第二次过程性考核——面向对象程序设计
第二次过程性考核
码云仓库链接:https://gitee.com/xywymxs/Myself.JAVA/tree/master/
更多代码片段详情请见码云:https://gitee.com/xywymxs/codes
7-1 学生类-构造函数
定义一个有关学生的Student类,内含类成员变量: String name、String sex、int age,所有的变量必须为私有(private)。
1.编写有参构造函数:能对name,sex,age赋值。
2.覆盖toString函数: 按照格式:类名 [name=, sex=, age=]输出。使用idea自动生成,然后在修改成该输出格式。
3.对每个属性生成setter/getter方法。
4.main方法中:输入1行name age sex , 调用上面的有参构造函数新建对象。
输入样例:
tom 15 male
输出样例:
Student [name='tom', sex='male', age=15]
程序设计思路:先引入java的输入函数,再定义Student类,之后定义Student的构造方法,定义toString方法,并按格式输出“类名 [name=, sex=, age=]”,最后在Main函数中调用子类。
涉及知识点:综合运用类与对象、子类与继承
代码:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 class Student{ 3 private String name; 4 private String sex; 5 private int age; 6 public Student(){ 7 this.name = "aaa"; 8 this.sex = "male"; 9 this.age = 111; 10 } 11 public void toString(String n, int a, String s){ 12 this.name = n; 13 this.sex = s; 14 this.age = a; 15 System.out.println("Student [name='"+this.name+"', sex='"+this.sex+"', age="+this.age+"]"); 16 } 17 } 18 public class Main{ 19 public static void main(String[] args){ 20 Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in); 21 String n = reader.next(); 22 int a = reader.nextInt(); 23 String s = reader.next(); 24 Student ww = new Student(); 25 ww.toString(n,a,s); 26 } 27 }
运行结果: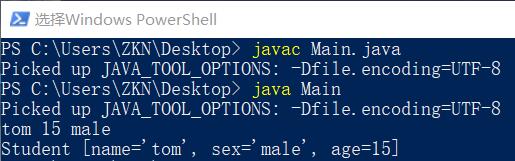
7-2 定义类
请补充以下代码,完成输出要求。(注意:需要提交完整代码)
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 5 int a,b,c,d,e; 6 a = in.nextInt(); 7 b = in.nextInt(); 8 c = in.nextInt(); 9 d = in.nextInt(); 10 e = in.nextInt(); 11 RR rr = new RR(); 12 double dd = rr.fun(a,b,c,d,e); 13 System.out.printf("%.2f",dd); 14 } 15 } 16 class RR{ 17 18 19 20 }
输入格式:在一行中给出5个不超过1000的正整数。
输出格式:输出5个整数的平均值,保留小数点后两位。
输入样例:
1 2 3 4 5
输出样例:
3.00
程序设计思路:由题可知,只需补全RR类,需要先定义RR类,之后只需在return传出返回值的时候编写平均数式子,这样输出的内容即为5个数的平均值。
涉及知识点:参数传值
代码:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 5 int a,b,c,d,e; 6 a = in.nextInt(); 7 b = in.nextInt(); 8 c = in.nextInt(); 9 d = in.nextInt(); 10 e = in.nextInt(); 11 RR rr = new RR(); 12 double dd = rr.fun(a,b,c,d,e); 13 System.out.printf("%.2f",dd); 14 } 15 } 16 class RR{ 17 public double fun(int a, int b, int c, int d, int e) 18 { 19 return (a+b+c+d+e)/5; 20 } 21 }
运行结果: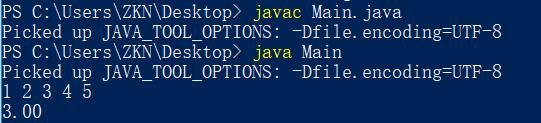
7-3 横平竖直
程序填空题。根据题目要求完善下面的代码。请提交完整代码。 一个木块如果高度比宽度大,我们说它是竖着放的,否则我们说它是平放的。 读入一个木块的高度和宽度。如果它是平放的,则输出A,否则输出B。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main{ 3 public static void main(String[] args){ 4 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 5 int height, width; 6 char status; 7 height = in.nextInt(); 8 width = in.nextInt(); 9 Board board = new Board(height, width); 10 status = board.getStatus(); 11 System.out.print(status); 12 } 13 } 14 class Board{ 15 int height, width; 16 public Board(int height, int width){ 17 this.height = height; 18 this.width = width; 19 } 20 public char getStatus(){ 21 if(height<=width){ 22 return status(1); 23 }else{ 24 return status(1.0); 25 } 26 } 27 public char status(double rate){ 28 29 } 30 public char status(int rate){ 31 32 33 } 34 }
输入格式:输入在一行中给出2个绝对值不超过1000的正整数A和B。
输出格式:在一行中输出一个字符A或者B。
输入样例:
50 50
输出样例:
A
程序设计思路:定义了重载方法,可知方法名相同,但参数列表中对应的某个参数的类型不同,通过比较,将返回值设为A和B,因为方法为char类型,所以将返回值用单引号引起。
涉及知识点:方法重载,参数传值
代码:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main{ 3 public static void main(String[] args){ 4 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 5 int height, width; 6 char status; 7 height = in.nextInt(); 8 width = in.nextInt(); 9 Board board = new Board(height, width); 10 status = board.getStatus(); 11 System.out.print(status); 12 } 13 } 14 class Board{ 15 private static final char A = 0; 16 private static final char B = 0; 17 int height, width; 18 public Board(int height, int width){ 19 this.height = height; 20 this.width = width; 21 } 22 public char getStatus(){ 23 if(height<=width){ 24 return status(1); 25 }else{ 26 return status(1.0); 27 } 28 } 29 public char status(double rate){ 30 return 'B'; 31 32 33 } 34 public char status(int rate){ 35 return 'A'; 36 37 } 38 }
运行结果:
7-4 程序改错题2
程序改错题。以下代码存在错误,请修改后提交。
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Animal animal = new Dog(); 4 animal.shout(); 5 animal.run(); 6 } 7 } 8 9 class Animal { 10 void shout() { 11 System.out.println("animal shout!"); 12 } 13 } 14 15 class Dog extends Animal { 16 void shout() { 17 super.shout(); 18 System.out.println("wangwang……"); 19 } 20 21 void run() { 22 System.out.println("Dog is running"); 23 } 24 }
输入样例:
无
输出样例:
animal shout!
wangwang……
Dog is running
程序设计思路:Animal是Dog的上转型对象,即不能操作子类新增的成员变量,也不能调用子类新增的方法;所以需要将对象的上转型对象再强制转换到一个子类对象,这时,该子类对象又具备了子类所有的属性和功能。
涉及知识点:自类的继承,对象的上转型对象
代码:
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Animal animal = new Dog(); 4 animal.shout(); 5 ((Dog) animal).run(); 6 } 7 } 8 9 class Animal { 10 void shout() { 11 System.out.println("animal shout!"); 12 } 13 } 14 15 class Dog extends Animal { 16 void shout() { 17 super.shout(); 18 System.out.println("wangwang……"); 19 } 20 21 void run() { 22 System.out.println("Dog is running"); 23 } 24 }
运行结果:
| 学习内容 | 代码(行) | 博客(字) |
| 类与对象、子类与继承 | 300 | 1200 |




