十九、最小生成树(普里姆算法)
普里姆算法介绍
普里姆(Prim)算法,是用来求加权连通图的最小生成树的算法。
基本思想
对于图G而言,V是所有顶点的集合;现在,设置两个新的集合U和T,其中U用于存放G的最小生成树中的顶点,T存放G的最小生成树中的边。 从所有uЄU,vЄ(V-U) (V-U表示出去U的所有顶点)的边中选取权值最小的边(u, v),将顶点v加入集合U中,将边(u, v)加入集合T中,如此不断重复,直到U=V为止,最小生成树构造完毕,这时集合T中包含了最小生成树中的所有边。
普里姆算法图解
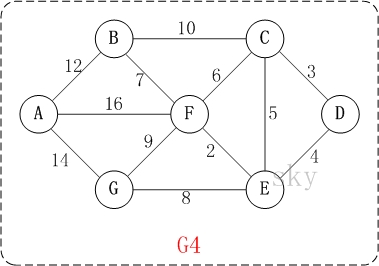
以上图G4为例,来对普里姆进行演示(从第一个顶点A开始通过普里姆算法生成最小生成树)。

初始状态:V是所有顶点的集合,即V={A,B,C,D,E,F,G};U和T都是空!
第1步:将顶点A加入到U中。
此时,U={A}。
第2步:将顶点B加入到U中。
上一步操作之后,U={A}, V-U={B,C,D,E,F,G};因此,边(A,B)的权值最小。将顶点B添加到U中;此时,U={A,B}。
第3步:将顶点F加入到U中。
上一步操作之后,U={A,B}, V-U={C,D,E,F,G};因此,边(B,F)的权值最小。将顶点F添加到U中;此时,U={A,B,F}。
第4步:将顶点E加入到U中。
上一步操作之后,U={A,B,F}, V-U={C,D,E,G};因此,边(F,E)的权值最小。将顶点E添加到U中;此时,U={A,B,F,E}。
第5步:将顶点D加入到U中。
上一步操作之后,U={A,B,F,E}, V-U={C,D,G};因此,边(E,D)的权值最小。将顶点D添加到U中;此时,U={A,B,F,E,D}。
第6步:将顶点C加入到U中。
上一步操作之后,U={A,B,F,E,D}, V-U={C,G};因此,边(D,C)的权值最小。将顶点C添加到U中;此时,U={A,B,F,E,D,C}。
第7步:将顶点G加入到U中。
上一步操作之后,U={A,B,F,E,D,C}, V-U={G};因此,边(F,G)的权值最小。将顶点G添加到U中;此时,U=V。
此时,最小生成树构造完成!它包括的顶点依次是:A B F E D C G。
邻接矩阵:
class Vertex
{
public char label;
public boolean wasVisited;
public Vertex(char lab)
{
label = lab;
wasVisited = false;
}
}
class UDGraph
{
private final int MAX_VERTS = 20;
private Vertex vertexList[];
private int adjMat[][];
private int nVerts;
public UDGraph()
{
vertexList = new Vertex[MAX_VERTS];
adjMat = new int[MAX_VERTS][MAX_VERTS];
nVerts = 0;
for(int i=0;i<MAX_VERTS;i++)
for(int j=0;j<MAX_VERTS;j++)
//最大值表示刚开始顶点间都不连接
adjMat[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
public void addVertex(char lab)
{
vertexList[nVerts++] = new Vertex(lab);
}
public void addEdge(int start,int end,int weight)
{
adjMat[start][end] = weight;
adjMat[end][start] = weight;//无向图
}
//最开始以vertexList[v]为最小生成树的起点
public void Prim(int v)
{
//存放剩余顶点到当前生成树的最短的一条边的权值
int lowcost[] = new int[MAX_VERTS];
int k=0;
for(int i=0;i<nVerts;i++)
{
//将vertexList数组下标第v个顶点到其它顶点的所有边当作候选边
lowcost[i] = adjMat[v][i];
}
//将vertexList[v]并入树中
vertexList[v].wasVisited = true;
System.out.println(vertexList[v].label);
//选中某个顶点后(这里是v),每次选取剩下顶点中的一个,一共要有nVerts-1个次
for(int i=0;i<nVerts-1;i++)
{
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//选出剩下顶点到生成数的最小边
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++)
{
if(!vertexList[j].wasVisited && lowcost[j]<min)
{
min = lowcost[j];
k=j;
}
}
vertexList[k].wasVisited = true;
System.out.println("----"+lowcost[k]+"----"+vertexList[k].label);
//将顶点k并入生成树,并更新剩下顶点到该生成树的最小边
for(int m=0;m<nVerts;m++)
{
//如果剩余顶点到k并入后的生成树的最小边小于并入前的生成树的最小边
if(!vertexList[m].wasVisited && adjMat[k][m]<lowcost[m])
lowcost[m] = adjMat[k][m];
}
}
}
}
public class MatrixUDG_Prim
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
UDGraph theGraph = new UDGraph();
theGraph.addVertex('A');// 0
theGraph.addVertex('B');// 1
theGraph.addVertex('C');// 2
theGraph.addVertex('D');// 3
theGraph.addVertex('E');// 4
theGraph.addVertex('F');// 5
theGraph.addEdge(0, 1,1);//AB
theGraph.addEdge(0, 2,4);//AC
theGraph.addEdge(0, 5,6);//AF
theGraph.addEdge(1, 3,8);//BD
theGraph.addEdge(1, 4,3);//BE
theGraph.addEdge(2, 4,9);//CE
theGraph.addEdge(2, 5,5);//CF
theGraph.addEdge(3, 4,7);//DE
theGraph.addEdge(3, 5,10);//DF
theGraph.addEdge(4, 5,2);//EF//从0开始,即顶点A开始
theGraph.Prim(0);
}
}
邻接表:
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Vertex
{
public char label;
public boolean wasVisited;
public Edge firstEdge;
public Vertex(char lab)
{
this.label = lab;
this.wasVisited = false;
firstEdge = null;
}
}
class Edge
{
public int dest;
public int weight;
public Edge nextEdge;
public Edge(int dest,int weight)
{
this.dest= dest;
this.weight = weight;
nextEdge = null;
}
}
class UDGraph
{
private final int MAX_VERTS = 20;//图的最大顶点数
private int nVerts = 0;//当前顶点数
private Vertex vertexList[];//顶点链表
public UDGraph()
{
vertexList = new Vertex[MAX_VERTS];
}
public void addVertex(char lab)
{
vertexList[nVerts++] = new Vertex(lab);
}
public void addEdge(int start,int end,int weight)
{
Edge startEdge = new Edge(start,weight);
Edge endEdge = new Edge(end,weight);
Edge edge2 = vertexList[start].firstEdge;
if(edge2==null)
{
vertexList[start].firstEdge = endEdge;
}else
{
while(edge2.nextEdge!=null)
edge2 = edge2.nextEdge;
edge2.nextEdge = endEdge;
}
Edge edge3 = vertexList[end].firstEdge;
if(edge3==null)
{
vertexList[end].firstEdge = startEdge;
}else
{
while(edge3.nextEdge!=null)
edge3 = edge3.nextEdge;
edge3.nextEdge = startEdge;
}
}
public void displayVertex(int v)
{
System.out.println(vertexList[v].label);
}
//最开始以vertexList[v]为最小生成树的起点
public void Prim(int v)
{
//存放剩余顶点到当前生成树的最短的一条边的权值
int lowcost[] = new int[MAX_VERTS];
int k=0;
//将vertexList数组下标第v个顶点到其它顶点的所有边当作候选边
for(int i=0;i<nVerts;i++)
{
lowcost[i] = getWeight(v, i);
}
//将vertexList[v]并入树中
vertexList[v].wasVisited = true;
System.out.println(vertexList[v].label);
//选中某个顶点后(这里是v),每次选取剩下顶点中的一个,一共要有nVerts-1个次
for(int i=0;i<nVerts-1;i++)
{
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//选出剩下顶点到生成数的最小边
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++)
{
if(!vertexList[j].wasVisited && lowcost[j]<min)
{
min = lowcost[j];
k=j;
}
}
vertexList[k].wasVisited = true;
System.out.println("----"+lowcost[k]+"----"+vertexList[k].label);
//将顶点k并入生成树,并更新剩下顶点到该生成树的最小边
for(int m=0;m<nVerts;m++){
//如果剩余顶点到k并入后的生成树的最小边小于并入前的生成树的最小边
if(!vertexList[m].wasVisited && getWeight(k, m)<lowcost[m])
lowcost[m] = getWeight(k, m);
}
}
}
/*
* 获取边<start, end>的权值;若start和end不是连通的,则返回无穷大。
*/
private int getWeight(int start, int end)
{
if (start==end)
return 0;
Edge currentEdge = vertexList[start].firstEdge;
while (currentEdge != null)
{
if (end==currentEdge.dest)
return currentEdge.weight;
currentEdge = currentEdge.nextEdge;
}
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
public class ListUDG_Prim
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
UDGraph theGraph = new UDGraph();
theGraph.addVertex('A'); // 0
theGraph.addVertex('B'); // 1
theGraph.addVertex('C'); // 2
theGraph.addVertex('D'); // 3
theGraph.addVertex('E'); // 4
theGraph.addVertex('F'); // 5
theGraph.addEdge(0, 1,1); //AB
theGraph.addEdge(0, 2,4); //AC
theGraph.addEdge(0, 5,6); //AF
theGraph.addEdge(1, 3,8); //BD
theGraph.addEdge(1, 4,3); //BE
theGraph.addEdge(2, 4,9); //CE
theGraph.addEdge(2, 5,5); //CF
theGraph.addEdge(3, 4,7); //DE
theGraph.addEdge(3, 5,10);//DF
theGraph.addEdge(4, 5,2); //EF//从0开始,即顶点A开始
theGraph.Prim(0);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号