validation.Valid;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
public class MyController {
ArrayList<String> hobbyList;
ArrayList<Pet> petList;
@RequestMapping("edit/{id}")
public String view(@PathVariable Integer id, Model model) {
System.out.println(id);
/* 模拟数据库查询,准备数据 */
hobbyList = new ArrayList<>();
hobbyList.add("篮球");
hobbyList.add("足球");
hobbyList.add("排球");
hobbyList.add("乒乓球");
model.addAttribute("hobbys", hobbyList);
petList = new ArrayList<>();
petList.add(new Pet(1, "狗"));
petList.add(new Pet(2, "猫"));
petList.add(new Pet(3, "鸟"));
petList.add(new Pet(4, "猪"));
model.addAttribute("pets", petList);
User user = new User();
// 文本框
user.setId(id);
user.setUsername("user1");
user.setPassword("145263");
user.setAge(20);
// 单选框
user.setGender("男");
// 复选框
String[] hobby = new String[]{"篮球", "足球", "排球"};
user.setHobby(hobby);
// 下拉框
user.setPet(new Pet(2, "猫"));
model.addAttribute("user", user);
return "/update.jsp";
}
@RequestMapping("update")
public String update(@Valid User user, BindingResult result, Model model) {
System.out.println(user);
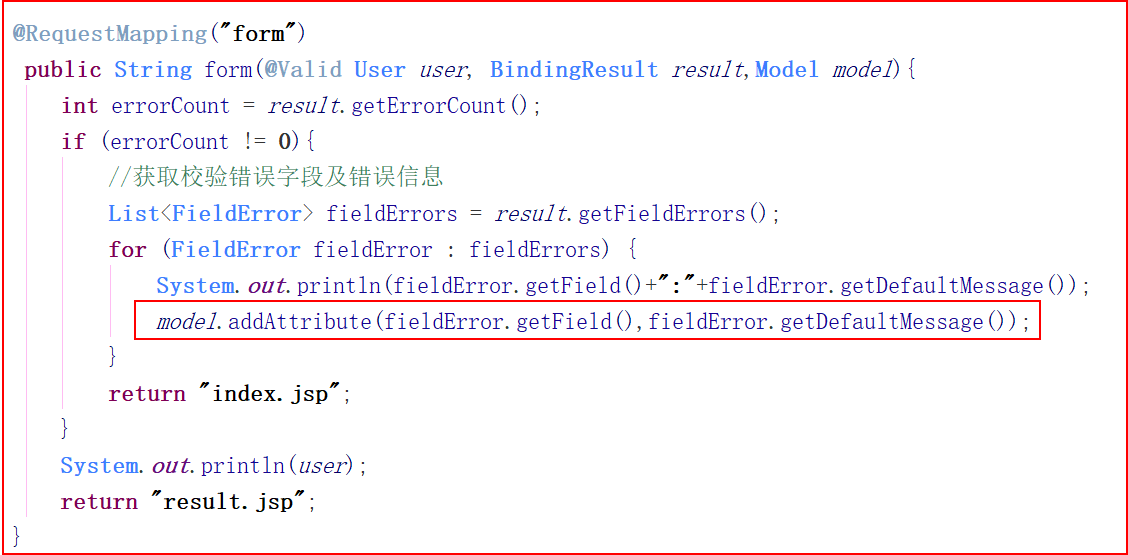
if (result.getErrorCount() != 0){
List<FieldError> fieldErrors = result.getFieldErrors();
for (FieldError fieldError : fieldErrors) {
System.out.println(fieldError.getField() + " : " + fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
}
model.addAttribute("hobbys", hobbyList);
model.addAttribute("pets", petList);
return "/update.jsp";
}
return "/result.jsp";
}
}
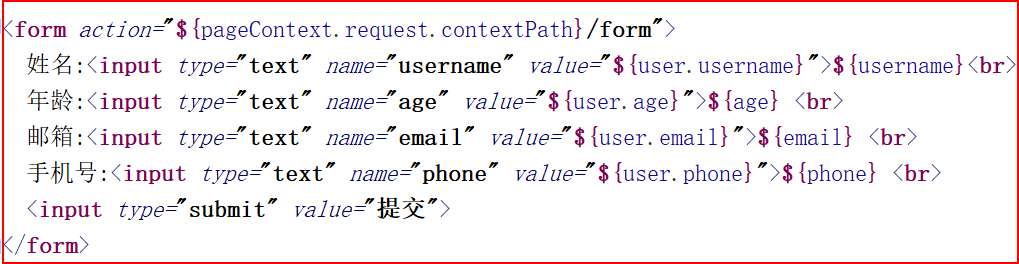
update.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" prefix="fm" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>更新界面</h1>
<fm:form modelAttribute="user" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/update">
<p>用户Id : <fm:input path="id"/> <fm:errors path="id" cssStyle="color: red"/></p>
<p>用户名 : <fm:input path="username"/> <fm:errors path="username" cssStyle="color: red"/> </p>
<p>密码 : <fm:input path="password"/> <fm:errors path="password" cssStyle="color: red"/></p>
<p>年龄 : <fm:input path="age"/> <fm:errors path="age" cssStyle="color: red"/></p>
<p>性别 : <fm:radiobutton path="gender" value="男" label="男"/>
<fm:radiobutton path="gender" value="女" label="女"/></p>
<p>爱好 : <fm:checkboxes path="hobby" items="${hobbys}"/></p>
<p>宠物 : <fm:select path="pet.id" items="${pets}" itemValue="id" itemLabel="name"/></p>
<p><input type="submit" value="更新"></p>
</fm:form>
</body>
</html>
结果页
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>结果页</h3>
${requestScope.user}
</body>
</html>
(2)使用原始表单错误信息写到Model中