xxqJava-Blog2
一、前言
(1)题目集四之凸四边形的计算:此次的题目集基于第三次作业三角形的判断又做了很大的提升。
(2)题目集五:凸五边形的计算,这次题目集两道题可以算是是一道题,我猜老师觉得我们写在一起代码会太长了提交不了分成了两部分。总而言之,言而总之,太难了我不太ok,于是网搜借鉴别人的代码,就这么巧搜到了原题,以下代码参考了csdn某博客的写法,但是但是我自己有思考挣扎,但为了取得高分,不得不学习别人的,加上自己的理解,一步一步对此进行分析。
(3)期中考试:相对于我们的作业来说更简单些,但是在限制的时间内将三道题完全写出来对于我来说还是相对困难的,因此我也没有拿到满分,还有一个测试点没有来得及找问题。这三道题一步步加内容考我们近期学的内容,从类的设计到继承与多态,再到容器类。
二、设计与分析
7-2 点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与四边形有关的计算。
以下四边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
4:输入六个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后四个点构成一个四边形或三角形,输出直线与四边形(也可能是三角形)相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出四边形(或三角形)被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与四边形或三角形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形的输入,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
后四个点构成三角形的情况:假设三角形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z 不与xy都相邻,如z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
5:输入五个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后四个点所构成的四边形(限定为凸四边形,不考虑凹四边形)或三角形(判定方法见选项4)的内部(若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle或者on the quadrilateral"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
基本输出格式见每种选项的描述。
异常情况输出:
如果不符合基本格式,输出"Wrong Format"。
如果符合基本格式,但输入点的数量不符合要求,输出"wrong number of points"。
注意:输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
选项1、2、3中,若四边形四个点中有重合点,输出"points coincide"。
选项4中,若前两个输入线的点重合,输出"points coincide"。
我的最终代码如下:

// package com.java.dao; import java.util.*; import static java.lang.Math.max; import static java.lang.Math.min; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String str = sc.nextLine(); //判断输入格式是否正确 if(!str.matches("^[1-5][:](([+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?))[,]([+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?))\\s?)+$")){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } //取出cmd,将串转化为浮点型 int cmd = str.charAt(0)-'0'; str = str.substring(2).trim(); String[] tmpstr = str.split(" |,"); double[] num = new double[30]; int cnt = 0; for(String s:tmpstr){ if(!check(s)){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } num[cnt++] = Double.parseDouble(s); } //将浮点型转化为坐标点型 Point[] p = new Point[10]; for(int i=0;i<cnt;i+=2){ p[i/2] = new Point(num[i],num[i+1]); } //点数不合法 if(cmd==1 || cmd==2 || cmd==3){ if(cnt != 8){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } } if(cmd==4){ if(cnt != 12){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } } if(cmd == 5){ if(cnt != 10){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } } if(cmd == 1){ try{ Quadrilateral q = new Quadrilateral(p[0],p[1],p[2],p[3]); System.out.printf("true %s\n",q.isParallelQuadrilateral()); }catch (Exception e){ if(e.getMessage().equals("not a quadrilateral")) System.out.println("false false"); else System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } if(cmd == 2) { try { Quadrilateral q = new Quadrilateral(p[0],p[1],p[2],p[3]); System.out.printf("%s %s %s\n",q.isDiamond(),q.isRectangle(),q.isSquare()); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("not a quadrilateral"); } } if(cmd == 3){ try{ Quadrilateral q = new Quadrilateral(p[0],p[1],p[2],p[3]); System.out.printf("%s %s %s\n",q.isConvexQuadrilateral(),change(q.sideLength()), change(q.area()) ); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } if(cmd == 4){ Line l = null; Quadrilateral q = null; try{ l = new Line(p[0],p[1]); }catch (Exception e){ //不构成直线 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); System.exit(0); } //构成四边形(执行有关四边形的计算) try{ q = new Quadrilateral(p[2],p[3],p[4],p[5]); solve(l,q); return; }catch (Exception e){ //可能构成三角形 try{ //保证以下代码正确,捕获异常并吞并 //以5号点作为s顶点 if(!p[2].isSameTo(p[4])) { //2,4点不重合 Line ll = new Line(p[2],p[4]); //3在ll之上,5在ll之外 if(p[3].inLineSegment_close(ll) && !p[5].inLineSegment_close(ll)) { Triangle t = new Triangle(p[2],p[4],p[5]); solve(l,t); return; } } else {//2,4点重合 if(!p[2].isSameTo(p[3])) { //但是2,3点不重合 Line ll = new Line(p[2],p[3]); if(!p[5].inLineSegment_close(ll)) { //5点在ll线之外 Triangle t = new Triangle(p[2],p[3],p[5]); solve(l,t); return; } } } //以2号点作为顶点 if(!p[3].isSameTo(p[5])) { Line ll = new Line(p[3],p[5]); if(p[4].inLineSegment_close(ll) && !p[2].inLine(ll)) { Triangle t = new Triangle(p[2],p[3],p[5]); solve(l,t); return; } } else { if(!p[3].isSameTo(p[4])){ Line ll = new Line(p[3],p[4]); if(!p[2].inLineSegment_close(ll)){ Triangle t = new Triangle(p[2],p[3],p[4]); solve(l,t); return; } } } //以4号点作为顶点 if(!p[3].isSameTo(p[5])) { Line ll = new Line(p[3],p[5]); if(p[2].inLineSegment_close(ll) && !p[4].inLine(ll)) { Triangle t = new Triangle(p[3],p[4],p[5]); solve(l,t); return; } } //以3号点作为顶点 if(!p[2].isSameTo(p[4])) { Line ll = new Line(p[2],p[4]); if(p[5].inLineSegment_close(ll) && !p[3].inLine(ll)){ Triangle t = new Triangle(p[2],p[3],p[4]); solve(l,t); return; } } //不构成三角形 System.out.println("not a quadrilateral or triangle"); }catch(Exception ee){} } } if(cmd == 5){ try{ //四点构成四边形 Quadrilateral q = new Quadrilateral(p[1],p[2],p[3],p[4]); int op = q.isContainPoint(p[0]); if(op == 0) System.out.println("in the quadrilateral"); else if(op == 1) System.out.println("on the quadrilateral"); else System.out.println("outof the quadrilateral"); }catch(Exception ee){ //不构成四边形,待确定是否构成三角形 try{ //以4号点作为s顶点 if(!p[1].isSameTo(p[3])){ //1,3点不重合 Line ll = new Line(p[1],p[3]); //2在ll之上,4在ll之外 if(p[2].inLineSegment_close(ll) && !p[4].inLineSegment_close(ll)){ Triangle t = new Triangle(p[1],p[3],p[4]); inTriangle(p[0],t); return; } } else{ //1,3点重合 if(!p[1].isSameTo(p[2])){ //但是2,3点不重合 Line ll = new Line(p[1],p[2]); if(!p[4].inLineSegment_close(ll)){ //5点在ll线之外 Triangle t = new Triangle(p[1],p[2],p[4]); inTriangle(p[0],t); return; } } } //以1号点作为顶点 if(!p[2].isSameTo(p[4])){ Line ll = new Line(p[2],p[4]); if(p[3].inLineSegment_close(ll) && !p[1].inLine(ll)){ Triangle t = new Triangle(p[1],p[2],p[4]); inTriangle(p[0],t); return; } } else{ if(!p[2].isSameTo(p[3])){ Line ll = new Line(p[2],p[3]); if(!p[1].inLineSegment_close(ll)){ Triangle t = new Triangle(p[1],p[2],p[3]); inTriangle(p[0],t); return; } } } //以3号点作为顶点 if(!p[2].isSameTo(p[4])){ Line ll = new Line(p[2],p[4]); if(p[1].inLineSegment_close(ll) && !p[3].inLine(ll)){ Triangle t = new Triangle(p[2],p[3],p[4]); inTriangle(p[0],t); return; } } //以2号点作为顶点 if(!p[1].isSameTo(p[3])){ Line ll = new Line(p[1],p[3]); if(p[4].inLineSegment_close(ll) && !p[2].inLine(ll)){ Triangle t = new Triangle(p[1],p[2],p[3]); inTriangle(p[0],t); return; } } //不构成三角形 System.out.println("not a quadrilateral or triangle"); }catch(Exception e){} } } } public static boolean check(String str) { return str.matches("^[+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)?|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?)$"); } public static void pr_ans(Object object, Point a,Point b,Point c){ double[] ans = new double[2]; if(object instanceof Triangle){ Triangle t= (Triangle) object; ans[0] = Triangle.area(a,b,c); ans[1] = t.area() - ans[0]; Arrays.sort(ans); System.out.printf("2 %s %s\n",change(ans[0]),change(ans[1])); }else if (object instanceof Quadrilateral){ Quadrilateral q= (Quadrilateral) object; ans[0] = Triangle.area(a,b,c); ans[1] = q.area() - ans[0]; Arrays.sort(ans); System.out.printf("2 %s %s\n",change(ans[0]),change(ans[1])); } } public static String change(double a){ String res = String.format("%.3f",a); res = res.replaceAll("0+?$", ""); if(res.charAt(res.length()-1) == '.') res+='0'; return res; } public static void solve(Line l,Triangle t){ //与任意一条边重合 if(l.isSameTo(t.ab) || l.isSameTo(t.ac) || l.isSameTo(t.bc)){ System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines"); return; } //与三条边的交点(值可能为null,即平行) Point p_ab = l.getIntersection(t.ab); Point p_ac = l.getIntersection(t.ac); Point p_bc = l.getIntersection(t.bc); //三交点是否位于边之内 boolean p_ab_in=false, p_ac_in =false, p_bc_in=false; if(p_ab != null) p_ab_in = p_ab.inLineSegment(t.ab); if(p_ac != null) p_ac_in = p_ac.inLineSegment(t.ac); if(p_bc != null) p_bc_in = p_bc.inLineSegment(t.bc); //任一角在直线之上(特判三角形的角) if(t.a.inLine(l)){ //与另一条边无交点或者交点在边之外 if(p_bc == null || !p_bc.inLineSegment_close(t.bc)){ System.out.println("1"); } else pr_ans(t,t.a,t.b,p_bc); return; } if(t.b.inLine(l)){ if(p_ac == null || !p_ac.inLineSegment_close(t.ac)){ System.out.println("1"); } else pr_ans(t,t.a,t.b,p_ac); return; } if(t.c.inLine(l)){ if(p_ab == null || !p_ab.inLineSegment_close(t.ab)){ System.out.println("1"); } else pr_ans(t,t.a,t.c,p_ab); return; } //两个交点 if(p_ab_in && p_bc_in){ pr_ans(t,t.b,p_ab,p_bc);return;} if(p_ab_in && p_ac_in){ pr_ans(t,t.a,p_ab,p_ac);return;} if(p_bc_in && p_ac_in){ pr_ans(t,t.c,p_bc,p_ac);return;} //无交点 System.out.println("0"); } //四边形交点情况 public static void solve(Line l,Quadrilateral q){ //与任意一条边重合 for(Line ll: q.lines){ if(l.isSameTo(ll)){ System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines"); return; } } //与四条边的交点,可能为null; Point p0 = l.getIntersection(q.lines[0]); Point p1 = l.getIntersection(q.lines[1]); Point p2 = l.getIntersection(q.lines[2]); Point p3 = l.getIntersection(q.lines[3]); //判断交点是否在边之上 boolean p0_in = false,p1_in = false,p2_in = false,p3_in = false; if(p0 != null) p0_in = p0.inLineSegment(q.lines[0]); if(p1 != null) p1_in = p1.inLineSegment(q.lines[1]); if(p2 != null) p2_in = p2.inLineSegment(q.lines[2]); if(p3 != null) p3_in = p3.inLineSegment(q.lines[3]); //任一角在直线l之上 if(q.points[0].inLine(l)){ //它的对角也在边之上 if(q.points[2].inLine(l)){ pr_ans(q,q.points[0],q.points[1],q.points[2]); } //对角的邻边任一与直线有交点 else if (p2_in){ //邻边之一 pr_ans(q,q.points[0],p2,q.points[3]); } else if (p1_in){ //邻边之二 pr_ans(q,q.points[0],p1,q.points[1]); } else{ System.out.println("1"); } return; } else if(q.points[1].inLine(l)){ //它的对角也在边之上 if(q.points[3].inLine(l)){ pr_ans(q,q.points[1],q.points[2],q.points[3]); } //对角的邻边任一与直线有交点 else if (p2_in){ //邻边之一 pr_ans(q,q.points[1],p2,q.points[2]); } else if (p3_in){ //邻边之二 pr_ans(q,q.points[1],p3,q.points[0]); } else{ System.out.println("1"); } return; } else if (q.points[2].inLine(l)) { //它的对角也在边之上 if(q.points[0].inLine(l)){ pr_ans(q,q.points[2],q.points[3],q.points[0]); } //对角的邻边任一与直线有交点 else if (p3_in){ //邻边之一 pr_ans(q,q.points[2],p3,q.points[3]); } else if (p0_in){ //邻边之二 pr_ans(q,q.points[2],p0,q.points[1]); } else{ System.out.println("1"); } return; } else if (q.points[3].inLine(l)) { //它的对角也在边之上 if(q.points[1].inLine(l)){ pr_ans(q,q.points[3],q.points[0],q.points[1]); } //对角的邻边任一与直线有交点 else if (p0_in){ //邻边之一 pr_ans(q,q.points[3],p0,q.points[0]); } else if (p1_in){ //邻边之二 pr_ans(q,q.points[3],p1,q.points[2]); } else{ System.out.println("1"); } return; } //两个交点(邻边) if(p0_in && p1_in){pr_ans(q,p0,p1,q.points[1]);return;} if(p1_in && p2_in){pr_ans(q,p1,p2,q.points[2]);return;} if(p2_in && p3_in){pr_ans(q,p2,p3,q.points[3]);return;} if(p3_in && p0_in){pr_ans(q,p3,p0,q.points[0]);return;} //对边 if(p0_in && p2_in){ double[] ans = new double[2]; ans[0] = Triangle.area(q.points[0],p0,p2) + Triangle.area(p0,p2,q.points[3]); ans[1] = Triangle.area(q.points[1],p0,p2) + Triangle.area(p0,p2,q.points[2]); Arrays.sort(ans); System.out.printf("2 %s %s\n",change(ans[0]),change(ans[1])); return; } if(p1_in && p3_in){ double[] ans = new double[2]; ans[0] = Triangle.area(q.points[1],p1,p3) + Triangle.area(p1,p3,q.points[0]); ans[1] = Triangle.area(q.points[2],p1,p3) + Triangle.area(p1,p3,q.points[3]); Arrays.sort(ans); System.out.printf("2 %s %s\n",change(ans[0]),change(ans[1])); return; } //0交点 System.out.println("0"); } //判断点在三角形哪里 public static void inTriangle(Point p,Triangle t){ int op = t.isContainPoint(p); if(op == 0) System.out.println("in the triangle"); else if (op == 1) System.out.println("on the triangle"); else System.out.println("outof the triangle"); } } class Point{ public double x, y; public Point(){ this.x = 0; this.y = 0; } public Point(double a,double b){ this.x = a; this.y = b; } public void print(){ System.out.printf("(%f,%f)\n",this.x,this.y); } //两点坐标相同 public boolean isSameTo(Point a){ return (this.x == a.x)&&(this.y == a.y); } //两点距离 public double disToPoint(Point another){ return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(this.x-another.x,2) + Math.pow(this.y-another.y,2)); } //判断是否在直线之上 public boolean inLine(Line l){ return Math.abs(l.a*this.x + l.b*this.y + l.c) < 0.000001; } //判断是否在线段之内(包括端点) public boolean inLineSegment_close(Line l) { //先判断是否在直线上 if (!(inLine(l))) return false; //根据区间端点判断 if (this.x >= min(l.sta.x, l.ed.x) && this.x <= max(l.sta.x, l.ed.x) && this.y >= min(l.sta.y, l.ed.y) && this.y <= max(l.sta.y, l.ed.y)) { return true; } else { return false; } } //判断是否在线段之内(不包括端点) public boolean inLineSegment(Line l) { //先判断是否在直线上 if (!(inLine(l))) return false; //根据区间端点判断 if (this.x > min(l.sta.x, l.ed.x) && this.x < max(l.sta.x, l.ed.x) && this.y > min(l.sta.y, l.ed.y) && this.y < max(l.sta.y, l.ed.y)) { return true; } else { return false; } } } class Line extends Point { public Point sta, ed; public double a,b,c; public Line(Point a,Point b)throws Exception{ if(a.isSameTo(b)){ throw new Exception("points coincide"); } this.sta = a; this.ed = b; this.a = (-(a.y-b.y)); this.b = (a.x-b.x); this.c = (-this.a*this.sta.x-this.b*this.sta.y); } public void print(){ System.out.printf("%fX + %fY + %f = 0\n",this.a,this.b,this.c); } //求线段长度 public double length(){ return this.sta.disToPoint(this.ed); } //判断是否平行 public boolean isParallelTo(Line another){ if(this.b==0 || another.b==0){ return (this.b == 0 && another.b == 0); } return ((this.a / this.b) == (another.a / another.b)); } //判断是否重合 public boolean isSameTo(Line another){ return this.isParallelTo(another) && (this.c==another.c); } //求两条直线交点 public Point getIntersection(Line another){ if(this.isParallelTo(another)) return null; Point res = new Point(); res.y = (another.a*this.c-this.a*another.c) / (this.a*another.b-another.a*this.b); res.x = (this.b*another.c-another.b*this.c) / (this.a*another.b-another.a*this.b); return res; } } class Triangle extends Point { public Point a,b,c; public Line ab,ac,bc; public Triangle(Point a, Point b, Point c)throws Exception{ try{ this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; this.ab = new Line(a,b); this.ac = new Line(a,c); this.bc = new Line(b,c); if(this.ab.isParallelTo(this.bc)){ throw new Exception("not a triangle"); } }catch(Exception e){ throw e; } } public void print(){ System.out.println("三个点坐标为:"); this.a.print();this.b.print();this.c.print(); System.out.println("三条线一般式为:"); this.ab.print();this.ac.print();this.bc.print(); } //求三角形的边长 public double sideLength(){ return this.ab.length() + this.ac.length() + this.bc.length(); } //求三角形面积 public double area(){ double p = this.sideLength() / 2; return Math.sqrt(p*(p-this.ab.length())*(p-this.ac.length())*(p-this.bc.length())); } //求三个点围成的图形面积(三点可能共线,面积为0) public static double area(Point a,Point b,Point c){ double len1 = a.disToPoint(b); double len2 = b.disToPoint(c); double len3 = c.disToPoint(a); double p = (len1+len2+len3) / 2; return Math.sqrt(p*(p-len1)*(p-len2)*(p-len3)); } // 判断某点是否在三角形之内,(0内,1边,2外); //面积法 public int isContainPoint(Point p){ //特判在边上的情况 if(p.inLineSegment_close(this.ab) || p.inLineSegment_close(this.bc) || p.inLineSegment_close(this.ac)){ return 1; } double s1 = Triangle.area(p,this.a,this.b); double s2 = Triangle.area(p,this.b,this.c); double s3 = Triangle.area(p,this.c,this.a); double res = s1+s2+s3 - this.area(); if(Math.abs(res) < 0.000001) return 0; return 2; } } class Quadrilateral{ public Point[] points; public Line[] lines; public Quadrilateral(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d)throws Exception{ try{ this.points = new Point[4]; this.lines = new Line[4]; this.points[0] = a; this.points[1] = b; this.points[2] = c; this.points[3] = d; this.lines[0] = new Line(this.points[0], this.points[1]); this.lines[1] = new Line(this.points[1], this.points[2]); this.lines[2] = new Line(this.points[2], this.points[3]); this.lines[3] = new Line(this.points[3], this.points[0]); if(lines[0].isParallelTo(lines[1]) || lines[0].isParallelTo(lines[3])){ throw new Exception("not a quadrilateral"); } if(lines[2].isParallelTo(lines[1]) || lines[2].isParallelTo(lines[3])){ throw new Exception("not a quadrilateral"); } Point p1 = lines[0].getIntersection(lines[2]); Point p2 = lines[1].getIntersection(lines[3]); if(p1 != null && p1.inLineSegment_close(lines[0]) && p1.inLineSegment_close(lines[2])) throw new Exception("not a quadrilateral"); if(p2 != null && p2.inLineSegment_close(lines[1]) && p2.inLineSegment_close(lines[3])) throw new Exception("not a quadrilateral"); }catch (Exception e){ throw e; } } //判断是否为平行四边形(对边分别平行) public boolean isParallelQuadrilateral(){ return this.lines[0].isParallelTo(this.lines[2]) && this.lines[1].isParallelTo(this.lines[3]); } //判断是否为菱形(平行四边形 + 四边长度相等) public boolean isDiamond(){ boolean v = this.lines[0].length() == this.lines[1].length() && this.lines[1].length() == this.lines[2].length() && this.lines[2].length() == this.lines[3].length(); return this.isParallelQuadrilateral() && v; } //判断是否为矩形(对角线相等) public boolean isRectangle(){ return this.points[0].disToPoint(this.points[2]) == this.points[1].disToPoint(this.points[3]); } //判断是否为正方形(菱形 + 矩形) public boolean isSquare(){ return this.isDiamond() && this.isRectangle(); } //判断是否为凸四边形(面积公式) public boolean isConvexQuadrilateral(){ double s1 = Triangle.area(points[0],points[1],points[2]); double s2 = Triangle.area(points[2],points[3],points[0]); double s3 = Triangle.area(points[1],points[2],points[3]); double s4 = Triangle.area(points[3],points[0],points[1]); double res = s1 + s2 - s3 - s4; return Math.abs(res) < 0.000001; } //判断一个点是否落在(凸)四边形内部(0内,1边,2外) //和Triangle类似,用面积法; public int isContainPoint(Point p){ if(p.inLineSegment_close(this.lines[0]) || p.inLineSegment_close(this.lines[1]) || p.inLineSegment_close(this.lines[2]) || p.inLineSegment_close(this.lines[3])){ return 1; } double s1 = Triangle.area(p,this.points[0],this.points[1]); double s2 = Triangle.area(p,this.points[1],this.points[2]); double s3 = Triangle.area(p,this.points[2],this.points[3]); double s4 = Triangle.area(p,this.points[3],this.points[0]); double res = s1+s2+s3+s4 - this.area(); if(Math.abs(res) < 0.000001) return 0; return 2; } //四边形周长 public double sideLength(){ return this.lines[0].length() + this.lines[1].length() +this.lines[2].length() +this.lines[3].length(); } //四边形面积(切分为两个三角形) public double area(){ double s1 = Triangle.area(this.points[0], this.points[1], this.points[2]); double s2 = Triangle.area(this.points[0], this.points[3], this.points[2]); double s3 = Triangle.area(this.points[1], this.points[0], this.points[3]); double s4 = Triangle.area(this.points[1], this.points[2], this.points[3]); return Math.min(s1+s2, s3+s4); } }
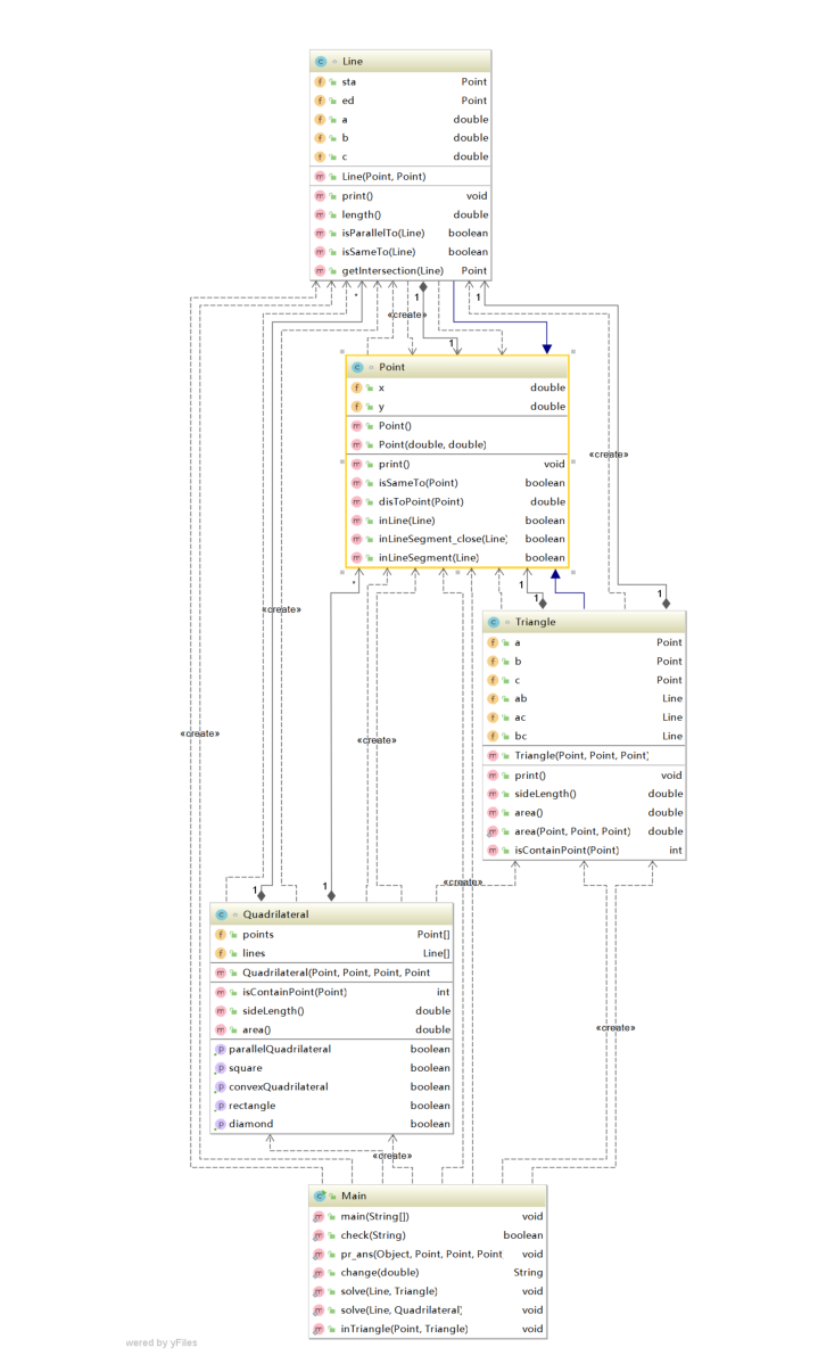
类图:
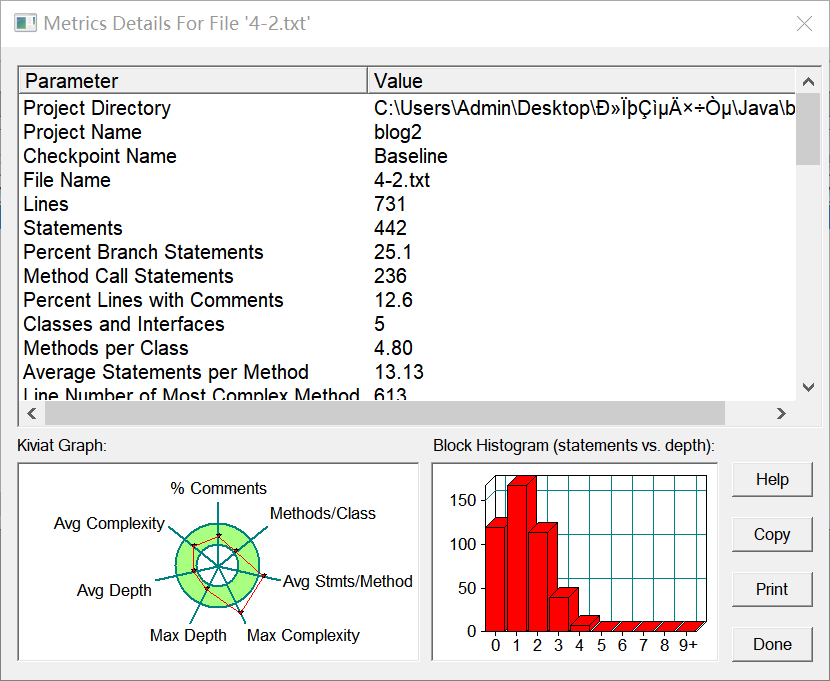
SourceMonitor的生成报表内容如下:
思路:
凸四边形的两条对角线将其分成两个三角形、分成的两个三角形面积相加等于四边形的面积,而显然这个结论对于凹四边形不成立,那么我们就可以利用这个结论进行解题,三角形面积用海伦公式求解,注意精度误差。
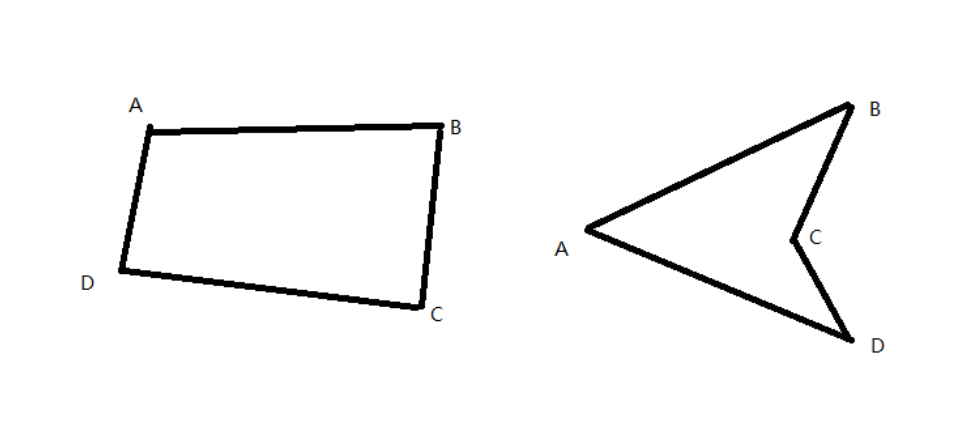
这道题写起来还是相对痛苦的,分类的过程方法复用性不高,若遇到其他情况得重新编写,这方面在下一题上需要重新设计,这次因为时间不太够,只能先拿分再说。在解题过程中遇到下图情况,请教同学后发现是没有考虑到线段与构成三角形其中一边重合的情况。

7-1 点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-1
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。
以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入五个点坐标,判断是否是五边形,判断结果输出true/false。
2:输入五个点坐标,判断是凹五边形(false)还是凸五边形(true),如果是凸五边形,则再输出五边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若五个点坐标无法构成五边形,输出"not a pentagon"
3:输入七个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后五个点构成一个凸五边形、凸四边形或凸三角形,输出直线与五边形、四边形或三角形相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与多边形形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后五个点不符合五边形输入,若前两点重合,输出"points coincide"。
以上3选项中,若输入的点无法构成多边形,则输出"not a polygon"。输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
基本输出格式见每种选项的描述。
异常情况输出:
如果不符合基本格式,输出"Wrong Format"。
如果符合基本格式,但输入点的数量不符合要求,输出"wrong number of points"。
注意:输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
输入样例1:
选项1,点重合。例如:
1:-1,-1 1,2 -1,1 1,0输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
wrong number of points我的最终代码如下:

import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.*; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String str = sc.nextLine(); //判断输入格式是否正确 if(!str.matches("^[1-5][:](([+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?))[,]([+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?))\\s?)+$")) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } //取出cmd,将串转化为浮点型 int cmd = str.charAt(0)-'0'; str = str.substring(2).trim(); String[] tmpstr = str.split(" |,"); double[] num = new double[30]; int cnt = 0; for(String s:tmpstr) { if(!check(s)) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } num[cnt++] = Double.parseDouble(s); } //将浮点型转化为坐标点型 Point[] p = new Point[10]; for(int i=0;i<cnt;i+=2) { p[i/2] = new Point(num[i],num[i+1]); } if(cmd == 1 || cmd == 2) { if(cnt != 10) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); System.exit(0); } } if(cmd == 3) { if(cnt != 14) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); System.exit(0); } } if(cmd == 1) { try { Pentagon pentagon = new Pentagon(new Point[]{p[0],p[1],p[2],p[3],p[4]}); System.out.println("true"); }catch (Exception reason) { System.out.println("false"); } } else if(cmd == 2){ try { Pentagon pentagon = new Pentagon(new Point[]{p[0],p[1],p[2],p[3],p[4]}); if(pentagon.isConvexGraphical) { System.out.printf("%s %s %s\n",pentagon.isConvexGraphical,change(pentagon.sideLength),change(pentagon.area)); } else System.out.println("false"); }catch (Exception reason) { System.out.println(reason.getMessage()); } } else if(cmd == 3) { Line line = null; try { line = new Line(p[0],p[1]); } catch (Exception reason) { System.out.println(reason.getMessage()); } Graphical graphical = new Graphical(new Point[]{p[2],p[3],p[4],p[5],p[6]}); if(graphical.status == -1) { System.out.println("not a polygon"); System.exit(0); } if(graphical.len == 5) { try { Pentagon pentagon = new Pentagon(graphical.points); solve(line,pentagon); }catch (Exception reason){} } if(graphical.len == 4) { try { Quadrilateral quadrilateral = new Quadrilateral(graphical.points); solve(line,quadrilateral); }catch (Exception reason){} } if(graphical.len == 3) { try { Triangle triangle = new Triangle(graphical.points); solve(line,triangle); }catch (Exception reason){} } } }//main public static void solve(Line line,Pentagon pentagon) { for(Line item:pentagon.lines) { if(line.isSameTo(item)) { System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines"); return; } } Point[] intersections = new Point[5]; for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { intersections[i] = line.getIntersection(pentagon.lines[i]); } boolean[] check = new boolean[]{false,false,false,false,false}; for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { if(intersections[i] != null) { check[i] = intersections[i].inLineSegment(pentagon.lines[i]); } } //以上求出交点,并求出交点是否在边之上 /*特判交点在角上面的情况*/ for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { if(pentagon.points[i].inLine(line)) { if(pentagon.points[(i+2)%pentagon.len].inLine(line)) { pr_ans(pentagon,pentagon.points[i], pentagon.points[(i+1)%pentagon.len], pentagon.points[(i+2)%pentagon.len]); } else if(pentagon.points[(i+3)%pentagon.len].inLine(line)) { pr_ans(pentagon,pentagon.points[i], pentagon.points[(i+3)%pentagon.len], pentagon.points[(i+4)%pentagon.len]); } else if(check[(i+2)%pentagon.len]) { Graphical tmp = new Graphical(new Point[]{pentagon.points[i], pentagon.points[(i+1)%pentagon.len], pentagon.points[(i+2)%pentagon.len], intersections[(i+2)%pentagon.len]}); double[] ans = new double[]{tmp.area, pentagon.area - tmp.area}; Arrays.sort(ans); System.out.printf("2 %s %s\n",change(ans[0]),change(ans[1])); } else if(check[(i+1)%pentagon.len]) { pr_ans(pentagon,pentagon.points[i], pentagon.points[(i+1)%pentagon.len], intersections[(i+1)%pentagon.len]); } else if(check[(i+3)%pentagon.len]) { pr_ans(pentagon,pentagon.points[i], pentagon.points[(i+4)%pentagon.len], intersections[(i+3)%pentagon.len]); } //一个交点 else { System.out.println("1"); } return; } } for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { if(check[i] && check[(i+2)%pentagon.len]) { Graphical tmp = new Graphical(new Point[]{intersections[i], pentagon.points[(i+1)%pentagon.len], pentagon.points[(i+2)%pentagon.len], intersections[(i+2)%pentagon.len]}); double[] ans = new double[]{tmp.area, pentagon.area - tmp.area}; Arrays.sort(ans); System.out.printf("2 %s %s\n",change(ans[0]),change(ans[1])); return; } if(check[i] && check[(i+3)%pentagon.len]) { Graphical tmp = new Graphical(new Point[]{intersections[i], pentagon.points[i], pentagon.points[(i+4)%pentagon.len], intersections[(i+3)%pentagon.len]}); double[] ans = new double[]{tmp.area, pentagon.area - tmp.area}; Arrays.sort(ans); System.out.printf("2 %s %s\n",change(ans[0]),change(ans[1])); return; } } System.out.println("0"); } public static void solve(Line line,Quadrilateral q) { //与任意一条边重合 for(Line item: q.lines) { if(line.isSameTo(item)) { System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines"); return; } } Point[] intersections = new Point[4]; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { intersections[i] = line.getIntersection(q.lines[i]); } boolean[] check = new boolean[]{false,false,false,false}; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { if(intersections[i] != null) { check[i] = intersections[i].inLineSegment(q.lines[i]); } } for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { if(q.points[i].inLine(line)) { //对角在line之上 if(q.points[(i+2)%q.len].inLine(line)) { pr_ans(q,q.points[i], q.points[(i+1)%q.len], q.points[(i+2)%q.len]); } //两个对边和line有交点 else if(check[(i+1)%q.len]) { pr_ans(q, q.points[i], q.points[(i+1)%q.len], intersections[(i+1)%q.len]); } else if(check[(i+2)%q.len]) { pr_ans(q, q.points[i], q.points[(i+3)%q.len], intersections[(i+2)%q.len]); } //就一个交点 else{ System.out.println("1"); } // return; } } /*两组对边和line有交点的情况*/ for(int i=0;i<2;i++) { if(check[i] && check[(i+2)%q.len]) { Graphical tmp = new Graphical(new Point[]{intersections[i], q.points[(i+1)%q.len], q.points[(i+2)%q.len], intersections[(i+2)%q.len]}); double[] ans = new double[]{tmp.area, q.area - tmp.area}; Arrays.sort(ans); System.out.printf("2 %s %s\n",change(ans[0]),change(ans[1])); return; } } /*无交点*/ System.out.println("0"); } public static void solve(Line line,Triangle triangle) { //与任意一条边重合 if(line.isSameTo(triangle.lines[0]) || line.isSameTo(triangle.lines[1]) || line.isSameTo(triangle.lines[2])) { System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines"); return; } //与三条边的交点(值可能为null,即平行) Point p_ab = line.getIntersection(triangle.lines[0]); Point p_bc = line.getIntersection(triangle.lines[1]); Point p_ca = line.getIntersection(triangle.lines[2]); //三交点是否位于边之内 boolean p_ab_in=false, p_bc_in =false, p_ca_in=false; if(p_ab != null) p_ab_in = p_ab.inLineSegment(triangle.lines[0]); if(p_bc != null) p_bc_in = p_bc.inLineSegment(triangle.lines[1]); if(p_ca != null) p_ca_in = p_ca.inLineSegment(triangle.lines[2]); //任一角在直线之上(特判三角形的角) if(triangle.points[0].inLine(line)) { //与另一条边无交点或者交点在边之外 if(p_ca == null || !p_ca.inLineSegment_close(triangle.lines[2])) { System.out.println("1"); } else pr_ans(triangle,triangle.points[0],triangle.points[1],p_ca); return; } if(triangle.points[1].inLine(line)) { if(p_ca == null || !p_ca.inLineSegment_close(triangle.lines[1])) { System.out.println("1"); } else pr_ans(triangle,triangle.points[0],triangle.points[1],p_ca); return; } if(triangle.points[2].inLine(line)) { if(p_ab == null || !p_ab.inLineSegment_close(triangle.lines[0])) { System.out.println("1"); } else pr_ans(triangle,triangle.points[0],triangle.points[2],p_ab); return; } //两个交点 if(p_ab_in && p_bc_in){ pr_ans(triangle,triangle.points[1],p_ab,p_bc);return;} if(p_bc_in && p_ca_in){ pr_ans(triangle,triangle.points[2],p_bc,p_ca);return;} if(p_ca_in && p_ab_in){ pr_ans(triangle,triangle.points[0],p_ca,p_ab);return;} //无交点 System.out.println("0"); } public static void pr_ans(Triangle t, Point a,Point b,Point c) { double[] ans = new double[2]; ans[0] = Triangle.area(a,b,c); ans[1] = t.area - ans[0]; Arrays.sort(ans); System.out.printf("2 %s %s\n",change(ans[0]),change(ans[1])); } public static void pr_ans(Quadrilateral q,Point a,Point b,Point c) { double[] ans = new double[2]; ans[0] = Triangle.area(a,b,c); ans[1] = q.area - ans[0]; Arrays.sort(ans); System.out.printf("2 %s %s\n",change(ans[0]),change(ans[1])); } public static void pr_ans(Pentagon pentagon,Point a,Point b,Point c) { double[] ans = new double[2]; ans[0] = Triangle.area(a,b,c); ans[1] = pentagon.area - ans[0]; Arrays.sort(ans); System.out.printf("2 %s %s\n",change(ans[0]),change(ans[1])); } public static boolean check(String str) { return str.matches("^[+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)?|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?)$"); } public static String change(double a) { String res = String.format("%.3f",a); res = res.replaceAll("0+?$", ""); if(res.charAt(res.length()-1) == '.') res+='0'; return res; } } class Point{ public double x, y; public Point(){ this.x = 0; this.y = 0; } public Point(double a,double b){ this.x = a; this.y = b; } public void print(){ String x = String.format("%.6f",this.x); String y = String.format("%.6f",this.y); x = x.replaceAll("0+?$", ""); y = y.replaceAll("0+?$", ""); System.out.printf("(%s , %s)\n",this.x,this.y); } //两点坐标相同 public boolean isSameTo(Point a){ return (this.x == a.x)&&(this.y == a.y); } //两点距离 public double disToPoint(Point another){ return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(this.x-another.x,2) + Math.pow(this.y-another.y,2)); } //判断是否在直线之上 public boolean inLine(Line l){ return Math.abs(l.a*this.x + l.b*this.y + l.c) < 0.000001; } //判断是否在线段之内(包括端点) public boolean inLineSegment_close(Line l){ if(!this.inLine(l)) return false; double res = this.disToPoint(l.sta) + this.disToPoint(l.ed) - l.length(); return Math.abs(res) < 0.000001; } //判断是否在线段之内(不包括端点) public boolean inLineSegment(Line l){ return this.inLineSegment_close(l) && (!this.isSameTo(l.sta)) && (!this.isSameTo(l.ed)); } public Point deepCopy(){ Point res = new Point(); res.x = this.x; res.y = this.y; return res; } public Point add(Point another){ Point res = this.deepCopy(); res.x += another.x; res.y += another.y; return res; } public Point sub(Point another){ Point res = this.deepCopy(); res.x -= another.x; res.y -= another.y; return res; } //求点集重心 public static Point focusPoint(Point[] points ){ Point res = new Point(0,0); for(Point item:points){ res = res.add(item); } res.x /= points.length; res.y /= points.length; return res; } } class Triangle extends Graphical{ public Triangle(Point[] points)throws Exception{ super(points); if(this.status == -1 || this.len != 3){ throw new Exception("not a triangle"); } } //求三个点围成的图形面积(三点可能共线,面积为0) public static double area(Point a,Point b,Point c){ double len1 = a.disToPoint(b); double len2 = b.disToPoint(c); double len3 = c.disToPoint(a); double p = (len1+len2+len3) / 2; return Math.sqrt(p*(p-len1)*(p-len2)*(p-len3)); } } class Quadrilateral extends Graphical{ public Quadrilateral(Point[] points)throws Exception{ super(points); if(this.status == -1 || this.len != 4){ throw new Exception("not a quadrilateral"); } } } class Pentagon extends Graphical { public Pentagon(Point[] points)throws Exception{ super(points); if(this.status == -1 || this.len != 5){ throw new Exception("not a pentagon"); } } } class Line{ public Point sta, ed; public double a,b,c; private final Point vector; public Line(Point a,Point b)throws Exception{ if(a.isSameTo(b)){ throw new Exception("points coincide"); } this.sta = a; this.ed = b; this.a = (-(a.y-b.y)); this.b = (a.x-b.x); this.c = (-this.a*this.sta.x-this.b*this.sta.y); this.vector = ed.sub(sta); } public void print(){ System.out.printf("%fX + %fY + %f = 0\n",this.a,this.b,this.c); } //求线段长度 public double length(){ return this.sta.disToPoint(this.ed); } //判断是否平行 public boolean isParallelTo(Line another){ if(this.b==0 || another.b==0){ return (this.b == 0 && another.b == 0); } return ((this.a / this.b) == (another.a / another.b)); } //判断是否重合 public boolean isSameTo(Line another){ return this.isParallelTo(another) && (this.sta.inLine(another)); } //求两条直线交点 public Point getIntersection(Line another){ if(this.isParallelTo(another)) return null; Point res = new Point(); res.y = (another.a*this.c-this.a*another.c) / (this.a*another.b-another.a*this.b); res.x = (this.b*another.c-another.b*this.c) / (this.a*another.b-another.a*this.b); return res; } //LineSegmentIntersection 获取线段交点,返回值可能为null public Point lsi(Line another){ Point res = this.getIntersection(another); if(res == null) return res; boolean ok = (res.inLineSegment_close(this) && res.inLineSegment_close(another)); return ok ? res:null; } //求向量模 public double vectorLength(){ return Math.sqrt( Math.pow(this.vector.x,2) + Math.pow(this.vector.y,2) ); } //求向量点积 public double vectorMul(Line another){ return (this.vector.x * another.vector.x) + (this.vector.y * another.vector.y); } //求向量叉积 public double vectorCrossMul(Line another){ return (this.vector.x * another.vector.y) - (another.vector.x * this.vector.y); } //求两向量夹角(非0向量) public double vectorAngle(Line another){ double cos_angle = this.vectorMul(another) / (this.vectorLength() * another.vectorLength()); return Math.acos(cos_angle); } } class Graphical { public int len=0,status=1; //多边形边数,状态 public Point[] points; public Line[] lines; public double sideLength = 0,area = 0; //边长,面积 public boolean isConvexGraphical = true; public String message = "init"; //信息 public Graphical(Point[] points){ this.points = new Point[points.length]; points = this.removeMulti(points); //去除重复点 if(points.length <=2 ){ this.status = -1; this.message = "Not enough points"; return; } //相邻边夹角0则去除中间点,夹角180则status:-1 for(int i=0;i<points.length;i++){ int first = i , second = (i+1)%points.length, third = (i+2)%points.length; try{ Line l1 = new Line(points[first],points[second]); Line l2 = new Line(points[second],points[third]); if( Math.abs(l1.vectorAngle(l2) - Math.PI) < 0.000001 ){ //夹角180 this.status = -1; this.message = "lines reverse coincidence"; return; } else if(Math.abs(l1.vectorAngle(l2)) > 0.000001){ //夹角不为0 this.points[this.len++] = points[second].deepCopy(); } }catch (Exception e){} } this.points = Arrays.copyOf(this.points,this.len); this.lines = new Line[this.len]; //初始化边 for(int i=0;i<this.len;i++){ try { int first = i, second = (i+1)%this.len; this.lines[i] = new Line(this.points[first], this.points[second]); }catch (Exception e){} } //判断任意不相邻边(线段交点)是否有交点 checkEdge(); Graphical.area(this); Graphical.sideLength(this); Graphical.checkConvex(this); } public void print(){ if(this.status == -1){ System.out.println(this.message); return; } System.out.println("点数为:"+this.len); for(int i=0;i<this.len;i++){ this.points[i].print(); } for(int i=0;i<this.len;i++){ this.lines[i].print(); } System.out.println("周长为:"+this.sideLength); System.out.println("面积为:"+this.area); System.out.println("凹凸性:"+this.isConvexGraphical); } //判断图形是否包含某个点返回值-1,0,1 (内部,边缘,外部) //由于只考虑凸多边形,用面积法就行 public int isContainPoint(Point p){ for(int i=0;i<this.len;i++){ //位于边之上 if(p.inLineSegment_close(this.lines[i])) return 0; } double s = 0; for(int i=0;i<this.len;i++){ s += Triangle.area(p,this.points[i], this.points[(i+1)%this.len]); } return Math.abs(s-this.area) < 0.000001 ? -1:1; } //判断两个图形类之间的关系() public String relationshipWith(Graphical g){ String[] name = new String[]{"triangle", "quadrilateral", "pentagon"}; //分离 if(this.isSeparatedFrom(g)){ return "no overlapping area between the previous "+name[this.len-3]+ " and the following "+name[g.len-3]; } //完全重合 if(this.isSameTo(g)) return "the previous "+name[this.len-3]+ " coincides with the following "+name[g.len-3]; //包含 if(this.isContainGra(g)){ return "the previous "+name[this.len-3]+ " contains the following "+name[g.len-3]; } //被包含 if(g.isContainGra(this)){ return "the previous "+name[this.len-3]+ " is inside the following "+name[g.len-3]; } //连接 if(this.overlappingArea(g) == 0){ return "the previous "+name[this.len-3]+ " is connected to the following "+name[g.len-3]; } //交错 return "the previous "+name[this.len-3]+ " is interlaced with the following "+name[g.len-3]; } //判断和另一个图形完全分离(重叠面积为0,并且任意点都在this之外) public boolean isSeparatedFrom(Graphical g){ boolean ok = true; int[] check2 = new int[g.len]; for(int i=0;i<g.len;i++){ check2[i] = this.isContainPoint(g.points[i]); } for(int item:check2){ if(item != 1) ok = false; } if(this.overlappingArea(g) !=0) ok = false; return ok; } //判断完全包含另一个图形(任意点都在this之内) public boolean isContainGra(Graphical g){ boolean ok = true; int[] check2 = new int[g.len]; for(int i=0;i<g.len;i++){ check2[i] = this.isContainPoint(g.points[i]); } for(int item:check2){ if(item == 1) ok = false; } return ok; } //判断两个图形是否一模一样(点完全重合) public boolean isSameTo(Graphical g){ if(this.len != g.len) return false; for(int i=0;i<this.len;i++){ boolean ok = false; for(int j=0;j<g.len;j++){ if(this.points[i].isSameTo(g.points[j])) ok = true; } if(!ok) return false; } return true; } //计算两个图形的重叠面积(交点加内部顶点构成重叠多边形) public double overlappingArea(Graphical g){ Point[] intersection = new Point[100]; int intersection_len = 0; for(Line item1:this.lines){ //求出两多边形的交点 for(Line item2: g.lines){ Point tmp = item1.lsi(item2); if(tmp != null){ intersection[intersection_len++] = tmp.deepCopy(); } } } for(Point item:g.points){ //顶点包含在内部 if(this.isContainPoint(item) == -1) intersection[intersection_len++] = item.deepCopy(); } for(Point item:this.points){ //顶点包含在内部 if(g.isContainPoint(item) == -1) intersection[intersection_len++] = item.deepCopy(); } /*排序交点数组*/ intersection = Arrays.copyOf(intersection,intersection_len); intersection = this.removeMulti(intersection); Point focus = Point.focusPoint(intersection); Point sta = intersection[0].deepCopy(); Arrays.sort(intersection,1,intersection.length, new Comparator<Point>() { @Override public int compare(Point o1, Point o2) { try{ Line origin =new Line(focus,sta); Line l1 = new Line(focus,o1); Line l2 = new Line(focus,o2); double angle1 = origin.vectorAngle(l1); double angle2 = origin.vectorAngle(l2); if(origin.vectorCrossMul(l1) < 0) angle1 = 2*Math.PI - angle1; if(origin.vectorCrossMul(l2) < 0) angle2 = 2*Math.PI - angle2; if(angle1-angle2 > 0.000001) return 1; if(Math.abs(angle1-angle2) < 0.000001) return 0; return -1; }catch (Exception reason){} return 0; } }); Graphical graphical = new Graphical(intersection); return graphical.area; } //去除所有重复点 private Point[] removeMulti(Point[] points){ Point[] tmp_points = new Point[points.length]; int tmp_len = 0; for(int i=0;i<points.length;i++){ boolean ok = true; for(int j=0;j<tmp_len;j++){ if(points[i].isSameTo(tmp_points[j])){ this.message = "points coincide"; ok = false; break; } } if(ok) tmp_points[tmp_len++] = points[i].deepCopy(); } return Arrays.copyOf(tmp_points,tmp_len); } //判断不相邻边是否有交点 private void checkEdge(){ for(int i=0;i<this.len;i++){ for(int j=i+2;j<this.len;j++){ if(i==0&&j==this.len-1) continue; Point p = this.lines[i].getIntersection(this.lines[j]); if(p==null) continue; if(p.inLineSegment_close(this.lines[i]) && p.inLineSegment_close(this.lines[j])){ this.status = -1; this.message = "Non adjacent edges have intersections"; return; } } } } //多边形面积 private static void area(Graphical e){ double res = 0; Point origin = new Point(0,0); for(int i=0;i<e.len;i++){ try{ Line l1 = new Line(origin,e.points[i]); Line l2 = new Line(origin,e.points[(i+1)%e.len]); res += 0.5 * l1.vectorCrossMul(l2); }catch (Exception reason){} } e.area = Math.abs(res); } //多边形周长 private static void sideLength(Graphical e){ double res = 0; for(int i=0;i<e.len;i++){ res += e.points[i].disToPoint(e.points[(i+1)%e.len]); } e.sideLength = res; } //多边形凹凸性 private static void checkConvex(Graphical e){ if(e.len == 3) return; int v = 0; for(int i=0;i<e.len;i++){ int first = i, second = (i+1)%e.len, thrid = (i+2)%e.len; try{ Line l1 = new Line(e.points[first], e.points[second]); Line l2 = new Line(e.points[first], e.points[thrid]); if(v==0){ if(l1.vectorCrossMul(l2) > 0) v = 1; else v = -1; } if(v == 1 && l1.vectorCrossMul(l2) < 0) e.isConvexGraphical = false; if(v == -1 && l1.vectorCrossMul(l2) > 0) e.isConvexGraphical = false; }catch (Exception reason){} } } //是否一样 }
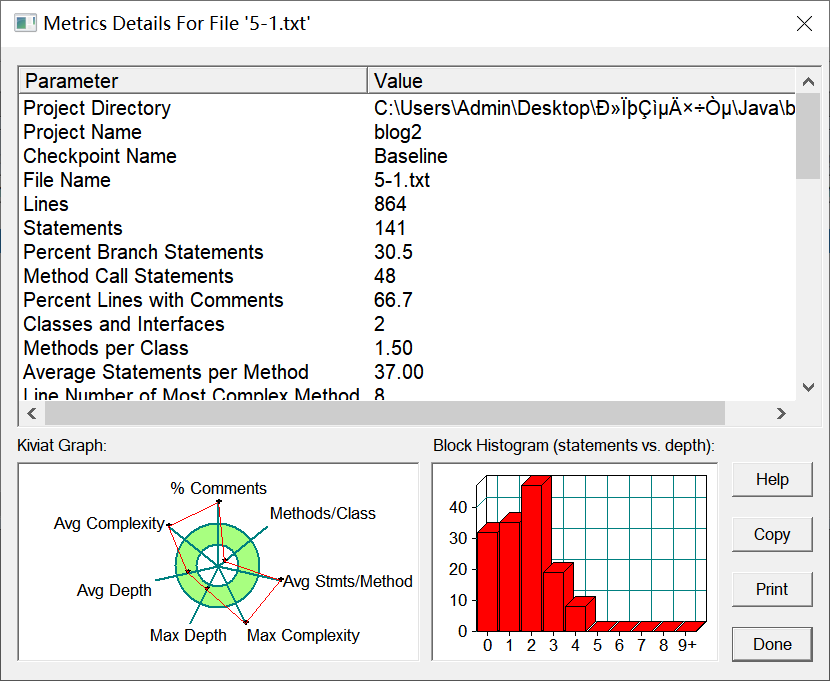
SourceMonitor的生成报表内容如下:
思路:
在四边形的基础上,我重新规划了我的类,多加了一个多边形类,将三、四、五边形的共同属性写在里面,使用继承从已有的类中派生出新的类,新的类能吸收已有类的数据属性和行为,并扩展新的能力。
由于我把大量时间花在第二题是逻辑思考上,第一题有几个测试点没过来不及修改没过,后来发现漏了选项三中没有交点情况则返回的语句,应该加上 if(intersection_len == 0) return 0就可以吧,我猜。但是这个代码分析报表结果我是没想到的,emmm有待提高。
7-2 点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算-2
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。
以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
4:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),判断它们两个之间是否存在包含关系(一个多边形有一条或多条边与另一个多边形重合,其他部分都包含在另一个多边形内部,也算包含)。
两者存在六种关系:1、分离(完全无重合点) 2、连接(只有一个点或一条边重合) 3、完全重合 4、被包含(前一个多边形在后一个多边形的内部)5、交错 6、包含(后一个多边形在前一个多边形的内部)。
各种关系的输出格式如下:
1、no overlapping area between the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon and the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
2、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is connected to the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
3、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon coincides with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
4、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is inside the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
5、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is interlaced with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
6、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon contains the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
5:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),输出两个多边形公共区域的面积。注:只考虑每个多边形被另一个多边形分割成最多两个部分的情况,不考虑一个多边形将另一个分割成超过两个区域的情况。
6:输入六个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后五个点所构成的多边形(限定为凸多边形,不考虑凹多边形),的内部(若是五边形输出in the pentagon/outof the pentagon,若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。输入入错存在冗余点要排除,冗余点的判定方法见选项5。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle/on the quadrilateral/on the pentagon"。
以上4、5、6选项输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
4:0,0 6,0 7,1 8,3 6,6 0,0 6,0 7,1 8,3 6,6输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
the previous pentagon coincides with the following pentagon我的最终代码如下:

import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Comparator; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String str = sc.nextLine(); //判断输入格式是否正确 if(!str.matches("^[1-6][:](([+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?))[,]([+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?))\\s?)+$")){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } //取出cmd,将串转化为浮点型 int cmd = str.charAt(0)-'0'; str = str.substring(2).trim(); String[] tmpstr = str.split(" |,"); double[] num = new double[30]; int cnt = 0; for(String s:tmpstr){ if(!check(s)){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } num[cnt++] = Double.parseDouble(s); } //将浮点型转化为坐标点型 Point[] p = new Point[10]; for(int i=0;i<cnt;i+=2){ p[i/2] = new Point(num[i],num[i+1]); } if(cmd==4) { Graphical graphical1 = new Graphical(new Point[]{p[0], p[1], p[2], p[3], p[4]}); Graphical graphical2 = new Graphical(new Point[]{p[5], p[6], p[7], p[8], p[9]}); System.out.println(graphical1.relationshipWith(graphical2)); } else if(cmd==5) { Graphical graphical1 = new Graphical(new Point[]{p[0], p[1], p[2], p[3], p[4]}); Graphical graphical2 = new Graphical(new Point[]{p[5], p[6], p[7], p[8], p[9]}); String res=String.format("%.3f",graphical1.overlappingArea(graphical2)); res = res.replaceAll("0+?$", ""); if(res.charAt(res.length()-1) == '.') res+='0'; System.out.println(res); } if(cmd==6){ Graphical graphical1 = new Graphical(new Point[]{p[1], p[2], p[3], p[4], p[5]}); int res = graphical1.isContainPoint(p[0]); String[] name = new String[]{"triangle", "quadrilateral", "pentagon"}; if(res == -1) System.out.println("in the "+name[graphical1.len-3]); if(res == 0) System.out.println("on the "+name[graphical1.len-3]); if(res == 1) System.out.println("outof the "+name[graphical1.len-3]); } } public static boolean check(String str) { return str.matches("[+-]?(0|(0\\.\\d+)?|[1-9][0-9]*(\\.\\d+)?)"); } } class Point{ public double x, y; public Point() { this.x = 0; this.y = 0; } public Point(double a,double b) { this.x = a; this.y = b; } //两点坐标相同 public boolean isSameTo(Point a){ return (this.x == a.x)&&(this.y == a.y); } //两点距离 public double disToPoint(Point another){ return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(this.x-another.x,2) + Math.pow(this.y-another.y,2)); } //判断是否在直线之上 public boolean inLine(Line l){ return Math.abs(l.a*this.x + l.b*this.y + l.c) < 0.000001; } //判断是否在线段之内(包括端点) public boolean inLineSegment_close(Line l){ if(!this.inLine(l)) return false; double res = this.disToPoint(l.sta) + this.disToPoint(l.ed) - l.length(); return Math.abs(res) < 0.000001; } public Point deepCopy(){ Point res = new Point(); res.x = this.x; res.y = this.y; return res; } public Point add(Point another){ Point res = this.deepCopy(); res.x += another.x; res.y += another.y; return res; } public Point sub(Point another){ Point res = this.deepCopy(); res.x -= another.x; res.y -= another.y; return res; } //求点集重心 public static Point focusPoint(Point[] points ){ Point res = new Point(0,0); for(Point item:points){ res = res.add(item); } res.x /= points.length; res.y /= points.length; return res; } } class Triangle extends Graphical{ public Triangle(Point[] points)throws Exception{ super(points); if(this.status == -1 || this.len != 3){ throw new Exception("not a triangle"); } } //求三个点围成的图形面积(三点可能共线,面积为0) public static double area(Point a,Point b,Point c){ double len1 = a.disToPoint(b); double len2 = b.disToPoint(c); double len3 = c.disToPoint(a); double p = (len1+len2+len3) / 2; return Math.sqrt(p*(p-len1)*(p-len2)*(p-len3)); } } class Line{ public Point sta, ed; public double a,b,c; private final Point vector; public Line(Point a,Point b)throws Exception{ if(a.isSameTo(b)){ throw new Exception("points coincide"); } this.sta = a; this.ed = b; this.a = (-(a.y-b.y)); this.b = (a.x-b.x); this.c = (-this.a*this.sta.x-this.b*this.sta.y); this.vector = ed.sub(sta); } //求线段长度 public double length(){ return this.sta.disToPoint(this.ed); } //判断是否平行 public boolean isParallelTo(Line another){ if(this.b==0 || another.b==0){ return (this.b == 0 && another.b == 0); } return ((this.a / this.b) == (another.a / another.b)); } //求两条直线交点 public Point getIntersection(Line another){ if(this.isParallelTo(another)) return null; Point res = new Point(); res.y = (another.a*this.c-this.a*another.c) / (this.a*another.b-another.a*this.b); res.x = (this.b*another.c-another.b*this.c) / (this.a*another.b-another.a*this.b); return res; } public Point lsi(Line another){ Point res = this.getIntersection(another); if(res == null) return res; boolean ok = (res.inLineSegment_close(this) && res.inLineSegment_close(another)); return ok ? res:null; } //求向量模 public double vectorLength(){ return Math.sqrt( Math.pow(this.vector.x,2) + Math.pow(this.vector.y,2) ); } //求向量点积 public double vectorMul(Line another){ return (this.vector.x * another.vector.x) + (this.vector.y * another.vector.y); } //求向量叉积 public double vectorCrossMul(Line another){ return (this.vector.x * another.vector.y) - (another.vector.x * this.vector.y); } //求两向量夹角(非0向量) public double vectorAngle(Line another){ double cos_angle = this.vectorMul(another) / (this.vectorLength() * another.vectorLength()); return Math.acos(cos_angle); } } class Graphical { public int len=0,status=1; //多边形边数,状态 public Point[] points; public Line[] lines; public double sideLength = 0,area = 0; //边长,面积 public boolean isConvexGraphical = true; public String message = "init"; //信息 public Graphical(Point[] points){ this.points = new Point[points.length]; points = this.removeMulti(points); //去除重复点 if(points.length <=2 ){ this.status = -1; this.message = "Not enough points"; return; } //相邻边夹角0则去除中间点,夹角180则status:-1 for(int i=0;i<points.length;i++){ int first = i , second = (i+1)%points.length, third = (i+2)%points.length; try{ Line l1 = new Line(points[first],points[second]); Line l2 = new Line(points[second],points[third]); if( Math.abs(l1.vectorAngle(l2) - Math.PI) < 0.000001 ){ //夹角180 this.status = -1; this.message = "lines reverse coincidence"; return; } else if(Math.abs(l1.vectorAngle(l2)) > 0.000001){ //夹角不为0 this.points[this.len++] = points[second].deepCopy(); } }catch (Exception e){} } this.points = Arrays.copyOf(this.points,this.len); this.lines = new Line[this.len]; //初始化边 for(int i=0;i<this.len;i++){ try { int first = i, second = (i+1)%this.len; this.lines[i] = new Line(this.points[first], this.points[second]); }catch (Exception e){} } //判断任意不相邻边(线段交点)是否有交点 checkEdge(); Graphical.area(this); Graphical.sideLength(this); Graphical.checkConvex(this); } //判断图形是否包含某个点返回值-1,0,1 (内部,边缘,外部) //由于只考虑凸多边形,用面积法就行 public int isContainPoint(Point p){ for(int i=0;i<this.len;i++){ //位于边之上 if(p.inLineSegment_close(this.lines[i])) return 0; } double s = 0; for(int i=0;i<this.len;i++){ s += Triangle.area(p,this.points[i], this.points[(i+1)%this.len]); } return Math.abs(s-this.area) < 0.000001 ? -1:1; } //判断两个图形类之间的关系() public String relationshipWith(Graphical g){ String[] name = new String[]{"triangle", "quadrilateral", "pentagon"}; //分离 if(this.isSeparatedFrom(g)){ return "no overlapping area between the previous "+name[this.len-3]+ " and the following "+name[g.len-3]; } //完全重合 if(this.isSameTo(g)) { return "the previous " + name[this.len - 3] + " coincides with the following " + name[g.len - 3]; } //包含 if(this.isContainGra(g)){ return "the previous "+name[this.len-3]+ " contains the following "+name[g.len-3]; } //被包含 if(g.isContainGra(this)){ return "the previous "+name[this.len-3]+ " is inside the following "+name[g.len-3]; } //连接 if(this.overlappingArea(g) == 0){ return "the previous "+name[this.len-3]+ " is connected to the following "+name[g.len-3]; } //交错 return "the previous "+name[this.len-3]+ " is interlaced with the following "+name[g.len-3]; } //判断和另一个图形完全分离(重叠面积为0,并且任意点都在this之外) public boolean isSeparatedFrom(Graphical g){ boolean ok = true; int[] check2 = new int[g.len]; for(int i=0;i<g.len;i++){ check2[i] = this.isContainPoint(g.points[i]); } for(int item:check2){ if(item != 1) ok = false; } if(this.overlappingArea(g) !=0) ok = false; return ok; } //判断完全包含另一个图形(任意点都在this之内) public boolean isContainGra(Graphical g){ boolean ok = true; int[] check2 = new int[g.len]; for(int i=0;i<g.len;i++){ check2[i] = this.isContainPoint(g.points[i]); } for(int item:check2){ if(item == 1) ok = false; } return ok; } //判断两个图形是否一模一样(点完全重合) public boolean isSameTo(Graphical g){ if(this.len != g.len) return false; for(int i=0;i<this.len;i++){ boolean ok = false; for(int j=0;j<g.len;j++){ if(this.points[i].isSameTo(g.points[j])) ok = true; } if(!ok) return false; } return true; } //计算两个图形的重叠面积(交点加内部顶点构成重叠多边形) public double overlappingArea(Graphical g){ Point[] intersection = new Point[100]; int intersection_len = 0; for(Line item1:this.lines){ //求出两多边形的交点 for(Line item2: g.lines){ Point tmp = item1.lsi(item2); if(tmp != null){ intersection[intersection_len++] = tmp.deepCopy(); } } } for(Point item:g.points){ //顶点包含在内部 if(this.isContainPoint(item) == -1) intersection[intersection_len++] = item.deepCopy(); } for(Point item:this.points){ //顶点包含在内部 if(g.isContainPoint(item) == -1) intersection[intersection_len++] = item.deepCopy(); } if(intersection_len==0) return 0; /*排序交点数组*/ intersection = Arrays.copyOf(intersection,intersection_len); intersection = this.removeMulti(intersection); Point focus = Point.focusPoint(intersection); Point sta = intersection[0].deepCopy(); Arrays.sort(intersection,1,intersection.length, new Comparator<Point>() { @Override public int compare(Point o1, Point o2) { try{ Line origin =new Line(focus,sta); Line l1 = new Line(focus,o1); Line l2 = new Line(focus,o2); double angle1 = origin.vectorAngle(l1); double angle2 = origin.vectorAngle(l2); if(origin.vectorCrossMul(l1) < 0) angle1 = 2*Math.PI - angle1; if(origin.vectorCrossMul(l2) < 0) angle2 = 2*Math.PI - angle2; if(angle1-angle2 > 0.000001) return 1; if(Math.abs(angle1-angle2) < 0.000001) return 0; return -1; }catch (Exception reason){} return 0; } }); Graphical graphical = new Graphical(intersection); return graphical.area; } //去除所有重复点 private Point[] removeMulti(Point[] points){ Point[] tmp_points = new Point[points.length]; int tmp_len = 0; for(int i=0;i<points.length;i++){ boolean ok = true; for(int j=0;j<tmp_len;j++){ if(points[i].isSameTo(tmp_points[j])){ this.message = "points coincide"; ok = false; break; } } if(ok) tmp_points[tmp_len++] = points[i].deepCopy(); } return Arrays.copyOf(tmp_points,tmp_len); } //判断不相邻边是否有交点 private void checkEdge(){ for(int i=0;i<this.len;i++){ for(int j=i+2;j<this.len;j++){ if(i==0&&j==this.len-1) continue; Point p = this.lines[i].getIntersection(this.lines[j]); if(p==null) continue; if(p.inLineSegment_close(this.lines[i]) && p.inLineSegment_close(this.lines[j])){ this.status = -1; this.message = "Non adjacent edges have intersections"; return; } } } } //多边形面积 private static void area(Graphical e){ double res = 0; Point origin = new Point(0,0); for(int i=0;i<e.len;i++){ try{ Line l1 = new Line(origin,e.points[i]); Line l2 = new Line(origin,e.points[(i+1)%e.len]); res += 0.5 * l1.vectorCrossMul(l2); }catch (Exception reason){} } e.area = Math.abs(res); } //多边形周长 private static void sideLength(Graphical e){ double res = 0; for(int i=0;i<e.len;i++){ res += e.points[i].disToPoint(e.points[(i+1)%e.len]); } e.sideLength = res; } //多边形凹凸性 private static void checkConvex(Graphical e){ if(e.len == 3) return; int v = 0; for(int i=0;i<e.len;i++){ int first = i, second = (i+1)%e.len, thrid = (i+2)%e.len; try{ Line l1 = new Line(e.points[first], e.points[second]); Line l2 = new Line(e.points[first], e.points[thrid]); if(v==0){ if(l1.vectorCrossMul(l2) > 0) v = 1; else v = -1; } if(v == 1 && l1.vectorCrossMul(l2) < 0) e.isConvexGraphical = false; if(v == -1 && l1.vectorCrossMul(l2) > 0) e.isConvexGraphical = false; }catch (Exception reason){} } } }
SourceMonitor的生成报表内容如下:
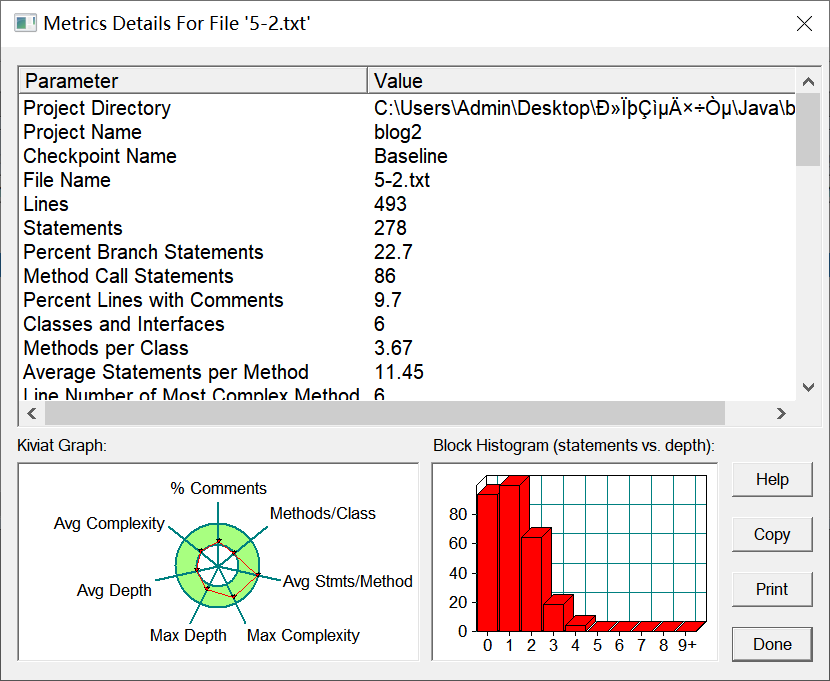
7-1 点与线(类设计)
我的代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); double x1=in.nextDouble(); double y1=in.nextDouble(); double x2=in.nextDouble(); double y2=in.nextDouble(); Point d=new Point(x1,y1); Point e=new Point(x2,y2); d.isright(x1,y1); e.isright(x2,y2); String color=in.next(); Line l=new Line(d,e,color); l.display(); } } class Point{ double x; double y; public Point(){ } public Point(double x,double y){ this.x=x; this.y=y; } public double getX() { return x; } public void setX(double x){ this.x=x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y=y; } public void display() { System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)",x,y); } public void isright(double x,double y) { if((x<=0||x>200)||(y<=0||y>200)) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } } class Line{ private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; private double distance; public Line(){ } public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color) { Point p3=new Point(p1.getX(),p1.getY()); Point p4=new Point(p2.getX(),p2.getY()); this.point1=p3; this.point2=p4; this.color=color; } public void setcolor() { this.color=color; } public String getcolor() { return color; } public double getdistance() { distance=Math.sqrt(Math.abs((point1.getX()-point2.getX())*(point1.getX()-point2.getX())+ (point1.getY()-point2.getY())*(point1.getY()-point2.getY() ))); this.distance=distance; return distance; } public void display() { double s; s=getdistance(); System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); point1.display(); System.out.println("\nThe line's end point's Coordinate is:"); point2.display(); System.out.printf("\nThe line's length is:%.2f",distance); } }
设计思路如图,设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息。
7-2 点线面问题重构(继承与多态)
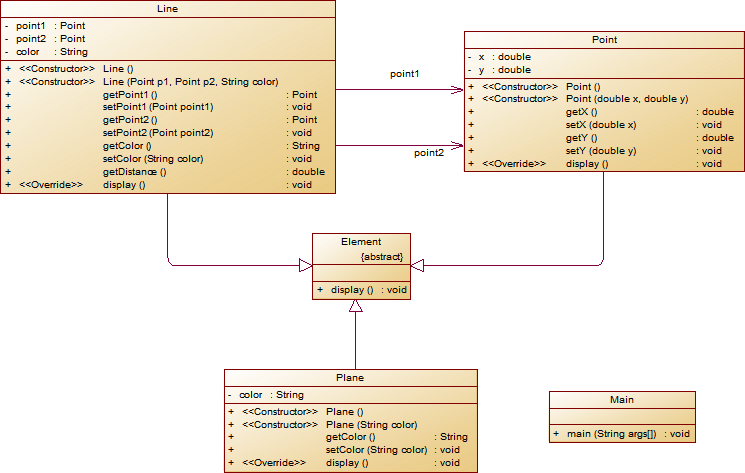
我的代码如下:
import java.text.DecimalFormat; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in); Point point1= new Point(input.nextDouble(),input.nextDouble()); Point point2= new Point(input.nextDouble(),input.nextDouble()); Line line = new Line(point1,point2,input.next()); Plane plane=new Plane(line.getColor()); if((point1.getX()<=0||point1.getX()>200)||(point1.getY()<=0)||(point1.getY()>200)) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } if((point2.getX()<=0||point2.getX()>200)||(point2.getY()<=0)||(point2.getY()>200)) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } line.display(); plane.display(); } } class Point extends Element{ private double x; private double y; public Point() { } public Point(double x, double y) { super(); this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x=x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y=y; } public void display() { if((x<=0||x>200)||(y<=0)||(y>200)) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } } class Line extends Element{ private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; public Line() { } public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color ) { super(); this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; this.color = color; } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1=point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2=point2; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color=color; } public static double getDistance(Point point1,Point point2) { double a; a=Math.sqrt((point1.getX()-point2.getX())*(point1.getX()-point2.getX())+(point1.getY()-point2.getY())*(point1.getY()-point2.getY())); return a; } public void display() { System.out.print("("); System.out.printf("%.2f,%.2f",point1.getX(),point1.getY()); System.out.println(")"); System.out.print("("); System.out.printf("%.2f,%.2f",point2.getX(),point2.getY()); System.out.println(")"); System.out.println("The line's color is:"+getColor()); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); System.out.print("("); System.out.printf("%.2f,%.2f",point1.getX(),point1.getY()); System.out.println(")"); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); System.out.print("("); System.out.printf("%.2f,%.2f",point2.getX(),point2.getY()); System.out.println(")"); System.out.print("The line's length is:"); System.out.printf("%.2f\n",getDistance(point1,point2)); } } class Plane extends Element{ private String color; public Plane(String color) { super(); this.color = color; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color=color; } public void display() { System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+getColor()); } } abstract class Element{ public abstract void display(); }
对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。
再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性。
7-3 点线面问题再重构(容器类)
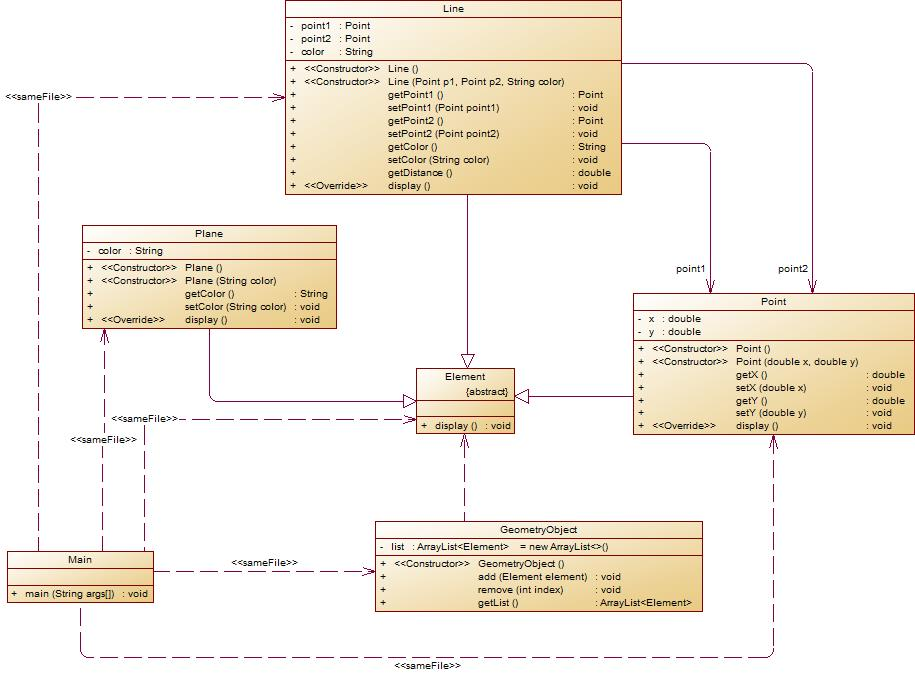
我的代码如下(测试点4未通过):
import java.text.DecimalFormat; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String []args) { Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in); int choice = input.nextInt(); ArrayList<Element> list = new ArrayList<Element>(); while(choice != 0) { switch(choice) { case 1://insert Point object into list Point point1= new Point(input.nextDouble(),input.nextDouble()); list.add(point1); break; case 2://insert Line object into list Point point3= new Point(input.nextDouble(),input.nextDouble()); Point point2= new Point(input.nextDouble(),input.nextDouble()); Line line = new Line(point3,point2,input.next()); list.add(line); break; case 3://insert Plane object into list Plane plane=new Plane(input.next()); list.add(plane); break; case 4://delete index - 1 object from list int index = input.nextInt(); list.remove(index-1); } choice = input.nextInt(); } for (Element element : list) { element.display(); } } } class Point extends Element{ private double x; private double y; public Point() { } public Point(double x, double y) { super(); this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x=x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y=y; } public void display() { if((x<=0||x>200)||(y<=0)||(y>200)) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); }else { System.out.print("("); System.out.printf("%.2f,%.2f",x,y); System.out.println(")"); } } } class Line extends Element{ private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; public Line() { } public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color ) { super(); this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; this.color = color; } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1=point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2=point2; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color=color; } public static double getDistance(Point point1,Point point2) { double a; a=Math.sqrt((point1.getX()-point2.getX())*(point1.getX()-point2.getX())+(point1.getY()-point2.getY())*(point1.getY()-point2.getY())); return a; } public void display() { System.out.println("The line's color is:"+getColor()); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); System.out.print("("); System.out.printf("%.2f,%.2f",point1.getX(),point1.getY()); System.out.println(")"); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); System.out.print("("); System.out.printf("%.2f,%.2f",point2.getX(),point2.getY()); System.out.println(")"); System.out.print("The line's length is:"); System.out.printf("%.2f\n",getDistance(point1,point2)); } } abstract class Element{ public abstract void display(); } class Plane extends Element{ private String color; public Plane(String color) { super(); this.color = color; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color=color; } public void display() { System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+getColor()); } } class GeometryObject{ ArrayList<Element> list = new ArrayList<Element>(); public GeometryObject() { super(); } public void add(Element element) { list.add(element); } public void remove(int index) { if(index>=0) list.remove(index); } public ArrayList<Element> getList(){ return list; } }
在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为ArrayList<Element>类型的对象(若不了解泛型,可以不使用<Element>)增加该类的add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象,输入结束后,按容器中的对象顺序分别调用每个对象的display()方法进行输出。
三、踩坑心得以及改进建议
Java编程中因首先针对抽象类及接口对项目搭建宏观整体框架。在通过对父类继承或对接口实现来填充程序内容已完善细节。对于整体框架的建立至关重要,关系到之后对细节实现的难易程度以及整体的可复用性。良好的框架使得代码的可复用性提高,同时对代码增加细节也将方便进行。因此在编写程序之前,因首先分析整体的执行顺序并对其中的复杂动作进行相应化简使得代码更易书写。
四、总结
在学习Java的面向对象的编程语言的特性。比如继承,构造器,抽象类,接口,方法的多态,重载,覆盖,Java的异常处理机制。对于一个没有面向对象语言背景的人来说,我觉得这个过程需要花很长很长时间,因为学习Java之前只有C语言的经验,花了很长时间,才彻底把这些概念都搞清楚,把书上面的例子反复的揣摩,修改,尝试,把那几章内容反复的看过来,看过去,看了很多遍,才彻底领悟了。学习中,要养成良好的习惯(写括号时要成对,字母大小写要区分,单词拼写要准确)。在学习的过程中,最好不是仅仅停留在java表层,不是抄书上的例子运行出结果就可以。要注意,即便对一个简单的例子也要有耐心去琢磨、调试、改动。在学习的过程中一定要动手做、试着写代码,而不是抱一本书看看就行。很多东西和体会必须自己动手才能真正属于自己。在 Java 的学习过程中,可能会遇到形形色色的问题不容易解决,应多去专业论坛了解相关的知识,书本上的知识有限。要会从网上搜索有用的信息加以整理,促进学习的深入和知识水平的提高。




