对java方法进行功能增强的三种方法
对java方法进行功能增强的方法
1.通过继承的方式
对哪个类中的方法进行增强,可以采用继承那个类的方式。通过继承该类,可以重写方法,如果还需要老方法的一些功能,使用super调用。
1 //需要增强类的study方法 2 public class Person { 3 public void study(){ 4 System.out.println("需要扩展的方法"); 5 } 6 }
1 //继承需要增强方法的类,重写方法 2 public class Student extends Person{ 3 @Override 4 public void study(){ 5 //方法前后可以增强 6 //有用到原先的方法 super调用父类 7 System.out.println("重写后的方法"); 8 } 9 }
2.通过装饰者模式
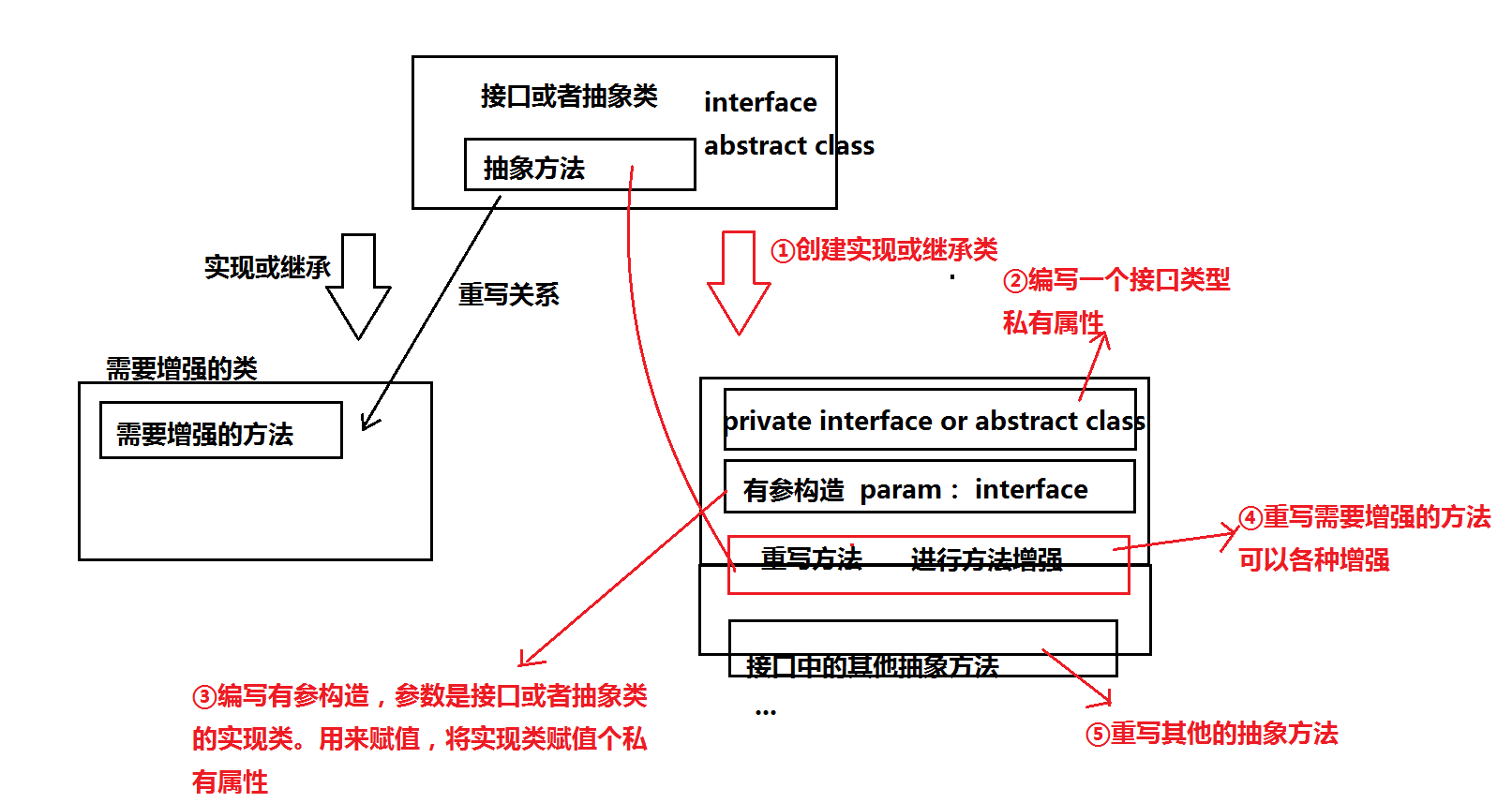
使用条件:需要对某接口或抽象类的实现类中重写的方法进行功能增强可以使用装饰者模式。
使用详解:
第一步:找到需要增强的实现类的接口,或者是抽象类,然后创建一个子类进行实现或者继承;
第二步:添加私有属性到创建的类,该私有属性为接口的实现类。
第三步:写一个有参构造,参数为接口的实现类,将实现类赋值给私有属性
第四步:重写需要增强的方法,这里面就可以各种增强了
第五步:重写其他的抽象方法,直接调用需要增强类的方法即可,
简单的案例:
有个家猫类实现类猫科接口,它有个吃的方法,现在有需求它的吃的方法已经不能满足了,增强它的吃的方法
1 //接口 2 public interface Cat { 3 //吃的方法 4 void eat(); 5 //玩的方法 6 void play(); 7 }
1 //需要增强的类 2 public class HomeCat implements Cat{ 3 4 @Override 5 public void eat() { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 System.out.println("吃鱼的方法"); 8 } 9 10 @Override 11 public void play() { 12 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 13 14 } 15 16 }
1 //进行增强的类 2 public class NewCat implements Cat{ 3 private Cat c; 4 public NewCat(Cat c){ 5 this.c=c; 6 } 7 //进行增强 8 @Override 9 public void eat() { 10 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 11 System.out.println("增强前"); 12 c.eat(); 13 System.out.println("增强后"); 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public void play() { 18 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 19 c.play(); 20 } 21 22 }
1 //测试类 2 public class Demo1 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 NewCat newcat=new NewCat(new HomeCat()); 5 newcat.eat(); 6 } 7 }
3.动态代理
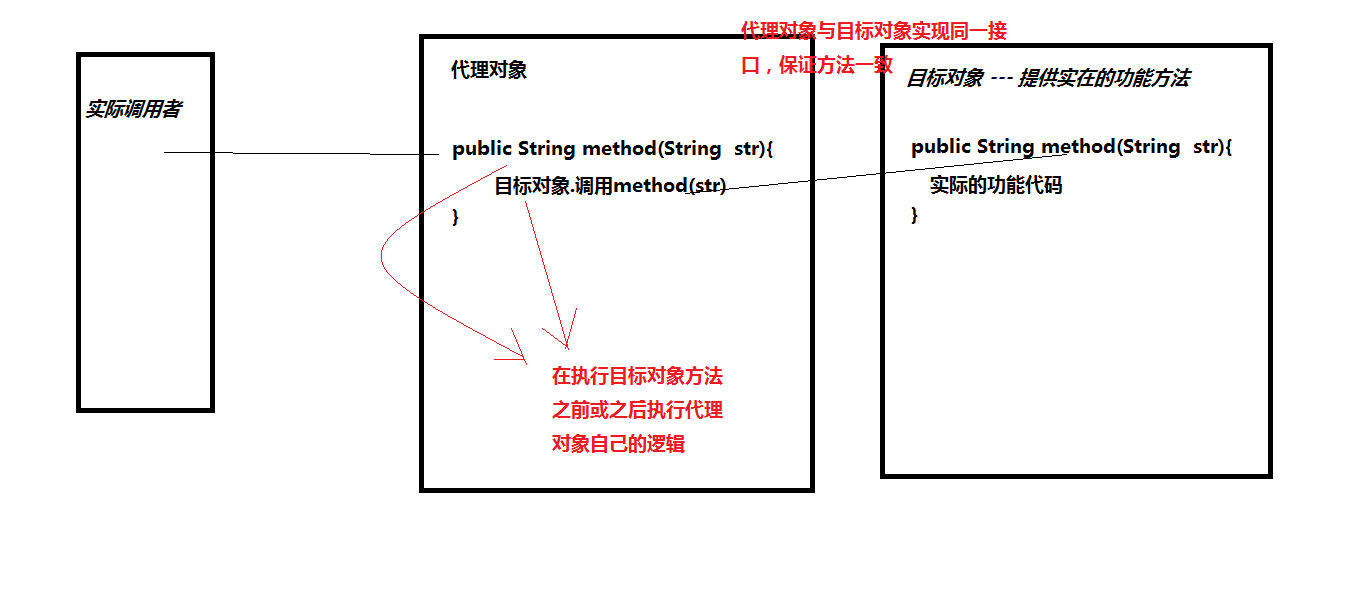
1 public interface TargetInterface { 2 3 public void method1(); 4 public String method2(); 5 public int method3(int x); 6 }
1 public class ProxyTest2 { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 final Target target = new Target(); 6 7 //动态创建代理对象 8 9 TargetInterface proxy = (TargetInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance( 10 target.getClass().getClassLoader(), 11 target.getClass().getInterfaces(), 12 new InvocationHandler() { 13 @Override 14 //被执行几次?------- 看代理对象调用方法几次 15 //代理对象调用接口相应方法 都是调用invoke 16 /* 17 * proxy:是代理对象 18 * method:代表的是目标方法的字节码对象 19 * args:代表是调用目标方法时参数 20 */ 21 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { 22 //反射知识点 23 Object invoke = method.invoke(target, args);//目标对象的相应方法 24 //retrun返回的值给代理对象 25 return invoke; 26 } 27 } 28 ); 29 30 proxy.method1();//调用invoke---Method:目标对象的method1方法 args:null 返回值null 31 String method2 = proxy.method2();//调用invoke---Method:目标对象的method2方法 args:null 返回值method2 32 int method3 = proxy.method3(100);////调用invoke-----Method:目标对象的method3方法 args:Object[]{100} 返回值100 33 34 System.out.println(method2); 35 System.out.println(method3); 36 37 } 38 39 }
1 public class Target implements TargetInterface{ 2 3 @Override 4 public void method1() { 5 System.out.println("method1 running..."); 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 public String method2() { 10 System.out.println("method2 running..."); 11 return "method2"; 12 } 13 14 @Override 15 public int method3(int x) { 16 return x; 17 } 18 19 20 21 }
不忘初心,方得始终





【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步