ASP.NET管道处理模型(二)
从上一章中我们知道Http的任何一个请求最终一定是由某一个具体的HttpHandler来处理的,不管是成功还是失败。
而具体是由哪一个HttpHandler来处理,则是由我们的配置文件来指定映射关系:后缀名与处理程序的关系(IHttpHandler---IHttpHandlerFactory) 。
但是我们都知道在MVC中访问时并没有使用什么后缀,而是使用路由去匹配,那这又是怎么回事呢?接下来我们就来谈谈这件事。
首先我们来看下MVC中到底是由哪个HttpHandler来处理的:
Home 控制器:
public class HomeController : Controller { public ActionResult Index() { ViewBag.CurrentHandler = base.HttpContext.CurrentHandler; return View(); } }
对应的 Index 视图:
@{ ViewBag.Title = "Home Page"; } <h2> This is Home/Index View </h2> <h1> @(ViewBag.CurrentHandler) </h1> <hr />
看看此时 HttpContext.CurrentHandler 的输出结果:
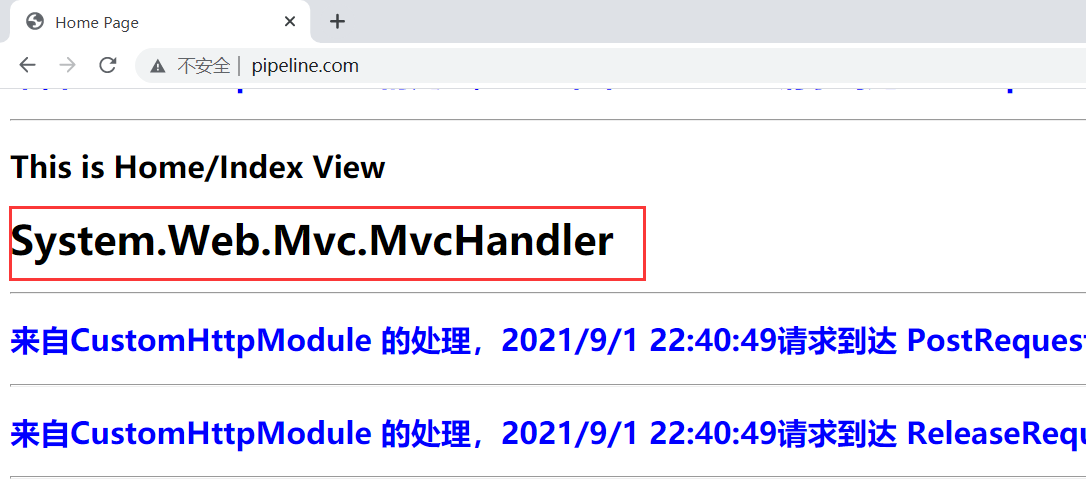
可以看到MVC中使用的HttpHandler是叫【System.Web.Mvc.MvcHandler】。
所谓MVC框架,其实就是在Asp.Net管道上扩展的,在PostResolveRequestCache事件扩展了UrlRoutingModule。
会在任何请求进来后,先进行路由匹配,如果匹配上了就指定HttpHandler为MvcHandler,没有匹配上就还是走原始流程。
那为什么要选择在PostResolveRequestCache这个事件进行扩展呢?
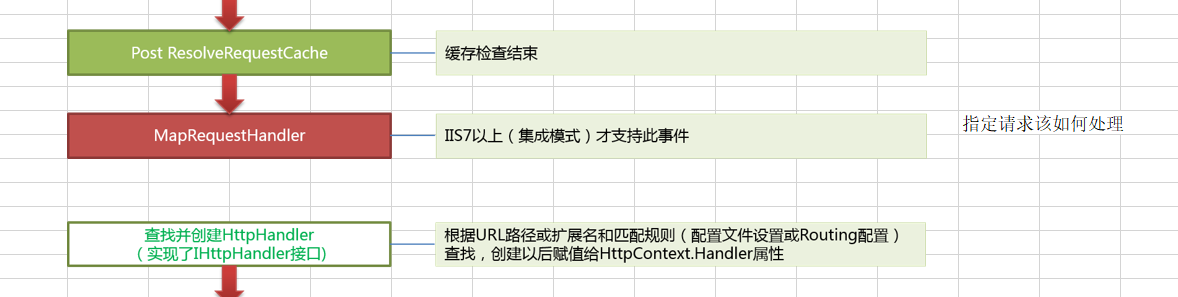
从图中我们可以得知在PostResolveRequestCache事件之后就要指定请求该如何处理了,因此我们也就能理解为什么要选择在PostResolveRequestCache这个事件上面进行MVC扩展了。
下面我们通过反编译工具来看一下 UrlRoutingModule 这个类:
using System; using System.Globalization; using System.Runtime.CompilerServices; using System.Web.Security; namespace System.Web.Routing { [TypeForwardedFrom("System.Web.Routing, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=Neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35")] public class UrlRoutingModule : IHttpModule { private static readonly object _contextKey = new object(); private static readonly object _requestDataKey = new object(); private RouteCollection _routeCollection; public RouteCollection RouteCollection { get { if (this._routeCollection == null) { this._routeCollection = RouteTable.Routes; } return this._routeCollection; } set { this._routeCollection = value; } } protected virtual void Dispose() { } protected virtual void Init(HttpApplication application) { if (application.Context.Items[UrlRoutingModule._contextKey] != null) { return; } application.Context.Items[UrlRoutingModule._contextKey] = UrlRoutingModule._contextKey; application.PostResolveRequestCache += new EventHandler(this.OnApplicationPostResolveRequestCache); } private void OnApplicationPostResolveRequestCache(object sender, EventArgs e) { HttpApplication httpApplication = (HttpApplication)sender; HttpContextBase context = new HttpContextWrapper(httpApplication.Context); this.PostResolveRequestCache(context); } [Obsolete("This method is obsolete. Override the Init method to use the PostMapRequestHandler event.")] public virtual void PostMapRequestHandler(HttpContextBase context) { } public virtual void PostResolveRequestCache(HttpContextBase context) { RouteData routeData = this.RouteCollection.GetRouteData(context); if (routeData == null) { return; } IRouteHandler routeHandler = routeData.RouteHandler; if (routeHandler == null) { throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentCulture, SR.GetString("UrlRoutingModule_NoRouteHandler"), new object[0])); } if (routeHandler is StopRoutingHandler) { return; } RequestContext requestContext = new RequestContext(context, routeData); context.Request.RequestContext = requestContext; IHttpHandler httpHandler = routeHandler.GetHttpHandler(requestContext); if (httpHandler == null) { throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, SR.GetString("UrlRoutingModule_NoHttpHandler"), new object[] { routeHandler.GetType() })); } if (!(httpHandler is UrlAuthFailureHandler)) { context.RemapHandler(httpHandler); return; } if (FormsAuthenticationModule.FormsAuthRequired) { UrlAuthorizationModule.ReportUrlAuthorizationFailure(HttpContext.Current, this); return; } throw new HttpException(401, SR.GetString("Assess_Denied_Description3")); } void IHttpModule.Dispose() { this.Dispose(); } void IHttpModule.Init(HttpApplication application) { this.Init(application); } } }
从上面的源码中我们大概可以知道:
1、首先它是根据HttpContextBase从RouteCollection中获取RouteData,判断RouteData是否为空(也就是判断路由是否匹配上),如果路由匹配失败则还是走原始的Asp.Net流程,否则就走MVC流程。从中可以知道MVC和WebForm是可以共存的。也能解释为啥指定后缀请求需要路由的忽略。
2、经过路由匹配得到RouteData,然后使用RouteData获取RouteHandler,接着再根据RouteHandler获取HttpHandler,最后将HttpContextBase上下文中的HttpHandler指定为这个HttpHandler。
3、看完下文你就会知道从RouteCollection中获取的这个RouteHandler其实就是MvcRouteHandler,而最终获取到的这个HttpHandler其实就是MvcHandler。
我们继续通过反编译工具 沿着 this.RouteCollection.GetRouteData(context) 往里找:
// System.Web.Routing.RouteCollection public RouteData GetRouteData(HttpContextBase httpContext) { if (httpContext == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("httpContext"); } if (httpContext.Request == null) { throw new ArgumentException(SR.GetString("RouteTable_ContextMissingRequest"), "httpContext"); } if (base.Count == 0) { return null; } bool flag = false; bool flag2 = false; if (!this.RouteExistingFiles) { flag = this.IsRouteToExistingFile(httpContext); flag2 = true; if (flag) { return null; } } using (this.GetReadLock()) { foreach (RouteBase current in this) { RouteData routeData = current.GetRouteData(httpContext); if (routeData != null) { RouteData result; if (!current.RouteExistingFiles) { if (!flag2) { flag = this.IsRouteToExistingFile(httpContext); } if (flag) { result = null; return result; } } result = routeData; return result; } } } return null; }
从此处我们可以发现,它是按照添加顺序进行匹配的,第一个吻合的就直接返回,后面的无效。
说到RouteCollection其实我们并不陌生,在路由配置的时候就有用到它:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Web; using System.Web.Mvc; using System.Web.Routing; namespace AspNetPipeline { /// <summary> /// 路由是按照注册顺序进行匹配,遇到第一个吻合的就结束匹配,每个请求只会被一个路由匹配上。 /// </summary> public class RouteConfig { public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) { //忽略路由 正则表达式 {resource}表示变量 a.axd/xxxx resource=a pathInfo=xxxx //.axd是历史原因,最开始都是WebForm,请求都是.aspx后缀,IIS根据后缀转发请求; //MVC出现了,没有后缀,IIS6以及更早版本,打了个补丁,把MVC的请求加上个.axd的后缀,然后这种都转发到网站 //新版本的IIS已经不需要了,遇到了就直接忽略,还是走原始流程 routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}"); //该行框架自带的 //.log后缀的请求忽略掉,不走MVC流程,而是用我们自定义的CustomHttpHandler处理器来处理 routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.log/{*pathInfo}"); routes.MapRoute( name: "Default", url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}", defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional } ); } } }
我们将光标移动到MapRoute这个方法,然后按F12查看源码,可以发现它是来自 RouteCollectionExtensions 这个扩展类,如下所示:
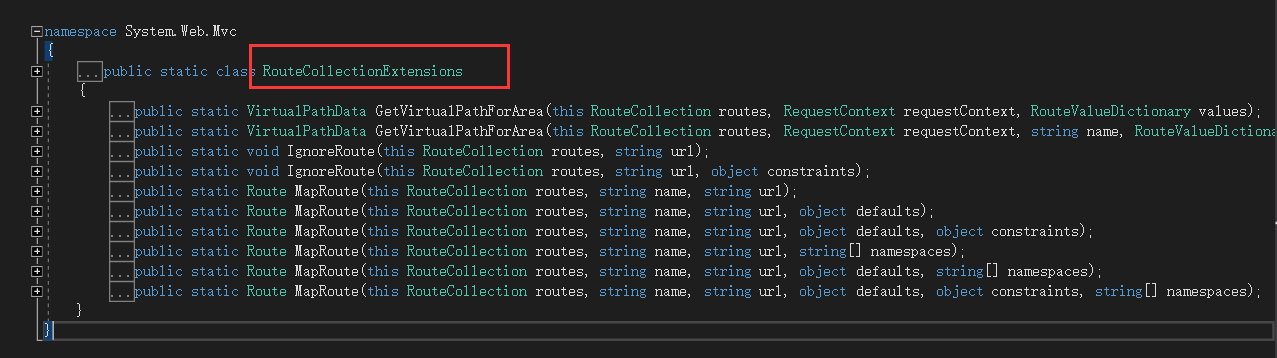
我们通过反编译工具找到这个类:
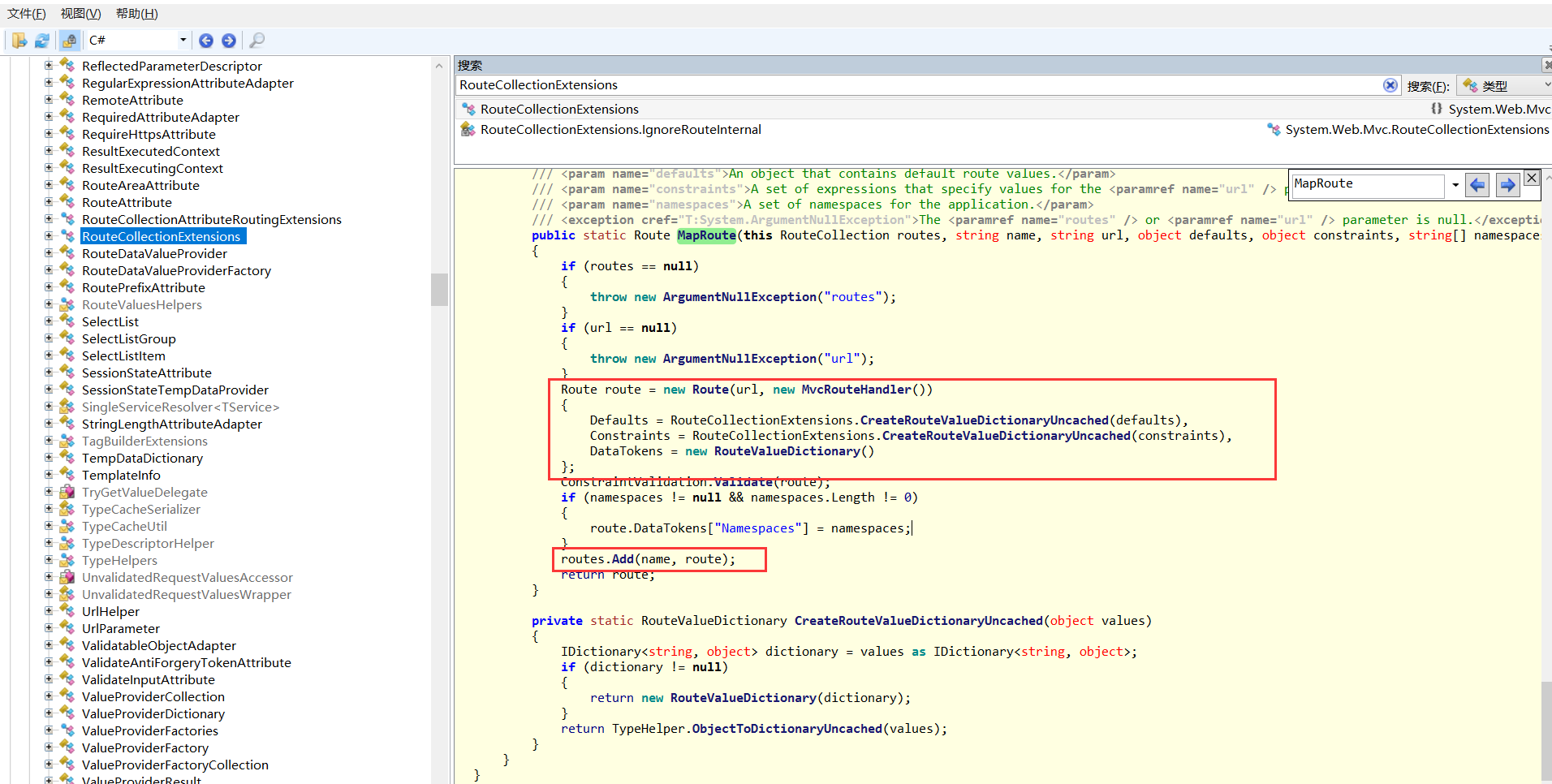
我们重点关注其中的MapRoute方法:
/// <summary>Maps the specified URL route and sets default route values, constraints, and namespaces.</summary> /// <returns>A reference to the mapped route.</returns> /// <param name="routes">A collection of routes for the application.</param> /// <param name="name">The name of the route to map.</param> /// <param name="url">The URL pattern for the route.</param> /// <param name="defaults">An object that contains default route values.</param> /// <param name="constraints">A set of expressions that specify values for the <paramref name="url" /> parameter.</param> /// <param name="namespaces">A set of namespaces for the application.</param> /// <exception cref="T:System.ArgumentNullException">The <paramref name="routes" /> or <paramref name="url" /> parameter is null.</exception> public static Route MapRoute(this RouteCollection routes, string name, string url, object defaults, object constraints, string[] namespaces) { if (routes == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("routes"); } if (url == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("url"); } Route route = new Route(url, new MvcRouteHandler()) { Defaults = RouteCollectionExtensions.CreateRouteValueDictionaryUncached(defaults), Constraints = RouteCollectionExtensions.CreateRouteValueDictionaryUncached(constraints), DataTokens = new RouteValueDictionary() }; ConstraintValidation.Validate(route); if (namespaces != null && namespaces.Length != 0) { route.DataTokens["Namespaces"] = namespaces; } routes.Add(name, route); return route; } private static RouteValueDictionary CreateRouteValueDictionaryUncached(object values) { IDictionary<string, object> dictionary = values as IDictionary<string, object>; if (dictionary != null) { return new RouteValueDictionary(dictionary); } return TypeHelper.ObjectToDictionaryUncached(values); }
可以看到RouteCollection字典容器的key就是路由配置中的name,这也就解释了路由配置中的name为啥需要唯一,另外RouteCollection字典容器的value存的是Route对象(正则规则 + MvcRouteHandler + 其它路由配置信息)。
我们继续通过反编译工具找到 MvcRouteHandler,如下所示:
using System; using System.Web.Mvc.Properties; using System.Web.Routing; using System.Web.SessionState; namespace System.Web.Mvc { /// <summary>Creates an object that implements the IHttpHandler interface and passes the request context to it.</summary> public class MvcRouteHandler : IRouteHandler { private IControllerFactory _controllerFactory; /// <summary>Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="T:System.Web.Mvc.MvcRouteHandler" /> class.</summary> public MvcRouteHandler() { } /// <summary>Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="T:System.Web.Mvc.MvcRouteHandler" /> class using the specified factory controller object.</summary> /// <param name="controllerFactory">The controller factory.</param> public MvcRouteHandler(IControllerFactory controllerFactory) { this._controllerFactory = controllerFactory; } /// <summary>Returns the HTTP handler by using the specified HTTP context.</summary> /// <returns>The HTTP handler.</returns> /// <param name="requestContext">The request context.</param> protected virtual IHttpHandler GetHttpHandler(RequestContext requestContext) { requestContext.HttpContext.SetSessionStateBehavior(this.GetSessionStateBehavior(requestContext)); return new MvcHandler(requestContext); } /// <summary>Returns the session behavior.</summary> /// <returns>The session behavior.</returns> /// <param name="requestContext">The request context.</param> protected virtual SessionStateBehavior GetSessionStateBehavior(RequestContext requestContext) { string text = (string)requestContext.RouteData.Values["controller"]; if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(text)) { throw new InvalidOperationException(MvcResources.MvcRouteHandler_RouteValuesHasNoController); } return (this._controllerFactory ?? ControllerBuilder.Current.GetControllerFactory()).GetControllerSessionBehavior(requestContext, text); } /// <summary>Returns the HTTP handler by using the specified request context.</summary> /// <returns>The HTTP handler.</returns> /// <param name="requestContext">The request context.</param> IHttpHandler IRouteHandler.GetHttpHandler(RequestContext requestContext) { return this.GetHttpHandler(requestContext); } } }
找到其中关键方法:
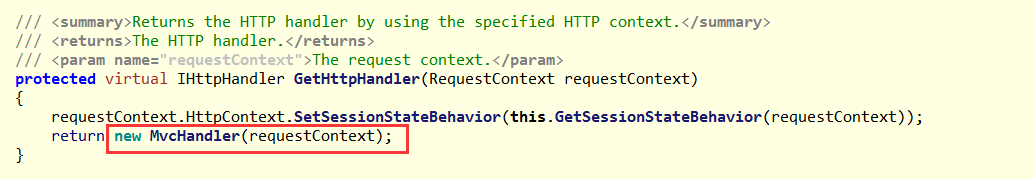
可以发现这个方法的返回值是固定写死的,就是返回MvcHandler的一个实例。由此我们知道从RouteCollection中获取的HttpHandler其实就是MvcHandler。
至此,我们对MVC的处理流程应该就有个大概认识了,下面我们通过一张图来总结一下MVC的处理流程:
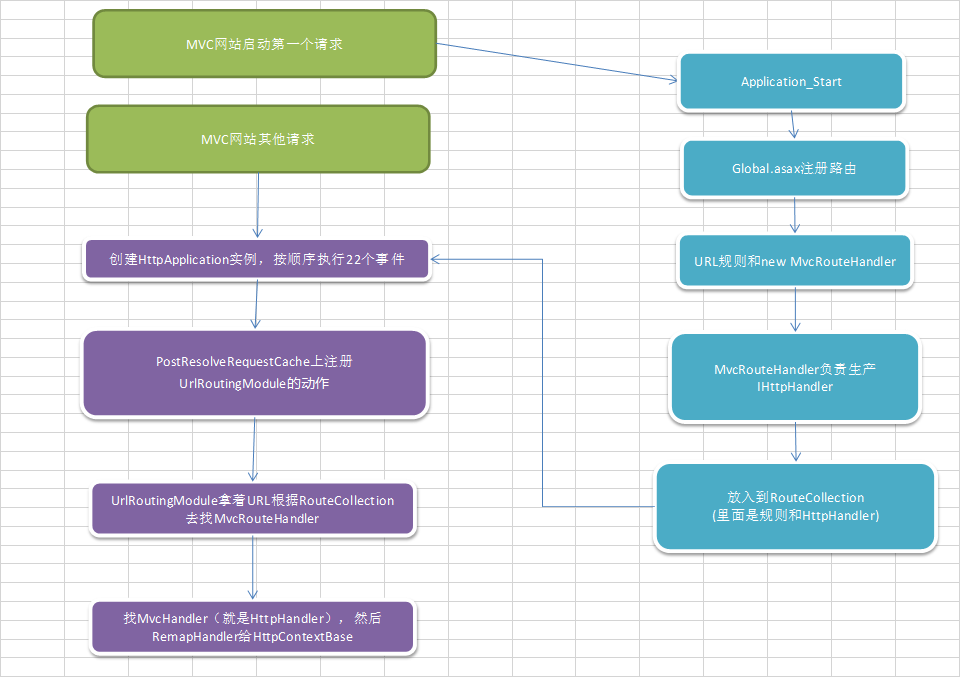
既然原理我们都知道了,那下面我们就可以去做一些有用的扩展。
例如:扩展我们的路由。
从上文中我们知道,路由配置其实就是将Route对象添加到RouteCollection字典中,而从反编译工具中我们可以得知Route的基类是RouteBase:
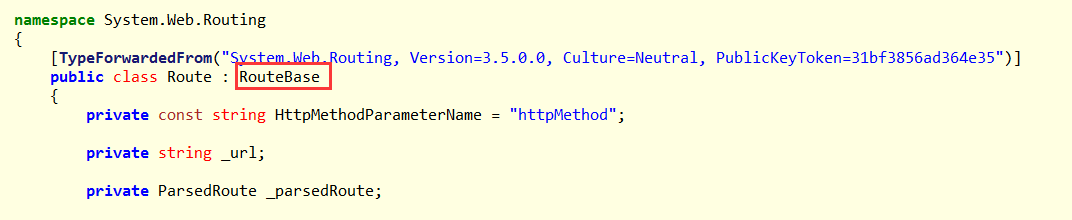
那下面我们就来自定义一个Route:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Web; using System.Web.Mvc; using System.Web.Routing; namespace AspNetPipeline.RouteExtend { /// <summary> /// 自定义路由 /// </summary> public class CustomRoute : RouteBase { /// <summary> /// 如果是 Chrome/74.0.3729.169 版本,允许正常访问,否则跳转提示页 /// </summary> /// <param name="httpContext"></param> /// <returns></returns> public override RouteData GetRouteData(HttpContextBase httpContext) { //httpContext.Request.Url.AbsoluteUri if (httpContext.Request.UserAgent.Contains("Chrome/74.0.3729.169")) { return null; //继续后面的 } else { RouteData routeData = new RouteData(this, new MvcRouteHandler()); //还是走MVC流程 routeData.Values.Add("controller", "home"); routeData.Values.Add("action", "refuse"); return routeData; //中断路由匹配 } } public override VirtualPathData GetVirtualPath(RequestContext requestContext, RouteValueDictionary values) { return null; } } }
然后将其添加到RouteCollection字典中:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Web; using System.Web.Mvc; using System.Web.Routing; using AspNetPipeline.RouteExtend; namespace AspNetPipeline { /// <summary> /// 路由是按照注册顺序进行匹配,遇到第一个吻合的就结束匹配,每个请求只会被一个路由匹配上。 /// </summary> public class RouteConfig { public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) { //忽略路由 正则表达式 {resource}表示变量 a.axd/xxxx resource=a pathInfo=xxxx //.axd是历史原因,最开始都是WebForm,请求都是.aspx后缀,IIS根据后缀转发请求; //MVC出现了,没有后缀,IIS6以及更早版本,打了个补丁,把MVC的请求加上个.axd的后缀,然后这种都转发到网站 //新版本的IIS已经不需要了,遇到了就直接忽略,还是走原始流程 routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}"); //该行框架自带的 //.log后缀的请求忽略掉,不走MVC流程,而是用我们自定义的CustomHttpHandler处理器来处理 routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.log/{*pathInfo}"); routes.Add("chrome", new CustomRoute()); routes.MapRoute( name: "Default", url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}", defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional } ); } } }
最后我们来访问一下 /home/index 页面,运行结果如下所示:
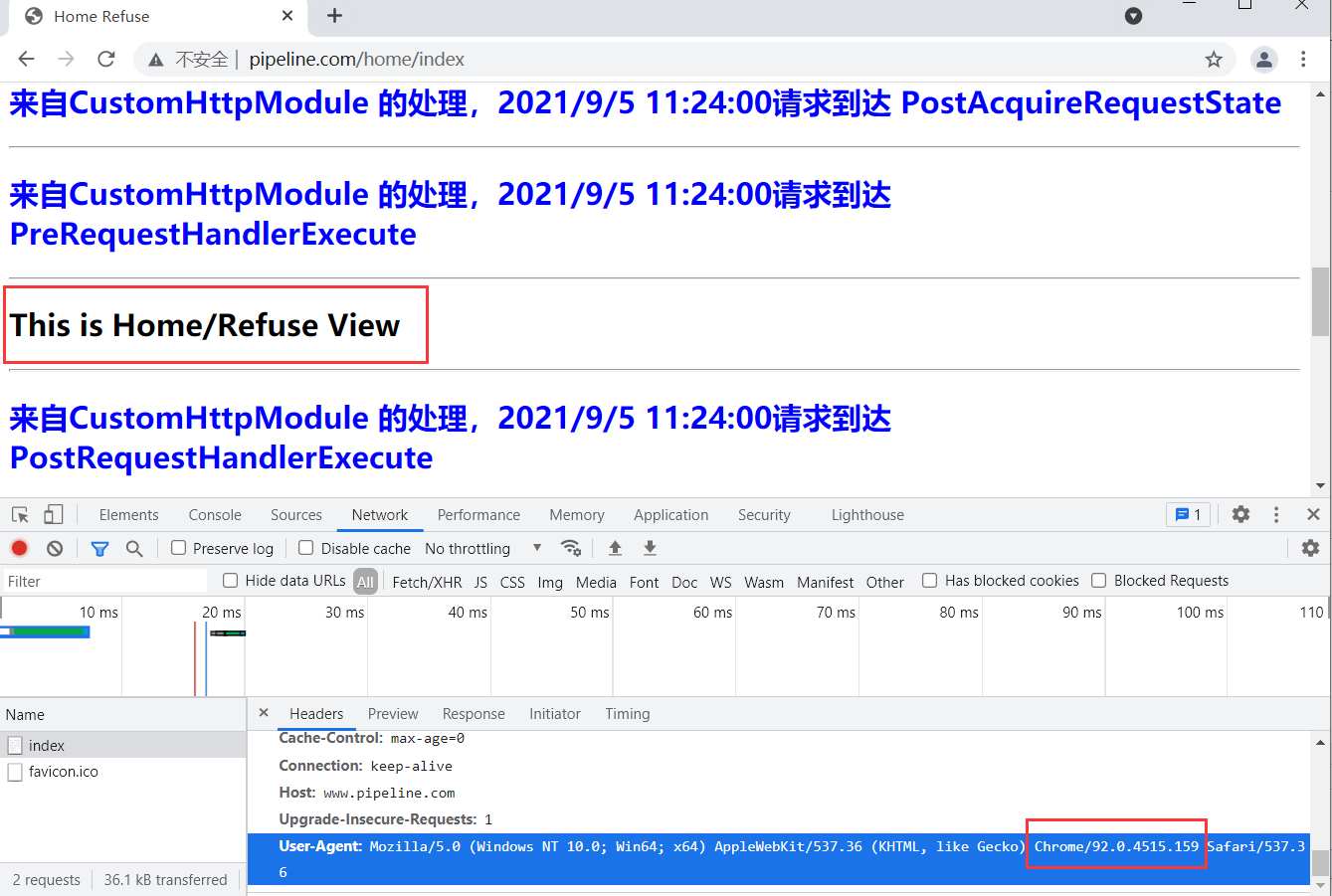
仔细观察后你会发现我们访问的是 /home/index 页面,但是此时却输出了 /home/refuse 页面,说明我们的路由扩展成功了。
除了去扩展Route,此外我们也可以去扩展MvcRouteHandler,如下所示:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Web; using System.Web.Mvc; using System.Web.Routing; using AspNetPipeline.Pipeline; namespace AspNetPipeline.RouteExtend { /// <summary> /// 自定义MvcRouteHandler /// </summary> public class CustomMvcRouteHandler : MvcRouteHandler { protected override IHttpHandler GetHttpHandler(RequestContext requestContext) { //requestContext.HttpContext.SetSessionStateBehavior(this.GetSessionStateBehavior(requestContext)); //return new MvcHandler(requestContext); return new CustomHttpHandler(); //将MvcHandler替换成自定义的HttpHandler } } }
同样的,我们将其添加到RouteCollection字典中:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Web; using System.Web.Mvc; using System.Web.Routing; using AspNetPipeline.RouteExtend; namespace AspNetPipeline { /// <summary> /// 路由是按照注册顺序进行匹配,遇到第一个吻合的就结束匹配,每个请求只会被一个路由匹配上。 /// </summary> public class RouteConfig { public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes) { //忽略路由 正则表达式 {resource}表示变量 a.axd/xxxx resource=a pathInfo=xxxx //.axd是历史原因,最开始都是WebForm,请求都是.aspx后缀,IIS根据后缀转发请求; //MVC出现了,没有后缀,IIS6以及更早版本,打了个补丁,把MVC的请求加上个.axd的后缀,然后这种都转发到网站 //新版本的IIS已经不需要了,遇到了就直接忽略,还是走原始流程 routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}"); //该行框架自带的 //.log后缀的请求忽略掉,不走MVC流程,而是用我们自定义的CustomHttpHandler处理器来处理 routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.log/{*pathInfo}"); routes.Add("config", new Route("log/{*pathInfo}", new CustomMvcRouteHandler())); routes.Add("chrome", new CustomRoute()); routes.MapRoute( name: "Default", url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}", defaults: new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional } ); } } }
最后我们来访问下 /log/a 运行结果如下所示:
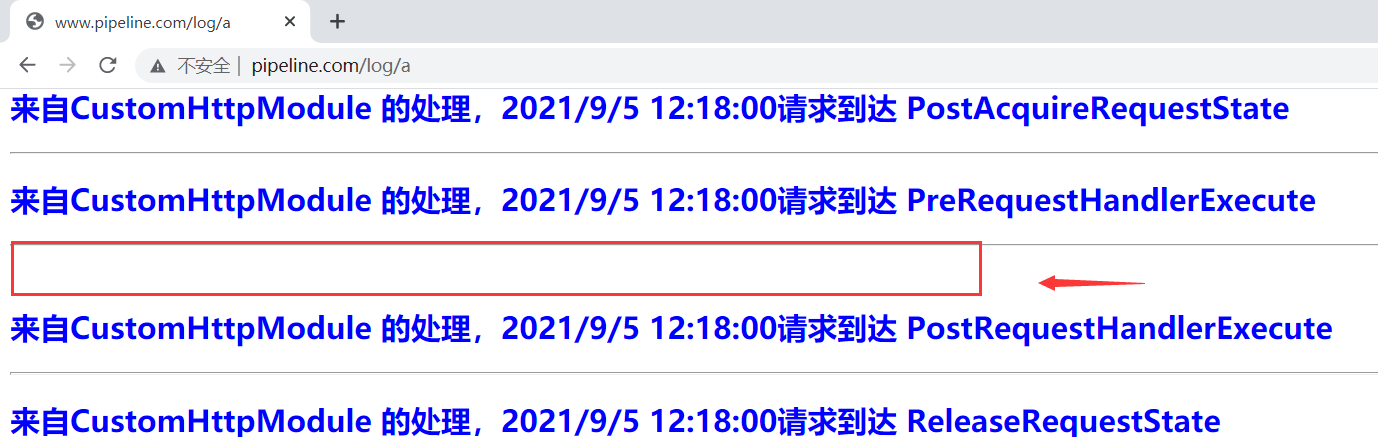
右键查看网页源代码:
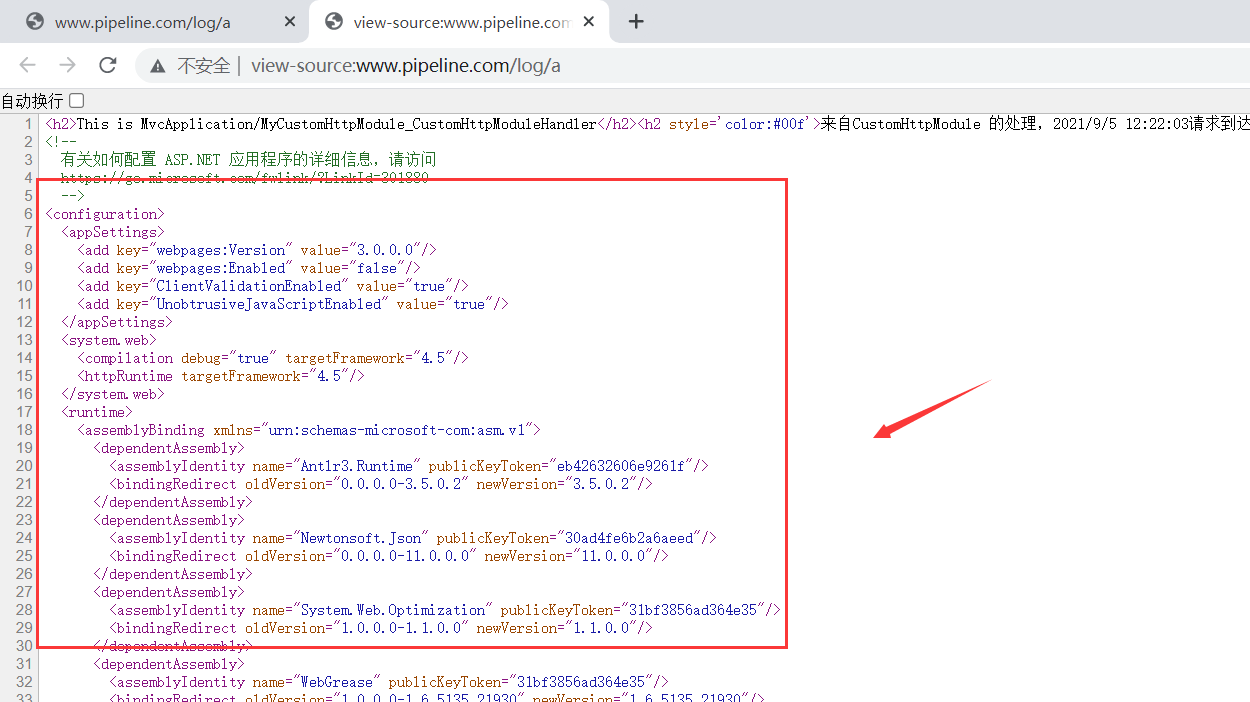
可以发现输出了我们想要的东西,说明我们的MvcRouteHandler扩展成功了。
小结:
1、扩展自己的Route,写入RouteCollection,可以自定义规则完成路由。
2、扩展HttpHandle,就可以为所欲为,跳出MVC框架。
至此本文就全部介绍完了,如果觉得对您有所启发请记得点个赞哦!!!
Demo源码:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Rb4uq0yB_iB3VsonwiCFKw 提取码:68r6
此文由博主精心撰写转载请保留此原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xyh9039/p/15216683.html
版权声明:如有雷同纯属巧合,如有侵权请及时联系本人修改,谢谢!!!



