node.js入门学习(一)环境安装,REPL,fs模块,path模块,http模块
目录:
一、node.js介绍
二、node.js有哪些特点
三、下载安装node.js,配置环境变量
四、node.js开发网站和传统PHP等开发网站的区别
五、REPL介绍
六、helloworld程序
七、案例:输出一个三角形
八、fs写入文件和读取文件
九、__dirname和__filename获取正在执行的js文件的路径
十、使用path模块进行路径拼接
十一、通过http模块构建一个简单的http服务程序
十二、Buffer
一、node.js介绍 <--返回目录
1.1、node.js是什么
官网首页总结:Node.js® 是一个基于 Chrome V8 引擎 的 JavaScript 运行时。
1)node.js是一个开发平台,就像java开发平台、.net开发平台、PHP开发平台、Apple开发平台一样。
- 什么是开发平台:有对应的编程语言、有语言运行时、有能实现特定功能的API(SDK Software Development Kit)
2)node.js平台使用的编程语言是JavaScript。
3)node.js平台是基于Chrome V8 JavaScript 引擎构建。
1.2、node.js可以做什么
1)基于node.js可以开发控制台程序(命令行程序、CLI程序)、桌面应用程序(GUI,要借助node-webkit、electron等框架实现)、web应用程序(网站)
2)PHP开发技术栈:LAMP - Linux Apache MySQL PHP
3)node.js全栈开发技术栈:MEAN- MongoDB Express Angular Node.js
二、node.js有哪些特点 <--返回目录
1)事件驱动:当事件被触发,执行传递过去的回调函数
2)非阻塞I/O模型:当执行I/O操作时,不会阻塞线程
3)单线程
4)拥有世界最大的开源库生态系统-npm
node.js在处理高并发、I/O密集场景性能优势明显。
- CPU密集:压缩、解压、加密、解密
- I/O密集:文件操作、网络操作、数据库操作
web常见场景:静态资源读取、数据库操作、渲染页面。
node.js的单线程:单线程只是针对主进程,I/O操作系统底层多线程调度。
三、下载安装node.js,配置环境变量 <--返回目录
node.js官方网站:https://nodejs.org/
中文网: http://nodejs.cn/
中文社区:https://cnodejs.org/
下载win 64为安装包:node-v10.16.0-x64.msi,双击安装

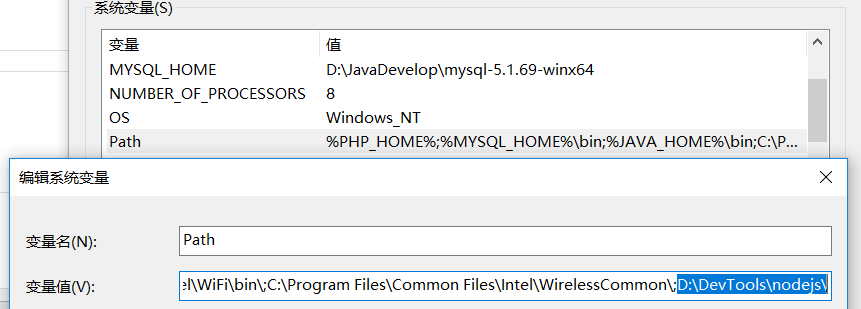
为了在任何目录下都可以使用node和npm命令,将这两个命令添加到环境变量path。我安装node时默认就添加到了环境变量。
四、node.js开发网站和传统PHP等开发网站的区别 <--返回目录
1)传统php、java、asp.net开发web程序需要web容器
2)node.js本身就是web服务器
- 接收用户请求后,根据不同的请求直接做对应处理
- 把处理后的结果返回给浏览器
五、REPL介绍 <--返回目录
1)REPL全称Read Eval Print Loop交互式解释器
- R 读取,读取用户输入,解析输入js数据结构并储存在内存中
- E 执行,执行输入的数据结构
- P 打印,输出结果
- L 循环,循环操作以上步骤直到用户两次按下Ctrl+c按钮退出
2)在REPL中编写程序,类似于浏览器开发人员工具中的控制台功能。
3)直接在控制台输入node命令,进入REPL环境。
4)按两次Ctrl+c 或者输入 .exit ,退出REPL界面

六、helloworld程序 <--返回目录
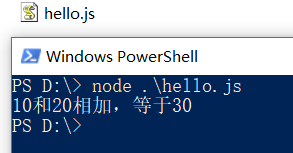
新建一个helloworld.js
var m = 10; var n = 20; function add(x, y) { return x + y; } console.log(m + "和"+ n + "相加,等于" + add(m,n));
在包含helloworld.js文件的目录下,shift+右键,在此处打开命令窗口;输入命令 node hel(tab补全),控制台会打印结果。
七、案例:输出一个三角形 <--返回目录
process模块是全局模块,直接使用;
for(var i = 0; i <10; i++) { for(var j = 0;j <=i; j++) { process.stdout.write("* "); } console.log(); }
八、fs写入文件和读取文件 <--返回目录
process模块是全局模块,直接使用;fs不是全局模块,要用require加载
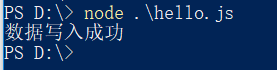
fs写入文件:
// 加载文件操作fs模块 var fs = require("fs"); // 文件写入 // fs.writeFile('文件路径','数据','选项',function(){}); fs.writeFile('./a.txt','hello world', 'utf-8', (err) => { // 如果err===null,表示写入文件成功 // 只要err不是null,就表示写入文件失败 if (err) { throw err; console.log("数据写入失败: " + err); } else { console.log("数据写入成功"); } });
fs文件追加内容:
fs.appendFile('./test.txt', 'bbbb', 'utf8', err => {
console.log('done')
})
fs读取文件:
// 加载文件操作fs模块 var fs = require("fs"); // fs.ReadFile('文件路径','选项',function(){}); // 文件路径'a.txt'是相对于执行node命令的路径 fs.readFile('./a.txt','utf-8',(err,data) => { if (err) { throw err; console.log("数据读取失败"); } else { console.log(data); } });
fs.stat() 判断是文件还是文件夹
fs.stat('./a.js', (err, stats) => {
if (err) {
console.log('文件不存在'); // 一般可以用来判断文件是否存在
return;
};
console.log(stats.isFile());
console.log(stats.isDirectory());
console.log(stats);
});
fs.rename() 重命名
fs.rename('./text', 'test.txt', err => {
if(err) throw err;
console.log('done!');
});
fs.unlink() 删除
fs.unlink('./test.txt', err => {});
fs.readdir() 读取文件夹内容
fs.readdir('../', (err, files) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(files);
})
fs.mkdir() 创建目录
fs.mkdir('test', err => {});
fs.watch() 监视文件或文件夹的变化
fs.watch('./', {recursive: true}, (eventType, filename) => {
console.log(eventType, filename);
});
fs同步的方法
const fs = require("fs");
// 同步的读取
var data = fs.readFileSync("./test.txt", 'utf8');
console.log("文件读取完成, data: ", data);
//同步的写入
fs.writeFileSync("./test.txt", '很好', 'utf8');
//同步的追加
fs.appendFileSync("./test.txt", '呵呵', 'utf8');
九、__dirname和__filename获取正在执行的js文件的路径 <--返回目录
前面的程序都是在hello.js所在目录执行node ./hello.js命令。如果进到c盘,执行node D:\hello.js命令,结果:
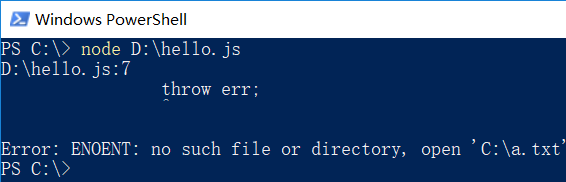
__dirname表示当前正在执行的js文件的所在目录;__filename表示当前正在执行的js文件的完整路径
//fs读取文件 // 加载文件操作fs模块 var fs = require("fs"); // fs.writeFile('文件路径','选项',function(){}); // fs.readFile(__dirname+'\\a.txt','utf-8',(err,data) => { fs.readFile(__dirname+'/a.txt','utf-8',(err,data) => { if (err) { throw err; console.log("数据读取失败"); } else { console.log(data); } });
所以,"./hello.js"中./是相对于执行node命令的路径,而不是相对于当前js文件的路径。
__dirname和__filename不是全局的,但是为什么使用的时候不需要通过require引入:
( function ("__dirname", "__filename") { //fs读取文件 // 加载文件操作fs模块 var fs = require("fs"); // fs.writeFile('文件路径','选项',function(){}); // fs.readFile(__dirname+'\\a.txt','utf-8',(err,data) => { fs.readFile(__dirname+'/a.txt','utf-8',(err,data) => { if (err) { throw err; console.log("数据读取失败"); } else { console.log(data); } }); } )("当前正在执行的js文件的所在目录","当前正在执行的js文件的完整路径");
总结:__dirname、__filename总是返回文件的绝对路径;
process.cwd()总是返回执行node命令所在文件夹;
require()方法总是相对当前文件;
pahth.resolve('./')是执行node命令所在文件夹
十、使用path模块进行路径拼接 <--返回目录
path会根据系统拼接成对应的路径,windows下格式是 \a\b\c
var path = require('path'); var str = path.join('/foo','bar','baz/asdf'); console.log(path); process.stdout.write(str); // \foo\bar\baz\asdf
const path = require('path')
// normalize: 将路径解析成标准的格式
console.log(path.normalize('/usr/local//bin')) // \usr\local\bin
console.log(path.normalize('/usr/local/../bin')) // \usr\\bin
// resolve: 将相对路径解析成绝对路径
console.log(path.resolve('./')) // D:\当前文件所在目录名
// basename: 取文件名, dirname: 文件夹, extname: 扩展名
const pathName1 = path.basename('c:/a/b.js')
console.log(pathName1) // b.js
const pathName2 = path.basename('c:\\a\\b.js')
console.log(pathName2) // b.js
const filePath = '/usr/local/bin/a.txt'
console.log(path.basename(filePath)) // a.txt
console.log(path.dirname(filePath)) // /usr/local/bin
console.log(path.extname(filePath)) // .txt
console.log('='.repeat(50))
// parse format
const parseResult = path.parse(filePath)
console.log(parseResult) // {root:'/', dir:'/usr/local/bin', base:'a.txt', ext:'.txt', name:'a'}
// parseResult对象中dir和base优先级高,即有这个两个属性,其他属性值忽略掉。因为有dir和base属性就可以完全拼接出完整的文件名
console.log(path.format(parseResult)) // /usr/local/bin\a.txt
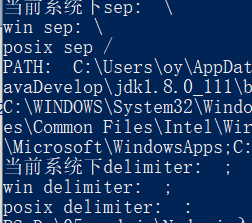
const path = require('path')
// sep delimiter win32 posix
console.log('当前系统下sep: ', path.sep)
console.log('win sep:', path.win32.sep)
console.log('posix sep', path.posix.sep)
console.log('PATH: ', process.env.path)
console.log('当前系统下delimiter: ', path.delimiter) // delimiter是PATH的分隔符
console.log('win delimiter: ', path.win32.delimiter)
console.log('posix delimiter: ', path.posix.delimiter)
十一、通过http模块构建一个简单的http服务程序 <--返回目录
第一步:在d:/hello.js写代码:
// 加载http模块 var http = require("http"); // 创建一个http服务对象 var server = http.createServer(); // 监听用户的请求 server.on('request', function(req,res) { res.setHeader('content-type','text/html;charset=utf-8'); res.write('<h1>hello 您好!</h1>'); res.end();//结束响应 }); // 开启服务 server.listen('8080', function() { console.log('服务器已经启动。'); });
第二步:cmd窗口输入node D:\hello.js运行程序
第三步:浏览器输入http://localhost:8080。
十二、Buffer <--返回目录
Buffer用于处理二进制数据流,类似数组,但是Buffer大小固定。
构造Buffer
console.log(Buffer.alloc(5)) // 默认0填充 console.log(Buffer.alloc(5, 1)) //0x1填充 console.log(Buffer.allocUnsafe(5)) // 保持原有数据 console.log(Buffer.from([1, 2, 3])) console.log(Buffer.from('test')) // 默认utf-8编码 console.log(Buffer.from('test', 'base64'))
Buffer的byteLength()、isBuffer()、concat()方法
/* Buffer.byteLength() Buffer.isBuffer() Buffer.concat() */ console.log(Buffer.byteLength('test')) // 4 console.log(Buffer.byteLength('测试')) // 6, utf-8编码 console.log(Buffer.isBuffer({})) // false console.log(Buffer.isBuffer(Buffer.from([1, 2, 3]))) // true const buf1 = Buffer.from('hello') const buf2 = Buffer.from('世界') const buf3 = Buffer.from('!') const buf = Buffer.concat([buf1, buf2]) console.log(buf.toString()) // hello世界!
buf.length、buf.toString([encoding])、buf.fill(value[, start, end])
const buf = Buffer.allocUnsafe(10) buf[2] = 0xff console.log(buf.length) console.log(buf) buf.fill(0xff) console.log(buf) const buf2 = Buffer.from('hello world') console.log(buf2.toString()) console.log(buf2.toString('base64'))
buf.equals()、buf.indexOf()
const buf1 = Buffer.from('test')
const buf2 = Buffer.from('test')
console.log(buf1.equals(buf2)) // 比较内容是否相同,true
console.log(buf1.indexOf('te')) // 0
console.log(buf1.indexOf('abc')) // 找不到,返回-1
---
posted on 2019-06-29 22:18 wenbin_ouyang 阅读(2073) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报