spring boot 数据层框架
SQL
数据源技术
数据源技术是Druid,运行时可以在日志中看到对应的数据源初始化信息,具体如下:
INFO 28600 --- [ main] c.a.d.s.b.a.DruidDataSourceAutoConfigure : Init DruidDataSource
INFO 28600 --- [ main] com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource : {dataSource-1} inited
如果不使用Druid数据源,程序运行后是什么样子呢?是独立的数据库连接对象还是有其他的连接池技术支持呢?将Druid技术对应的starter去掉再次运行程序可以在日志中找到如下初始化信息:
INFO 31820 --- [ main] com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource : HikariPool-1 - Starting...
INFO 31820 --- [ main] com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource : HikariPool-1 - Start completed.
springboot提供了3款内嵌数据源技术,分别如下:
- HikariCP
- Tomcat提供DataSource
- Commons DBCP
第一种,HikartCP,这是springboot官方推荐的数据源技术,作为默认内置数据源使用。
第二种,Tomcat提供的DataSource,如果不想用HikartCP,并且使用tomcat作为web服务器进行web程序的开发,使用这个。为什么是Tomcat,不是其他web服务器呢?因为web技术导入starter后,默认使用内嵌tomcat,既然都是默认使用的技术了,那就一用到底,数据源也用它的。有人就提出怎么才能不使用HikartCP用tomcat提供的默认数据源对象呢?把HikartCP技术的坐标排除掉就OK了。
第三种,DBCP,这个使用的条件就更苛刻了,既不使用HikartCP也不使用tomcat的DataSource时,默认用这个。
配置druid时使用druid的starter对应的配置如下:
spring:
datasource:
druid:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_db?serverTimezone=UTC
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: root
换成是默认的数据源HikariCP后,直接吧druid删掉就行了,如下:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_db?serverTimezone=UTC
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: root
当然,也可以写上是对hikari做的配置,但是url地址要单独配置,如下:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_db?serverTimezone=UTC
hikari:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: root
这就是配置hikari数据源的方式。如果想对hikari做进一步的配置,可以继续配置其独立的属性。例如:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_db?serverTimezone=UTC
hikari:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: root
maximum-pool-size: 50
如果不想使用hikari数据源,使用tomcat的数据源或者DBCP配置格式也是一样的。
总结
- springboot技术提供了3种内置的数据源技术,分别是Hikari、tomcat内置数据源、DBCP
- 配置 Hikari 时可以不指定名称,但是指定了就需要将 url 单独配置
持久化技术
持久化解决方案。数据层技术 JdbcTemplate,spring技术提供的,回归到jdbc最原始的编程形式来进行数据层的开发。
步骤①:导入jdbc对应的坐标,记得是starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency
步骤②:自动装配JdbcTemplate对象
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot15SqlApplicationTests {
@Test
void testJdbcTemplate(@Autowired JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate){
}
}
步骤③:使用JdbcTemplate实现查询操作(非实体类封装数据的查询操作)
@Test
void testJdbcTemplate(@Autowired JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate){
String sql = "select * from tbl_book";
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql);
System.out.println(maps);
}
步骤④:使用JdbcTemplate实现查询操作(实体类封装数据的查询操作)
@Test
void testJdbcTemplate(@Autowired JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate){
String sql = "select * from tbl_book";
RowMapper<Book> rm = new RowMapper<Book>() {
@Override
public Book mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Book temp = new Book();
temp.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
temp.setName(rs.getString("name"));
temp.setType(rs.getString("type"));
temp.setDescription(rs.getString("description"));
return temp;
}
};
List<Book> list = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rm);
System.out.println(list);
}
步骤⑤:使用JdbcTemplate实现增删改操作
@Test
void testJdbcTemplateSave(@Autowired JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate){
String sql = "insert into tbl_book values(3,'springboot1','springboot2','springboot3')";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql);
}
如果想对JdbcTemplate对象进行相关配置,可以在yml文件中进行设定,具体如下:
spring:
jdbc:
template:
query-timeout: -1 # 查询超时时间
max-rows: 500 # 最大行数
fetch-size: -1 # 缓存行数
总结
- SpringBoot内置JdbcTemplate持久化解决方案
- 使用JdbcTemplate需要导入spring-boot-starter-jdbc的坐标
数据库技术
springboot提供了3款内置的数据库,分别是
- H2
- HSQL
- Derby
以上三款数据库除了可以独立安装之外,还可以像是tomcat服务器一样,采用内嵌的形式运行在spirngboot容器中。内嵌在容器中运行,必须是java对象,这三款数据库底层都是使用java语言开发的。
我们一直使用MySQL数据库就挺好的,为什么有需求用这个呢?原因就在于这三个数据库都可以采用内嵌容器的形式运行,在应用程序运行后,如果我们进行测试工作,此时测试的数据无需存储在磁盘上,但是又要测试使用,内嵌数据库就方便了,运行在内存中,该测试测试,该运行运行,等服务器关闭后,一切烟消云散,多好,省得你维护外部数据库了。这也是内嵌数据库的最大优点,方便进行功能测试。
下面以H2数据库为例讲解如何使用这些内嵌数据库
步骤①:导入H2数据库对应的坐标,一共2个
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
步骤②:将工程设置为web工程,启动工程时启动H2数据库
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
步骤③:通过配置开启H2数据库控制台访问程序,也可以使用其他的数据库连接软件操作
spring:
h2:
console:
enabled: true
path: /h2
web端访问路径/h2,访问密码123456,如果访问失败,先配置下列数据源,启动程序运行后再次访问/h2路径就可以正常访问了
datasource:
url: jdbc:h2:~/test
hikari:
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
username: sa
password: 123456
步骤④:使用JdbcTemplate或MyBatisPlus技术操作数据库
注意:上线时,把内存级数据库关闭,采用MySQL数据库作为数据持久化方案,关闭方式就是设置enabled属性为false即可。
总结
- H2内嵌式数据库启动方式,添加坐标,添加配置
- H2数据库线上运行时请务必关闭
到这里SQL相关的数据层解决方案就讲完了,现在的可选技术就丰富的多了。
- 数据源技术:Druid、Hikari、tomcat DataSource、DBCP
- 持久化技术:MyBatisPlus、MyBatis、JdbcTemplate
- 数据库技术:MySQL、H2、HSQL、Derby
现在开发程序时就可以在以上技术中任选一种组织成一套数据库解决方案了。
NoSQL
SpringBoot整合Redis
步骤①:导入springboot整合redis的starter坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
上述坐标可以在创建模块的时候通过勾选的形式进行选择,归属NoSQL分类中
步骤②:进行基础配置
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
操作redis,最基本的信息就是操作哪一台redis服务器,所以服务器地址属于基础配置信息,不可缺少。但是即便你不配置,目前也是可以用的。因为以上两组信息都有默认配置,刚好就是上述配置值。
步骤③:使用springboot整合redis的专用客户端接口操作,此处使用的是RedisTemplate
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot16RedisApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void set() {
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set("age",41);
}
@Test
void get() {
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Object age = ops.get("name");
System.out.println(age);
}
@Test
void hset() {
HashOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
ops.put("info","b","bb");
}
@Test
void hget() {
HashOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
Object val = ops.get("info", "b");
System.out.println(val);
}
}
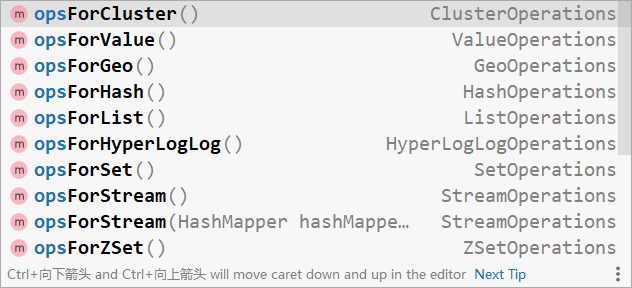
在操作redis时,需要先确认操作何种数据,根据数据种类得到操作接口。例如使用opsForValue()获取string类型的数据操作接口,使用opsForHash()获取hash类型的数据操作接口,剩下的就是调用对应api操作了。各种类型的数据操作接口如下:
总结
- springboot整合redis步骤
- 导入springboot整合redis的starter坐标
- 进行基础配置
- 使用springboot整合redis的专用客户端接口RedisTemplate操作
StringRedisTemplate
由于redis内部不提供java对象的存储格式,因此当操作的数据以对象的形式存在时,会进行转码,转换成字符串格式后进行操作。为了方便开发者使用基于字符串为数据的操作,springboot整合redis时提供了专用的API接口StringRedisTemplate,你可以理解为这是RedisTemplate的一种指定数据泛型的操作API。
@SpringBootTest
public class StringRedisTemplateTest {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Test
void get(){
ValueOperations<String, String> ops = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
String name = ops.get("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
}
redis客户端选择
springboot整合redis技术提供了多种客户端兼容模式,默认提供的是lettucs客户端技术,也可以根据需要切换成指定客户端技术,例如jedis客户端技术,切换成jedis客户端技术操作步骤如下:
步骤①:导入jedis坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
jedis坐标受springboot管理,无需提供版本号
步骤②:配置客户端技术类型,设置为jedis
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
client-type: jedis
步骤③:根据需要设置对应的配置
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
client-type: jedis
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 16
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 16
lettcus与jedis区别
- jedis连接Redis服务器是直连模式,当多线程模式下使用jedis会存在线程安全问题,解决方案可以通过配置连接池使每个连接专用,这样整体性能就大受影响
- lettcus基于Netty框架进行与Redis服务器连接,底层设计中采用StatefulRedisConnection。 StatefulRedisConnection自身是线程安全的,可以保障并发访问安全问题,所以一个连接可以被多线程复用。当然lettcus也支持多连接实例一起工作
总结
- springboot整合redis提供了StringRedisTemplate对象,以字符串的数据格式操作redis
- 如果需要切换redis客户端实现技术,可以通过配置的形式进行
SpringBoot整合MongoDB
MongoDB是一个开源、高性能、无模式的文档型数据库,它是NoSQL数据库产品中的一种,是最像关系型数据库的非关系型数据库。
步骤①:导入springboot整合MongoDB的starter坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
上述坐标也可以在创建模块的时候通过勾选的形式进行选择,同样归属NoSQL分类中
步骤②:进行基础配置
spring:
data:
mongodb:
uri: mongodb://localhost/数据库
步骤③:使用springboot整合MongoDB的专用客户端接口MongoTemplate来进行操作
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot17MongodbApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setId(2);
book.setName("springboot2");
book.setType("springboot2");
book.setDescription("springboot2");
mongoTemplate.save(book);
}
@Test
void find(){
List<Book> all = mongoTemplate.findAll(Book.class);
System.out.println(all);
}
}
总结
- springboot整合MongoDB步骤
- 导入springboot整合MongoDB的starter坐标
- 进行基础配置
- 使用springboot整合MongoDB的专用客户端接口MongoTemplate操作
SpringBoot整合ES
ES(Elasticsearch)是一个分布式全文搜索引擎,重点是全文搜索。
步骤①:导入springboot整合ES的starter坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
步骤②:进行基础配置
spring:
elasticsearch:
rest:
uris: http://localhost:9200
配置ES服务器地址,端口9200
步骤③:使用springboot整合ES的专用客户端接口ElasticsearchRestTemplate来进行操作
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot18EsApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchRestTemplate template;
}
上述操作形式是ES早期的操作方式,使用的客户端被称为Low Level Client,这种客户端操作方式性能方面略显不足,于是ES开发了全新的客户端操作方式,称为High Level Client。高级别客户端与ES版本同步更新,但是springboot最初整合ES的时候使用的是低级别客户端,所以企业开发需要更换成高级别的客户端模式。
下面使用高级别客户端方式进行springboot整合ES,操作步骤如下:
步骤①:导入springboot整合ES高级别客户端的坐标,此种形式目前没有对应的starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
步骤②:使用编程的形式设置连接的ES服务器,并获取客户端对象
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot18EsApplicationTests {
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@Test
void testCreateClient() throws IOException {
HttpHost host = HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200");
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(host);
client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
client.close();
}
}
配置ES服务器地址与端口9200,记得客户端使用完毕需要手工关闭。由于当前客户端是手工维护的,因此不能通过自动装配的形式加载对象。
步骤③:使用客户端对象操作ES,例如创建索引
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot18EsApplicationTests {
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@Test
void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {
HttpHost host = HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200");
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(host);
client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books");
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
client.close();
}
}
高级别客户端操作是通过发送请求的方式完成所有操作的,ES针对各种不同的操作,设定了各式各样的请求对象,上例中创建索引的对象是CreateIndexRequest,其他操作也会有自己专用的Request对象。
当前操作我们发现,无论进行ES何种操作,第一步永远是获取RestHighLevelClient对象,最后一步永远是关闭该对象的连接。在测试中可以使用测试类的特性去帮助开发者一次性的完成上述操作,但是在业务书写时,还需要自行管理。将上述代码格式转换成使用测试类的初始化方法和销毁方法进行客户端对象的维护。
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot18EsApplicationTests {
@BeforeEach //在测试类中每个操作运行前运行的方法
void setUp() {
HttpHost host = HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200");
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(host);
client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
}
@AfterEach //在测试类中每个操作运行后运行的方法
void tearDown() throws IOException {
client.close();
}
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@Test
void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books");
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
}
创建索引(IK分词器):
@Test
void testCreateIndexByIK() throws IOException {
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books");
String json = "{\n" +
" \"mappings\":{\n" +
" \"properties\":{\n" +
" \"id\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"name\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\":\"ik_max_word\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\":\"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"type\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"description\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\":\"ik_max_word\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\":\"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"all\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\":\"ik_max_word\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";
//设置请求中的参数
request.source(json, XContentType.JSON);
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
IK分词器是通过请求参数的形式进行设置的,设置请求参数使用request对象中的source方法进行设置,至于参数是什么,取决于你的操作种类。当请求中需要参数时,均可使用当前形式进行参数设置。
添加文档:
@Test
//添加文档
void testCreateDoc() throws IOException {
Book book = bookDao.selectById(1);
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("books").id(book.getId().toString());
String json = JSON.toJSONString(book);
request.source(json,XContentType.JSON);
client.index(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
添加文档使用的请求对象是IndexRequest,与创建索引使用的请求对象不同。
批量添加文档:
@Test
//批量添加文档
void testCreateDocAll() throws IOException {
List<Book> bookList = bookDao.selectList(null);
BulkRequest bulk = new BulkRequest();
for (Book book : bookList) {
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("books").id(book.getId().toString());
String json = JSON.toJSONString(book);
request.source(json,XContentType.JSON);
bulk.add(request);
}
client.bulk(bulk,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
批量做时,先创建一个BulkRequest的对象,可以将该对象理解为是一个保存request对象的容器,将所有的请求都初始化好后,添加到BulkRequest对象中,再使用BulkRequest对象的bulk方法,一次性执行完毕。
按id查询文档:
@Test
//按id查询
void testGet() throws IOException {
GetRequest request = new GetRequest("books","1");
GetResponse response = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
String json = response.getSourceAsString();
System.out.println(json);
}
根据id查询文档使用的请求对象是GetRequest。
按条件查询文档:
@Test
//按条件查询
void testSearch() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("books");
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
builder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("all","spring"));
request.source(builder);
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
String source = hit.getSourceAsString();
//System.out.println(source);
Book book = JSON.parseObject(source, Book.class);
System.out.println(book);
}
}
按条件查询文档使用的请求对象是SearchRequest,查询时调用SearchRequest对象的termQuery方法,需要给出查询属性名,此处支持使用合并字段,也就是前面定义索引属性时添加的all属性。
总结
- springboot整合ES步骤
- 导入springboot整合ES的High Level Client坐标
- 手工管理客户端对象,包括初始化和关闭操作
- 使用High Level Client根据操作的种类不同,选择不同的Request对象完成对应操作





· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 按钮权限的设计及实现