Python的WEB框架有Django、Tornado、Flask 等多种,Django相较与其他WEB框架其优势为:大而全,框架本身集成了ORM、模型绑定、模板引擎、缓存、Session等诸多功能。
基本配置
一、创建django程序
- 终端命令:django-admin startproject sitename
- IDE创建Django程序时,本质上都是自动执行上述命令
其他常用命令:
python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0
python manage.py startapp appname
python manage.py syncdb
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py createsuperuser
二、程序目录
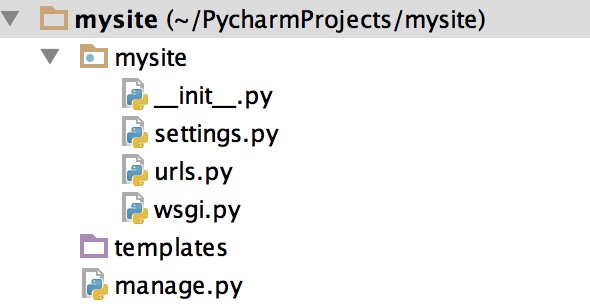
三、配置文件
1、数据库
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
DATABASES = { 'default': { 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql', 'NAME':'dbname', 'USER': 'root', 'PASSWORD': 'xxx', 'HOST': '', 'PORT': '', }} |
2、模版
|
1
2
3
|
TEMPLATE_DIRS = ( os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'templates'), ) |
3、静态文件
|
1
2
3
|
STATICFILES_DIRS = ( os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'static'), ) |
路由系统
1、单一路由对应
|
1
|
url(r'^index$', views.index), |
2、基于正则的路由
|
1
2
|
url(r'^index/(\d*)', views.index),url(r'^manage/(?P<name>\w*)/(?P<id>\d*)', views.manage), |
3、添加额外的参数
|
1
|
url(r'^manage/(?P<name>\w*)', views.manage,{'id':333}), |
4、为路由映射设置名称
|
1
2
|
url(r'^home', views.home, name='h1'),url(r'^index/(\d*)', views.index, name='h2'), |
设置名称之后,可以在不同的地方调用,如:
- 模板中使用生成URL {% url 'h2' 2012 %}
- 函数中使用生成URL reverse('h2', args=(2012,)) 路径:django.urls.reverse
- Model中使用获取URL 自定义get_absolute_url() 方法
![]() View Code
View Code
获取请求匹配成功的URL信息:request.resolver_match
5、根据app对路由规则进行分类
|
1
|
url(r'^web/',include('web.urls')), |
6、命名空间
a. project.urls.py
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
from django.conf.urls import url,includeurlpatterns = [ url(r'^a/', include('app01.urls', namespace='author-polls')), url(r'^b/', include('app01.urls', namespace='publisher-polls')),] |
b. app01.urls.py
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
from django.conf.urls import urlfrom app01 import viewsapp_name = 'app01'urlpatterns = [ url(r'^(?P<pk>\d+)/$', views.detail, name='detail')] |
c. app01.views.py
|
1
2
3
|
def detail(request, pk): print(request.resolver_match) return HttpResponse(pk) |
以上定义带命名空间的url之后,使用name生成URL时候,应该如下:
- v = reverse('app01:detail', kwargs={'pk':11})
- {% url 'app01:detail' pk=12 pp=99 %}
django中的路由系统和其他语言的框架有所不同,在django中每一个请求的url都要有一条路由映射,这样才能将请求交给对一个的view中的函数去处理。其他大部分的Web框架则是对一类的url请求做一条路由映射,从而是路由系统变得简洁。
通过反射机制,为django开发一套动态的路由系统Demo: 点击下载
模板
1、模版的执行
模版的创建过程,对于模版,其实就是读取模版(其中嵌套着模版标签),然后将 Model 中获取的数据插入到模版中,最后将信息返回给用户。
 View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code View Code
View Code2、模版语言
模板中也有自己的语言,该语言可以实现数据展示
- {{ item }}
- {% for item in item_list %} <a>{{ item }}</a> {% endfor %}
forloop.counter
forloop.first
forloop.last - {% if ordered_warranty %} {% else %} {% endif %}
- 母板:{% block title %}{% endblock %}
子板:{% extends "base.html" %}
{% block title %}{% endblock %} - 帮助方法:
{{ item.event_start|date:"Y-m-d H:i:s"}}
{{ bio|truncatewords:"30" }}
{{ my_list|first|upper }}
{{ name|lower }}
3、自定义simple_tag
a、在app中创建templatetags模块
b、创建任意 .py 文件,如:xx.py
c、在使用自定义simple_tag的html文件中导入之前创建的 xx.py 文件名
|
1
|
{% load xx %} |
d、使用simple_tag
|
1
2
|
{% my_simple_time 1 2 3%}{% my_input 'id_username' 'hide'%} |
e、在settings中配置当前app,不然django无法找到自定义的simple_tag
更多见文档:https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.10/ref/templates/language/
中间件
django 中的中间件(middleware),在django中,中间件其实就是一个类,在请求到来和结束后,django会根据自己的规则在合适的时机执行中间件中相应的方法。
在django项目的settings模块中,有一个 MIDDLEWARE_CLASSES 变量,其中每一个元素就是一个中间件,如下图。
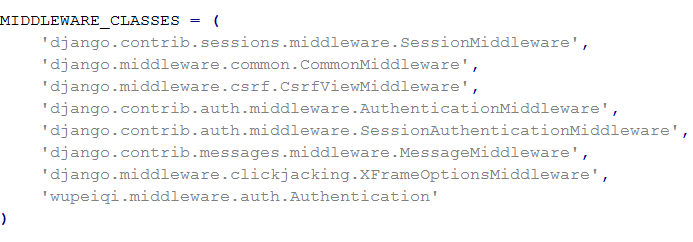
与mange.py在同一目录下的文件夹 wupeiqi/middleware下的auth.py文件中的Authentication类
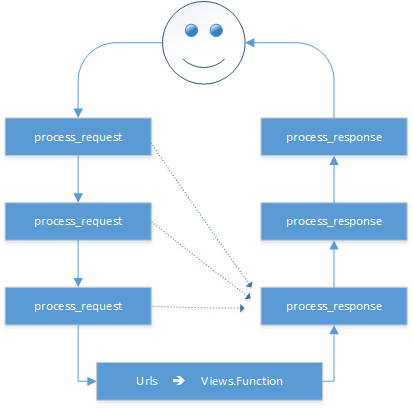
中间件中可以定义四个方法,分别是:
- process_request(self,request)
- process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs)
- process_template_response(self,request,response)
- process_exception(self, request, exception)
- process_response(self, request, response)
以上方法的返回值可以是None和HttpResonse对象,如果是None,则继续按照django定义的规则向下执行,如果是HttpResonse对象,则直接将该对象返回给用户。
自定义中间件
1、创建中间件类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
class RequestExeute(object): def process_request(self,request): pass def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs): i =1 pass def process_exception(self, request, exception): pass def process_response(self, request, response): return response |
2、注册中间件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
MIDDLEWARE_CLASSES = ( 'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware', 'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware', 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware', 'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware', 'django.contrib.auth.middleware.SessionAuthenticationMiddleware', 'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware', 'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware', 'wupeiqi.middleware.auth.RequestExeute',) |
admin
django amdin是django提供的一个后台管理页面,改管理页面提供完善的html和css,使得你在通过Model创建完数据库表之后,就可以对数据进行增删改查,而使用django admin 则需要以下步骤:
- 创建后台管理员
- 配置url
- 注册和配置django admin后台管理页面
1、创建后台管理员
|
1
|
python manage.py createsuperuser |
2、配置后台管理url
|
1
|
url(r'^admin/', include(admin.site.urls)) |
3、注册和配置django admin 后台管理页面
a、在admin中执行如下配置
b、设置数据表名称
c、打开表之后,设定默认显示,需要在model中作如下配置
d、为数据表添加搜索功能
e、添加快速过滤
更多:http://docs.30c.org/djangobook2/chapter06/


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号