前言:
题目集01题目较多,偏向于基本的java的一些代码、方法的用法
题目集02题目较少,考核重点为输入字符串,并对字符串做变换或判断及判断其中某个或多个字符
题目集03题目最少难度也最高,考察的知识是类之间的关系及相互调用,是面向对象程序设计的基础,创建的类繁多且复杂
(2)设计与分析:重点对题目的提交源码进行分析
SourceMonitor有关度量值知识信息摘抄
度量值
1. 总行数(Lines)
包括空行在内的代码行数。
2. 语句数(Statements)
语句是以分号结尾的。分支语句if,循环语句for、while,跳转语句goto都被计算在内。
3. 分支语句比例(Percent Branch Statements)
该值表示分支语句占语句数目的比例,这里的“分支语句”指的是使程序不顺序执行的语句,包括if、else、for、while、break、continue、goto、switch、case、default和return。需要注意的是,do不被计算在内,因为其对应的while已经计算了。另外,异常处理的catch也被作为一个分支计算。
4. 注释比例(Percent Lines with Comments)
该值指示注释行(包括/*……*/和//……形式的注释)占总行数的比例。一般公司会对每个文档的header或者footer部分进行特殊的声明注释,可以再工程属性中设置过滤,不计算在内。
5. 类个数(Classes)
包括class的个数。
6. 平均每个类方法数(Methods per Class)
平均每个类的方法数,即包括内联和非内联的,template函数在内的类方法数除以所有类的个数。
7. 函数个数(Functions)
所有函数的个数。
8. 平均每个函数包含的语句数目(Average Statements per Method)
总的函数语句数目除以函数数目得到该值。
9. 函数圈复杂度(Function Complexity)
圈复杂度指示一个函数可执行路径的数目,以下语句为圈复杂度的值贡献1:if/else/for/while语句,三元运算符语句,if/for/while判断条件中的"&&"或“||”,switch语句,后接break/goto/ return/throw/continue语句的case语句,catch/except语句等。对应有最大圈复杂度(Max Complexity)和平均圈复杂度(Avg Complexity)。
10. 函数深度(Block Depth)
函数深度指示函数中分支嵌套的层数。对应有最大深度(Max Depth)和平均深度(Avg Depth)。
题目集02
7-2
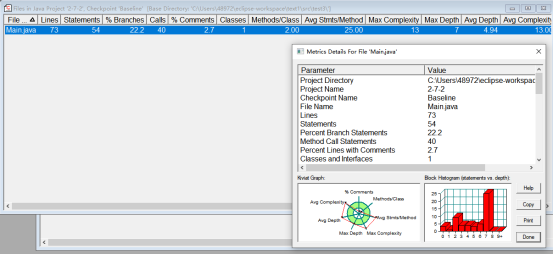
根据Kiviat图分析有四个维度的实际测量值超出了期望值范围,应该更加注重一些边界测试和其他细节上如“数据第几位的校验”。
题目集03
7-1
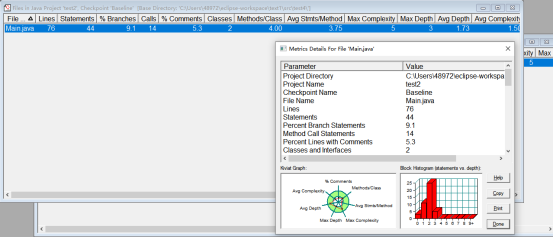
有其中四个实际测试值低于期望值,第一次接触根据主方法来补充类的题型难免有些无措,但是这道题比较简单只需要掌握返回值得方法的写法即可
7-2
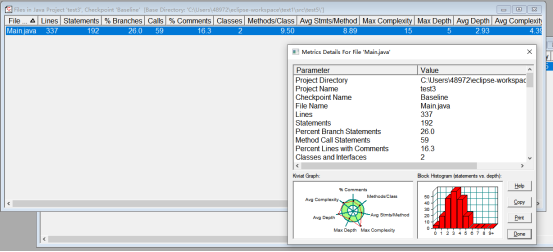
本题代码中有两个维度实际测试值超出期望值,在AVG depth、max complexity平均复杂程度 和最大复杂程度上超过了期望值,应该减少for、if等循环、判断语句的嵌套层数以减少代码的复杂程度。
7-3

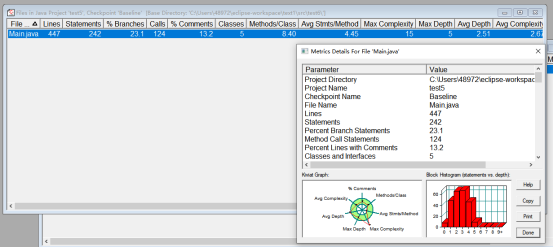
最大复杂程度实际测试值超出期望值依然是存在的问题,本题一些方法的创建与第二题大体相似,在类图设计上这种聚合的关系我认为相对复杂,在类DateUtil中调用类Year中的方法时书写起来十分麻烦。
而聚合二的这种聚合关系我认为更好。
(3)采坑心得:
题目集01:
7-1:身体质量指数测算
- Scanner input = new Scanner(System in);
有时候经常忘记什么地方是空格什么地方用“. ”连接:Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
- double BMI = countBMI();
有时候调用方法会忘记声明其中的参数double BMI = countBMI(tall,weight);
- Math.pow(tall,2);
记得当时还不会用乘方的方法,现在记住了
7-2:长度质量计量单位换算
- double weight = input next.Double();
做的时候还是没记住空格在哪”.”在哪(Ps。现在肯定知道了)double weight = input.nextDouble();
- System.out.println(countChange2(weight)+countChange1(loong));
输出要求中2数据要以空格隔开,输出时文字要用“ ”而方法却不用
System.out.println(countChange2(weight)+" "+countChange1(loong));
- double pound = 0;
声明变量是double类型,但是方法要求返回flout类型,所以在return之前将double型转为flout型
float b = (float)pound; return b;
7-3:奇数求和
- int[] b = new int[ ];
后面[ ]中写的是数组的长度int[] b = new int[10];
7-4:房产税费计算
- if(time=1)
有事粗心大意if语句中判断时少一个“=”
- System.out.println((float)q+" "+(float)y+" "+(float)j+" "+(float)c);
输出时数据精度不符合标准时要用flout转换
7-5:游戏角色选择
- int player = nextInt();
有时候调用这个方法会忘记写input,I也可能会忘记大写 int player = input.nextInt();
7-6:学号识别
- str.length()
用于判断字符串长度
2.str.charAt(2)==2
判断字符串中第2位是不是2,因为是在字符串中所以str.charAt(2)=='2'要加单引号
7-7:巴比伦法求平方近似值
1. while(Math.abs(nextGuess-lastGuess)>=0.00001)
Math.abs()计算变量平方的方法
7-8二进制数值提取
- while(str.charAt(i)!='-' )
判断字符串是不是有“-”或者其他时候要加单引号
7-7:判断三角形类型
- double x = input.nextDouble(), y = input.nextDouble(), z = input.nextDouble();
可以这样一起输入double型变量
题目集02
7-1字母数字转换
- char cs[] = str.toCharArray();
toCharArray()将字符串转换为字符数组
- byte words[] = new byte[cs.length];
字节数组用ASCLL码来判定字母的大小
- println与print
println 在输出之后会有一个换行而print却没有
题目集03
7-1用类解决一元二次方程
- 在创建Main class以外的class时要注意 { }的位置自己创建的class是在Main class外面的
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
.......
}
}
class QuadraticEquation{
}
- 在类中创建方法时要注意返回的类型double、int.....或者是void不返回值
除void外如果没有return 值 都会报错
3.public QuadraticEquation(double a,double b,double c){
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
变量名重复时在方法中要用this定义,来区分当前对象。
7-2:日期类设计
- 在日期类中创建的方法getPreviousNDays()中的内存超时
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(
date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() +
" and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:"
+ fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class DateUtil {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public int a[] = new int[20];
public DateUtil(DateUtil d){
this.day = d.getDay();
this.month = d.getMonth();
this.year = d.getYear();
a[1] = 31; a[2] = 28; a[3] = 31; a[4] = 30; a[5] = 31; a[6] = 30;
a[7] = 31; a[8] = 31; a[9] = 30; a[10] = 31; a[11] = 30; a[12] = 31;
}
public DateUtil(int year, int month, int day){
this.year=year;
this.month=month;
this.day=day;
a[1]=31; a[2]=28; a[3]=31; a[4]=30; a[5]=31; a[6]=30;
a[7]=31; a[8]=31; a[9]=30; a[10]=31; a[11]=30; a[12]=31;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity(){
if(year>=1820&&year<=2020&&month>=1&&month<=12) {
if (this.isLeapYear(year)&&month==2 ) {
if(day<=29&&day>0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
else{
if(day>0&&day<=a[month])
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
else
return false;
}
public boolean isLeapYear(int year){
if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int m) {
while(m >= 366){
if(this.isLeapYear(year) && month <= 2){
if(month == 2 && day == 29){
day = 1;
month = 3;
}
year++;
m = m - 366;
}
else if(this.isLeapYear(year+1) && month > 2){
year++;
m = m - 366;
}
else{
year++;
m = m - 365;
}
}
a[2]=28;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
day++;
if(month==2&&this.isLeapYear(year)){
if(day>29){
month++;
day=1;
}
}
else {
if(day>a[month]){
month++;
day=1;
if(month>12)
{
year++;
month=1;
}
}
}
}
return this;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){
while(n > 365){
if(this.isLeapYear(year) && month > 2){
n = n - 366;
year--;
}
else if(this.isLeapYear(year - 1) && month <= 2){
n = n - 366;
year--;
}
else{
n = n - 365;
year--;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
day--;
if(day <= 0){
month--;
if(month <= 0){
month=12;
year--;
}
if(isLeapYear(year) && month == 2)
day=29;
else
day=a[month];
}
}
return this;
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil c){
if(this.year > c.getYear())
return true;
else if(this.year == c.getYear() && this.month > c.getMonth())
return true;
else if(this.year == c.getYear() && this.month == c.getMonth() && this.day > c.getDay())
return true;
return false;
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil b){
if( b.getYear() != this.year)
return false;
else if( b.getDay() != this.day)
return false;
else if( b.getMonth() != this.month)
return false;
else
return true;
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){
int res = 0;
a[2]=28;
boolean b = this.compareDates(date);
DateUtil d = new DateUtil(this);
if(b){
while(d.getYear()-date.getYear()>=2){
if(d.isLeapYear(d.getYear()) && d.getMonth() > 2)
res = res + 366;
else if(d.isLeapYear(d.getYear() - 1) && d.getMonth() <= 2)
res = res + 366;
else
res = res + 365;
d.setYear(d.getYear() - 1);
}
while(true){
if(d.equalTwoDates(date))
break;
res++;
d.setDay(d.getDay() - 1);
if(d.getDay() <= 0){
d.setMonth(d.getMonth() - 1);
if(d.getMonth() <= 0){
d.setMonth(12);
d.setYear(d.getYear() - 1);
}
if(isLeapYear(d.getYear()) && d.getMonth() == 2)
d.setDay(29);
else
d.setDay(d.a[d.getMonth()]);
}
}
}
else{
while(date.getYear() - d.getYear() >= 2){
if(d.isLeapYear(d.getYear()) && d.getMonth() <= 2)
res = res + 366;
else if(d.isLeapYear(d.getYear() + 1) && d.getMonth() > 2)
res = res + 366;
else
res = res + 365;
d.setYear(d.getYear() + 1);
}
while(true){
if(d.equalTwoDates(date))
break;
res++;
d.setDay(d.getDay() + 1);
if(isLeapYear(d.getYear()) && d.getMonth() == 2){
if(d.getDay() > 29){
d.setMonth(d.getMonth() + 1);
d.setDay(1);
}
}
else if(d.getDay() > d.a[d.getMonth()]){
d.setMonth(d.getMonth() + 1);
d.setDay(1);
if(d.getMonth() > 12){
d.setMonth(1);
d.setYear(d.getYear() + 1);
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
public String showDate(){
return year + "-" + month + "-" + day;
}
}
} 调用类创造一个新的对象,新对象中的变量,需要这样来使用如:date.year
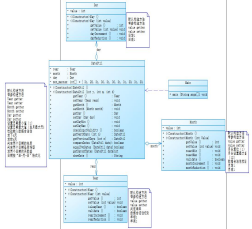
7-3聚合如何看类图,菱形连接箭头表示实体关系宏,关系宏分为两类:A类,B类,但B类包含类,类是完整的,但B类是一部分,换句话说,B类不是一个水平关系,所以我们应该以A班的方式叫B班。
-
在这个主题中,主题要求建立四个类别,即历史,今天,蒙蒂和年份,它们之间的关系是蒙蒂包含的年份,蒙蒂包含的日子,今天包含的日期。这就是为什么我想在确定一年的年份之前在类DateUtil中调用IsleapYear()。获取月份。一年。有叶的;当然,这就是我们在DateUtil类中所称的IsleapYear()方法,而不需要添加日期。当然,当我们在主方法中调用它时,我们需要添加“日期”。
当我们调用上面描述的方法或变量时,这是非常复杂的,但是在Eclipse中,当我们进入Plus类时,这是非常复杂的。
7-4聚合二
- 在聚合二中依然是那四个类,但是这次不同的是类Day类Month类Year都包含于类DateUtil中,不同之处也是显而易见的
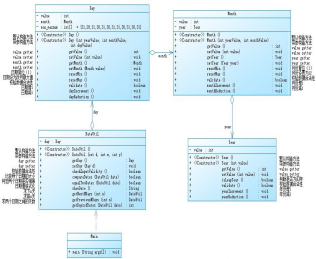
如图,(上图是聚合二,下图是聚合一)
我们可以发现原本在类Day类Month类Year中的方法到聚合二中有明显变少,而类DateUtil中的方法却明显变多,类Day类Month类Year中有许多功能相似的方法,因此在聚合二中减少了像聚合一中的套娃行为,只需getYear().isLeapYear()如此就可以调用类Year中的方法。
(4)改进建议:对相应题目的编码改进给出自己的见解,做到可持续改进
题目01
这次的题目集,思路较为清晰,难度较低,相较于在main方法中计算,我选择在main方法外自己创建了一个方法来计算题目所需的数据,这样一来逻辑变得更加简单,我认为增加了可读性,并且对于初学java如何创建方法、调用方法起到了一定的帮助。如7-1:
public static double countBMI(double tall,double weight){
double BMI = 0;
BMI = weight / Math.pow(tall,2);
return BMI;
}
题目03
7-2
考虑到第一个n天和第二个n天,因为一年的值范围非常大,我决定从年开始,将年转换为天,将月转换为天,然后计算剩余的天。因此,该代码中使用了几个循环和几个句子。为了返回正确的数据,这个计算方法已经修改了好几次,几乎已经过时,不适用于问题7-3。修改后,我将结果更改为计算连续累积。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(
date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() +
" and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:"
+ fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class DateUtil {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public int a[] = new int[20];
public DateUtil(DateUtil d){
this.day = d.getDay();
this.month = d.getMonth();
this.year = d.getYear();
a[1] = 31; a[2] = 28; a[3] = 31; a[4] = 30; a[5] = 31; a[6] = 30;
a[7] = 31; a[8] = 31; a[9] = 30; a[10] = 31; a[11] = 30; a[12] = 31;
}
public DateUtil(int year, int month, int day){
this.year=year;
this.month=month;
this.day=day;
a[1]=31; a[2]=28; a[3]=31; a[4]=30; a[5]=31; a[6]=30;
a[7]=31; a[8]=31; a[9]=30; a[10]=31; a[11]=30; a[12]=31;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity(){
if(year>=1820&&year<=2020&&month>=1&&month<=12) {
if (this.isLeapYear(year)&&month==2 ) {
if(day<=29&&day>0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
else{
if(day>0&&day<=a[month])
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
else
return false;
}
public boolean isLeapYear(int year){
if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int m) {
while(m >= 366){
if(this.isLeapYear(year) && month <= 2){
if(month == 2 && day == 29){
day = 1;
month = 3;
}
year++;
m = m - 366;
}
else if(this.isLeapYear(year+1) && month > 2){
year++;
m = m - 366;
}
else{
year++;
m = m - 365;
}
}
a[2]=28;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
day++;
if(month==2&&this.isLeapYear(year)){
if(day>29){
month++;
day=1;
}
}
else {
if(day>a[month]){
month++;
day=1;
if(month>12)
{
year++;
month=1;
}
}
}
}
return this;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){
while(n > 365){
if(this.isLeapYear(year) && month > 2){
n = n - 366;
year--;
}
else if(this.isLeapYear(year - 1) && month <= 2){
n = n - 366;
year--;
}
else{
n = n - 365;
year--;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
day--;
if(day <= 0){
month--;
if(month <= 0){
month=12;
year--;
}
if(isLeapYear(year) && month == 2)
day=29;
else
day=a[month];
}
}
return this;
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil c){
if(this.year > c.getYear())
return true;
else if(this.year == c.getYear() && this.month > c.getMonth())
return true;
else if(this.year == c.getYear() && this.month == c.getMonth() && this.day > c.getDay())
return true;
return false;
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil b){
if( b.getYear() != this.year)
return false;
else if( b.getDay() != this.day)
return false;
else if( b.getMonth() != this.month)
return false;
else
return true;
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){
int res = 0;
a[2]=28;
boolean b = this.compareDates(date);
DateUtil d = new DateUtil(this);
if(b){
while(d.getYear()-date.getYear()>=2){
if(d.isLeapYear(d.getYear()) && d.getMonth() > 2)
res = res + 366;
else if(d.isLeapYear(d.getYear() - 1) && d.getMonth() <= 2)
res = res + 366;
else
res = res + 365;
d.setYear(d.getYear() - 1);
}
while(true){
if(d.equalTwoDates(date))
break;
res++;
d.setDay(d.getDay() - 1);
if(d.getDay() <= 0){
d.setMonth(d.getMonth() - 1);
if(d.getMonth() <= 0){
d.setMonth(12);
d.setYear(d.getYear() - 1);
}
if(isLeapYear(d.getYear()) && d.getMonth() == 2)
d.setDay(29);
else
d.setDay(d.a[d.getMonth()]);
}
}
}
else{
while(date.getYear() - d.getYear() >= 2){
if(d.isLeapYear(d.getYear()) && d.getMonth() <= 2)
res = res + 366;
else if(d.isLeapYear(d.getYear() + 1) && d.getMonth() > 2)
res = res + 366;
else
res = res + 365;
d.setYear(d.getYear() + 1);
}
while(true){
if(d.equalTwoDates(date))
break;
res++;
d.setDay(d.getDay() + 1);
if(isLeapYear(d.getYear()) && d.getMonth() == 2){
if(d.getDay() > 29){
d.setMonth(d.getMonth() + 1);
d.setDay(1);
}
}
else if(d.getDay() > d.a[d.getMonth()]){
d.setMonth(d.getMonth() + 1);
d.setDay(1);
if(d.getMonth() > 12){
d.setMonth(1);
d.setYear(d.getYear() + 1);
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
public String showDate(){
return year + "-" + month + "-" + day;
}
}
}代码的篇幅不仅大幅缩短而且逻辑也更加清晰简单。
(5)总结:
-
熟悉用java语言写的一些简单的程序,java和c语言写的规范不一样,比如{网站规范}
学习如何创建类,调用类创建新对象,调用其他类中的方法、对象和变量。
熟悉和掌握Java中的一些常用方法
一些基础知识还没有完全掌握,如中子类的输入、继承、母类与子类之间的关系、母类与子类之间的关系等一系列常用方法在线版本的代码发生的例子,然后解码其含义,多阅读一些关于多态性遗传的论文,并参加一些网络论坛和其他讨论。
在线上课的状态必须始终保持,采用笔记本电脑和手写体相结合的注册方式,课后稍作整理
在我的业余时间,在CSDN和一些开源网站上看到一些老手为我们写的新阶段的Java学习帮助解释代码,注释,理解,然后在eclipse中练习然后调试调试
尽快完成PTA实验,用更多的时间总结PTA中的一些问题,以便下次有足够的材料。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号