[LOJ#3022][网络流]「CQOI2017」老 C 的方块
-
定义有特殊边相邻的格子颜色为黑,否则为白
-
可以看出,题目给出的限制条件的本质是如果两个小方块所在的格子 \(x\) 和 \(y\) 为两个相邻的黑格,那么 \(x\) 和 \(y\) 之间必然有一者满足其上下左右的所有白格内都没有小方块
-
即对于这样的 \(x\) 和 \(y\) ,需要以下三个条件至少满足一个:
-
(1)用 \(\min(w_x,w_y)\) 的代价删除 \(x\) 和 \(y\) 上的其中一个小方块
-
(2)把与 \(x\) 相邻的白格内的小方块全部删掉
-
(3)把与 \(y\) 相邻的白格内的小方块全部删掉
-
故考虑对于所有的白格 \(i\) ,拆成两个点 \(i_0\) 和 \(i_1\) ,并连边 \(<i_0,i_1,w_i>\)
-
对于所有的黑格组(相邻且之间有特殊边的两个黑格)\((x,y)\) ,也建立两个点,第一个点向第二个点连容量为 \(\min(w_x,w_y)\) 的边
-
这时候我们就有一个比较明显的最小割模型了
-
即对于需要「至少满足一个」的条件集合进行串联,需要「全部满足」的条件集合进行并联
-
具体地,如下图:
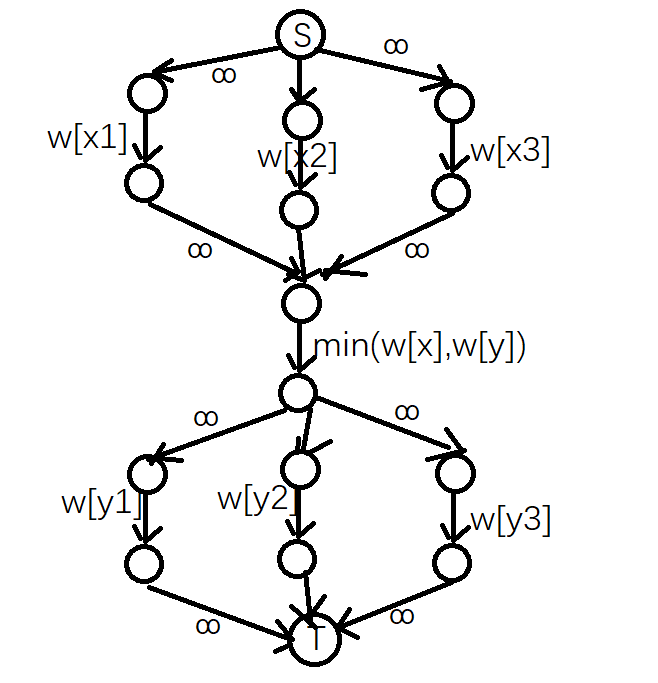
-
其中 \(x_1,x_2,x_3\) 表示与 \(x\) 相邻的白格, \(y_1,y_2,y_3\) 同理
-
以下设上图中 \(x_1,x_2,x_3\) 对应的三条边在第一层, \(\min(w_x,w_y)\) 对应的边在第二层, \(y_1,y_2,y_3\) 对应的三条边在第三层
-
至于 \(\min(w_x,w_y)\) 的边为什么一定要放在中间,后面会说
-
我们会发现一个问题:一个白格会属于 \(3\) 个黑格,直接建图会导致不同的黑格组之间互相影响
-
所以正确的建图方式是:设 \(x\) 在 \(y\) 左边,则要判断黑哥所在行号的奇偶性
-
若在奇行则 \(S\) 到 \(T\) 的路径上依次限制与 \(x\) 相邻的白格 \(\rightarrow\) 黑格组 \((x,y)\) 本身 \(\rightarrow\) 与 \(y\) 相邻的白格,否则反过来
-
考虑这样做的正确性:易得这么建图可以使得对于任意一个白格对应的限制边只在一层(第一层或第三层)中出现
-
如果一个白格 \(i\) 同时属于两个黑格组且位于第一层,且边 \(<i_0,i_1>\) 没有被割掉,那么显然这两个黑格组的第一层限制都必然不会被满足了,这时即使不同的黑格组之间互相影响也不会对最终的答案造成影响。第三层同理
-
而这时候如果 \(\min(w_x,w_y)\) 不在第二层而在第一层,那么假设这时候 \(i\) 位于第二层,有两个黑格组 \(X\) 和 \(Y\) ,\(X\) 只割掉了第三层,\(Y\) 只割掉了第一层,那么由于保留了边 \(<i_0,i_1>\) 之后 \(X\) 和 \(Y\) 的第二层能互通,故这时源点到汇点有一条 \(S\rightarrow X_1\rightarrow X_2\rightarrow Y_2\rightarrow Y_3\rightarrow T\) 的路径,这时就不合法了
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
template <class T>
inline void read(T &res)
{
res = 0; bool bo = 0; char c;
while (((c = getchar()) < '0' || c > '9') && c != '-');
if (c == '-') bo = 1; else res = c - 48;
while ((c = getchar()) >= '0' && c <= '9')
res = (res << 3) + (res << 1) + (c - 48);
if (bo) res = ~res + 1;
}
template <class T>
inline T Min(const T &a, const T &b) {return a < b ? a : b;}
const int N = 1e5 + 10, M = 3e5 + 5, L = 4e6 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, X[N], Y[N], w[N], ecnt = 1, nxt[L], adj[M], go[L], cap[L], len, que[M],
lev[M], cur[M], S, T, ans;
std::map<int, int> is[N];
int which(int x, int op) {return (x << 1) + op;}
void add_edge(int u, int v, int w)
{
nxt[++ecnt] = adj[u]; adj[u] = ecnt; go[ecnt] = v; cap[ecnt] = w;
nxt[++ecnt] = adj[v]; adj[v] = ecnt; go[ecnt] = u; cap[ecnt] = 0;
}
bool bfs()
{
for (int i = S; i <= T; i++) lev[i] = -1, cur[i] = adj[i];
lev[que[len = 1] = S] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++)
{
int u = que[i];
for (int e = adj[u], v = go[e]; e; e = nxt[e], v = go[e])
if (cap[e] && lev[v] == -1)
{
lev[que[++len] = v] = lev[u] + 1;
if (v == T) return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int dinic(int u, int flow)
{
if (u == T) return flow;
int res = 0, delta;
for (int &e = cur[u], v = go[e]; e; e = nxt[e], v = go[e])
if (cap[e] && lev[u] < lev[v])
{
delta = dinic(v, Min(cap[e], flow - res));
if (delta)
{
cap[e] -= delta; cap[e ^ 1] += delta;
res += delta; if (res == flow) break;
}
}
if (res < flow) lev[u] = -1;
return res;
}
void add(int i, int j, int op)
{
if (op) add_edge(S, which(j, 0), INF), add_edge(which(j, 1), which(i, 0), INF);
else add_edge(which(i, 1), which(j, 0), INF), add_edge(which(j, 1), T, INF);
}
int main()
{
read(n); read(n); read(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
read(X[i]), read(Y[i]), read(w[i]), is[X[i]][Y[i]] = i;
S = 1; T = n + 1 << 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (X[i] % 4 != (Y[i] + 1) % 2 * 2 + 1 && X[i] % 4 != Y[i] % 2 * 2)
add_edge(which(i, 0), which(i, 1), w[i]);
if (X[i] % 4 != (Y[i] + 1) % 2 * 2 + 1) continue;
int x = X[i], y = Y[i], j;
if (!(j = is[x + 1][y])) continue;
add_edge(which(i, 0), which(i, 1), Min(w[i], w[j]));
if (j = is[x - 1][y]) add(i, j, y & 1);
if (j = is[x][y - 1]) add(i, j, y & 1);
if (j = is[x][y + 1]) add(i, j, y & 1);
if (j = is[x + 2][y]) add(i, j, !(y & 1));
if (j = is[x + 1][y - 1]) add(i, j, !(y & 1));
if (j = is[x + 1][y + 1]) add(i, j, !(y & 1));
}
while (bfs()) ans += dinic(S, INF);
return std::cout << ans << std::endl, 0;
}


