线程的静态方法
1、currentThread()方法
package day02; public class ThreadTest01 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }
执行结果:
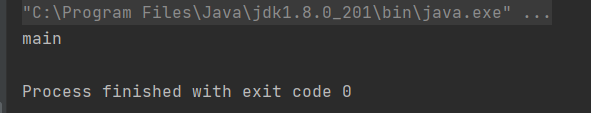
因为是在main函数中运行的,所以得到线程的名字是main。
2、sleep()方法
- sleep()方法的作用是在指定的毫秒数内让当前正在执行的线程休眠暂停执行。这个正在执行的线程指的是this.currentThread()返回的线程。
- sleep方法不会释放锁,也就是说如果当前线程持有对某个对象的锁,则即使调用sleep方法,其他线程也无法访问这个对象。
1 public class ThreadTest03 { 2 3 private int i = 10; 4 5 private Object object = new Object(); 6 7 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 11 ThreadTest03 sm = new ThreadTest03(); 12 13 MyThread thread1 = sm.new MyThread(); 14 15 MyThread thread2 = sm.new MyThread(); 16 17 thread1.start(); 18 19 thread2.start(); 20 21 } 22 23 24 25 class MyThread extends Thread { 26 27 @Override 28 29 public void run() { 30 31 synchronized (object) { 32 33 i++; 34 35 try { 36 37 System.out.println("i=" + i); 38 39 System.out.println("Thread Name:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",进入睡眠"); 40 41 Thread.sleep(1000); 42 43 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 44 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 47 } 48 49 System.out.println("Thread Name:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",睡眠结束"); 50 51 i++; 52 53 System.out.println("i=" + i); 54 55 56 57 } 58 59 } 60 61 } 62 63 }
执行结果:
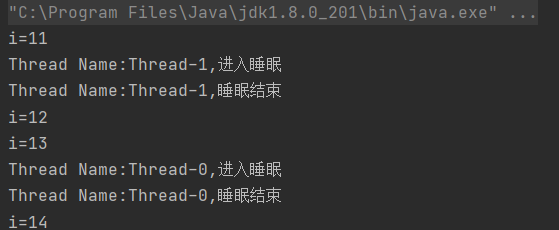
- 当Thread-0进入睡眠状态之后,Thread-1并没有去执行具体的任务。只有当Thread-0执行完之后,此时Thread-0释放了对象锁,Thread-1才开始执行。
- 如果调用了sleep方法,必须捕获InterruptedException异常或者将该异常向上层抛出。
- 当线程睡眠时间满后,不一定会立即得到执行,因为此时可能CPU正在执行其他的任务。所以说调用sleep方法相当于让线程进入阻塞状态。
3、yield()方法
- 与sleep方法类似,不会释放锁。
- 调用yield方法会让当前线程交出CPU权限,让CPU去执行其他的线程。
- yield方法只能让拥有优先级的线程获取CPU执行时间的机会,调用该方法不会让线程进入阻塞状态,而是让线程重回就绪状态,它只需要等待重新获取CPU执行的时间。
1 package day02; 2 3 4 5 public class ThreadTest04 { 6 7 8 9 class MyThread extends Thread { 10 11 @Override 12 13 14 15 public void run() { 16 17 long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); 18 19 int count = 0; 20 21 for (int i = 0; i < 50000000; i++) { 22 23 count = count + (i + 1); 24 25 Thread.yield(); 26 27 28 29 } 30 31 long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); 32 33 System.out.println("用时:" + (endTime - beginTime) + "(ms)"); 34 35 36 37 } 38 39 } 40 41 42 43 public static void main(String[] args) { 44 45 Thread thread1 = new ThreadTest04().new MyThread(); 46 47 thread1.start(); 48 49 50 51 } 52 53 }
执行结果:
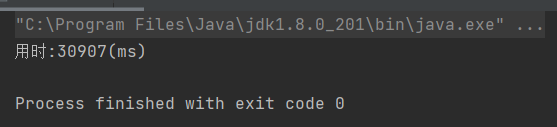
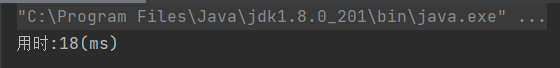
注释Thread.yilde(); 之后,执行结果:
欢迎批评指正,提出问题,谢谢!


