ThreadLocal源码分析
1.ThreadLocal 是什么?
在JDK 1.2的版本中就提供java.lang.ThreadLocal,ThreadLocal为解决多线程程序的并发问题提供了一种新的思路。使用这个工具类可以很简洁地编写出优美的多线程程序。
ThreadLocal并不是一个Thread,而是Thread的局部变量。在JDK5.0中,ThreadLocal已经支持泛型,该类的类名已经变为ThreadLocal<T>。API方法也相应进行了调整,新版本的API方法分别是void set(T value)、T get()以及T initialValue()。
2.ThreadLocal 的作用?
ThreadLocal是解决线程安全问题一个很好的思路,它通过为每个线程提供一个独立的变量副本解决了变量并发访问的冲突问题。在很多情况下,ThreadLocal比直接使用synchronized同步机制解决线程安全问题更简单,更方便,且结果程序拥有更高的并发性。在Java的多线程编程中,为保证多个线程对共享变量的安全访问,通常会使用synchronized来保证同一时刻只有一个线程对共享变量进行操作。这种情况下可以将类变量放到ThreadLocal类型的对象中,使变量在每个线程中都有独立拷贝,不会出现一个线程读取变量时而被另一个线程修改的现象。最常见的ThreadLocal使用场景为用来解决数据库连接、Session管理等。
3.ThreadLocal的源码分析
我们从源码中了解ThreadLocal的原理,下面来看一下具体ThreadLocal是如何实现的。
ThreadLocal类中提供了几个方法:
1.public T get() { }
2.public void set(T value) { }
3.public void remove() { }
4.protected T initialValue(){ }
get()方法是用来获取ThreadLocal在当前线程中保存的变量副本,set()用来设置当前线程中变量的副本,remove()用来移除当前线程中变量的副本,initialValue()是一个protected方法,一般是用来在使用时进行重写的,它是一个延迟加载方法,下面会详细说明。
3.1、ThreadLocal一些重要的成员变量以及公共方法
//线程获取threadLocal.get()时 如果是第一次在某个 threadLocal对象上get时,会给当前线程分配一个value
//这个value 和 当前的threadLocal对象 被包装成为一个 entry 其中 key是 threadLocal对象,value是threadLocal对象给当前线程生成的value
//这个entry存放到 当前线程 threadLocals 这个map的哪个桶位? 与当前 threadLocal对象的threadLocalHashCode 有关系。
// 使用 threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1) 的到的位置 就是当前 entry需要存放的位置。
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
/**
* The next hash code to be given out. Updated atomically. Starts at
* zero.
* 创建ThreadLocal对象时 会使用到,每创建一个threadLocal对象 就会使用nextHashCode 分配一个hash值给这个对象。
*/
private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode =
new AtomicInteger();
/**
* The difference between successively generated hash codes - turns
* implicit sequential thread-local IDs into near-optimally spread
* multiplicative hash values for power-of-two-sized tables.
* 每创建一个ThreadLocal对象,这个ThreadLocal.nextHashCode 这个值就会增长 0x61c88647 。
* 这个值 很特殊,它是 斐波那契数 也叫 黄金分割数。hash增量为 这个数字,带来的好处就是 hash分布非常均匀。
*/
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
/**
* Returns the next hash code.
* 创建新的ThreadLocal对象时 会给当前对象分配一个hash,使用这个方法。
*/
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}
3.2、get方法源码的实现
/**
* 返回当前线程与当前ThreadLocal对象相关联的 线程局部变量,这个变量只有当前线程能访问到。
* 如果当前线程 没有分配,则给当前线程去分配(使用initialValue方法)
*/
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//获取到当前线程Thread对象的 ThreadLocalMap引用
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
//key:当前threadLocal对象
//调用map.getEntry() 方法 获取ThreadLocalMap 中该threadLocal关联的 entry
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);(后面在介绍)
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
//执行到这里有几种情况?
//1.当前线程对应的threadLocalMap是空
//2.当前线程与当前threadLocal对象没有生成过相关联的 线程局部变量..
//setInitialValue方法初始化当前线程与当前threadLocal对象 相关联的value。
//且 当前线程如果没有threadLocalMap的话,还会初始化创建map。
return setInitialValue(); (后面在介绍)
}
/**
* 返回此线程上的ThreadLocalMap对象
*/
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
3.3、set方法源码的实现
/**
* 修改当前线程与当前threadLocal对象相关联的 线程局部变量。
* 如果ThreadLocalMap对象还没有创建,则先创建ThreadLocalMap对象,然后在给他赋值
*/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//获取到当前线程Thread对象的 ThreadLocalMap引用
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
//调用threadLocalMap.set方法 进行重写 或者 添加(稍后介绍)。
map.set(this, value);
else
//执行到这里,说明当前线程还未创建 threadLocalMap对象。
//参数1:当前线程 参数2:线程与当前threadLocal相关的局部变量
createMap(t, value);
}
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
//传递t 的意义就是 要访问 当前这个线程 t.threadLocals 字段,给这个字段初始化。
//new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue)
//创建一个ThreadLocalMap对象 初始 k-v 为 : this <当前threadLocal对象> ,线程与当前threadLocal相关的局部变量(稍后介绍)
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
3.4、remove方法源码的实现
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
//条件成立:说明当前线程已经初始化过 threadLocalMap对象了
if (m != null)
//调用threadLocalMap.remove( key = 当前threadLocal)(稍后介绍)
m.remove(this);
}
3.4、initialValue方法源码的实现
/**
* 默认返回null,一般情况下 咱们都是需要重写这个方法的。
* @return
*/
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
4.ThreadLocalMap的源码分析
你直接调用ThreadLocal方法其实都是调用ThreadLocalMap方法来实现的,严格意义上ThreadLocalMap的代码才是ThreadLocal的核心代码,ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal的一个静态内部类。
4.1、ThreadLocalMap类的成员变量和一些共有方法
/**
* key 使用的是弱引用保留,key保存的是threadLocal对象。
* value 使用的是强引用,value保存的是 threadLocal对象与当前线程相关联的 value。
*
* entry#key 这样设计有什么好处呢?
* 当threadLocal对象失去强引用且对象GC回收后,散列表中的与 threadLocal对象相关联的 entry#key 再次去key.get() 时,拿到的是null。
* 站在map角度就可以区分出哪些entry是过期的,哪些entry是非过期的。
*/
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
/**
* The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two.
* 初始化当前map内部 散列表数组的初始长度 16,散列表的长度必须是2的幂次方倍
*/
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
/**
* The table, resized as necessary.
* table.length MUST always be a power of two.
* threadLocalMap 内部散列表数组引用,数组的长度 必须是 2的次方数
*/
private Entry[] table;
/**
* The number of entries in the table.
* 当前散列表数组 占用情况,存放多少个entry。
*/
private int size = 0;
/**
* The next size value at which to resize.
* 扩容触发阈值,初始值为: len * 2/3
* 触发后调用 rehash() 方法。
* rehash() 方法先做一次全量检查全局 过期数据,把散列表中所有过期的entry移除。
* 如果移除之后 当前 散列表中的entry 个数仍然达到 threshold - threshold/4 就进行扩容。
*/
private int threshold; // Default to 0
/**
* Set the resize threshold to maintain at worst a 2/3 load factor.
* 将阈值设置为 (当前数组长度 * 2)/ 3。
*/
private void setThreshold(int len) {
threshold = len * 2 / 3;
}
/**
* Increment i modulo len.
* 返回散列表下一个坐标
*/
private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);
}
/**
* Decrement i modulo len.
* 返回散列表上一个坐标
*/
private static int prevIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i - 1 >= 0) ? i - 1 : len - 1);
}
/**
* Construct a new map initially containing (firstKey, firstValue).
* ThreadLocalMaps are constructed lazily, so we only create
* one when we have at least one entry to put in it.
*
* 因为Thread.threadLocals字段是延迟初始化的,只有线程第一次存储 threadLocal-value 时 才会创建 threadLocalMap对象。
*
* firstKey :threadLocal对象
* firstValue: 当前线程与threadLocal对象关联的value。
*/
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
//寻址算法:key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1)
//table数组的长度一定是 2 的次方数。
//2的次方数-1 有什么特征呢? 转化为2进制后都是1. 16==> 1 0000 - 1 => 1111
//1111 与任何数值进行&运算后 得到的数值 一定是 <= 1111
//i 计算出来的结果 一定是 <= B1111
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
//创建entry对象 存放到 指定位置的slot中
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
//设置size=1
size = 1;
//设置扩容阈值 (当前数组长度 * 2)/ 3 => 16 * 2 / 3 => 10
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
4.2、getEntry源码分析
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
//路由规则: ThreadLocal.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1) ==》 index
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
//条件一:成立 说明slot有值
//条件二:成立 说明 entry#key 与当前查询的key一致,返回当前entry 给上层就可以了。
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
//有几种情况会执行到这里?
//1.e == null
//2.e.key != key
//getEntryAfterMiss 方法 会继续向当前桶位后面继续搜索 e.key == key 的entry.
//为什么这样做呢??
//因为 存储时 发生hash冲突后,并没有在entry层面形成 链表.. 存储时的处理 就是线性的向后找到一个可以使用的slot,并且存放进去。
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
/**
* Version of getEntry method for use when key is not found in
* its direct hash slot.
*
* @param key the thread local object threadLocal对象 表示key
* @param i the table index for key's hash code key计算出来的index
* @param e the entry at table[i] table[index] 中的 entry
* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such
*/
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//条件:e != null 说明 向后查找的范围是有限的,碰到 slot == null 的情况,搜索结束。
//e:循环处理的当前元素
while (e != null) {
//获取当前slot 中entry对象的key
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
//条件成立:说明向后查询过程中找到合适的entry了,返回entry就ok了。
if (k == key)
return e;
//条件成立:说明当前slot中的entry#key 关联的 ThreadLocal对象已经被GC回收了.. 因为key 是弱引用, key = e.get() == null.
if (k == null)
//做一次 探测式过期数据回收。
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
//更新index,继续向后搜索。
i = nextIndex(i, len);
//获取下一个slot中的entry。
e = tab[i];
}
//执行到这里,说明关联区段内都没找到相应数据。
return null;
}
/**
* table[staleSlot] 就是一个过期数据,以这个位置开始 继续向后查找过期数据,直到碰到 slot == null 的情况结束。
*/
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//因为是过期数据,把数据变为null,方便gc
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
size--;
// Rehash until we encounter null
Entry e;
int i;
//for循环从 staleSlot + 1的位置开始搜索过期数据,直到碰到 slot == null 结束。
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
//进入到for循环里面 当前entry一定不为null
//获取当前遍历节点 entry 的key.
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
//条件成立:说明老表中的当前位置的entry 是一个过期数据..和之前的解决方法一样
if (k == null) {
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
//执行到这里,说明当前遍历的slot中对应的entry 是非过期数据
//因为前面有可能清理掉了几个过期数据。
//且当前entry 存储时有可能碰到hash冲突了,往后偏移存储了,这个时候 应该去优化位置,让这个位置更靠近 正确位置。
//这样的话,查询的时候 效率才会更高!
//重新计算当前entry对应的 index
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
//条件成立:说明存储时候,发生过hash冲突,然后向后偏移过了
if (h != i) {
tab[i] = null;
//while循环 就是拿到一个距离h最近的一个可以使用的slot。
while (tab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
//将数据存放到 新表的 合适的slot中。
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
//返回的是第一个为tab[i] == null的数据
return i;
}
下图为expungeStaleEntry函数一次执行的过程
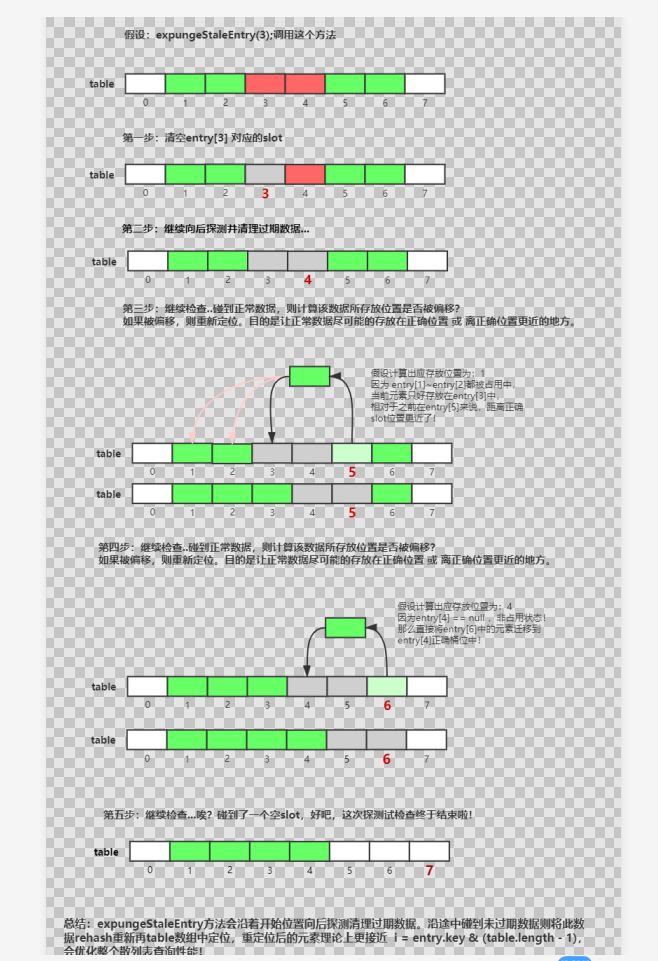
4.3、ThreadLocalMap中set方法源码分析
/**
* Set the value associated with key.
* 使用set方法 给当前线程添加 threadLocal-value 键值对。
* @param key the thread local object
* @param value the value to be set
*/
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
//以当前key对应的slot位置 向后查询,找到可以使用的slot。
//什么slot可以使用呢??
//1.k == key 说明是替换
//2.碰到一个过期的 slot ,这个时候 咱们可以强行占用呗。
//3.查找过程中 碰到 slot == null 了。
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
//条件成立:说明当前set操作是一个替换操作。
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
//条件成立:说明 向下寻找过程中 碰到entry#key == null 的情况了,说明当前entry 是过期数据。
if (k == null) {
//碰到一个过期的 slot ,这个时候 咱们可以强行占用呗。
//替换过期数据的逻辑。
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
//执行到这里,说明for循环碰到了 slot == null 的情况。
//在合适的slot中 创建一个新的entry对象。
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
//做一次启发式清理
//条件一:!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) 成立,说明启发式清理工作 未清理到任何数据..
//条件二:sz >= threshold 成立,说明当前table内的entry已经达到扩容阈值了..会触发rehash操作。
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
/**
* Replace a stale entry encountered during a set operation
* with an entry for the specified key. The value passed in
* the value parameter is stored in the entry, whether or not
* an entry already exists for the specified key.
*
* As a side effect, this method expunges all stale entries in the
* "run" containing the stale entry. (A run is a sequence of entries
* between two null slots.)
*
* key: 键 threadLocal对象
* value: val
* staleSlot: 上层方法 set方法,迭代查找时 发现的当前这个slot是一个过期的 entry。
*/
private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value,
int staleSlot) {
//获取散列表
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//临时变量
Entry e;
//表示 开始探测式清理过期数据的 开始下标。默认从当前 staleSlot开始。
int slotToExpunge = staleSlot;
//以当前staleSlot开始 向前迭代查找,找有没有过期的数据。for循环一直到碰到null结束。
for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = prevIndex(i, len))
//条件成立:说明向前找到了过期数据,更新 探测清理过期数据的开始下标为 i
if (e.get() == null)
slotToExpunge = i;
//以当前staleSlot向后去查找,直到碰到null为止。
for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
//条件成立:说明是一个 替换逻辑。
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
//交换位置的逻辑..
tab[i] = tab[staleSlot];
tab[staleSlot] = e;
// Start expunge at preceding stale entry if it exists
//条件成立:
// 1.说明replaceStaleEntry 一开始时 的向前查找过期数据 并未找到过期的entry.
// 2.向后检查过程中也未发现过期数据..
if (slotToExpunge == staleSlot)
//开始探测式清理过期数据的下标 修改为 当前循环的index。
slotToExpunge = i;
//cleanSomeSlots :启发式清理
//expungeStaleEntry:以这个位置开始 继续向后查找过期数据,直到碰到 slot == null 的情况结束,返回的位置为最后结束位置,为null
//len: tab表的长度
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
return;
}
//条件1:k == null 成立,说明当前遍历的entry是一个过期数据..
//条件2:slotToExpunge == staleSlot 成立,一开始时 的向前查找过期数据 并未找到过期的entry.
if (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot)
slotToExpunge = i;
}
//什么时候执行到这里呢?
//向后查找过程中 并未发现 k == key 的entry,说明当前set操作 是一个添加逻辑..
//直接将新数据添加到 table[staleSlot] 对应的slot中。
// If key not found, put new entry in stale slot
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value);
// If there are any other stale entries in run, expunge them
//条件成立:除了当前staleSlot 以外 ,还发现其它的过期slot了.. 所以要开启 清理数据的逻辑..
if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot)
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
}
/*
* 参数 i 启发式清理工作开始位置
* 参数 n 一般传递的是 table.length ,这里n 也表示结束条件。
* @return true if any stale entries have been removed.
*/
private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {
//表示启发式清理工作 是否清楚过过期数据
boolean removed = false;
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
do {
//这里为什么不是从i就检查呢?
//因为cleanSomeSlots(i = expungeStaleEntry(???), n) expungeStaleEntry(???) 返回值一定是null。
//获取当前i的下一个 下标
i = nextIndex(i, len);
Entry e = tab[i];
//条件一:e != null 成立
//条件二:e.get() == null 成立,说明当前slot中保存的entry 是一个过期的数据..
if (e != null && e.get() == null) {
n = len;
removed = true;
//以当前过期的slot为开始节点 做一次 探测式清理工作
i = expungeStaleEntry(i);
}
} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0);
return removed;
}
4.4、ThreadLocalMap中rehash和resize方法源码分析
/**
* 在set方法调用该方法条件
* 条件一:!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) 成立,说明启发式清理工作 未清理到任何数据..
* 条件二:sz >= threshold 成立,说明当前table内的entry已经达到扩容阈值了..会触发rehash操作。
*/
private void rehash() {
//这个方法执行完后,当前散列表内的所有过期的数据,都会被干掉。
expungeStaleEntries();
// Use lower threshold for doubling to avoid hysteresis
//条件成立:说明清理完 过期数据后,当前散列表内的entry数量仍然达到了 threshold * 3/4,真正触发 扩容!
if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4)
//扩容。
resize();
}
/**
* Expunge all stale entries in the table.
*/
private void expungeStaleEntries() {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = tab[j];
if (e != null && e.get() == null)
expungeStaleEntry(j);
}
}
/**
* Double the capacity of the table.
*/
private void resize() {
Entry[] oldTab = table;
int oldLen = oldTab.length;
//扩容后新表的长度为老表的2倍
int newLen = oldLen * 2;
Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];
int count = 0;
//遍历老表 迁移数据到新表。
for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {
//访问老表的指定位置的slot
Entry e = oldTab[j];
if (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null; // Help the GC
} else {
//执行到这里,说明老表的当前位置的元素是非过期数据 正常数据,需要迁移到扩容后的新表。。
//计算出当前entry在扩容后的新表的 存储位置。
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);
//while循环 就是拿到一个距离h最近的一个可以使用的slot。
while (newTab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, newLen);
//将数据存放到 新表的 合适的slot中。
newTab[h] = e;
//数量+1
count++;
}
}
}
//设置下一次触发扩容的指标。当前表的长度乘以3分之2
setThreshold(newLen);
size = count;
table = newTab;
}



