PTA4-6次作业
1.前言:
第四次作业难度较前三次更大,新增有多选题、填空题,不仅要考虑错选(直接错)、少选(部分错)和多选(直接错),还需考虑顺序问题(BCD与CBD要求结果相同)这给判断是否正确的难度增加了一个档次,同时还出现了多试卷多人答题的情形,虽然删除了第三次作业中删除题目的部分,但整体难度仍旧较高,若前几次作业效果不理想,这次作业更加难以动手。第五次作业是新的题目,与前四次无关,其要求写家居强电电路模拟程序,该次作业限定条件多,难度小,但也需为后面的作业打好基础,该次作业只要求一整个串联,但要把开关、分档调速器、连续调速器、白炽灯、日光灯、吊扇类先建立好,并确定好继承关系,串联类和并联类暂时不用可搭好框架以备不时之需。第六次作业是在第五次作业基础上添加并联对象和串联对象,还添加了落地扇类,总体难度上升。
2.设计与分析:
第四次作业:
修改输入提取内容后,修改答案类与答卷类,在主函数中修改答案判断条件,添加Kquestion与Zquestion类区分多选和填空题,无需多加方法,继承构造就行,主要用于区分
Kquestion与Zquestion类如下:
点击查看代码
public class Kquestion extends Question {
public Kquestion(int num,String content,String standard_answer){
super(num,content,standard_answer);
}
}
public class Zquestion extends Question {
public Zquestion(int num,String content,String standard_answer){
super(num,content,standard_answer);
}
}
内容乏善可陈,在主函数中修改部分如下:
点击查看代码
int flag=1;
for(AnswerPaper r : listAnswerPaper)
{
flag=1;
for (Paper p:listPaper)
{
if(r.getNum()==p.getNum())
{
flag=0;
for(int i = 0; i < p.getList().size()&& i < r.getList().size(); i++)
{
Question w=p.getList().get(i);
Answer x=r.getList().get(i);
if(w.getNum()==num_of_cut)
{
x.setGrade(0);
System.out.println("the question "+w.getNum()+" invalid~0");
}
else
{
if(p.getHaveque())
{
System.out.print(w.getContent()+"~"+x.getAnswer()+"~");
if(w.getStandard_Answer().equals(x.getAnswer()))
{
System.out.println("true");
x.setGrade(p.getScore(i));
r.setSum(p.getScore(i));
}
else if(w.getStandard_Answer().contains(x.getAnswer()))
{
System.out.println("partially correct");
x.setGrade((int) p.getScore(i)/2);
r.setSum((int) p.getScore(i)/2);
}
else
{
System.out.println("false");
x.setGrade(0);
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("non-existent question~0");
x.setGrade(0);
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < p.getList().size() - r.getList().size(); i++)
{
System.out.println("answer is null");
}
int flag1=0;
for(int j = 0;j<listStudent.size();j++){
if(r.getNums().equals(listStudent.get(j).getNum()))
{
System.out.print(r.getNums()+" "+listStudent.get(j).getName()+": ");
for(int i = 0; i < p.getList().size(); i++)
{
if(i < r.getList().size())
{
Answer x=r.getList().get(i);
System.out.print(x.getGrade());
}
else
System.out.print("0");
if(i!=p.getList().size()-1)
System.out.print(" ");
else
System.out.print("~");
}
System.out.println(r.getSum());
flag1=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag1==0)
{
System.out.println(r.getNums()+" not found");
}
}
}
}
if(flag==1)
System.out.println("The test paper number does not exist");
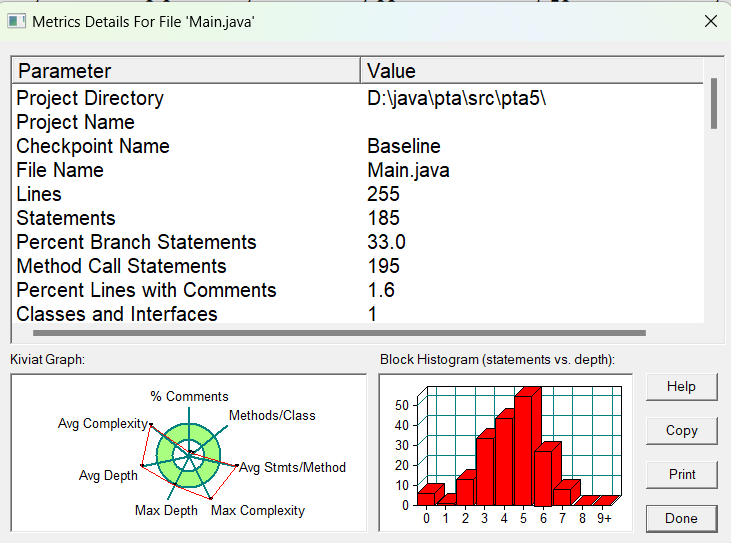
SourceMontor的生成报表如下:
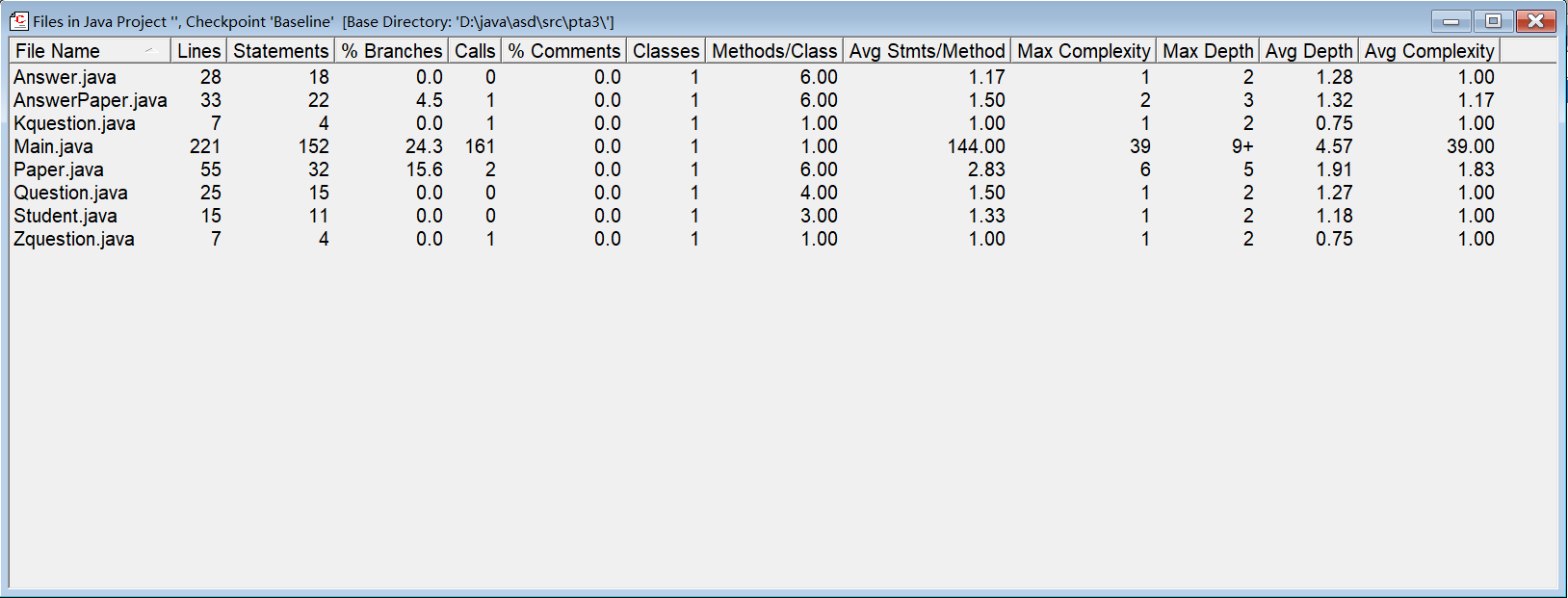
由此可见代码任存在许多的不足(方法的功能较为单一、最复杂方法行的数量过高有待优化、代码中的块结构相对简单、注释少等),第四次作业在第三次作业的基础上增加了多选题和填空题,导致答案判断频频出错,另外,作业中还增加了多试卷,多学生,使得顺序输出失败,且乱序输入也需添加条件使其顺序。这次作业我做出了一部分改进,开始有意识的遵循或运用单一职责原则、开闭原则、迪米特法则。因改动小,时间分配问题,得分很低。
第五次作业:
设置总的父类Equipment,让装置分为受控与控制分别继承,添加各子类,读取输入并储存个部分电器,根据要求进行状态调整,最后重置输入、输出电压,调整参数,再按要求顺序输出即可。因为只有一条干路,无需考虑太多情况,只需优先判断开关状态,且添加开关打开时整个电路断路最优先即可。
主要部分在主函数中其它用电器、控制器大体相同,只展示其一。
Fan(用电器):
点击查看代码
private double speed;
public Fan(double inputV,String name){
super(inputV,name);
this.speed=0;
}
public void setDeviation(double inputV,double outputV){
this.deviation=inputV-outputV;
}
public void setSpeed(){
if(this.deviation<80){
this.speed=0;
}
else if(this.deviation==80){
this.speed=80;
}
else if(this.deviation>80&&this.deviation<=150){
this.speed=80+4.00*(deviation-80);
}
else if(this.deviation>150){
this.speed=360;
}
}
点击查看代码
protected int state;
public Switch(double inputV,String name){
super(inputV,name);
this.state=0;
}
public void setState(){
if(this.state==0) {
this.state = 1;
}
else{
this.state = 0;
}
}
public void setOutputV(){
if(this.state==0){
this.outputV=0;
}
else if(this.state==1){
this.outputV=this.inputV;
}
}
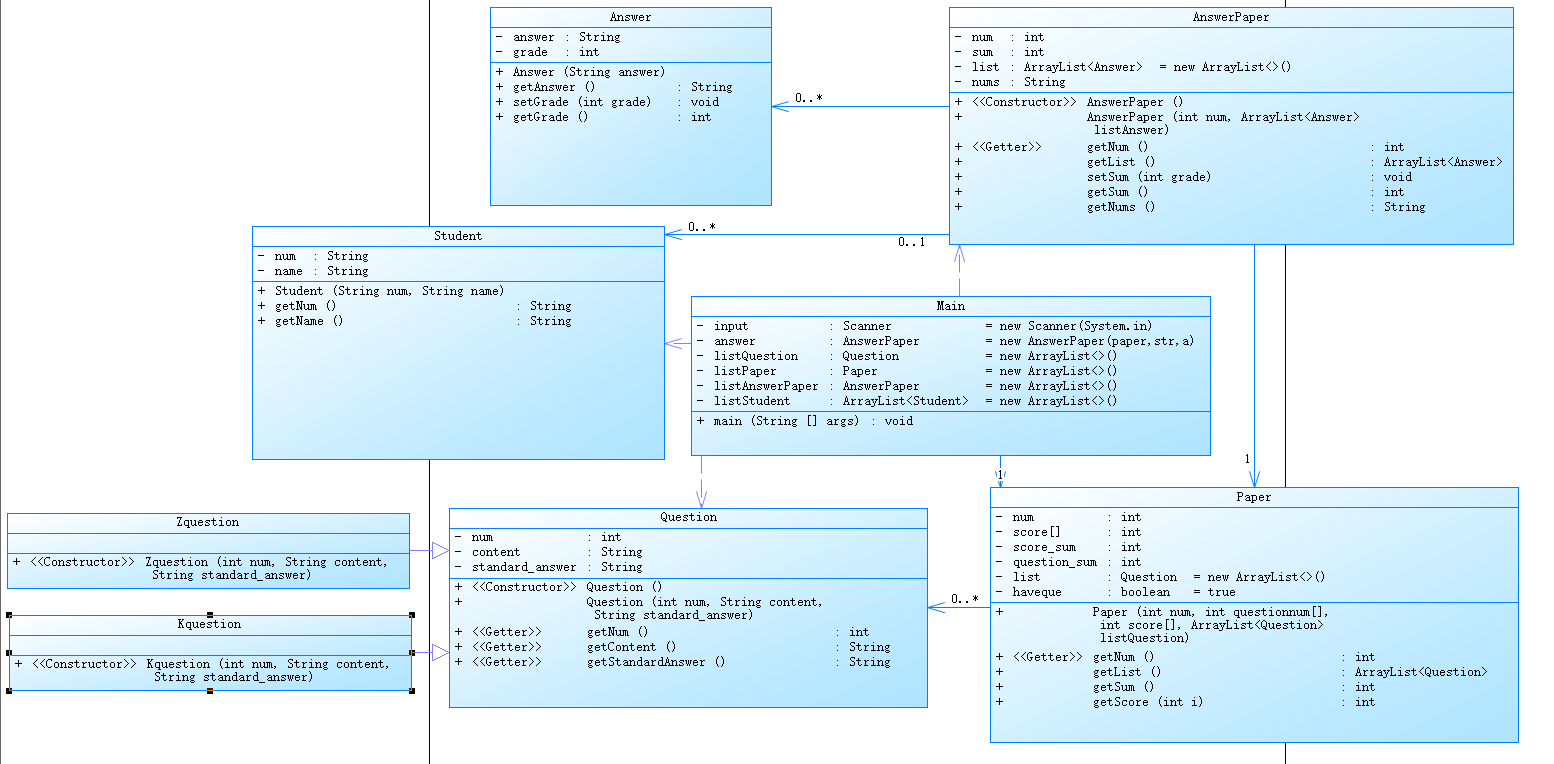
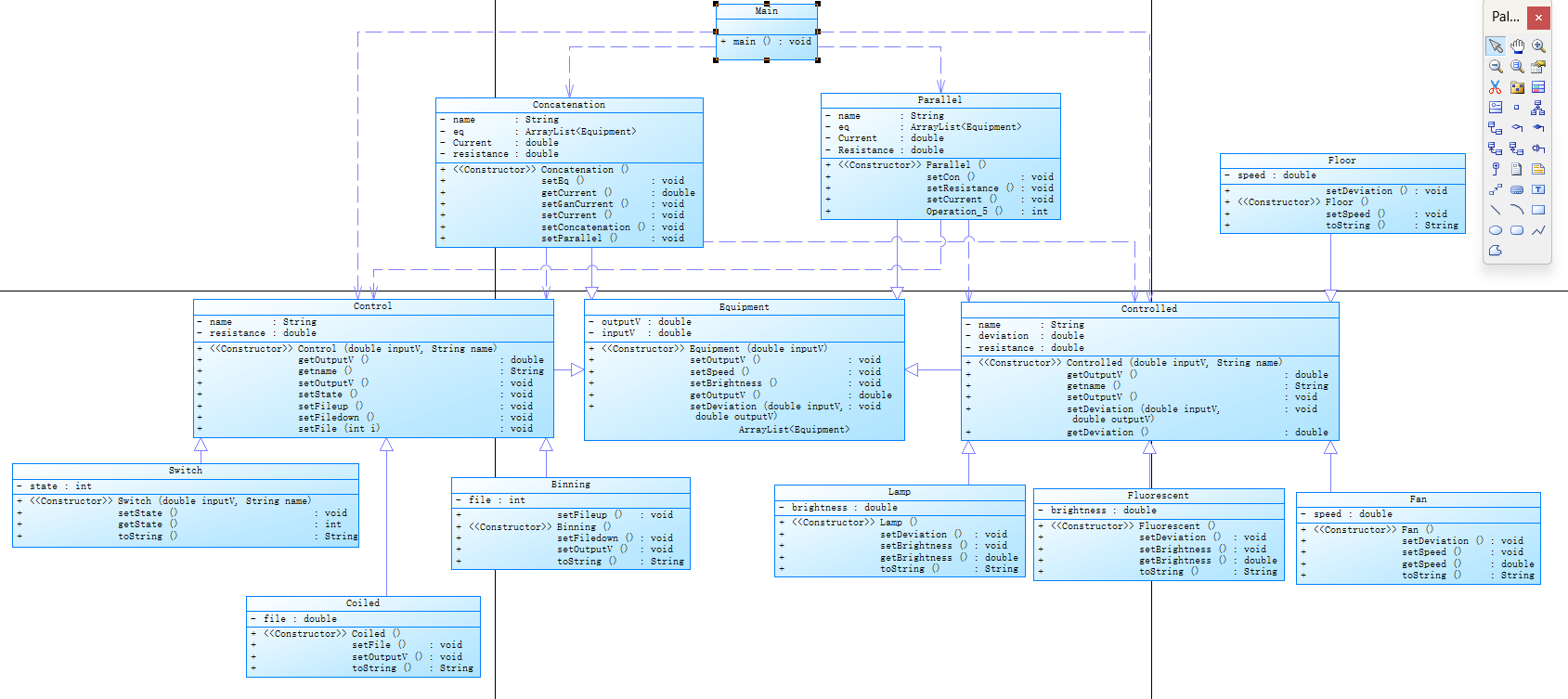
类图如下:
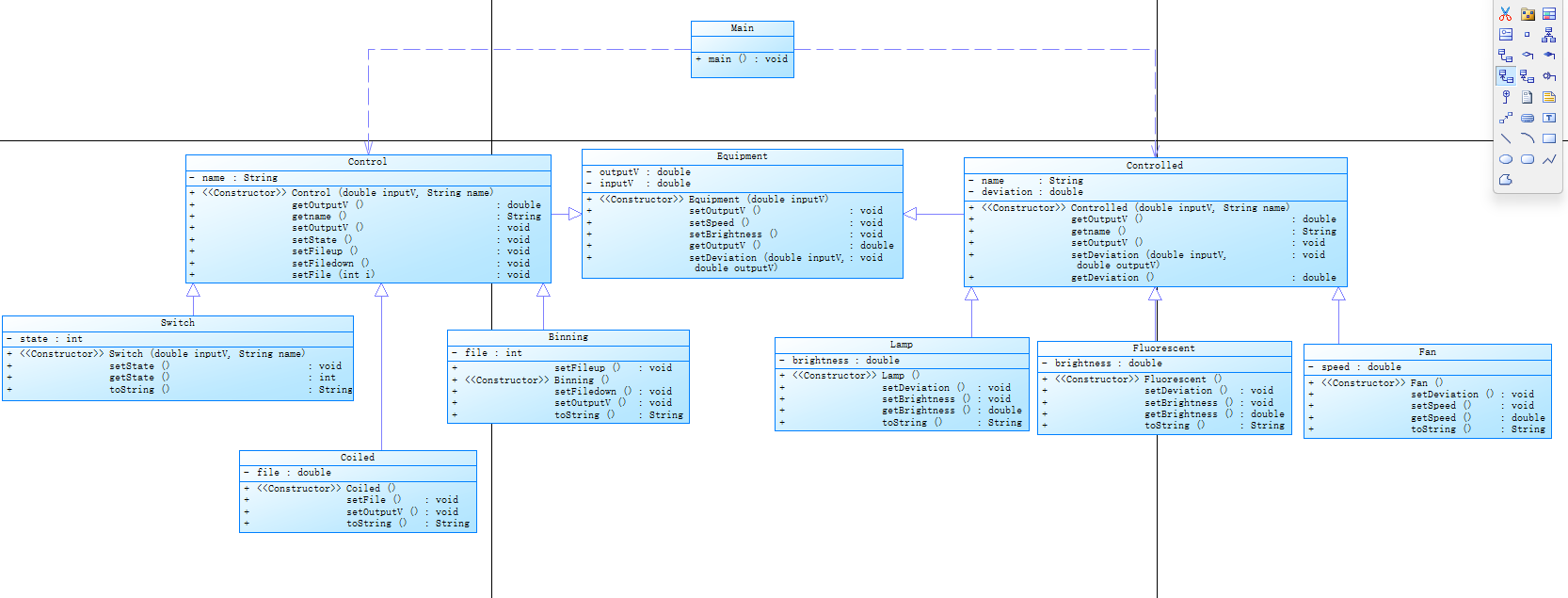
第六次作业:
第六次作业在第五次作业的基础上增加了串联和并联对象,关键点在于将每个电器指向同一个对象再改变状态,不考虑乱序输入的情况使得并联好写很多,另外添加了电阻,同时电流亦不可少,新增落地扇类,实际可归于受控类的子类,但由于对象数量增多,数字不再具有唯一性,使得储存查询对应难度上升,我就因为指向的对象错误导致修改状态时未修改到正确的对象至错。
还有注释问题,时间线长到可以让人模糊类中方法的作用,添加注释才可以更好的修改,此次作业使用了许多类,但是并没有遵守或运用单一职责原则、开闭原则、迪米特法则,且许多判定过程写在了主方法中,而不是写在类中作为类的方法,更没有代理类。因为在敲之前,很多逻辑部分并没有思考清楚,导致代码出现了许多的冗余及不必要的代码,我意识到了写注释的重要性。写注释不仅有益于在写代码过程中清晰自己的逻辑,更有益于改代码过程中读懂自己之前写的代码。在主函数中的输出和修改状态部分,未找到简便快捷的方法,过多的全循环使得代码过于浪费空间且耗时,无效循环非常多。因接口与抽象类不熟练,未使用。
在串联类和并联类中都添加了电器类数组,将主函数中的提取过程放在了其中,简化了主函数。
点击查看代码
if (matcher1.find()) {
String name = matcher1.group(1);
String a = matcher1.group(2);
String b = matcher1.group(3);
String c = matcher1.group(4);
Equipment test = new Concatenation(0, name);
test.setEq(b,hmCon,hmPa);
hmCon.put(name, test);
} else if (matcher2.find()) {
String name = matcher2.group(1);
String a = matcher2.group(2);
Equipment test = new Parallel(0, name);
test.setCon(a,hmCon);
hmPa.put(name, test);
点击查看代码
public void setEq(String str,HashMap<String,Equipment> hm1,HashMap<String,Equipment> hm2) {
String test = str.replaceAll("\\[", "").replaceAll("\\]", "");
String str1[] = str.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < str1.length; i++) {
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("([A-Z])([0-9])-[12]");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str1[i]);
Pattern pattern1 = Pattern.compile("([A-Z])([0-9])-[A-Z]+");
Matcher matcher1 = pattern1.matcher(str1[i]);
if (matcher.find()) {
String name = matcher.group(1) + matcher.group(2);
String a = matcher.group(1);
if (i == 0) {
if (a.equals("K")) {
Equipment sw = new Switch(this.inputV, name);
eq.add(sw);
} else if (a.equals("F")) {
Equipment bi = new Binning(this.inputV, name);
eq.add(bi);
} else if (a.equals("L")) {
Equipment co = new Coiled(this.inputV, name);
eq.add(co);
} else if (a.equals("B")) {
Equipment la = new Lamp(this.inputV, name);
eq.add(la);
} else if (a.equals("R")) {
Equipment fl = new Fluorescent(this.inputV, name);
eq.add(fl);
} else if (a.equals("D")) {
Equipment fa = new Fan(this.inputV, name);
eq.add(fa);
} else if (a.equals("A")) {
Equipment floor = new Floor(this.inputV, name);
eq.add(floor);
}
} else if (i !=0 ) {
if(!name.equals(this.eq.get(eq.size()-1).getname())){
if (a.equals("K")) {
Equipment sw = new Switch(eq.get(eq.size()-1).getOutputV(), name);
eq.add(sw);
} else if (a.equals("F")) {
Equipment bi = new Binning(eq.get(eq.size()-1).getOutputV(), name);
eq.add(bi);
} else if (a.equals("L")) {
Equipment co = new Coiled(eq.get(eq.size()-1).getOutputV(), name);
eq.add(co);
} else if (a.equals("B")) {
Equipment la = new Lamp(eq.get(eq.size()-1).getOutputV(), name);
eq.add(la);
} else if (a.equals("R")) {
Equipment fl = new Fluorescent(eq.get(eq.size()-1).getOutputV(), name);
eq.add(fl);
} else if (a.equals("D")) {
Equipment fa = new Fan(eq.get(eq.size()-1).getOutputV(), name);
eq.add(fa);
} else if (a.equals("A")) {
Equipment floor = new Floor(eq.get(eq.size()-1).getOutputV(), name);
eq.add(floor);
}
}
else {
}
}
} else if (matcher1.find()) {
String name1 = matcher1.group(1) + matcher1.group(2);
String a1 = matcher1.group(1);
if (i == 0) {
if (a1.equals("T")) {
Equipment con = new Concatenation(this.inputV, name1);
eq.add(con);
} else if (a1.equals("M")) {
Equipment pa = new Parallel(this.inputV, name1);
eq.add(pa);
}
}
else if(i != 0 && !name1.equals(eq.get(eq.size()-1).getname())) {
if (a1.equals("T")) {
Equipment con = new Concatenation(eq.get(eq.size()-1).getOutputV(), name1);
eq.add(con);
} else if (a1.equals("M")) {
Equipment pa = new Parallel(eq.get(eq.size()-1).getOutputV(), name1);
eq.add(pa);
}
}
}
}
int j=0;
for(String key:hm1.keySet()) {
if(this.eq.get(j).getname().equals(key)) {
this.eq.set(j, hm1.get(key));
}
j++;
}
j=0;
for(Equipment t:eq) {
for(String key:hm2.keySet()) {
if(t.getname().equals(key)) {
this.eq.set(j, hm2.get(key));
}
j++;
}
}
}
点击查看代码
public void setCon(String str,HashMap<String,Equipment> hm){
String test = str.replaceAll("\\[", "").replaceAll("\\]", "");
String str1[] = str.split(" ");
for(int i = 0; i < str1.length; i++) {
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("(T[0-9])");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str1[i]);
if (matcher.find()) {
String name = matcher.group(1);
Equipment con = new Concatenation(this.inputV, name);
eq.add(con);
}
}
int j=0;
for(String key:hm.keySet()) {
if(this.eq.get(j).getname().equals(key)) {
this.eq.set(j, hm.get(key));
}
j++;
}
}
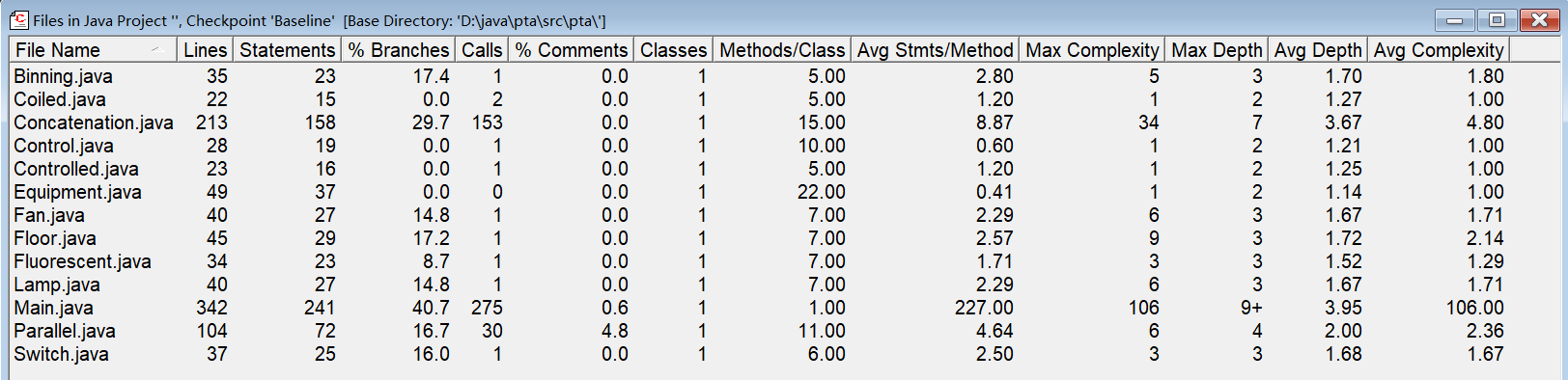
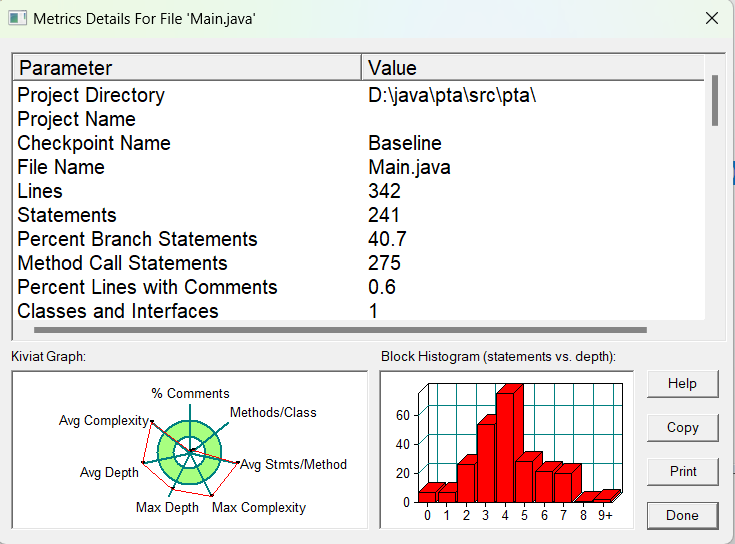
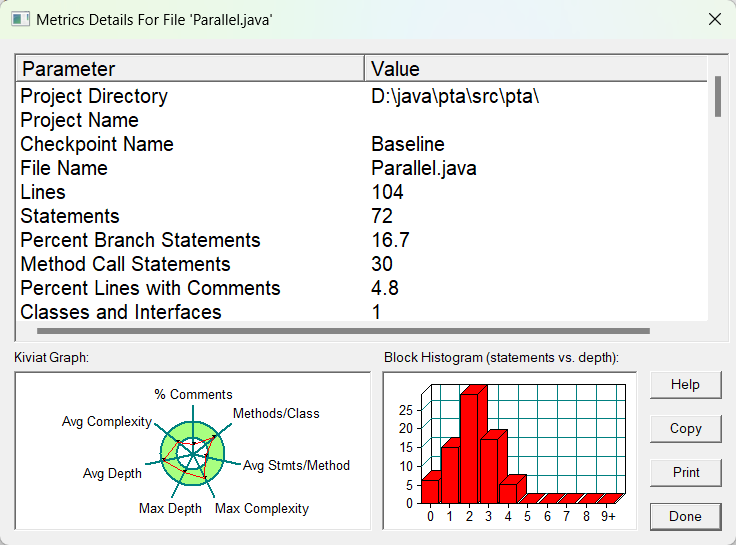
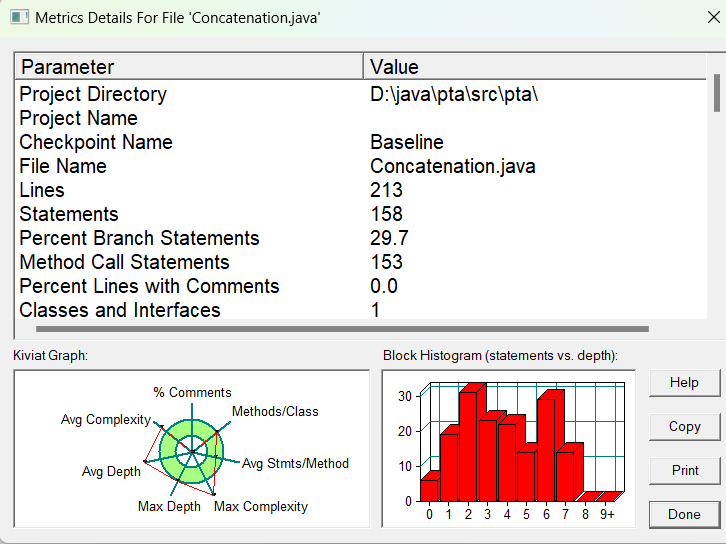
由主要的三个函数和总体来看,不足还是有很多。
根据此报表,以下是改进方向:
减少方法调用:方法调用可能会导致代码执行效率降低。尝试合并或简化方法调用,以减少方法的调用次数。
增加注释:注释严重不足,有很多的空间来添加注释,从而提高代码的可读性和维护性。
控制方法复杂度:平均每方法语句数过多,这可能表明某些方法过于复杂。尝试分解这些方法为更小的、更专注的部分。
管理块深度:最大块深度为太大,这可能会影响代码的性能。优化块结构,使其更加扁平化,以减少执行时间。
使用接口以简化代码。
类图如下:
采坑心得:
第四次作业:
多选题答案若为ABCD,作答为AC,直接用contains识别不出部分正确,AB可识别(字符串相连才可直接用,否则用多循环)。
第五次作业:
注意分档调速器挡位可加可减
输出时要按题目要求的顺序输出,不可只按线路顺序输出
在调整开关时,干路开关断一个,整个线路断路
第六次作业:
在并联提取时,传前面记录的串联电路,以指向同一对象,否则后面开关转换无法深入到真正的开关
输出时对每一种电器内部排序
修改状态时的优先级按先开关后按线路顺序
改进建议:
写代码时提前画好类图以减少遗漏。
排序优先于修改状态更好
多考虑优先级问题,先将预定状态确定后再传电压
总结:
1.学到了:
Java基础语法
封装、继承、多态的实现(结构体实现封装,组合实现继承,接口实现多态)
接口的定义和实现(一个类可以实现多个接口 使用关键字interface来定义接口。)
抽象类和接口的区别
ArrayList、LinkedList、HashMap的使用方法
2.需要进一步学习及研究:
在写代码之前,要将整个代码的逻辑部分设计好,避免出现写到中途手忙脚乱的现象。
提升代码的可复用性,注重设计中的开闭原则。
每次写完代码都会出现数组越界的情况,原因大概是思考逻辑时,无法面面俱到。多敲代码以提升自己的思考能力以及逻辑能力。画设计图、类图是个不错的选择。
在对象传递与赋值时找错对象,画出空间概念图可避免
3.建议:
希望能有完整的思路和过程展示,以供观摩
希望测试点点明测试方向。
希望挑出常用的难点讲




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~