SpringBoot日志
1、日志框架分类和选择
2、slf4j使用原理以及springboot如何整合日志
2.1、如何在系统中使用SLF4j (https://www.slf4j.org)
2.2、使用slf4j门面 + 其他实现的原理
2.3、不同框架使用不同日志框架如果整合?
2.4、SpringBoot日志关系
2.5、总结
3、springboot日志配置和使用
4、springboot使用日志配置文件
5、一个 logback-spring.xml 配置示例
6、springboot切换日志框架
1、日志框架分类和选择 <--返回目录

2、slf4j使用原理以及springboot如何整合日志 <--返回目录
2.1、如何在系统中使用SLF4j (https://www.slf4j.org) <--返回目录
以后开发的时候,日志记录方法的调用,不应该来直接调用日志的实现类,而是调用日志抽象层里面的方法;
给系统里面导入slf4j的jar和 logback的实现jar
import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorld.class); logger.info("Hello World"); } }
2.2、使用slf4j门面 + 其他实现的原理 <--返回目录
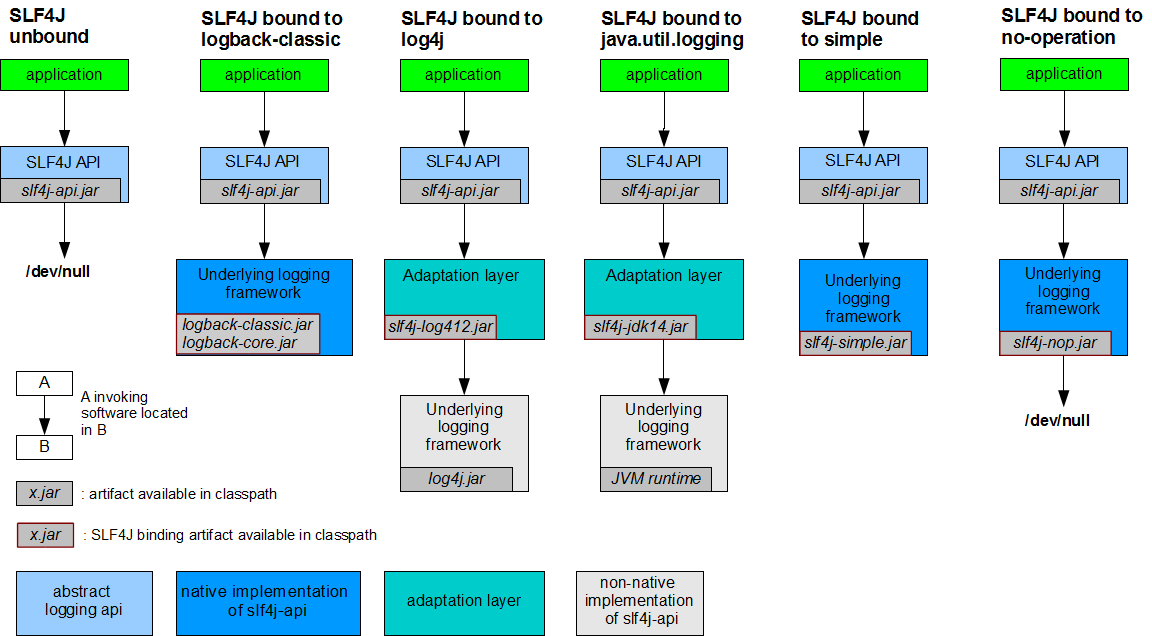
使用1:slf4j.jar + logback相关jar
使用2:slf4j.jar + slf4j-log412.jar + log4j.jar
2.3、不同框架使用不同日志框架如果整合? <--返回目录
springboot(slf4j+logback): Spring(commons-logging)、Hibernate(jboss-logging)、MyBatis、xxxx
统一日志记录,即使是别的框架和我一起统一使用slf4j进行输出?
如何让系统中所有的日志都统一到slf4j;
1、将系统中其他日志框架先排除出去;
2、用中间包来替换原有的日志框架;
3、我们导入slf4j其他的实现
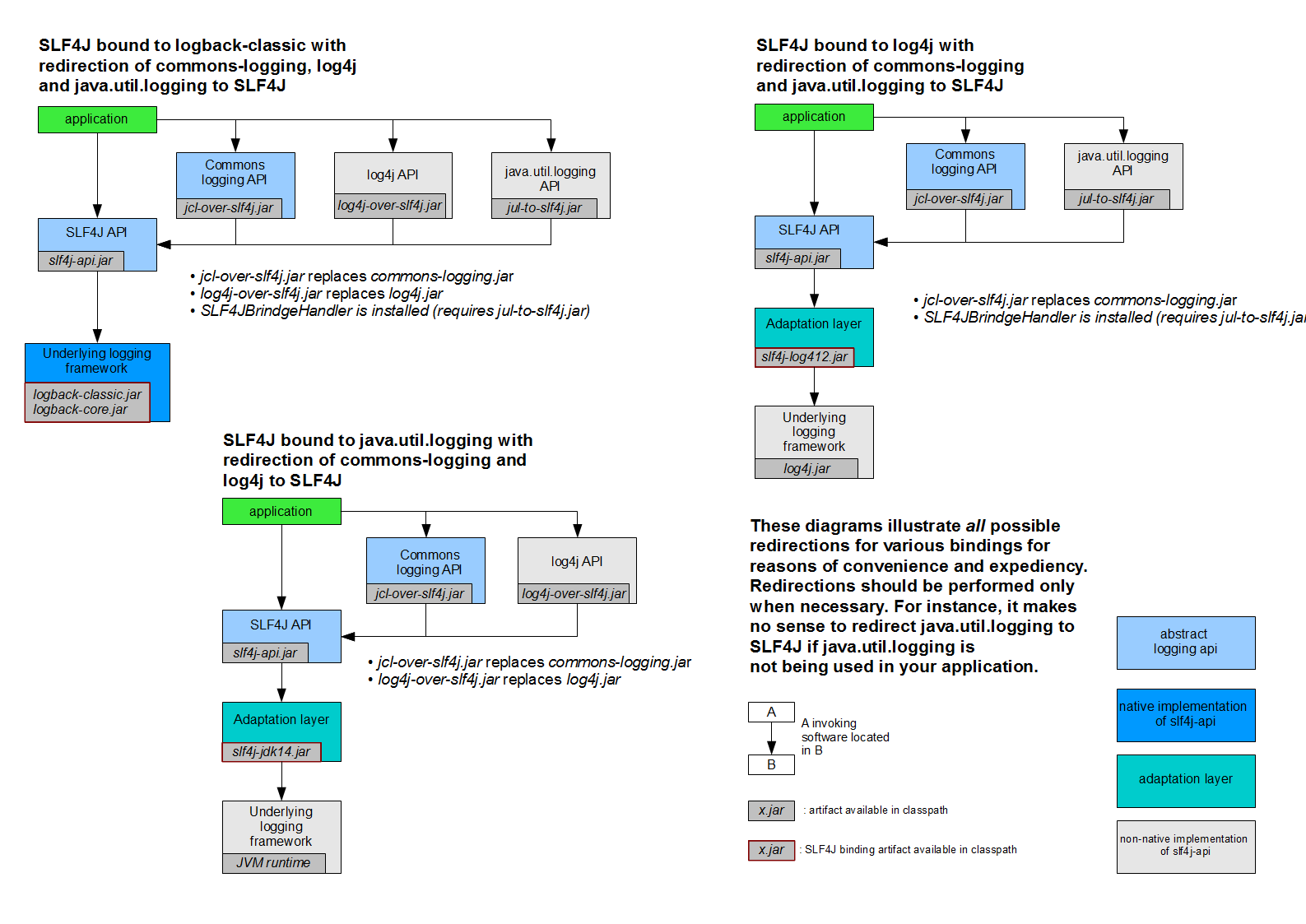
例子:比如commons-beanutils使用了commons-logging(jcl),如何整合为slf4j实现
Demo

import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; public class Demo { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Demo.class); public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { User u = new User(); BeanUtils.setProperty(u, "id", 12); BeanUtils.setProperty(u, "ab", 12); System.out.println(u); logger.info(u.toString()); } }
build.gradle

plugins {
id 'java'
}
group 'org.example'
version '1.0-SNAPSHOT'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation('commons-beanutils:commons-beanutils:1.9.4') {
exclude group: "commons-logging", module: "commons-logging"
}
implementation 'ch.qos.logback:logback-classic:1.2.10'
implementation 'org.slf4j:jcl-over-slf4j:1.7.36'
}
logback.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <configuration debug="false" scan="true" scanPeriod="1 seconds"> <contextName>logback</contextName> <property name="log.path" value="./log/logback.log"/> <appender name="console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender"> <filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.ThresholdFilter"> <level>debug</level> </filter> <encoder> <pattern>%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} %-5level (%-33file:%line\) : %msg%n </pattern> </encoder> </appender> <appender name="file" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender"> <file>${log.path}</file> <prudent>true</prudent> <rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy"> <fileNamePattern>${log.path}.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.txt</fileNamePattern> </rollingPolicy> <encoder> <pattern>%date %level [%thread] %logger{36} >>> %msg%n</pattern> </encoder> </appender> <!-- <logger name="org.apache.commons.beanutils.converters" additivity="false"> <level value="INFO"/> <appender-ref ref="console"/> <appender-ref ref="file"/> </logger>--> <root level="debug"> <appender-ref ref="console"/> <!--<appender-ref ref="file"/>--> </root> </configuration>
2.4、SpringBoot日志关系 <--返回目录
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐logging</artifactId> </dependency>
spring‐boot‐starter‐logging 底层依赖关系
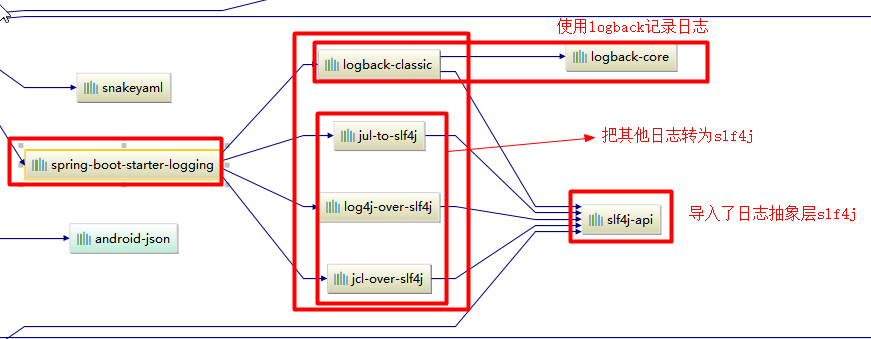
2.5、总结 <--返回目录
1)、SpringBoot底层也是使用slf4j+logback的方式进行日志记录
2)、SpringBoot也把其他的日志都替换成了slf4j;
3)、中间替换包?
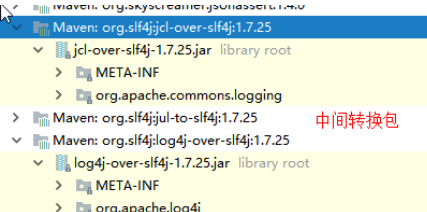
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public abstract class LogFactory {
static String UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION_IN_JCL_OVER_SLF4J =
"http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#unsupported_operation_in_jcl_over_slf4j";
static LogFactory logFactory = new SLF4JLogFactory();
4)、如果我们要引入其他框架?一定要把这个框架的默认日志依赖移除掉?
Spring框架用的是commons-logging;
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring‐core</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>commons‐logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons‐logging</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency>
SpringBoot能自动适配所有的日志,而且底层使用slf4j+logback的方式记录日志,引入其他框架的时候,只需要
把这个框架依赖的日志框架排除掉即可;
3、springboot日志配置和使用 <--返回目录
SpringBoot默认给我们使用的是info级别的
//记录器 Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass()); @Test public void contextLoads() { //System.out.println(); //日志的级别; //由低到高 trace<debug<info<warn<error //可以调整输出的日志级别;日志就只会在这个级别以以后的高级别生效 logger.trace("这是trace日志..."); logger.debug("这是debug日志..."); //SpringBoot默认给我们使用的是info级别的,没有指定级别的就用SpringBoot默认规定的级别;root级别 logger.info("这是info日志..."); logger.warn("这是warn日志..."); logger.error("这是error日志..."); }
SpringBoot修改日志的默认配置
logging.level.com.atguigu=trace #logging.path= # 不指定路径在当前项目下生成springboot.log日志 # 可以指定完整的路径; #logging.file=G:/springboot.log # 在当前磁盘的根路径下创建spring文件夹和里面的log文件夹;使用 spring.log 作为默认文件 logging.path=/spring/log # 在控制台输出的日志的格式 logging.pattern.console=%d{yyyy‐MM‐dd} [%thread] %‐5level %logger{50} ‐ %msg%n # 指定文件中日志输出的格式 logging.pattern.file=%d{yyyy‐MM‐dd} === [%thread] === %‐5level === %logger{50} ==== %msg%n
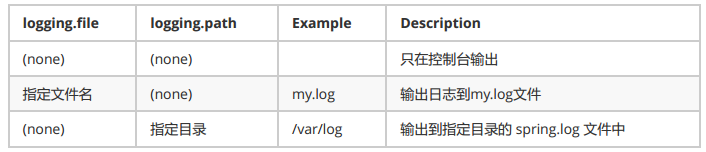
<!--日志输出格式: %d表示日期时间, %thread表示线程名, %‐5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度 %logger{50} 表示logger名字最长50个字符,否则按照句点分割。 %msg:日志消息, %n是换行符--> %d{yyyy‐MM‐dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %‐5level %logger{50} ‐ %msg%n
4、springboot使用日志配置文件 <--返回目录
给类路径下放上每个日志框架自己的配置文件即可;SpringBoot就不使用他默认配置的了
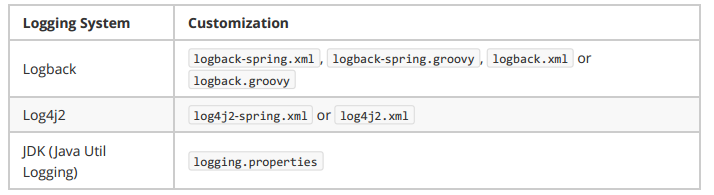
logback.xml:直接就被日志框架识别了;
logback-spring.xml:日志框架就不直接加载日志的配置项,由SpringBoot解析日志配置,可以使用SpringBoot
的高级Profile功能。所以推荐使用logback-spring.xml。
logback-spring.xml中使用Profile功能的例子:
<appender name="stdout" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender"> <!‐‐ 日志输出格式: %d表示日期时间, %thread表示线程名, %‐5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度 %logger{50} 表示logger名字最长50个字符,否则按照句点分割。 %msg:日志消息, %n是换行符 ‐‐> <layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout"> <springProfile name="dev"> <pattern>%d{yyyy‐MM‐dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} ‐‐‐‐> [%thread] ‐‐‐> %‐5level%logger{50} ‐ %msg%n</pattern> </springProfile> <springProfile name="!dev"> <pattern>%d{yyyy‐MM‐dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} ==== [%thread] ==== %‐5level%logger{50} ‐ %msg%n</pattern> </springProfile> </layout> </appender>
如果使用logback.xml作为日志配置文件,还要使用profile功能,会有以下错误
no applicable action for [springProfile]
5、一个 logback-spring.xml 配置示例 <--返回目录

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- scan:当此属性设置为true时,配置文件如果发生改变,将会被重新加载,默认值为true。 scanPeriod:设置监测配置文件是否有修改的时间间隔,如果没有给出时间单位,默认单位是毫秒当scan为true时,此属性生效。默认的时间间隔为1分钟。 debug:当此属性设置为true时,将打印出logback内部日志信息,实时查看logback运行状态。默认值为false。 --> <configuration scan="false" scanPeriod="60 seconds" debug="false"> <!-- 定义日志的根目录 --> <property name="LOG_HOME" value="/app/log" /> <!-- 定义日志文件名称 --> <property name="appName" value="atguigu-springboot"></property> <!-- ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender 表示控制台输出 --> <appender name="stdout" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender"> <!-- 日志输出格式: %d表示日期时间, %thread表示线程名, %-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度 %logger{50} 表示logger名字最长50个字符,否则按照句点分割。 %msg:日志消息, %n是换行符 --> <layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout"> <springProfile name="dev"> <pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} ----> [%thread] ---> %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern> </springProfile> <springProfile name="!dev"> <pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} ==== [%thread] ==== %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern> </springProfile> </layout> </appender> <!-- 滚动记录文件,先将日志记录到指定文件,当符合某个条件时,将日志记录到其他文件 --> <appender name="appLogAppender" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender"> <!-- 指定日志文件的名称 --> <file>${LOG_HOME}/${appName}.log</file> <!-- 当发生滚动时,决定 RollingFileAppender 的行为,涉及文件移动和重命名 TimeBasedRollingPolicy: 最常用的滚动策略,它根据时间来制定滚动策略,既负责滚动也负责出发滚动。 --> <rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy"> <!-- 滚动时产生的文件的存放位置及文件名称 %d{yyyy-MM-dd}:按天进行日志滚动 %i:当文件大小超过maxFileSize时,按照i进行文件滚动 --> <fileNamePattern>${LOG_HOME}/${appName}-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}-%i.log</fileNamePattern> <!-- 可选节点,控制保留的归档文件的最大数量,超出数量就删除旧文件。假设设置每天滚动, 且maxHistory是365,则只保存最近365天的文件,删除之前的旧文件。注意,删除旧文件是, 那些为了归档而创建的目录也会被删除。 --> <MaxHistory>365</MaxHistory> <!-- 当日志文件超过maxFileSize指定的大小是,根据上面提到的%i进行日志文件滚动 注意此处配置SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy是无法实现按文件大小进行滚动的,必须配置timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy --> <timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeAndTimeBasedFNATP"> <maxFileSize>100MB</maxFileSize> </timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy> </rollingPolicy> <!-- 日志输出格式: --> <layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout"> <pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [ %thread ] - [ %-5level ] [ %logger{50} : %line ] - %msg%n</pattern> </layout> </appender> <!-- logger主要用于存放日志对象,也可以定义日志类型、级别 name:表示匹配的logger类型前缀,也就是包的前半部分 level:要记录的日志级别,包括 TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR additivity:作用在于children-logger是否使用 rootLogger配置的appender进行输出, false:表示只用当前logger的appender-ref,true: 表示当前logger的appender-ref和rootLogger的appender-ref都有效 --> <!-- hibernate logger --> <logger name="com.atguigu" level="debug" /> <!-- Spring framework logger --> <logger name="org.springframework" level="debug" additivity="false"></logger> <!-- root与logger是父子关系,没有特别定义则默认为root,任何一个类只会和一个logger对应, 要么是定义的logger,要么是root,判断的关键在于找到这个logger,然后判断这个logger的appender和level。 --> <root level="info"> <appender-ref ref="stdout" /> <appender-ref ref="appLogAppender" /> </root> </configuration>
6、springboot切换日志框架 <--返回目录
可以按照slf4j的日志适配图,进行相关的切换。
slf4j+log4j的方式:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId> <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> </exclusion> <exclusion> <artifactId>log4j-over-slf4j</artifactId> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> </dependency>
切换为log4j2
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starte-web</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-log4j2</artifactId> </dependency>
其他参考:
posted on 2020-11-22 19:06 wenbin_ouyang 阅读(127) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报