SpringBoot集成Thymeleaf及使用
1、认识thymeleaf
2、SpringBoot集成Thymeleaf环境配置
3、标准变量表达式 ${} 和 th:text
4、选择变量表达式 *{} 和 th:object
5、链接(URL)表达式 和 th:href
6、th标签之th:action
7、th标签之th:each
8、其他th标签
9、thymeleaf字面量
10、Thymeleaf的字符串拼接
11、Thymeleaf的内置对象
12、公共页面抽取
1、认识thymeleaf <--返回目录
thymeleaf是一个流行的模板引擎,该模板引擎采用java语言开发。
模板引擎是一个技术名词,是跨领域跨平台的概念,在java语言体系下有模板引擎,在c#、PHP语言体系下也有模板引擎,甚至在JavaScript也会用到模板引擎技术。
java生态下的模板引擎有thymeleaf、freemarker、velocity、beetl(国产)等。
thymeleaf模板引擎既能用于web环境下,也能用于非web环境下,在非web环境下,它能直接显示模板上的静态数据,在web环境下,它能像jsp一样从后台接收数据并替换掉模板上的静态数据。
thymeleaf是基于html的,以html标签为载体,thymeleaf要寄托在html的标签下实现对数据的展示。
thymeleaf的官方网站:http://www.thymeleaf.org
springboot集成了thymeleaf模板技术,并且springboot官方也推荐使用thymeleaf来替代jsp技术。thymeleaf是另外一种模板技术,它本身并不属于springboot,springboot只是很好地集成了这种模板技术,作为前端页面的数据展示。
2、SpringBoot集成Thymeleaf环境配置 <--返回目录
springboot使用thymeleaf作为视图展示时,约定将模板文件放置在src/main/resources/templates目录下,静态资源放在src/main/resources/static目录下。
项目结构
依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency>
application.properties
# 开发阶段,建议关闭thymeleaf的缓存
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
#使用遗留的html5以去掉对html标签的校验
spring.thymeleaf.mode=LEGACYHTML5
在使用springboot的过程中,如果使用thymeleaf作为模板文件,则要求html格式必须为严格的html5格式,必须有结束标签,否则会报错;
如果不想对标签进行严格的验证,使用spring.thymeleaf.mode=LEGACYHTML5去掉验证,去掉该验证,则需要引入如下依赖,否则会报错;
<dependency> <groupId>net.sourceforge.nekohtml</groupId> <artifactId>nekohtml</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.unbescape</groupId> <artifactId>unbescape</artifactId> <version>1.1.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
NekoHTML是一个java语言的html扫描器和标签补全器,这个解析器能够扫描html文件并"修正"html文档中的常见错误。NekoHTML能增补缺失的父元素、自动用结束标签关闭相应的元素,修复不匹配的内嵌元素标签等。
IndexController
@Controller public class IndexController { @RequestMapping("/hello/thymeleaf") public String hello(Model model) { model.addAttribute("msg", "springboot集成thymeleaf"); return "test"; } }
在 src/main/resources/templates 下面创建 模板文件 test.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>标题</title> </head> <body> <span th:text="${msg}">span默认文本内容</span> </body> </html>
启动程序,访问http://localhost:8080/hello/thymeleaf 。
3、标准变量表达式 ${} 和 th:text <--返回目录
thymeleaf有5种表达式:
${}: 标准变量表达式
*{}: 选择变量表达式
#{}: 消息(i18n)表达式
@{}: 链接(URL)表达式
~{}: 片段表达式
${}: 标准变量表达式
@Controller public class IndexController { @RequestMapping("/hello/thymeleaf") public String hello(Model model) { model.addAttribute("msg", "springboot集成thymeleaf"); User user = new User(); user.setId(1); user.setName("张三"); user.setAge(10); model.addAttribute("user", user); return "test"; } }
<!DOCTYPE html> <html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>标题</title> </head> <body> <span th:text="${msg}">span默认文本内容</span><br/> id: <span th:text="${user.id}">1</span> name: <span th:text="${user.name}">xxx</span> age: <span th:text="${user.age}">18</span> </body> </html>
4、选择变量表达式 *{} 和 th:object <--返回目录
*{}: 选择变量表达式
标准变量表达式和选择变量表达式可以混合使用 ; 先用 th:object来绑定 user 对象, 然后用 * 来代表这个 user 对象
<!DOCTYPE html> <html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>标题</title> </head> <body> <span th:text="${msg}">span默认文本内容</span><br/> <div th:object="${user}"> id: <span th:text="*{id}">1</span> name: <span th:text="*{name}">xxx</span> age: <span th:text="*{age}">18</span> <br/> id: <span th:text="${user.id}">1</span> name: <span th:text="${user.name}">xxx</span> age: <span th:text="${user.age}">18</span> </div> </body> </html>
5、链接(URL)表达式 和 th:href <--返回目录

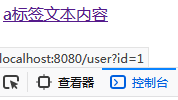
<!DOCTYPE html> <html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>标题</title> </head> <body> <a href="#" th:href="'http://localhost:8080/user?id=' + ${user.id}">a标签文本内容</a> <a href="#" th:href="@{'http://localhost:8080/user?id=' + ${user.id}}">a标签文本内容</a> </body> </html>
@Controller public class IndexController { @RequestMapping("/hello/thymeleaf") public String hello(Model model) { User user = new User(); user.setId(1); user.setName("张三"); user.setAge(10); model.addAttribute("user", user); return "test"; } @RequestMapping("/user") @ResponseBody public String getUserById(Integer id) { System.out.println("id=" + id); return "id=" + id; } }
访问 http://localhost:8080/hello/thymeleaf
6、th标签之th:action <--返回目录
th:action 例子:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>标题</title> </head> <body> <form th:action="@{/user}"> id:<input type="text" name="id" value=""/> <input type="submit" value="提交" /> </form> </body> </html>
@Controller public class IndexController { @RequestMapping("/hello/thymeleaf") public String hello(Model model) { return "test"; } @RequestMapping("/user") @ResponseBody public String getUserById(Integer id) { System.out.println("id=" + id); return "id=" + id; } }
7、th标签之th:each <--返回目录

@RequestMapping("/hello/thymeleaf")
public String hello(Model model) {
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(i);
user.setName("张三" + i);
user.setAge(20 + i);
userList.add(user);
}
model.addAttribute("userList", userList);
return "test";
}
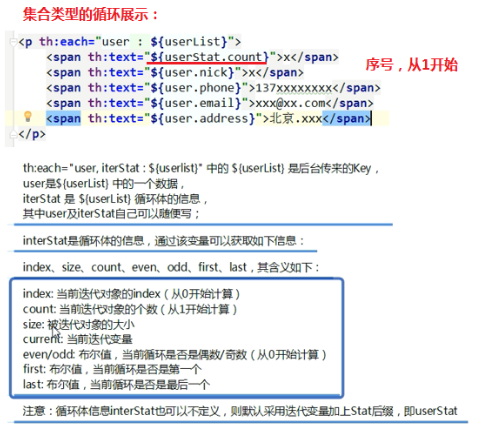
<body> <p th:each="user: ${userList}"> <span th:text="${user.id}" >xxx</span> <span th:text="${user.name}" >xxx</span> <span th:text="${user.age}" >xxx</span> </p> </body>
8、其他th标签 <--返回目录
th:name , th:id , th:src , th:href
th标签之th:if
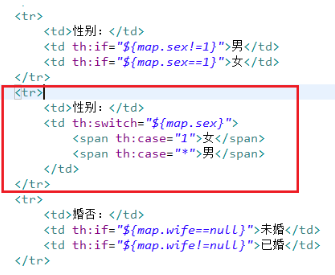
<span th:if="${sex eq 1}">男</span> <span th:if="${sex eq 2}">女</span>
th标签之th:unless 与 th:if 相反
th标签之th:switch/th:case




9、thymeleaf字面量 <--返回目录
10、Thymeleaf的字符串拼接 <--返回目录
11、Thymeleaf的内置对象 <--返回目录
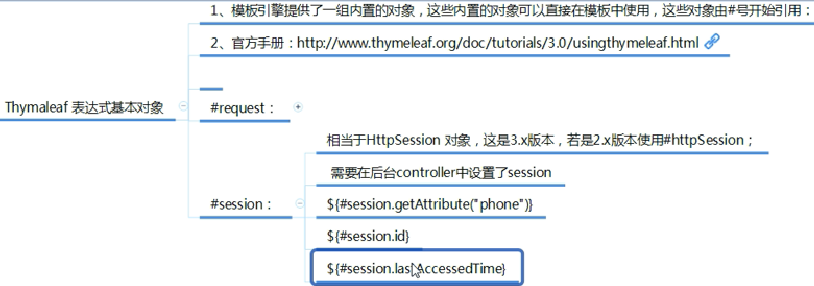
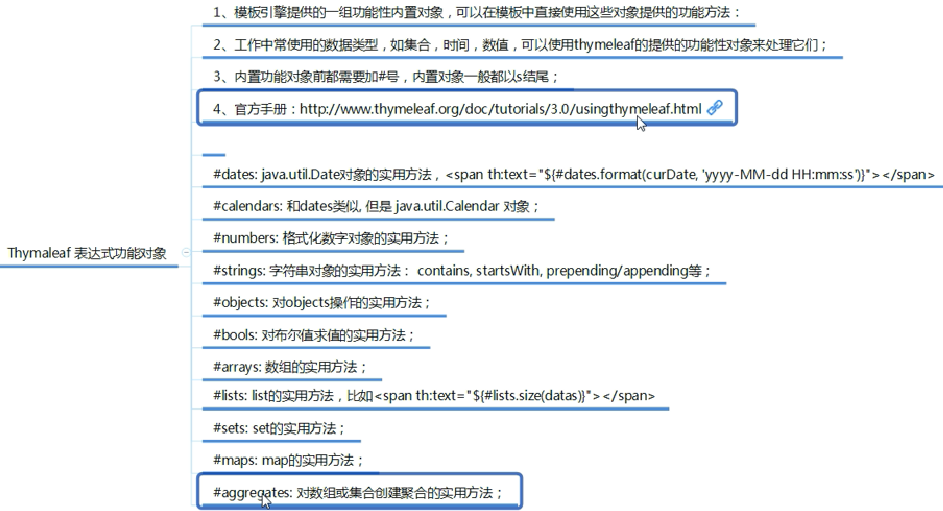
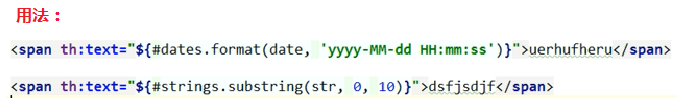
登陆错误消息的显示
<p style="color: red" th:text="${msg}" th:if="${not #strings.isEmpty(msg)}"></p>
12、公共页面抽取 <--返回目录
1、抽取公共片段 <div th:fragment="copy"> © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery </div> 2、引入公共片段 <div th:insert="~{footer :: copy}"></div> ~{templatename::selector}:模板名::选择器 ~{templatename::fragmentname}:模板名::片段名 3、默认效果: insert的公共片段在div标签中 如果使用th:insert等属性进行引入,可以不用写~{}: 行内写法可以加上:[[~{}]];[(~{})];
三种引入公共片段的th属性:
th:insert:将公共片段整个插入到声明引入的元素中
th:replace:将声明引入的元素替换为公共片段
th:include:将被引入的片段的内容包含进这个标签中
<!-- 公共片段 --> <footer th:fragment="copy"> © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery </footer> 三种引入方式 <div th:insert="footer :: copy"></div> <div th:replace="footer :: copy"></div> <div th:include="footer :: copy"></div> 三种引入方式效果分别为 <div> <footer> © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery </footer> </div> <footer> © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery </footer> <div> copy; 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery </div>
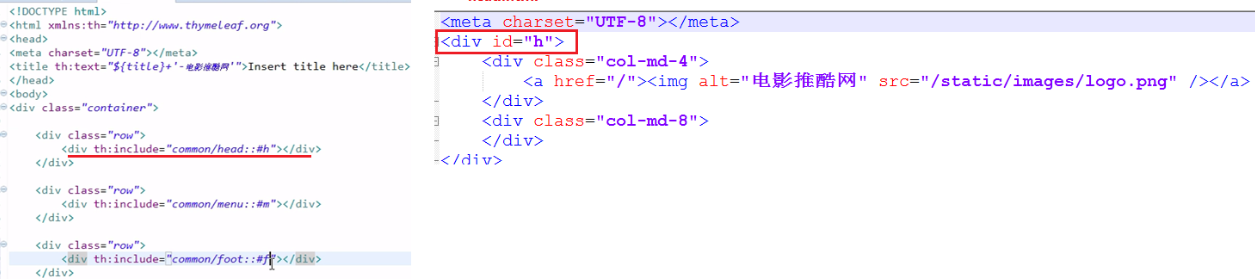
另外,也可以在引入公共片段时传入参数
<!‐‐引入侧边栏;传入参数‐‐> <div th:replace="commons/bar::#sidebar(activeUri='emps')"></div>
---
posted on 2020-11-15 16:37 wenbin_ouyang 阅读(12573) 评论(1) 编辑 收藏 举报






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架