计算回形针方向
摘要
本篇来用OpenCV实现Halcon中一个计算回形针方向的实例clip.hdev,并构建了计算角度函数和画箭头函数,得到的角度与halcon例程相差无多。
原图如下:
Halcon代码比较简单,这里也贴出来:
dev_update_window ('off') read_image (Clip, 'clip') get_image_size (Clip, Width, Height) dev_close_window () dev_open_window (0, 0, Width / 2, Height / 2, 'black', WindowID) dev_display (Clip) set_display_font (WindowID, 14, 'mono', 'true', 'false') disp_continue_message (WindowID, 'black', 'true') stop () binary_threshold (Clip, Dark, 'max_separability', 'dark', UsedThreshold) connection (Dark, Single) select_shape (Single, Selected, 'area', 'and', 5000, 10000) dev_set_draw ('fill') dev_set_colored (12) dev_display (Selected) disp_continue_message (WindowID, 'black', 'true') stop () dev_display (Clip) dev_set_color ('green') dev_display (Selected) orientation_region (Selected, Phi) area_center (Selected, Area, Row, Column) dev_set_line_width (3) dev_set_draw ('margin') Length := 80 dev_set_color ('blue') disp_arrow (WindowID, Row, Column, Row - Length * sin(Phi), Column + Length * cos(Phi), 4) disp_message (WindowID, deg(Phi)$'3.1f' + ' deg', 'image', Row, Column - 100, 'black', 'false') dev_update_window ('on')
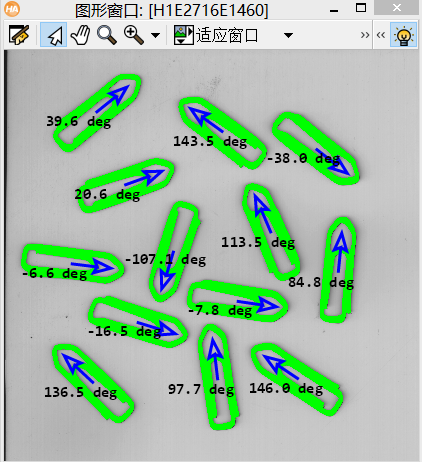
可以看到halcon的思路是:
① 读取图像
② 二值化
③ 根据面积剔除非回形针的region
④ 计算每个region的方向和中心
⑤ 画箭头,结果输出
但是opencv中没有计算角度的函数和画箭头的函数,因此需要我们自己定义。
opecv实现:
(一)构建角度计算函数
double calLineAngle(Point&ptStrat, Point&ptEnd) { const double PI = 3.1415926; double angle = 0; if (ptStrat.x==ptEnd.x) { angle = 90; } else if (ptStrat.y==ptEnd.y) { angle = 0; } else { angle = atan((double)(ptEnd.y - ptStrat.y) / (ptEnd.x - ptStrat.x))*(180 / PI); if (angle<0) { angle = abs(angle); } else if (angle>0) { angle = 180 - angle; } if (ptEnd.y-ptStrat.y>0&&ptEnd.x-ptStrat.x) { angle = angle - 180; } } return angle; }
atan 和 atan2 都是求反正切函数,如:有两个点 point(x1,y1), 和 point(x2,y2);那么这两个点形成的斜率的角度计算方法分别是:
- float angle = atan( (y2-y1)/(x2-x1) );
- float angle = atan2( y2-y1, x2-x1 );
atan 和 atan2 区别:
1:参数的填写方式不同;
2:atan2 的优点在于 如果 x2-x1等于0 依然可以计算,但是atan函数就会导致程序出错;
(二)构建画箭头函数
void drawArrow(Mat&img, Point pStart, Point pEnd, int len, int alpha, Scalar color, int thickness, int lineType) { const double PI = 3.1415926; Point arrow; //计算theat角 double angel = atan2((double)(pStart.y - pEnd.y), (double)(pStart.x - pEnd.x)); line(img, pStart, pEnd, color, thickness, lineType); //计算箭角边的另一端的端点位置(上面的还是下面的要看箭头的指向,即pStart和pEnd的位置) arrow.x = pEnd.x + len * cos(angel + PI * alpha / 180); arrow.y = pEnd.y + len * sin(angel + PI * alpha / 180); line(img, pEnd, arrow, color, thickness, lineType); arrow.x = pEnd.x + len * cos(angel - PI * alpha / 180); arrow.y = pEnd.y + len * sin(angel - PI * alpha / 180); line(img, pEnd, arrow, color, thickness, lineType); }
(三)主函数
int main(int argc, char** argv) { double pointToLineDist(Point&pt, Point&lineStart, Point&lineEnd); double calLineAngle(Point&ptStrat, Point&ptEnd); void drawArrow(Mat&img, Point pStart, Point pEnd, int len, int alpha, Scalar color, int thickness, int lineType); Mat src = imread("D:/opencv练习图片/回形针方向.png"); imshow("输入图像", src); Mat gray, binary; cvtColor(src, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY); //阈值处理 threshold(gray, binary, 150, 255, THRESH_BINARY_INV); imshow("二值化", binary); //寻找轮廓 vector<vector<Point> > contours; findContours(binary, contours, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_NONE,Point()); cout << contours.size() << endl; //轮廓分析,找到工件 for (size_t i = 0; i < contours.size(); ++i) { //计算轮廓大小 double area = contourArea(contours[i]); if (area < 12000)continue; double max_dist = 0; Moments mm = moments(contours[i],false); Point ptCenter = Point(mm.m10 / mm.m00, mm.m01 / mm.m00); Point ptFarthest; for (int j = 0; j < contours[i].size(); j++) { double distance = sqrt(pow(contours[i][j].x - ptCenter.x, 2) + pow(contours[i][j].y - ptCenter.y, 2)); if (distance>max_dist) { ptFarthest = Point(contours[i][j].x, contours[i][j].y); max_dist = distance; } } cout << max_dist << endl; drawContours(src, contours, i, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 5, 8); drawArrow(src, ptCenter, ptFarthest, 25, 30, Scalar(255,0,255), 3, 8); double angle = calLineAngle(ptCenter, ptFarthest); cout << angle << endl; char strAngle[20]; sprintf_s(strAngle, "%0.1fdegree", angle); putText(src, strAngle, ptCenter, FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.8, Scalar(0, 255, 255), 2, 8); } imshow("结果", src); waitKey(0); return 0; }

参考于:OpenCV与AI深度学习


