十六、图的遍历(深度,广度)
1. 深度优先搜索介绍
图的深度优先搜索(Depth First Search),和树的先序遍历比较类似。
它的思想:假设初始状态是图中所有顶点均未被访问,则从某个顶点v出发,首先访问该顶点,然后依次从它的各个未被访问的邻接点出发深度优先搜索遍历图,直至图中所有和v有路径相通的顶点都被访问到。 若此时尚有其他顶点未被访问到,则另选一个未被访问的顶点作起始点,重复上述过程,直至图中所有顶点都被访问到为止。
显然,深度优先搜索是一个递归的过程。
2. 深度优先搜索图解
2.1 无向图的深度优先搜索
下面以"无向图"为例,来对深度优先搜索进行演示。

对上面的图G1进行深度优先遍历,从顶点A开始。
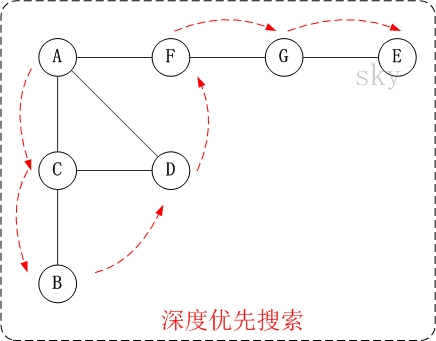
第1步:访问A。
第2步:访问(A的邻接点)C。
在第1步访问A之后,接下来应该访问的是A的邻接点,即"C,D,F"中的一个。但在本文的实现中,顶点ABCDEFG是按照顺序存储,C在"D和F"的前面,因此,先访问C。
第3步:访问(C的邻接点)B。
在第2步访问C之后,接下来应该访问C的邻接点,即"B和D"中一个(A已经被访问过,就不算在内)。而由于B在D之前,先访问B。
第4步:访问(C的邻接点)D。
在第3步访问了C的邻接点B之后,B没有未被访问的邻接点;因此,返回到访问C的另一个邻接点D。
第5步:访问(A的邻接点)F。
前面已经访问了A,并且访问完了"A的邻接点B的所有邻接点(包括递归的邻接点在内)";因此,此时返回到访问A的另一个邻接点F。
第6步:访问(F的邻接点)G。
第7步:访问(G的邻接点)E。
因此访问顺序是:A -> C -> B -> D -> F -> G -> E
邻接矩阵:
class StackX
{
private int maxSize ;
private int[] st;
private int top;
public StackX(int s)
{
maxSize = s;
st = new int[maxSize];
top = -1;
}
public void push(int j)
{
st[++top] = j;
}
public int pop()
{
return st[top--];
}
public int peek()
{
return st[top];
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return (top==-1);
}
}
class Vertex
{
public char label;
public boolean wasVisited;
public Vertex(char lab)
{
label = lab;
wasVisited = false;
}
}
class UDGraph
{
private final int MAX_VERTS = 20;
private Vertex vertexList[];
private int adjMat[][];
private int nVerts;
private StackX theStack;
public UDGraph()
{//无向图
vertexList = new Vertex[MAX_VERTS];
adjMat = new int[MAX_VERTS][MAX_VERTS];
nVerts = 0;
for(int i=0;i<MAX_VERTS;i++)
for(int j=0;j<MAX_VERTS;j++)
adjMat[i][j] = 0;
theStack = new StackX(MAX_VERTS);
}
public void addVertex(char lab)
{
vertexList[nVerts++] = new Vertex(lab);
}
public void addEdge(int start,int end)
{
adjMat[start][end] = 1;
adjMat[end][start] = 1;//无向图
}
public void displayVertex(int v)
{
System.out.println(vertexList[v].label);
}
public void dfs()
{
vertexList[0].wasVisited = true;
displayVertex(0);
theStack.push(0);
while(!theStack.isEmpty())
{
int v = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(theStack.peek());
if(v == -1)
theStack.pop();
else
{
vertexList[v].wasVisited = true;
displayVertex(v);
theStack.push(v);
}
}
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++)
vertexList[j].wasVisited = false;
}
public int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int v)
{
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++)
if(adjMat[v][j]==1 && vertexList[j].wasVisited==false)
return j;
return -1;
}
}
public class MatrixUDG_DFS
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
UDGraph theGraph = new UDGraph();
theGraph.addVertex('A'); // 0 (start for mst)
theGraph.addVertex('B'); // 1
theGraph.addVertex('C'); // 2
theGraph.addVertex('D'); // 3
theGraph.addVertex('E'); // 4
theGraph.addEdge(0, 1); // AB
theGraph.addEdge(0, 2); // AC
theGraph.addEdge(0, 3); // AD
theGraph.addEdge(0, 4); // AE
theGraph.addEdge(1, 2); // BC
theGraph.addEdge(1, 3); // BD
theGraph.addEdge(1, 4); // BE
theGraph.addEdge(2, 3); // CD
theGraph.addEdge(2, 4); // CE
theGraph.addEdge(3, 4); // DE
System.out.println("dbs");
theGraph.dfs();
}
}
邻接链表:
import java.util.ArrayList;
class StackX
{
private int maxSize ;
private Vertex[] st;
private int top;
public StackX(int s)
{
maxSize = s;
st = new Vertex[maxSize];
top = -1;
}
public void push(Vertex vertex)
{
st[++top] = vertex;
}
public Vertex pop()
{
return st[top--];
}
public Vertex peek()
{
return st[top];
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return (top==-1);
}
}
class Vertex
{
public char label;
public boolean wasVisited;
public Edge firstEdge;
public Vertex(char lab)
{
this.label = lab;
this.wasVisited = false;
firstEdge = null;
}
}
class Edge
{
public int dest;
public Edge nextEdge;
public Edge(int dest)
{
this.dest= dest;
nextEdge = null;
}
}
class UDGraph
{
private final int MAX_VERTS = 20;//图的最大顶点数
private int nVerts = 0;//当前顶点数
private Vertex vertexList[];//顶点链表
private StackX theStack;
private ArrayList<Vertex> dfs;
public UDGraph()
{
vertexList = new Vertex[MAX_VERTS];
theStack = new StackX(20);
dfs = new ArrayList<Vertex>();
}
public void addVertex(Vertex vertex)
{
//vertex.indexId = nVerts;
vertexList[nVerts++] = vertex;
}
public void addEdge(int start,int end)
{
Edge startEdge = new Edge(start);
Edge endEdge = new Edge(end);
Edge edge2 = vertexList[start].firstEdge;
if(edge2==null)
{
vertexList[start].firstEdge = endEdge;
}else
{
while(edge2.nextEdge!=null)
edge2 = edge2.nextEdge;
edge2.nextEdge = endEdge;
}
Edge edge3 = vertexList[end].firstEdge;
if(edge3==null)
{
vertexList[end].firstEdge = startEdge;
}else
{
while(edge3.nextEdge!=null)
edge3 = edge3.nextEdge;
edge3.nextEdge = startEdge;
}
}
public void displayVertex(int v)
{
System.out.println(vertexList[v].label);
}
//返回顶点v的一个邻接点并且是未访问过的
public Vertex getAdjUnvisitedVertex(Vertex vertex)
{
Edge currentEdge = vertex.firstEdge;
while(currentEdge != null )
{
if(!vertexList[currentEdge.dest].wasVisited)
return vertexList[currentEdge.dest];
currentEdge = currentEdge.nextEdge;
}
return null;
}
public void dfs()
{
vertexList[0].wasVisited = true;
dfs.add(vertexList[0]);
theStack.push(vertexList[0]);
Vertex vertex;
while(!theStack.isEmpty())
{
vertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(theStack.peek());
if(vertex == null)
theStack.pop();
else
{
vertex.wasVisited = true;
dfs.add(vertex);
theStack.push(vertex);
}
}
//遍历完成,清楚所有访问标志位
for(int i=0;i<nVerts;i++)
vertexList[i].wasVisited = false;
}
public void displayDFS()
{
for(int i=0;i<dfs.size();i++)
System.out.print(dfs.get(i).label);
System.out.println("");
}
}
public class ListUDG_DFS2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
UDGraph theGraph = new UDGraph();
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('A'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('B'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('C'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('D'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('E'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('F'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('G'));
theGraph.addEdge(0, 1); //AB
theGraph.addEdge(0, 2); //AC
theGraph.addEdge(0, 3); //AD
theGraph.addEdge(1, 4); //BE
theGraph.addEdge(2, 5); //CF
theGraph.addEdge(3, 4); //DE
theGraph.addEdge(1, 6); //BG
theGraph.addEdge(3, 5);
System.out.println("dbs");
theGraph.dfs();
theGraph.displayDFS();
}
}
2.2 有向图的深度优先搜索
下面以"有向图"为例,来对深度优先搜索进行演示。

对上面的图G2进行深度优先遍历,从顶点A开始。
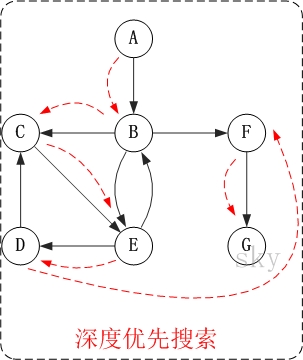
第1步:访问A。
第2步:访问B。
在访问了A之后,接下来应该访问的是A的出边的另一个顶点,即顶点B。
第3步:访问C。
在访问了B之后,接下来应该访问的是B的出边的另一个顶点,即顶点C,E,F。在本文实现的图中,顶点ABCDEFG按照顺序存储,因此先访问C。
第4步:访问E。
接下来访问C的出边的另一个顶点,即顶点E。
第5步:访问D。
接下来访问E的出边的另一个顶点,即顶点B,D。顶点B已经被访问过,因此访问顶点D。
第6步:访问F。
接下应该回溯"访问A的出边的另一个顶点F"。
第7步:访问G。
因此访问顺序是:A -> B -> C -> E -> D -> F -> G
邻接矩阵:
class StackX
{
private int maxSize ;
private int[] st;
private int top;
public StackX(int s)
{
maxSize = s;
st = new int[maxSize];
top = -1;
}
public void push(int j)
{
st[++top] = j;
}
public int pop()
{
return st[top--];
}
public int peek()
{
return st[top];
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return (top==-1);
}
}
class Vertex
{
public char label;
public boolean wasVisited;
public Vertex(char lab)
{
label = lab;
wasVisited = false;
}
}
class DGraph
{
private final int MAX_VERTS = 20;
private Vertex vertexList[];
private int adjMat[][];
private int nVerts;
private StackX theStack;
public DGraph()
{
vertexList = new Vertex[MAX_VERTS];
adjMat = new int[MAX_VERTS][MAX_VERTS];
nVerts = 0;
for(int i=0;i<MAX_VERTS;i++)
for(int j=0;j<MAX_VERTS;j++)
adjMat[i][j] = 0;
theStack = new StackX(MAX_VERTS);
}
public void addVertex(char lab)
{
vertexList[nVerts++] = new Vertex(lab);
}
public void addEdge(int start,int end)
{
adjMat[start][end] = 1;
}
public void displayVertex(int v)
{
System.out.println(vertexList[v].label);
}
public void dfs()
{
vertexList[0].wasVisited = true;
displayVertex(0);
theStack.push(0);
while(!theStack.isEmpty())
{
int v = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(theStack.peek());
if(v == -1)
theStack.pop();
else
{
vertexList[v].wasVisited = true;
displayVertex(v);
theStack.push(v);
}
}
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++)
vertexList[j].wasVisited = false;
}
public int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int v)
{
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++)
if(adjMat[v][j]==1 && vertexList[j].wasVisited==false)
return j;
return -1;
}
}
public class MatrixDG_DFS
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DGraph theGraph = new DGraph();
theGraph.addVertex('A'); // 0 (start for mst)
theGraph.addVertex('B'); // 1
theGraph.addVertex('C'); // 2
theGraph.addVertex('D'); // 3
theGraph.addVertex('E'); // 4
theGraph.addEdge(0, 1); // AB
theGraph.addEdge(0, 2); // AC
theGraph.addEdge(1, 3); // BD
theGraph.addEdge(1, 4); // BE
theGraph.addEdge(2, 3); // CD
theGraph.addEdge(4, 2);
System.out.println("dbs");
theGraph.dfs();
}
}
邻接链表 :
import java.util.ArrayList;
class StackX
{
private int maxSize ;
private Vertex[] st;
private int top;
public StackX(int s)
{
maxSize = s;
st = new Vertex[maxSize];
top = -1;
}
public void push(Vertex vertex)
{
st[++top] = vertex;
}
public Vertex pop()
{
return st[top--];
}
public Vertex peek()
{
return st[top];
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return (top==-1);
}
}
class Vertex
{
public char label;
public boolean wasVisited;
public Edge firstEdge;
public Vertex(char lab)
{
this.label = lab;
this.wasVisited = false;
firstEdge = null;
}
}
class Edge
{
public int dest;
public Edge nextEdge;
public Edge(int dest)
{
this.dest= dest;
nextEdge = null;
}
}
class DGraph
{
private final int MAX_VERTS = 20;//图的最大顶点数
private int nVerts = 0;//当前顶点数
private Vertex vertexList[];//顶点链表
private StackX theStack;
private ArrayList<Vertex> dfs;
public DGraph()
{
vertexList = new Vertex[MAX_VERTS];
theStack = new StackX(20);
dfs = new ArrayList<Vertex>();
}
public void addVertex(Vertex vertex)
{
//vertex.indexId = nVerts;
vertexList[nVerts++] = vertex;
}
public void addEdge(int start,int end)
{
Edge endEdge = new Edge(end);
Edge currentEdge = vertexList[start].firstEdge;
if(currentEdge==null)
{
vertexList[start].firstEdge = endEdge;
}else
{
while(currentEdge.nextEdge!=null)
currentEdge = currentEdge.nextEdge;
currentEdge.nextEdge = endEdge;
}
}
public void displayVertex(int v)
{
System.out.println(vertexList[v].label);
}
//返回顶点v的一个邻接点并且是未访问过的
public Vertex getAdjUnvisitedVertex(Vertex vertex)
{
Edge currentEdge = vertex.firstEdge;
while(currentEdge != null )
{
if(!vertexList[currentEdge.dest].wasVisited)
return vertexList[currentEdge.dest];
currentEdge = currentEdge.nextEdge;
}
return null;
}
public void dfs()
{
vertexList[0].wasVisited = true;
dfs.add(vertexList[0]);
theStack.push(vertexList[0]);
Vertex vertex;
while(!theStack.isEmpty())
{
vertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(theStack.peek());
if(vertex == null)
theStack.pop();
else
{
vertex.wasVisited = true;
dfs.add(vertex);
theStack.push(vertex);
}
}
//遍历完成,清楚所有访问标志位
for(int i=0;i<nVerts;i++)
vertexList[i].wasVisited = false;
}
public void displayDFS()
{
for(int i=0;i<dfs.size();i++)
System.out.print(dfs.get(i).label);
System.out.println("");
}
}
public class ListDG_DFS
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DGraph theGraph = new DGraph();
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('A'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('B'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('C'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('D'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('E'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('F'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('G'));
theGraph.addEdge(0, 1); //AB
theGraph.addEdge(0, 2); //AC
theGraph.addEdge(0, 3); //AD
theGraph.addEdge(1, 4); //BE
theGraph.addEdge(2, 5); //CF
theGraph.addEdge(3, 4); //DE
theGraph.addEdge(1, 6); //BG
theGraph.addEdge(3, 5); //DF
System.out.println("dbs");
theGraph.dfs();
theGraph.displayDFS();
}
}
广度优先搜索的图文介绍
1. 广度优先搜索介绍
广度优先搜索算法(Breadth First Search),又称为"宽度优先搜索"或"横向优先搜索",简称BFS。
它的思想是:从图中某顶点v出发,在访问了v之后依次访问v的各个未曾访问过的邻接点,然后分别从这些邻接点出发依次访问它们的邻接点,并使得“先被访问的顶点的邻接点先于后被访问的顶点的邻接点被访问,直至图中所有已被访问的顶点的邻接点都被访问到。如果此时图中尚有顶点未被访问,则需要另选一个未曾被访问过的顶点作为新的起始点,重复上述过程,直至图中所有顶点都被访问到为止。
换句话说,广度优先搜索遍历图的过程是以v为起点,由近至远,依次访问和v有路径相通且路径长度为1,2...的顶点。
2. 广度优先搜索图解
2.1 无向图的广度优先搜索
下面以"无向图"为例,来对广度优先搜索进行演示。还是以上面的图G1为例进行说明。
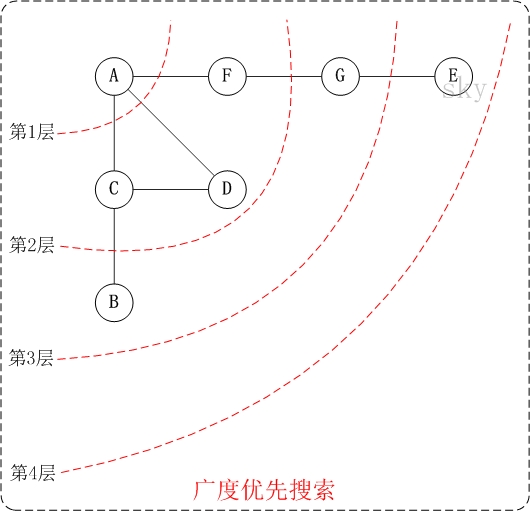
第1步:访问A。
第2步:依次访问C,D,F。
在访问了A之后,接下来访问A的邻接点。前面已经说过,在本文实现中,顶点ABCDEFG按照顺序存储的,C在"D和F"的前面,因此,先访问C。再访问完C之后,再依次访问D,F。
第3步:依次访问B,G。
在第2步访问完C,D,F之后,再依次访问它们的邻接点。首先访问C的邻接点B,再访问F的邻接点G。
第4步:访问E。
在第3步访问完B,G之后,再依次访问它们的邻接点。只有G有邻接点E,因此访问G的邻接点E。
因此访问顺序是:A -> C -> D -> F -> B -> G -> E
邻接矩阵:
class Queue
{
private final int maxSize;
private int[] queArray;
private int front;
private int rear;
public Queue(int s)
{
maxSize = s;
queArray = new int[maxSize];
front = rear = 0;
}
public boolean insert(int j)
{
if(isFull())
return false;
else
{
queArray[rear] = j;
rear=(rear+1)%maxSize;
return true;
}
}
public int remove()
{
if(isEmpty())
return -1;
else
{
int value = queArray[front];
front = (front+1)%maxSize;
return value;
}
}
public int peekFront()
{
if(!isEmpty())
return queArray[front];
else
return -1;
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return (front==rear);
}
public boolean isFull()
{
return (front==(rear+1)%maxSize);
}
}
class Vertex
{
public char label;
public boolean wasVisited;
public Vertex(char lab)
{
label = lab;
wasVisited = false;
}
}
class UDGraph
{
private final int MAX_VERTS = 20;
private Vertex vertexList[];
private int adjMat[][];
private int nVerts;
private Queue theQueue;
public UDGraph()
{
vertexList = new Vertex[MAX_VERTS];
adjMat = new int[MAX_VERTS][MAX_VERTS];
nVerts = 0;
for(int i=0;i<MAX_VERTS;i++)
for(int j=0;j<MAX_VERTS;j++)
adjMat[i][j] = 0;
theQueue = new Queue(MAX_VERTS);
}
public void addVertex(char lab)
{
vertexList[nVerts++] = new Vertex(lab);
}
public void addEdge(int start,int end)
{
adjMat[start][end] = 1;
adjMat[end][start] = 1;//无向图
}
public void displayVertex(int v){
System.out.println(vertexList[v].label);
}
public void bfs(){
vertexList[0].wasVisited = true;
displayVertex(0);
theQueue.insert(0);
int v2;
while(!theQueue.isEmpty())
{
int v1 = theQueue.remove();
while((v2 = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(v1)) != -1)
{
vertexList[v2].wasVisited = true;
displayVertex(v2);
theQueue.insert(v2);
}
}
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++)
vertexList[j].wasVisited = false;
}
public int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int v)
{
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++)
if(adjMat[v][j]==1 && vertexList[j].wasVisited==false)
return j;
return -1;
}
}
public class MatrixUDG_BFS
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
UDGraph theGraph = new UDGraph();
theGraph.addVertex('A'); // 0 (start for mst)
theGraph.addVertex('B'); // 1
theGraph.addVertex('C'); // 2
theGraph.addVertex('D'); // 3
theGraph.addVertex('E'); // 4
theGraph.addEdge(0, 1); // AB
theGraph.addEdge(0, 2); // AC
theGraph.addEdge(1, 3); // BD
theGraph.addEdge(1, 4); // BE
theGraph.addEdge(2, 3); // CD
theGraph.addEdge(4, 2);
theGraph.bfs();
System.out.println();
}
}
邻接链表:
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Queue
{
private final int maxSize;
private Vertex[] queArray;
private int front;
private int rear;
public Queue(int s)
{
maxSize = s;
queArray = new Vertex[maxSize];
front = rear = 0;
}
public boolean insert(Vertex vertex)
{
if(isFull())
return false;
else
{
queArray[rear] = vertex;
rear=(rear+1)%maxSize;
return true;
}
}
public Vertex remove()
{
if(isEmpty())
return null;
else
{
Vertex vertex = queArray[front];
front = (front+1)%maxSize;
return vertex;
}
}
public Vertex peekFront()
{
if(!isEmpty())
return queArray[front];
else
return null;
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return (front==rear);
}
public boolean isFull()
{
return (front==(rear+1)%maxSize);
}
}
class Vertex
{
public char label;
public boolean wasVisited;
public Edge firstEdge;
public Vertex(char lab)
{
this.label = lab;
this.wasVisited = false;
firstEdge = null;
}
}
class Edge
{
public int dest;
public Edge nextEdge;
public Edge(int dest)
{
this.dest= dest;
nextEdge = null;
}
}
class UDGraph
{
private final int MAX_VERTS = 20;//图的最大顶点数
private int nVerts = 0;//当前顶点数
private Vertex vertexList[];//顶点链表
private Queue theQueue;
private ArrayList<Vertex> bfsList;
public UDGraph()
{
vertexList = new Vertex[MAX_VERTS];
theQueue = new Queue(MAX_VERTS);
bfsList = new ArrayList<Vertex>();
}
public void addVertex(Vertex vertex)
{
//vertex.indexId = nVerts;
vertexList[nVerts++] = vertex;
}
public void addEdge(int start,int end)
{
Edge startEdge = new Edge(start);
Edge endEdge = new Edge(end);
Edge edge2 = vertexList[start].firstEdge;
if(edge2==null)
{
vertexList[start].firstEdge = endEdge;
}else
{
while(edge2.nextEdge!=null)
edge2 = edge2.nextEdge;
edge2.nextEdge = endEdge;
}
Edge edge3 = vertexList[end].firstEdge;
if(edge3==null)
{
vertexList[end].firstEdge = startEdge;
}else
{
while(edge3.nextEdge!=null)
edge3 = edge3.nextEdge;
edge3.nextEdge = startEdge;
}
}
public void displayVertex(int v)
{
System.out.println(vertexList[v].label);
}
//返回顶点v的一个邻接点并且是未访问过的
public Vertex getAdjUnvisitedVertex(Vertex vertex)
{
Edge currentEdge = vertex.firstEdge;
while(currentEdge != null )
{
if(!vertexList[currentEdge.dest].wasVisited)
return vertexList[currentEdge.dest];
currentEdge = currentEdge.nextEdge;
}
return null;
}
public void bfs()
{
vertexList[0].wasVisited = true;
bfsList.add(vertexList[0]);
theQueue.insert(vertexList[0]);
Vertex vertex2;
while(!theQueue.isEmpty())
{
Vertex vertex1 = theQueue.remove();
while((vertex2 = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(vertex1)) != null)
{
vertex2.wasVisited = true;
bfsList.add(vertex2);
theQueue.insert(vertex2);
}
}
//遍历完成,清楚所有访问标志位
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++)
vertexList[j].wasVisited = false;
}
public void displayBFS()
{
for(int i=0;i<bfsList.size();i++)
System.out.print(bfsList.get(i).label);
System.out.println("");
}
}
public class ListUDG_BFS
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
UDGraph theGraph = new UDGraph();
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('A'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('B'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('C'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('D'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('E'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('F'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('G'));
theGraph.addEdge(0, 1);//AB
theGraph.addEdge(0, 3);//AD
theGraph.addEdge(1, 4);//BE
theGraph.addEdge(2, 5);//CF
theGraph.addEdge(3, 4);//DE
theGraph.addEdge(1, 6);//BG
theGraph.addEdge(3, 5);//DF
System.out.println("bfs");
theGraph.bfs();
theGraph.displayBFS();
}
}
2.2 有向图的广度优先搜索
下面以"有向图"为例,来对广度优先搜索进行演示。还是以上面的图G2为例进行说明。
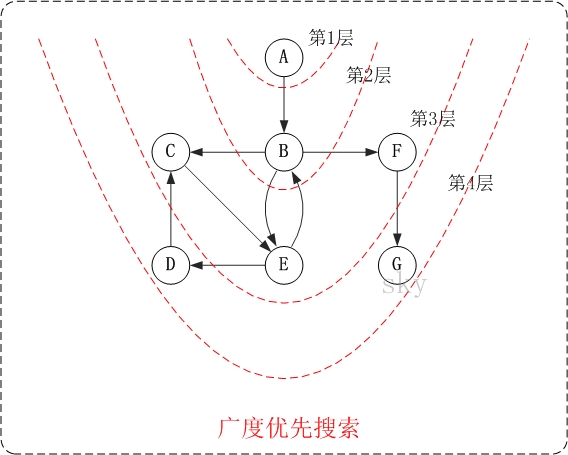
第1步:访问A。
第2步:访问B。
第3步:依次访问C,E,F。
在访问了B之后,接下来访问B的出边的另一个顶点,即C,E,F。前面已经说过,在本文实现中,顶点ABCDEFG按照顺序存储的,因此会先访问C,再依次访问E,F。
第4步:依次访问D,G。
在访问完C,E,F之后,再依次访问它们的出边的另一个顶点。还是按照C,E,F的顺序访问,C的已经全部访问过了,那么就只剩下E,F;先访问E的邻接点D,再访问F的邻接点G。
因此访问顺序是:A -> B -> C -> E -> F -> D -> G
class Queue
{
private final int maxSize;
private int[] queArray;
private int front;
private int rear;
public Queue(int s)
{
maxSize = s;
queArray = new int[maxSize];
front = rear = 0;
}
public boolean insert(int j)
{
if(isFull())
return false;
else
{
queArray[rear] = j;
rear=(rear+1)%maxSize;
return true;
}
}
public int remove()
{
if(isEmpty())
return -1;
else
{
int value = queArray[front];
front = (front+1)%maxSize;
return value;
}
}
public int peekFront()
{
if(!isEmpty())
return queArray[front];
else
return -1;
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return (front==rear);
}
public boolean isFull()
{
return (front==(rear+1)%maxSize);
}
}
class Vertex
{
public char label;
public boolean wasVisited;
public Vertex(char lab)
{
label = lab;
wasVisited = false;
}
}
class DGraph
{
private final int MAX_VERTS = 20;
private Vertex vertexList[];
private int adjMat[][];
private int nVerts;
private Queue theQueue;
public DGraph()
{
vertexList = new Vertex[MAX_VERTS];
adjMat = new int[MAX_VERTS][MAX_VERTS];
nVerts = 0;
for(int i=0;i<MAX_VERTS;i++)
for(int j=0;j<MAX_VERTS;j++)
adjMat[i][j] = 0;
theQueue = new Queue(MAX_VERTS);
}
public void addVertex(char lab)
{
vertexList[nVerts++] = new Vertex(lab);
}
public void addEdge(int start,int end)
{
adjMat[start][end] = 1; }
public void displayVertex(int v)
{
System.out.println(vertexList[v].label);
}
public void bfs()
{
vertexList[0].wasVisited = true;
displayVertex(0);
theQueue.insert(0);
int v2;
while(!theQueue.isEmpty())
{
int v1 = theQueue.remove();
while((v2 = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(v1)) != -1)
{
vertexList[v2].wasVisited = true;
displayVertex(v2);
theQueue.insert(v2);
}
}
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++)
vertexList[j].wasVisited = false;
}
public int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int v)
{
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++)
if(adjMat[v][j]==1 && vertexList[j].wasVisited==false)
return j;
return -1;
}
}
public class MatrixDG_BFS
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DGraph theGraph = new DGraph();
theGraph.addVertex('A'); // 0 (start for mst)
theGraph.addVertex('B'); // 1
theGraph.addVertex('C'); // 2
theGraph.addVertex('D'); // 3
theGraph.addVertex('E'); // 4
theGraph.addEdge(0, 1); // AB
theGraph.addEdge(0, 2); // AC
theGraph.addEdge(1, 3); // BD
theGraph.addEdge(1, 4); // BE
theGraph.addEdge(2, 3); // CD
theGraph.addEdge(4, 2);
theGraph.bfs();
System.out.println();
}
}
邻接链表:
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Queue
{
private final int maxSize;
private Vertex[] queArray;
private int front;
private int rear;
public Queue(int s)
{
maxSize = s;
queArray = new Vertex[maxSize];
front = rear = 0;
}
public boolean insert(Vertex vertex)
{
if(isFull())
return false;
else
{
queArray[rear] = vertex;
rear=(rear+1)%maxSize;
return true;
}
}
public Vertex remove()
{
if(isEmpty())
return null;
else
{
Vertex vertex = queArray[front];
front = (front+1)%maxSize;
return vertex;
}
}
public Vertex peekFront()
{
if(!isEmpty())
return queArray[front];
else
return null;
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return (front==rear);
}
public boolean isFull()
{
return (front==(rear+1)%maxSize);
}
}
class Vertex
{
public char label;
public boolean wasVisited;
public Edge firstEdge;
public Vertex(char lab)
{
this.label = lab;
this.wasVisited = false;
firstEdge = null;
}
}
class Edge
{
public int dest;
public Edge nextEdge;
public Edge(int dest)
{
this.dest= dest;
nextEdge = null;
}
}
class DGraph
{
private final int MAX_VERTS = 20;//图的最大顶点数
private int nVerts = 0;//当前顶点数
private Vertex vertexList[];//顶点链表
private Queue theQueue;
private ArrayList<Vertex> bfsList;
public DGraph()
{
vertexList = new Vertex[MAX_VERTS];
theQueue = new Queue(MAX_VERTS);
bfsList = new ArrayList<Vertex>();
}
public void addVertex(Vertex vertex)
{
//vertex.indexId = nVerts;
vertexList[nVerts++] = vertex;
}
public void addEdge(int start,int end)
{
Edge endEdge = new Edge(end);
Edge currentEdge = vertexList[start].firstEdge;
if(currentEdge==null)
{
vertexList[start].firstEdge = endEdge;
}else
{
while(currentEdge.nextEdge!=null)
currentEdge = currentEdge.nextEdge;
currentEdge.nextEdge = endEdge;
}
}
public void displayVertex(int v)
{
System.out.println(vertexList[v].label);
}
//返回顶点v的一个邻接点并且是未访问过的
public Vertex getAdjUnvisitedVertex(Vertex vertex)
{
Edge currentEdge = vertex.firstEdge;
while(currentEdge != null )
{
if(!vertexList[currentEdge.dest].wasVisited)
return vertexList[currentEdge.dest];
currentEdge = currentEdge.nextEdge;
}
return null;
}
public void bfs()
{
vertexList[0].wasVisited = true;
bfsList.add(vertexList[0]);
theQueue.insert(vertexList[0]);
Vertex vertex2;
while(!theQueue.isEmpty())
{
Vertex vertex1 = theQueue.remove();
while((vertex2 = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(vertex1)) != null)
{
vertex2.wasVisited = true;
bfsList.add(vertex2);
theQueue.insert(vertex2);
}
}
//遍历完成,清楚所有访问标志位
for(int j=0;j<nVerts;j++)
vertexList[j].wasVisited = false;
}
public void displayBFS()
{
for(int i=0;i<bfsList.size();i++)
System.out.print(bfsList.get(i).label);
System.out.println("");
}
}
public class ListDG_BFS
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DGraph theGraph = new DGraph();
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('A'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('B'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('C'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('D'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('E'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('F'));
theGraph.addVertex(new Vertex('G'));
theGraph.addEdge(0, 1);//AB
theGraph.addEdge(0, 2);//AC
theGraph.addEdge(0, 3);//AD
theGraph.addEdge(1, 4);//BE
theGraph.addEdge(2, 5);//CF
theGraph.addEdge(3, 4);//DE
theGraph.addEdge(1, 6);//BG
theGraph.addEdge(3, 5);//DF
System.out.println("bfs");
theGraph.bfs();
theGraph.displayBFS();
}
}


