《Python数据可视化之matplotlib实践》 源码 第二篇 精进 第七章
图 7.1


import matplotlib as mpl import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np mpl.rcParams["font.sans-serif"]=["SimHei"] mpl.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"]=False fig, ax1 = plt.subplots() t=np.arange(0.05, 10.0, 0.01) s1=np.exp(t) ax1.plot(t, s1, c="b", ls="-") ax1.set_xlabel("x坐标轴") ax1.set_ylabel("以e为底指数函数", color="b") ax1.tick_params("y", colors="b") ax2=ax1.twinx() s2=np.cos(t**2) ax2.plot(t, s2, c="r", ls=":") ax2.set_ylabel("余弦函数", color="r") ax2.tick_params("y", colors="r") plt.show()
=====================================================
图 7.2
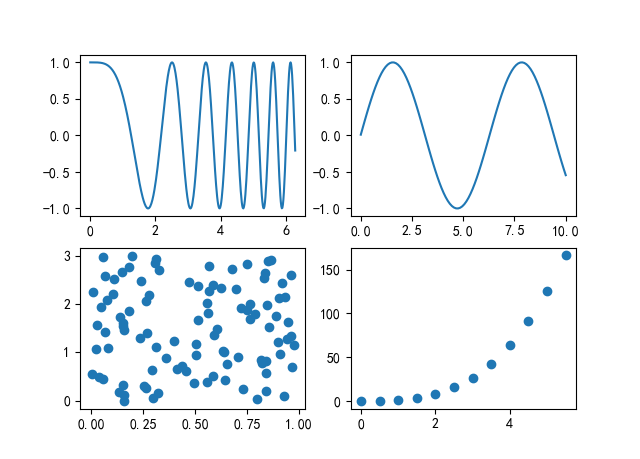

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np x1=np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 400) y1=np.cos(x1**2) x2=np.linspace(0.01, 10, 100) y2=np.sin(x2) x3=np.random.rand(100) y3=np.linspace(0, 3, 100) x4=np.arange(0, 6, 0.5) y4=np.power(x4, 3) fig, ax=plt.subplots(2, 2) ax1=ax[0, 0] ax1.plot(x1, y1) ax2=ax[0, 1] ax2.plot(x2, y2) ax3=ax[1, 0] ax3.scatter(x3, y3) ax4=ax[1, 1] ax4.scatter(x4, y4) plt.show()
=====================================================
图 7.3


import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np x1=np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 400) y1=np.cos(x1**2) x2=np.linspace(0.01, 10, 100) y2=np.sin(x2) x3=np.random.rand(100) y3=np.linspace(0, 3, 100) x4=np.arange(0, 6, 0.5) y4=np.power(x4, 3) fig, ax=plt.subplots(2, 2, sharex="all") ax1=ax[0, 0] ax1.plot(x1, y1) ax2=ax[0, 1] ax2.plot(x2, y2) ax3=ax[1, 0] ax3.scatter(x3, y3) ax4=ax[1, 1] ax4.scatter(x4, y4) plt.show()
=====================================================
图 7.4
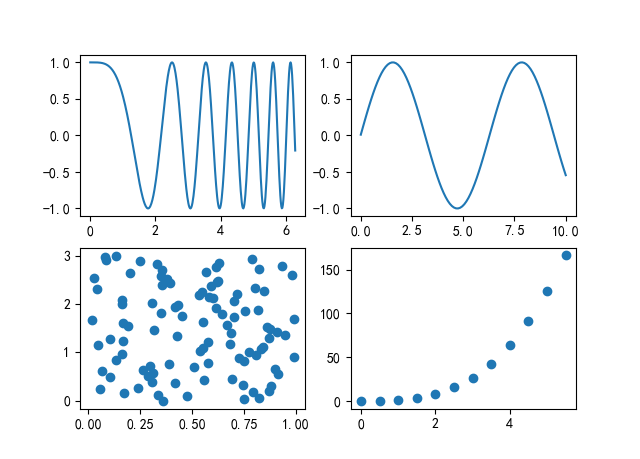

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np x1=np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 400) y1=np.cos(x1**2) x2=np.linspace(0.01, 10, 100) y2=np.sin(x2) x3=np.random.rand(100) y3=np.linspace(0, 3, 100) x4=np.arange(0, 6, 0.5) y4=np.power(x4, 3) fig, ax=plt.subplots(2, 2, sharex="none") ax1=ax[0, 0] ax1.plot(x1, y1) ax2=ax[0, 1] ax2.plot(x2, y2) ax3=ax[1, 0] ax3.scatter(x3, y3) ax4=ax[1, 1] ax4.scatter(x4, y4) plt.show()
=====================================================
图 7.5
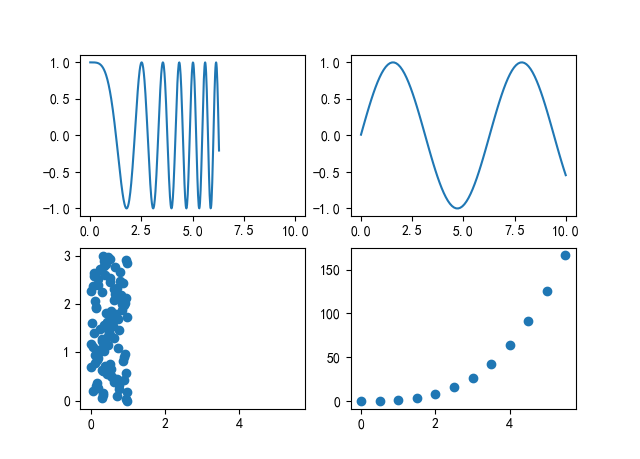

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np x1=np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 400) y1=np.cos(x1**2) x2=np.linspace(0.01, 10, 100) y2=np.sin(x2) x3=np.random.rand(100) y3=np.linspace(0, 3, 100) x4=np.arange(0, 6, 0.5) y4=np.power(x4, 3) fig, ax=plt.subplots(2, 2, sharex="row") ax1=ax[0, 0] ax1.plot(x1, y1) ax2=ax[0, 1] ax2.plot(x2, y2) ax3=ax[1, 0] ax3.scatter(x3, y3) ax4=ax[1, 1] ax4.scatter(x4, y4) plt.show()
=====================================================
图 7.6
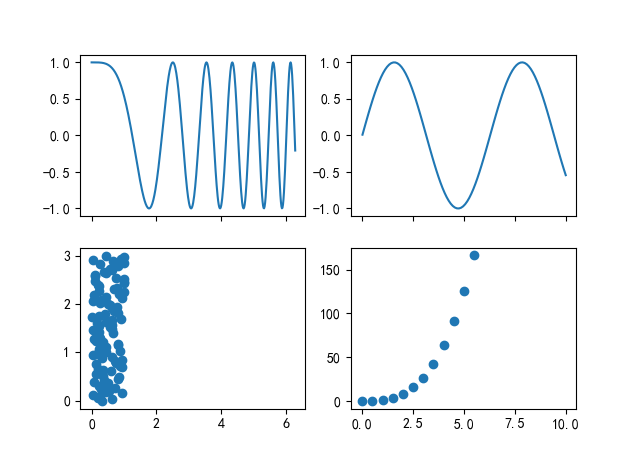

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np x1=np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 400) y1=np.cos(x1**2) x2=np.linspace(0.01, 10, 100) y2=np.sin(x2) x3=np.random.rand(100) y3=np.linspace(0, 3, 100) x4=np.arange(0, 6, 0.5) y4=np.power(x4, 3) fig, ax=plt.subplots(2, 2, sharex="col") ax1=ax[0, 0] ax1.plot(x1, y1) ax2=ax[0, 1] ax2.plot(x2, y2) ax3=ax[1, 0] ax3.scatter(x3, y3) ax4=ax[1, 1] ax4.scatter(x4, y4) plt.show()
=====================================================
图 7.7

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np x=np.linspace(0.0, 10.0, 200) y=np.cos(x)*np.sin(x) y2=np.exp(-x)*np.sin(x) y3=3*np.sin(x) y4=np.power(x, 0.5) fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3, ax4)=plt.subplots(4, 1, sharex="all") fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0) ax1.plot(x, y, ls="-", lw=2) ax1.set_yticks(np.arange(-0.6, 0.7, 0.2)) ax1.set_ylim(-0.7, 0.7) ax2.plot(x, y2, ls="-", lw=2) ax2.set_yticks(np.arange(-0.05, 0.36, 0.1)) ax2.set_ylim(-0.1, 0.4) ax3.plot(x, y3, ls="-", lw=2) ax3.set_yticks(np.arange(-3, 4, 1)) ax3.set_ylim(-3.5, 3.5) ax4.plot(x, y4, ls="-", lw=2) ax4.set_yticks(np.arange(0.0, 3.6, 0.5)) ax4.set_ylim(0.0, 4.0) plt.show()
=====================================================
图 7.8


import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np x1=np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 400) y1=np.cos(x1**2) x2=np.linspace(0.01, 10, 100) y2=np.sin(x2) x3=np.random.rand(100) y3=np.linspace(0, 3, 100) x4=np.arange(0, 6, 0.5) y4=np.power(x4, 3) fig, ax=plt.subplots(2, 2) ax1=plt.subplot(221) ax1.plot(x1, y1) ax2=plt.subplot(222) ax2.plot(x2, y2) ax3=plt.subplot(223) ax3.scatter(x3, y3) ax4=plt.subplot(224, sharex=ax1) ax4.scatter(x4, y4) plt.show()
=====================================================
图 7.9


import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np x1=np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 400) y1=np.cos(x1**2) x2=np.linspace(0.01, 10, 100) y2=np.sin(x2) x3=np.random.rand(100) y3=np.linspace(0, 3, 100) x4=np.arange(0, 6, 0.5) y4=np.power(x4, 3) fig, ax=plt.subplots(2, 2) ax1=plt.subplot(221) ax1.plot(x1, y1) ax2=plt.subplot(222) ax2.plot(x2, y2) ax3=plt.subplot(223) plt.autoscale(enable=True, axis="both", tight=True) ax3.scatter(x3, y3) ax4=plt.subplot(224, sharex=ax1) ax4.scatter(x4, y4) plt.show()
=====================================================
本博客是博主个人学习时的一些记录,不保证是为原创,个别文章加入了转载的源地址,还有个别文章是汇总网上多份资料所成,在这之中也必有疏漏未加标注处,如有侵权请与博主联系。
如果未特殊标注则为原创,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议。
posted on 2020-07-05 11:42 Angry_Panda 阅读(504) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号