P1080 国王游戏
题目描述
恰逢 HH H国国庆,国王邀请n nn 位大臣来玩一个有奖游戏。首先,他让每个大臣在左、右手上面分别写下一个整数,国王自己也在左、右手上各写一个整数。然后,让这 nnn 位大臣排成一排,国王站在队伍的最前面。排好队后,所有的大臣都会获得国王奖赏的若干金币,每位大臣获得的金币数分别是:排在该大臣前面的所有人的左手上的数的乘积除以他自己右手上的数,然后向下取整得到的结果。
国王不希望某一个大臣获得特别多的奖赏,所以他想请你帮他重新安排一下队伍的顺序,使得获得奖赏最多的大臣,所获奖赏尽可能的少。注意,国王的位置始终在队伍的最前面。
输入格式
第一行包含一个整数n nn,表示大臣的人数。
第二行包含两个整数 aaa和 bbb,之间用一个空格隔开,分别表示国王左手和右手上的整数。
接下来 nn n行,每行包含两个整数a aa 和 bbb,之间用一个空格隔开,分别表示每个大臣左手和右手上的整数。
输出格式
一个整数,表示重新排列后的队伍中获奖赏最多的大臣所获得的金币数。
输入输出样例
输入 #1 复制
3
1 1
2 3
7 4
4 6
输出 #1 复制
2
说明/提示
【输入输出样例说明】
按1 11、222、333 这样排列队伍,获得奖赏最多的大臣所获得金币数为 222;
按 111、333、222 这样排列队伍,获得奖赏最多的大臣所获得金币数为2 22;
按 222、111、333 这样排列队伍,获得奖赏最多的大臣所获得金币数为 222;
按2 22、333、11 1这样排列队伍,获得奖赏最多的大臣所获得金币数为9 99;
按 333、111、22 2这样排列队伍,获得奖赏最多的大臣所获得金币数为 222;
按3 33、222、111 这样排列队伍,获得奖赏最多的大臣所获得金币数为 999。
因此,奖赏最多的大臣最少获得 22 2个金币,答案输出 222。
【数据范围】
对于 20%的数据,有 1≤n≤10,0<a,b<81≤ n≤ 10,0 < a,b < 81≤n≤10,0<a,b<8;
对于 40%的数据,有1≤n≤20,0<a,b<8 1≤ n≤20,0 < a,b < 81≤n≤20,0<a,b<8;
对于 60%的数据,有 1≤n≤1001≤ n≤1001≤n≤100;
对于 60%的数据,保证答案不超过 10910^9109;
对于 100%的数据,有 1≤n≤1,000,0<a,b<100001 ≤ n ≤1,000,0 < a,b < 100001≤n≤1,000,0<a,b<10000。
NOIP 2012 提高组 第一天 第二题
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>void read(T &x)
{
char ch;
x=0;
int f=1;
for(;ch<'0'||ch>'9';ch=getchar()) if(ch=='-') f=-1;
for(;ch>='0'&&ch<='9';ch=getchar()) x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(ch&15);
x*=f;
}
int a,b;
const int N=10005;
struct node
{
int l,r;
}dc[1010];
struct hp
{
int num[N];
hp & operator =(const char *);
hp & operator =(int);
hp();
hp(int);
hp operator + (const hp &)const ;
hp operator - (const hp &) const ;
hp operator * (const hp &) const;
hp operator / (int ) const;
bool operator > (const hp &) const;
bool operator < (const hp &)const ;
bool operator <= (const hp &) const;
bool operator >= (const hp &b) const ;
};
hp & hp::operator = (const char *c)
{
memset(num,0,sizeof(num));
int n=strlen(c),j=1,k=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(k==10000) j++,k=1;
num[j]+=k*(c[n-i]-'0');
k*=10;
}
num[0]=j;
return *this;
}
hp & hp::operator = (int a)
{
char s[5000];
sprintf(s,"%d",a);
return *this=s;
}
hp::hp() {memset(num,0,sizeof(num));num[0]=1;}
hp::hp(int n) {*this=n;}
hp hp::operator - (const hp &b) const //减法
{
hp c;
c.num[0]=num[0];
for(int i=1;i<=c.num[0];i++)
{
c.num[i]+=num[i]-b.num[i];
if(c.num[i]<0)
{
c.num[i]+=10000;
c.num[i+1]--;
}
}
while(c.num[c.num[0]]==0&&c.num[0]>1) c.num[0]--;
return c;
}
bool hp::operator > (const hp &b) const
{
if(num[0]!=b.num[0]) return num[0]>b.num[0];
for(int i=num[0];i>=1;i--)
{
if(num[i]!=b.num[i])
return (num[i]>b.num[i]);
}
return false;
}
bool hp::operator < (const hp &b) const {return b>*this;}
bool hp::operator <= (const hp &b) const {return !(*this>b);}
bool hp::operator >= (const hp &b) const {return !(b>*this);}
bool cmp(node a,node b)
{
return a.l*a.r<b.l*b.r;
}
hp hp::operator * (const hp &b) const //乘法
{
hp c;
c.num[0]=num[0]+b.num[0]+1;
for(int i=1;i<=num[0];i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=b.num[0];j++)
{
c.num[i+j-1]+=num[i]*b.num[j];
c.num[i+j]+=c.num[i+j-1]/10000;
c.num[i+j-1]%=10000;
}
}
while(c.num[c.num[0]]==0&&c.num[0]>1) c.num[0]--;
return c;
}
//hp hp::operator / (const hp& b) const //二分优化除法
//{
// hp c,d;
// c.num[0]=num[0]+b.num[0]+1;
// d.num[0]=0;
// for(int i=num[0];i>=1;i--)
// {
// memmove(d.num+2,d.num+1,sizeof(d.num)-sizeof(int)*2);
// d.num[0]++;
// d.num[1]=num[i];
// int l=0,r=9999,mid;
// while(l<r)
// {
// mid=(l+r)>>1;
// if(b*hp(mid)<=d) l=mid+1;
// else r=mid;
// }
// c.num[i]=r-1;
// d=d-b*hp(r-1);
// }
// while(c.num[c.num[0]]==0&&c.num[0]>1) c.num[0]--;
// return c;
//}
//hp hp::operator / (const hp &b) const
//{
// hp c, d;
// c.num[0] = num[0]+b.num[0]+1;
// d.num[0] = 0;
// for (int i=num[0];i>=1;i--)
// {
// // 以下三行的含义是:d=d*10000+num[i];
// memmove(d.num+2, d.num+1, sizeof(d.num)-sizeof(int)*2);
// d.num[0]++;
// d.num[1]=num[i];
//
// // 以下循环的含义是:c.num[i]=d/b; d%=b;
// while (d >= b)
// {
// d=d-b;
// c.num[i]++;
// }
//
// }
// while (c.num[c.num[0]]==0&&c.num[0]>1) c.num[0]--; // 99999999/99999999
//
// return c;
//}
hp hp::operator / (int b) const
{
hp c;
int p=0;
c.num[0]=num[0];
for(int i=num[0];i>=1;i--)
{
p=p*10000+num[i];
memmove(c.num+2, c.num+1, sizeof(c.num)-sizeof(int)*2);
c.num[1]=p/b;
p%=b;
}
while(c.num[0]>0&&c.num[c.num[0]]==0) c.num[0]--;
return c;
}
ostream & operator << (ostream & o,hp &n) //输出
{
o<<n.num[n.num[0]];
for(int i=n.num[0]-1;i>=1;i--)
{
o.width(4);
o.fill('0');
o<<n.num[i];
}
return o;
}
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
//hp C[1010];
int main()
{
//freopen("test.txt","r",stdin);
int n;
read(n);
n++;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
read(dc[i].l);
read(dc[i].r);
}
sort(dc+2,dc+n+1,cmp);
hp maxn;
hp sum=1;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
sum=sum*hp(dc[i].l);
if(maxn<sum/dc[i+1].r)
{
maxn=sum/dc[i+1].r;
}
}
cout<<maxn<<endl;
return 0;
}
思路
网上关于此题贪心策略的解释:
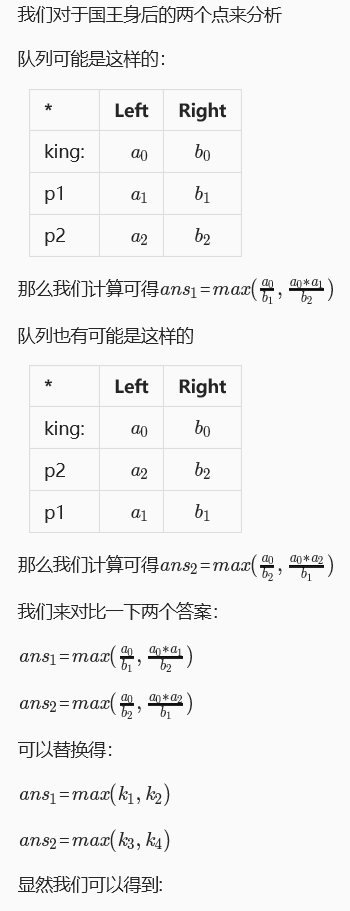

排序完之后,就是高精度的计算了,容易出错的地方就是除法吧,这里是高精除以单精,如果把整数转成高精度计算,很容易出错,高精除高精一般不会用到。



